Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nursing Care Plan 2
Hochgeladen von
KM TopacioOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing Care Plan 2
Hochgeladen von
KM TopacioCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nursing Care Plan
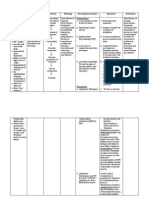
Name: D. L. Cues Nursing Diagnosi s Increased cardiac output related to severe preeclam psia as manifeste d by the blood pressure reading and the admitting diagnosis of the patient Age: 34 y/o Analysis Sex: Female Goals & Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale Evaluation
Objective Cues: -BP reading: 160/110 -the patient has an admitting diagnosis of chronic hypertensio n with superimpos ed preeclampsia -edema from both higher & lower extremities with moderate indention (2+) -marked protenuria (3+) Subjective Cues: -the patient said that she is hypertensiv e even
A woman has severe preeclampsia when her blood pressure has risen to 160 mm Hg systolic and 110 mm Hg diastolic or above. Marked protenuria, 3+ or 4+ on a random urine sample. Extreme edema will be noticeable as puffiness in a womans face or hands. If Cerebral edema occurs, reports may be voiced of visual disturbances such as blurred vision or seeing spots before
Goal: After 8 hours shift the clients condition will not progressed to eclampsia Objectives: 1. After nursing 5 minutes of Intervention clients due antihypertensive medications will be administered effectively as doctors order Effectiveness - The clients blood pressure was stabilized - All predisposing factors of seizure were eliminated - The client did not experienced seizures Efficiency All resources were available to solve the health problem. Adequacy The Interventions were adequate to solve the The woman is placed on bed health problem. rest, primarily on her left side, Appropriateness to decrease pressure on the All interventions were vena cava, thereby increasing appropriate to solve the venous return, circulatory health problem. Acceptable volume and renal perfusion. Improved renal blood flow All interventions were helps decrease Angiotensin II acceptable to the client to levels, promotes dieresis, and solve the health problem. lowers blood pressure. A look at Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care by Ladewig, London, Drugs used to treat hypertension work to alter the normal reflexes that control blood pressure. Treatment for essential hypertension does not cure the disease but aimed at maintaining the blood pressure within normal limits to prevent the damage that hypertension can cause. Focus on Nursing Pharmacology by Amy M. Karch page 674
Administer due antihypertensive medications as doctors order
2. After 5 minutes of Assist the client nursing to her left side intervention the lying position. client will be assisted appropriately on her left side lying position.
before she got pregnant -the patient said that her blurry vision worsened
the eyes.
Davidson Chapter 15 page 343 Provide an environment conducive to rest. Bed rest must be complete. Stimuli that may bring on a seizure should be reduced. A look at Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care by Ladewig, London, Davidson Chapter 15 page 343 Stress is another stimulus capable of increasing blood pressure and evoking seizures in a woman with severe preeclampsia. Allow her opportunities to express her feelings about what is happening. Clear explanations help her accept the need for visitor restrictions and not to cheat on bed rest. Maternal & Child health Nursing: Care of the Childbearing and Childbearing Family by Adele Pillitteri Unit 3 Chapter 15 paeg 430 Magnesium sulfate is the treatment of choice for convulsions. Its depressant action on the CNS reduces the possibility of seizure. A look at Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care by Ladewig, London, Davidson Chapter 15 page 343
Ref.: Maternal 3. After 5 minutes of & Child nursing Health intervention the Nursing: Care client will be able of the to rest Childbearing comfortably. & Childbearing Family by Adele Pillitteri 4. After 10 minutes Unit 3 of nursing Chapter 15 pg intervention 427 -438. stress causing seizures will be eliminated effectively.
Give clear explanation of what is happening and what is planned to the client. Allow her to express her feelings.
5. After 5 minutes of nursing intervention the clients due anticonvulsions medications will be administered effectively as doctors order.
Administer due anti-convulsions medications as doctors order.
6. After nursing intervention the client will be given meals appropriate for her condition.
Check if the meal given to the client is appropriate for the clients condition.
A High-protein, moderate sodium diet is given as long as the woman is alert and has no nausea or indication of impending seizure. A look at Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care by Ladewig, London, Davidson Chapter 15 page 343
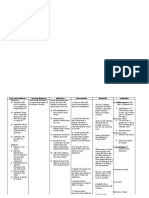
Cues
Nursing Diagnosi s Excessiv e fluid volume related to excess sodium intake as manifeste d by -swelling of the lower and upper extremitie s -Input and Output differenc e
Analysis
Goals & Objectives
Nursing Interventions
Rationale
Evaluation
SUBJECTIV E - The patient noticed that her feet became swollen at her third trimester until now. OBJECTIVE -Weak appearance -Swelling of the lower extremities and upper extremities -Test on the physical exam to determine
Goal: After 8 hours Fluid volume excess (FVE) shift the clients fluid refers to an volume will be isotonic balanced as expansion of evidenced by the balanced I & O, and ECF caused free of signs of by the edema abnormal retention of Objectives: water and sodium in 1. After 8 hours shift approximately the clients I & O the same will be monitored proportions in and recorded which they accurately. normally exist in the ECF. It is always 2. After nursing secondary to intervention the an increase in clients fluid the total body volume will be
Monitor and record I & O.
Provides a comparative baseline and evaluates the effectiveness of diuretic therapy. Nurses Pocket Guide page 329 Diuretics are routinely used in heart failure to remove excessive sodium and water to relieve symptoms
Administer diuretic medications as doctors order.
Effectiveness - The clients excess fluid were excreted - The clients I &O was balanced - The clients extremities had no signs of edema Efficiency All resources were available to solve the health problem.
whether it is pitting/ nonpitting edema. MEASURE MENT: -I&O q 2 (Refer on the Lab results part)
sodium stabilized by content, administering her which, in turn, due diuretic leads to an medications increase in effectively as total body doctors order. water. Because 3. After nursing there is intervention the isotonic clients fluid retention of volume will be body stabilized by substances, positioning her to the her left side lying serum sodium position. concentration remains essentially normal.
associated with pulmonary congestion and edema. Basic Pharmacology for Nurses by Clayton, Stock, Harroun; Chapter 29 page 463 Assist the client to her left side lying position. The woman is placed on bed rest, on her left side, to decrease pressure on the vena cava, thereby increasing renal perfusion. Improved renal blood flow helps decrease Angiotensin II levels and promotes dieresis. A look at Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care by Ladewig, London, Davidson Chapter 15 page 343 Promoting diuresis helps relieve fluid retention. Helping the postpartal woman use the toilet, if possible, or the bedpan prevents urinary retention and bladder overdistention in most cases. A look at Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care by Ladewig, London, Davidson Chapter 30 page 816 Increase venous blood flow; reduce tissue pressure and risk of skin breakdown. Nurses Pocket Guide page 330
Adequacy The Interventions were adequate to solve the health problem. Appropriateness All interventions were appropriate to solve the health problem. Acceptable All interventions were acceptable to the client to solve the health problem.
4. After nursing intervention the clients fluid volume will be stabilized by assisting her to void appropriately and adequately.
Assist the client use the toilet, if possible, or the bedpan.
5. After nursing the clients extremities will be relieved from edema
Elevate edematous extremities.
Cues
Nursing Diagnosi s Acute pain related to surgical incision as manifeste d by the verbalizat ions of the client.
Analysis
Goals & Objectives
Nursing Interventions
Rationale
Evaluation
SUBJECTIV E - The patient had undergone LTCS. - Pain on incision site. - The patient said that she cannot sleep because of pain felt on incision site. - she said that that the pain is in the rate of 7 out of 10 OBJECTIVE - The patient was ordered of Mefenamic acid. - The patient was wearing an abdominal binder. - difficulty in moving and positioning
Goal: After 30 Unpleasant sensory and minutes of nursing emotional intervention the experience clients pain will be arising from alleviated as actual or verbalized by the potential client tissue Objective damage or describe 1. After 5 minutes of terms of such nursing damage; intervention the sudden or clients due slow onset of analgesics will be any intensity administered from mild to effectively as severe with doctors order an anticipated or predictable end and 2. After 5 minutes of duration of nursing less than 6 intervention the months clients pain will be managed effectively by nonpharmacologic pain management
Administer analgesics as needed as doctors order.
Use of analgesics relieves the womans pain and enables her to be more mobile and active. A look at Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care by Ladewig, London, Davidson Chapter 30 page 826 Promote comfort through proper positioning, and reduction of noxious stimuli such as noise and unpleasant odors to promote nonpharmacological pain management. A look at Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care by Ladewig, London, Davidson Chapter 30 page 826 These visits distract the woman from painful sensations and help reduce her fear and anxiety.
Provide comfort measures.
Effectiveness - The client was relieved from pain - The client was able to verbalize/report changes of intensity of pain Efficiency All resources were available to solve the health problem. Adequacy The Interventions were adequate to solve the health problem. Appropriateness All interventions were appropriate to solve the health problem. Acceptable All interventions were acceptable to the client to solve the health problem.
3. After nursing intervention the client will be provided proper
Encourage visits of significant others.
distraction from pain
A look at Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care by Ladewig, London, Davidson Chapter 30 page 826 Educate client how to use breathing techniques. Breathing techniques increase womans pain threshold, permit relaxation, provide sense of control and allow the uterus to function more efficiently. A look at Contemporary Maternal-Newborn Nursing Care by Ladewig, London, Davidson Chapter 19 page 459 Instruct patient to report pain as soon as it begins as timely intervention is more likely to be successful in alleviating pain. Nurses Pocket Guide page 502
4. After 10 minutes of nursing intervention the client will be able to properly utilize breathing techniques to alleviate pain.
5. After 3 minutes of nursing intervention the client will verbalize her perception of pain
Instruct client to verbalize/report changes of intensity of pain
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NCP HemothoraxDokument3 SeitenNCP HemothoraxMichael John F. NatividadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Interaction Immediate Cause Goal: Effectivenes SDokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Interaction Immediate Cause Goal: Effectivenes SCatherine Kaye Marquez RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP CSDokument4 SeitenSP CSKhan HansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valdez Reflective-Questions PDFDokument3 SeitenValdez Reflective-Questions PDFDexel Lorren ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teething:diaper Dermatitis NCPDokument2 SeitenTeething:diaper Dermatitis NCPMARK OLVIER E. MELCHORNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Name: DRT Age: 67 Diagnosis: Cva 2° To HPNKristina Marie Parulan RnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanDokument5 SeitenManage Bronchiectasis Nursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP (Acute Pain)Dokument2 SeitenNCP (Acute Pain)jennilois100% (1)
- Risk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.Dokument2 SeitenRisk For Aspiration Related To Esophageal Compromise Affecting The Lower Esophageal Sphincter As Evidenced by Heart Burn.eleinsamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument10 SeitenNursing Care PlanMalou SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Weakness NCPDokument1 SeiteBody Weakness NCPtwicetrashNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - ERDokument5 SeitenNCP - ERAnnelore ArcayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeDokument4 SeitenHealthcare - Nursing Care Plan - Excess Fluid VolumeBenjamin CañalitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryDokument1 SeiteNursing Care Plan Risk For InjuryAce Dioso TubascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioDokument5 SeitenNCP Micu Hascvd Cad - RioRio BonifacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeDokument2 SeitenTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeMiar QuestNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Acute PainDokument3 SeitenNCP Acute PainNathalie kate petallarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal & Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenNursing Diagnosis Analysis Goal & Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationLP BenozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsDokument3 SeitenNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To The Accumulation of Secretions As Evidence by Decrease in Respiratory Rate and NGT and ET Tube Attached and Crackles at The Left Base of The LungsSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument1 SeiteAsessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationChelsea Mae Bagalay GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheDokument14 SeitenAnswer: 59.5 KG: Rationale: Although All of These Clients Might Experience Fluid Volume Deficit, TheMikeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medication ThalassemiaDokument3 SeitenMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actual NCPDokument2 SeitenActual NCPbaki0146Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study NCP ActualDokument3 SeitenCase Study NCP Actualdhamy florNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan for Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pao NCPDokument3 SeitenPao NCPJay VillasotoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Verbal and or Written CommunicationDokument2 SeitenImpaired Verbal and or Written CommunicationHanya Bint Potawan100% (1)
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDokument13 SeitenAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- Drug StudiesDokument32 SeitenDrug StudiesKelly ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan NCP Group 3 Fatigue ..Dokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan NCP Group 3 Fatigue ..Aerron Severus Secano ShuldbergNoch keine Bewertungen
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDokument1 SeiteNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 4Dokument1 SeiteNCP 4marohunkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument4 SeitenNursing Care PlanKath RubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlansDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plansapi-19762967Noch keine Bewertungen
- ASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoDokument1 SeiteASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoCherie MayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examples of Therapeutic and Non Therapeutic Communication TechniquesDokument6 SeitenExamples of Therapeutic and Non Therapeutic Communication TechniquesReya Mae OrcajadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Ward Journal Binwag BSN 2aDokument2 SeitenPediatric Ward Journal Binwag BSN 2aVincentus BinNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP For StokeDokument5 SeitenNCP For StokeMemedNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP 3Dokument3 SeitenNCP 3Grae TaclobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health-Perception-Health-Management PatternDokument3 SeitenHealth-Perception-Health-Management PatternBela MillenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impaired Physical MobilityDokument2 SeitenImpaired Physical MobilityAbdelhafiz SusmiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDokument6 SeitenAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- LortabDokument1 SeiteLortabSheri490Noch keine Bewertungen
- NCP MRMDokument2 SeitenNCP MRMKhloe Cristel Llanes Torres100% (1)
- NCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaDokument2 SeitenNCP - Acute Pain Related To EdemaChenime Añana0% (1)
- Content: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderDokument4 SeitenContent: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderRaffy Sebastian Seballos100% (1)
- NCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Dokument6 SeitenNCP - Ineffective Airway Clearance (Mary Ann Solomon)Karissa GuerreroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For LYING inDokument4 SeitenNursing Care Plan For LYING inKarissa CiprianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spina Bifida NCPDokument3 SeitenSpina Bifida NCPShahzad GulfamNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument7 SeitenNCPAbbie TantengcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument3 SeitenNCPMichael John F. NatividadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDokument2 SeitenIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seizure NCPDokument2 SeitenSeizure NCPChristine Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Pain NCPDokument1 SeiteAcute Pain NCPRyan PanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bowel incontinence diagnosis and interventionsDokument9 SeitenBowel incontinence diagnosis and interventionsners_gun100% (1)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Dog Bite InjuryDokument3 SeitenNURSING CARE PLAN Dog Bite Injurykarrey danielNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan 2Dokument6 SeitenNursing Care Plan 2ayanori_boyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 1 PDFDokument62 SeitenSet 1 PDFAlyssa MontimorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set 1Dokument62 SeitenSet 1Alyssa MontimorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter of Intent 1Dokument1 SeiteLetter of Intent 1KM TopacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTP UretentionDokument3 SeitenHTP UretentionKM TopacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1987 ConstitutionDokument49 Seiten1987 ConstitutionAerwin AbesamisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychiatric Diagnosis CodesDokument9 SeitenPsychiatric Diagnosis CodesKM TopacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gordon'S Fuctional Pattern: A) Health Perception and Health Management PatternDokument2 SeitenGordon'S Fuctional Pattern: A) Health Perception and Health Management PatternKM TopacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Teaching PlanDokument3 SeitenHealth Teaching PlanKM TopacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReportDokument36 SeitenReportKM TopacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- O0 Lactose Intolerance 0oDokument3 SeitenO0 Lactose Intolerance 0oKM TopacioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monitoring of OHS Objectives & TargetsDokument2 SeitenMonitoring of OHS Objectives & TargetsNomaan MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 768 - Edited by Yashwardhan Bansal - MEDICAL NEGLIGENCE AND MALPRACTICE A THREAT TO HUMANITY - Shivani UpadhyayDokument12 Seiten768 - Edited by Yashwardhan Bansal - MEDICAL NEGLIGENCE AND MALPRACTICE A THREAT TO HUMANITY - Shivani UpadhyayANDREW JOSEPHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poster On 9 StepsDokument1 SeitePoster On 9 StepsJOHN TAIPINoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Glucose Tolerance TestDokument4 SeitenOral Glucose Tolerance TestCyna Jane Yao AlcularNoch keine Bewertungen
- APA Reply HofferDokument128 SeitenAPA Reply HofferVictoria VictoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Templates For Planning and M&E (AIP, WFP, SMEA Templates)Dokument6 SeitenTemplates For Planning and M&E (AIP, WFP, SMEA Templates)Genzo TaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advancing Nursing Informatics in The Next 5-10 Years: What Are The Next Steps?Dokument3 SeitenAdvancing Nursing Informatics in The Next 5-10 Years: What Are The Next Steps?HandiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standards For Improving The Quality of Care For Small and Sick Newborns in Health Facilities 2020Dokument152 SeitenStandards For Improving The Quality of Care For Small and Sick Newborns in Health Facilities 2020Shuaib KauchaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Cause or Etiology of Pott's DiseaseDokument5 SeitenCommon Cause or Etiology of Pott's DiseaseStan Aves GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schonert-Reichl-Educating The Heart As Well As The MindDokument7 SeitenSchonert-Reichl-Educating The Heart As Well As The MindnewoldnoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bombshell by Suzanne Somers - ExcerptDokument12 SeitenBombshell by Suzanne Somers - ExcerptCrown Publishing GroupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiger NutsDokument4 SeitenTiger NutsMohd Idris MohiuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHO Global Report Traditional & Complementary Medicine 2019Dokument228 SeitenWHO Global Report Traditional & Complementary Medicine 2019Ellyana PerwitasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical BacteriologyDokument108 SeitenMedical BacteriologyTamarah YassinNoch keine Bewertungen
- PED011 Final Req 15Dokument3 SeitenPED011 Final Req 15macabalang.yd501Noch keine Bewertungen
- Abilify Drug Study: Therapeutic Effects, Indications, Contraindications and Adverse ReactionsDokument6 SeitenAbilify Drug Study: Therapeutic Effects, Indications, Contraindications and Adverse ReactionsLuige AvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common mental health problems screeningDokument5 SeitenCommon mental health problems screeningSaralys MendietaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring Burnout 2009Dokument23 SeitenMeasuring Burnout 2009Eduardo Denise100% (1)
- A Message From Dauphin County Chairman Jeff Haste To Citizens of PADokument2 SeitenA Message From Dauphin County Chairman Jeff Haste To Citizens of PAPennLiveNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT Behavioral ProblemsDokument11 SeitenPT Behavioral ProblemsAmy LalringhluaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternative SystemDokument26 SeitenAlternative Systemsameena vNoch keine Bewertungen
- AHA Activity Hazard AnalysisDokument24 SeitenAHA Activity Hazard AnalysisElvyn Fabellore HerreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eneza Ujumbe: The Voices of Mathare YouthDokument4 SeitenEneza Ujumbe: The Voices of Mathare YouthakellewagumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6-WHO-Practical Steps For WASH in HCFDokument70 Seiten6-WHO-Practical Steps For WASH in HCFash amenNoch keine Bewertungen
- BBA Enrollment Form Front Page PDFDokument2 SeitenBBA Enrollment Form Front Page PDFYaj EstefanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategi Koping Ibu Dengan Anak Penderita Kanker (Studi Deskriptif Di Komunitas Peduli Anak Kanker Dan Penyakit Kronis Lainnya)Dokument15 SeitenStrategi Koping Ibu Dengan Anak Penderita Kanker (Studi Deskriptif Di Komunitas Peduli Anak Kanker Dan Penyakit Kronis Lainnya)Yan ParirakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viii. Nursing Care Plan: Asessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenViii. Nursing Care Plan: Asessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationhehehe29Noch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Eric P. Alim Year & Section: CMT-1Dokument27 SeitenName: Eric P. Alim Year & Section: CMT-1Ariel BobisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF)Dokument9 SeitenDengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF)Muhamad Hilal Rizki KusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument10 SeitenNursing Care PlanGinel Laquiores100% (1)