Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
SQL Server Difference FAQs-10
Hochgeladen von
Umar AliCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
SQL Server Difference FAQs-10
Hochgeladen von
Umar AliCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1.Difference between OLTP and OLAP S.No 1 OLTP Abbreviation: OLTP stands for transactional processing .
2 Meaning: OLTP is designed to efficiently process high volumes of transactions, instantly recording business events (such as a sales invoice payment) and reflecting changes as they occur. 3 Used in: OLAP Abbreviation: Online OLAP stands for Online analytical processing . Meaning: OLAP is designed for analysis and decision support, allowing exploration of often hidden relationships in large amounts of data by providing unlimited views of multiple relationships at any cross-section of defined business dimensions. Used in:
ERP, TX system, Client Server Data warehouse application - MOLAP, Architecture, Desktop application ROLAP, HOLAP 4 Data Provision: Current data 5 Type of Database Transactions: Short database transactions 6 Type of update/insert/delete: Online update/insert/delete 7 Normalization/Denomalization: Data Provision: Current and historical data Type of Database Transactions: Long database transactions Type of update/insert/delete: Batch update/insert/delete Normalization/Denomalization:
Normalization is promoted (1st Denormalization is promoted normal form, second normal form (Dimension and Fact design). and third normal form). 8 Volume of Transactions: High volume of transactions 9 Transaction Recovery Needed: Transaction recovery is necessary 10 Amount of Index Requirement: Less Index Volume of Transactions: Low volume of transactions Transaction Recovery Needed: Transaction recovery is not necessary Amount of Index Requirement: More Index
11 12
Amount of Join Requirement: More Joins Model:
Amount of Join Requirement: Less Joins Model:
Adopts an entity relationship(ER) Adopts star, snowflake or fact model constellation model and a subjectoriented database design 13 Orientation: Orientation:
Customer-oriented, used for data Market-oriented, used for data analysis analysis and querying by clerks, by knowledge workers( managers, clients and IT professionals executives, analysis) 14 Source: Daily transactions. 15 Motive: Source: OLTP Motive: and search by
Faster insert, updates, deletes and Faster analysis improve data quality by reducing combining tables. redundancy. 16 SQL complexity: Simple and Medium. SQL complexity:
Highly complex due to analysis and forecasting.
2.Difference between DTS and SSIS S.No 1 2 DTS DTS stands for Transformation Services SSIS Data SSIS stands for Sql Server Integration Services
DTS is a set of objects using an SSIS is an ETL tool provided by ETS tool to extract, transform, Microsoft to extra data from different and load information to or from a sources. database DTS was originally part of the SSIS is a component of the Microsoft Microsoft SQL Server 2000 SQL Server 2005 Uses Activex Script No Deployment available wizard Uses Scripting Language is Deployment wizard is available
3 4 5 6
Limited Set of Transformation Huge of Transformations available available
7 8 9 10
Does not support BI Functionality Single Task at a time It is Unmanaged script DTS can develop Enterprise manager
Completely supports process of BI Multi Tasks run parallely It is managed by CLR
end
to
end
through SSIS can develop through Business Intelligence Development Studio (BIDS, nothing but new version of VS IDE)
11 12
We can deploy only at local server It can be deployed using multiple server using BIDS Designer contains Single Pane SSIS designer contains 4 design panes: a) Control Flow b) Data Flow c) Event Handlers & d) Package Explorer. Event Handler Available Solution Explorer is available, with packages, connections and Data Source Views (DSV)
13 14
No Event Hander No Solution Explorer
15
Connection and other values are It can be controlled dynamically using static, not controlled at runtime. configuration
And, further updates on difference between questions and answers, please visit my blog @ http://onlydifferencefaqs.blogspot.in/
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Jquery Difference FAQS Compiled-1Dokument10 SeitenJquery Difference FAQS Compiled-1Umar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Patterns Difference FAQS Compiled-1Dokument8 SeitenDesign Patterns Difference FAQS Compiled-1Umar Ali100% (1)
- HTML Difference FAQS Compiled-1Dokument3 SeitenHTML Difference FAQS Compiled-1Umar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- XML Difference FAQS Compiled-1Dokument7 SeitenXML Difference FAQS Compiled-1Umar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.N o Difference Between Category URLDokument19 SeitenS.N o Difference Between Category URLUmar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- LINQ Vs SQL KeywordsDokument1 SeiteLINQ Vs SQL KeywordsUmar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Is and As Operators in C#Dokument3 SeitenDifference Between Is and As Operators in C#Umar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between IIS 5.0 and IIS 6.0Dokument1 SeiteDifference Between IIS 5.0 and IIS 6.0Umar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diff BTW TFS N SVN PDFDokument2 SeitenDiff BTW TFS N SVN PDFmuthucharamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- General Service ListDokument77 SeitenGeneral Service ListMustafa GüneşNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agatthiyar's Saumya Sagaram - A Quick Summary of The Ashta KarmaDokument5 SeitenAgatthiyar's Saumya Sagaram - A Quick Summary of The Ashta KarmaBujji JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes Ilw1501 Introduction To LawDokument11 SeitenNotes Ilw1501 Introduction To Lawunderstand ingNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of English Culture and Literature MidDokument4 SeitenHistory of English Culture and Literature Midfirdasalsa59Noch keine Bewertungen
- EF 3rd Upper Interm File 8 TEST PDFDokument4 SeitenEF 3rd Upper Interm File 8 TEST PDFfriboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook PDFDokument91 SeitenHandbook PDFMohammad Suriyaidulman RianseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synonym and AntonymDokument4 SeitenSynonym and Antonymjean wongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interjections Worksheet PDFDokument1 SeiteInterjections Worksheet PDFLeonard Patrick Faunillan Bayno100% (1)
- CaseLaw RundownDokument1 SeiteCaseLaw RundownTrent WallaceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schema and Reading Comprehension Relative To Academic Performance of Grade 10 Students at Binulasan Integrated SchoolDokument12 SeitenSchema and Reading Comprehension Relative To Academic Performance of Grade 10 Students at Binulasan Integrated SchoolShenly EchemaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- M-10 Content+Previous Years QuestionDokument65 SeitenM-10 Content+Previous Years QuestionOnline Physics Care by Syed Al-NahiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProbabilityDokument29 SeitenProbabilitymaryroseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ashwin Murthy TortsDokument28 SeitenAshwin Murthy Tortssaurabh kapurNoch keine Bewertungen
- I/O Reviewer Chapter 1Dokument3 SeitenI/O Reviewer Chapter 1luzille anne alertaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Following The Path of The Eagle - David Oyedepo - 230720 - 123245Dokument173 SeitenFollowing The Path of The Eagle - David Oyedepo - 230720 - 123245sakurablossxmyt1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Manila Trading & Supply Co. v. Manila Trading Labor Assn (1953)Dokument2 SeitenManila Trading & Supply Co. v. Manila Trading Labor Assn (1953)Zan BillonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acctg 604 Basic Framework of Mas Cost Managemet PDFDokument55 SeitenAcctg 604 Basic Framework of Mas Cost Managemet PDFKookie100% (1)
- Consent For MTP PDFDokument4 SeitenConsent For MTP PDFMajid SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- LLCE CoursDokument18 SeitenLLCE CoursDaphné ScetbunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Legal Advice Problems and AnswersDokument4 SeitenSample Legal Advice Problems and AnswersJake Bryson DancelNoch keine Bewertungen
- QuestionnaireDokument4 SeitenQuestionnairevishal chauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1940 - English Missal - Order of MassDokument15 Seiten1940 - English Missal - Order of MassDavid ConleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Against The Legalization of Drugs - James Q. WilsonDokument9 SeitenAgainst The Legalization of Drugs - James Q. WilsonOhLord VaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIDP Business Ethics and Social Responsibility PDFDokument7 SeitenFIDP Business Ethics and Social Responsibility PDFRachell Mae Bondoc 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Digitalization On Business ModelsDokument20 SeitenThe Impact of Digitalization On Business ModelsFaheemullah HaddadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sampling TechDokument5 SeitenSampling TechJAMZ VIBESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Implementation & EvaluationDokument121 SeitenCurriculum Implementation & Evaluationwaseem555100% (2)
- Mind Map The Process of WritingDokument1 SeiteMind Map The Process of WritingBIBB-0622 NISHA JONGNoch keine Bewertungen
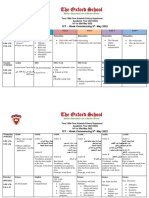
- Term 3 Mid-Term Assessment ScheduleDokument9 SeitenTerm 3 Mid-Term Assessment ScheduleRabia MoeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Tips For Better Legal WritingDokument12 Seiten10 Tips For Better Legal WritingYvzNoch keine Bewertungen