Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Corneal Ulcer
Hochgeladen von
imortaljeoOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Corneal Ulcer
Hochgeladen von
imortaljeoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CORNEAL ULCER
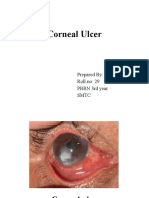
Concept: Local necrosis of the corneal tissue due to an invasion by bacteria, fungi, viruses or acanthamoeba. Causes: Corneal ulcers are mainly caused by staphylococcus, pseudomonas, and streptococcus pneumonea. The invasion of the bacteria with frequency is caused by sleeping with the contacts lens, the inadequate sterilization, corneal trauma and foreign objects. It can also occur as a complication of queratitis by herpes, neurotrofic queratitis and gonorrea. It can also be the result of a disorder of the corneal nutrition secondary to a deficiency of vitamin A or proteic deficiency. Other causes are due to disorders of the eyelids for example the incomplete closure of the eyelid, bells paralysis and trauma of the eyelid. Signs and symptoms: Pain and the sensation of foreign object, photophobia, tears, however these can be minimum. The corneal ulcer starts with a dull and grey superficial opacity, and then it turns necrotic and discharges leaving an excavated ulcer. The epithelial alteration turns green, when dyed with fluorescein. Peri-corneal intense redness if very frequent and in prolong cases the blood vessels can go into the cornea through the limbo. The ulcer can cover the whole cornea and can go deeper in some occasion pus can be found in the anterior chamber. There could be ulceration without significant infiltration in the queratitis by herpes. The ulcers caused by fungi have a more chronic course than the ones caused by bacteria; they show a more dense infiltration sometimes small dispersed lesions on the borders of the cornea. The ulcers caused by acanthamoeba are extremely painful, they can also present transitory epithelial defects and multiple stromal infiltration.
MOOREN ULCER.
The mooren ulcer is a very rare disease probably caused by an autoimmune response to antigens of the corneal estroma. Classification: according to the clinical signs, the finding with fluorescein and the response to the treatment we can identify 3 types. 1. Unilateral ulcer affects mainly elderly women of white skin complexion.
a. Progressive ulcer, extremely painful and associated with the obliteration of the superficial juxtalimbic superficial vascular plexus. b. Treatment is very difficult since the response to systemic and topic immunotherapy is very scarce. 2. Bilateral aggressive ulcer affects mainly young people from Hindu origin it is less painful than the unilateral ulcer. a. Circumferential progressive ulcer. The angiography with fluorescein show new vascular proliferation that extends to the base of the ulcer. b. The initial treatment is with intravenous methylprednisolone followed by topic and systemic corticosteroids and cytotoxic agents. Topic cephalosporin may also have a roll. 3. The painless bilateral ulcer affects mid-age, malnourished, Hindu patients. a. Progressive peripheral groove with minimal inflammatory response that heals spontaneously. b. The treatment include the improvement of diet and treatment of the associated infection The common signs of all moorens ulcers in chronological order are: Peripheral corneal infiltration 2-3 from the eyes limbo Corneal ulceration in the shape of a half moon Circumferential and central dissemination The healing phase is characterized by thinning and vascularization and scaring. Cataract can form secondarily, but perforation is rare and the sclera is not affected.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Clinical Presentation On Corneal Ulcers Power PointDokument24 SeitenClinical Presentation On Corneal Ulcers Power Pointgideon A. owusu86% (7)
- ChorioretinitisDokument13 SeitenChorioretinitisrada tri rosi kurniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacterial Keratitis PritiDokument58 SeitenBacterial Keratitis Pritipriti08988% (8)
- KeratitisDokument36 SeitenKeratitisBakri Bayquni0% (2)
- Acute Pain NCPDokument2 SeitenAcute Pain NCPfaye-pamatmat-257080% (5)
- Keratitis KonjungtivitisDokument81 SeitenKeratitis KonjungtivitisAngnes Dera MustikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corneal Bacterial UlcerDokument48 SeitenCorneal Bacterial UlcerAkansha Rastogi100% (1)
- Journal Reading: Update On The Management of Infectious KeratitisDokument35 SeitenJournal Reading: Update On The Management of Infectious KeratitisninataniaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bacterial Infections of Oral CavityDokument63 SeitenBacterial Infections of Oral CavityAkash Anilkumar Malini60% (5)
- KeratitisDokument32 SeitenKeratitiscrushnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grodno State Medical University: Assistant Lecturer of The Department of OphthalmologyDokument37 SeitenGrodno State Medical University: Assistant Lecturer of The Department of Ophthalmologypriti089Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microbialkeratitisbhatti 160607231414Dokument56 SeitenMicrobialkeratitisbhatti 160607231414RanveerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmology - Diseases of CorneaDokument18 SeitenOphthalmology - Diseases of CorneajbtcmdtjjvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grodno State Medical University: Assistant Lecturer of The Department of OphthalmologyDokument37 SeitenGrodno State Medical University: Assistant Lecturer of The Department of OphthalmologyDenisse LizarragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conditions of The CorneaDokument38 SeitenConditions of The Corneac/risaaq yuusuf ColoowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Superficial Skin Infections and The Use of Topical and Systemic Antibiotics in General PracticeDokument4 SeitenSuperficial Skin Infections and The Use of Topical and Systemic Antibiotics in General Practicepeter_mrNoch keine Bewertungen
- CorneaDokument58 SeitenCorneaMishiko DumbadzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye Emergency: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedDokument63 SeitenEye Emergency: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedYousef Al-AmeenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocular Manifestations in AIDSDokument27 SeitenOcular Manifestations in AIDSAnumeha Jindal100% (1)
- Tubkut Srilanka JournalDokument7 SeitenTubkut Srilanka JournalMusdalifah MimousNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAME:-Puspendu Maity. ROLL: - 16101717014. Reg. No: - 171611210014. Subject: - Corneal Ulcer. Semester: - 7 SemesterDokument15 SeitenNAME:-Puspendu Maity. ROLL: - 16101717014. Reg. No: - 171611210014. Subject: - Corneal Ulcer. Semester: - 7 SemesterKumar jit MaityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology of Eyelid, Conjunctiva and CorneaDokument19 SeitenPathology of Eyelid, Conjunctiva and CorneaX And ZNoch keine Bewertungen
- RED EYE WITH DECREASED VISION FixedDokument70 SeitenRED EYE WITH DECREASED VISION FixedChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- RKDF Dental College Bhopal: Department of PeriodonticsDokument40 SeitenRKDF Dental College Bhopal: Department of Periodonticsananya saxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viral Keratitis: Current ConceptsDokument8 SeitenViral Keratitis: Current ConceptsDini MayrisdayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ulcers and Vesicles2Dokument24 SeitenUlcers and Vesicles2Kelly MayerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuliah InfeksiDokument88 SeitenKuliah InfeksiuupupupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjunctiva Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument101 SeitenConjunctiva Anatomy and PhysiologyPurva KeswaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corneal Ulcer: Prepared By: Renuka Shrestha Roll No: 29 PBBN 3rd Year SMTCDokument41 SeitenCorneal Ulcer: Prepared By: Renuka Shrestha Roll No: 29 PBBN 3rd Year SMTCsushma shresthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome American Academy of OpthalmologyDokument2 SeitenStevens-Johnson Syndrome American Academy of OpthalmologybellabelbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keratitis 09Dokument29 SeitenKeratitis 09somebody_maNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tinea Cruris Imp Points With ReferencesDokument35 SeitenTinea Cruris Imp Points With ReferencesSyed Saqib AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of External EarDokument19 SeitenDiseases of External EarMohamed Khaled TahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjunctivitis: by PGMI Jasleen MonrealDokument77 SeitenConjunctivitis: by PGMI Jasleen MonrealJade MonrealNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKDokument19 SeitenDR - Ali's Uworld Notes For Step 2 CKuyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Background: Group A StreptococcusDokument4 SeitenBackground: Group A StreptococcusCoral Srinivasa RamaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin and Soft Tissue Infection InfoDokument4 SeitenSkin and Soft Tissue Infection InfoPresura Andreea IulianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConjunctivitisDokument52 SeitenConjunctivitisFiona H.D.100% (2)
- MolluscumDokument3 SeitenMolluscumSatria Jaya PerkasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 15. Nummular Eczema, Lichen Simplex Chronicus, and Prurigo NodularisDokument11 SeitenChapter 15. Nummular Eczema, Lichen Simplex Chronicus, and Prurigo NodularisandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ToxoDokument10 SeitenToxoDaniyal Aziz KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.bacterial Infection-2Dokument146 Seiten3.bacterial Infection-2Biruk WorkuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture - 8 - Fungal Infections of PNSDokument3 SeitenLecture - 8 - Fungal Infections of PNSAmy KochNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sporothrix and M LepraeDokument6 SeitenSporothrix and M LepraeVictor Juris AnonuevoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Corneal Ulcer?Dokument23 SeitenWhat Is Corneal Ulcer?Sol JoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erythema MultiformeDokument5 SeitenErythema MultiformeNicco MarantsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- P ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Dokument48 SeitenP ('t':3) Var B Location Settimeout (Function (If (Typeof Window - Iframe 'Undefined') (B.href B.href ) ), 15000)Nauli PanjaitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continuing Education ActivityDokument6 SeitenContinuing Education ActivityMuhammed GhaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Herpes Zoster (Shingles) : Muhammad Abdullah Dept. of Dermatology DHQ Hospital FaisalabadDokument26 SeitenHerpes Zoster (Shingles) : Muhammad Abdullah Dept. of Dermatology DHQ Hospital FaisalabadwaleedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kul Mata MerahDokument56 SeitenKul Mata MerahZulfan ZulfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seborrhoeic Dermatitis in AdultsDokument29 SeitenSeborrhoeic Dermatitis in AdultskdwazirNoch keine Bewertungen
- MucormycosisDokument18 SeitenMucormycosisMd. Shafiqul Islam DewanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis: - Dr. Zulfiqar AliDokument30 SeitenVernal Keratoconjunctivitis: - Dr. Zulfiqar AliAsad FrazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of CorneaDokument170 SeitenDiseases of CorneaLavanya MadabushiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmia NeonatorumDokument30 SeitenOphthalmia NeonatorumLing TaerahkunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Otitis & Keratitis Pada HewanDokument14 SeitenOtitis & Keratitis Pada HewanDaffa AmaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas BacaDokument20 SeitenTugas BacaAyu WulansariNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Conjunctiva: Lecture One DR - Ali.a.taqiDokument56 SeitenThe Conjunctiva: Lecture One DR - Ali.a.taqiJorge Esteban Novelo PavíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Makalah SelulitisDokument26 SeitenMakalah Selulitisdr WiyogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head InjuryDokument22 SeitenHead InjuryNguyễn Ly100% (1)
- Dozois 5e Chapter05 TIFDokument22 SeitenDozois 5e Chapter05 TIFrebeccaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sulcus Vocalis Our Experience-DikonversiDokument5 SeitenSulcus Vocalis Our Experience-DikonversiNuni SukindarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital DiseaseDokument39 SeitenCongenital DiseaseRavi SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- West Visayas State University Medical Center E. Lopez St. Jaro Iloilo CityDokument7 SeitenWest Visayas State University Medical Center E. Lopez St. Jaro Iloilo CityRegine Marie EspañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATI DRUG TABLES Module4 Respiratory Glucocorticoids InhalationDokument1 SeiteATI DRUG TABLES Module4 Respiratory Glucocorticoids InhalationnoeyeshaveseenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperthermia in Cancer Treatment: Cabuy E. Reliable Cancer Therapies. Energy-Based Therapies. 2011 1 (2) :1-48Dokument48 SeitenHyperthermia in Cancer Treatment: Cabuy E. Reliable Cancer Therapies. Energy-Based Therapies. 2011 1 (2) :1-48Eliza LlenzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 WartsprotocolDokument9 Seiten14 WartsprotocolLakshmi Deepak INoch keine Bewertungen
- 1. Đề ôn tập GHK1 - Môn Anh 10 - Đề số 1Dokument14 Seiten1. Đề ôn tập GHK1 - Môn Anh 10 - Đề số 1Nguyễn Đ.KhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disorders of The Eye OriginalDokument115 SeitenDisorders of The Eye OriginalKwabena AmankwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Various Homoeopathic Trials in Patients of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An UpdateDokument6 SeitenFundamentals of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Various Homoeopathic Trials in Patients of Rheumatoid Arthritis: An UpdateHomoeopathic PulseNoch keine Bewertungen
- MycosisDokument5 SeitenMycosisMaiWahidGaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dengue (Break Bone Fever) - FAQ, DPH-TAMIL NADU, IndiaDokument3 SeitenDengue (Break Bone Fever) - FAQ, DPH-TAMIL NADU, IndiaDr.SagindarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nausea and Vomiting (Algorithm) PDFDokument2 SeitenNausea and Vomiting (Algorithm) PDFAnggie Anggriyana0% (1)
- Coagulation Profile in Diabetes MellitusDokument5 SeitenCoagulation Profile in Diabetes MellitusAsfandyar RoghaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fgi Guidelines 2014 Hop TocDokument10 SeitenFgi Guidelines 2014 Hop TocZaw Moe KhineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compilation of Nutri Ed ProgramsDokument5 SeitenCompilation of Nutri Ed ProgramsDarwell Chann RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wound Care DescriptionDokument4 SeitenWound Care DescriptionRodriguez, Joyce Ann G.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ofra Ayalon Healing Trauma With Metaphoric Cards PDFDokument3 SeitenOfra Ayalon Healing Trauma With Metaphoric Cards PDFKrisztina MkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aplastic AnemiaDokument3 SeitenAplastic AnemiaFrancis JuneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indicative Term Sheet Bank Islami Pakistan Limited Akbar Chowk Branch, LahoreDokument6 SeitenIndicative Term Sheet Bank Islami Pakistan Limited Akbar Chowk Branch, LahoreSaadatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gender Dysphoria: Agnes B. Padilla MD, DPBP, FppaDokument25 SeitenGender Dysphoria: Agnes B. Padilla MD, DPBP, FppaSivaganesh Paidi100% (2)
- ADHD Parent Questionnaire PDFDokument4 SeitenADHD Parent Questionnaire PDFklichtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theta EnergeticsDokument37 SeitenTheta Energeticsghandhi4351100% (4)
- Basic EKG Dysrhythmia IdentificationDokument40 SeitenBasic EKG Dysrhythmia IdentificationIlda Dhe Devis Spaho100% (1)
- Drug De-Addiction Programme (DDAP) Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MOH&FW), Government of IndiaDokument19 SeitenDrug De-Addiction Programme (DDAP) Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MOH&FW), Government of IndiaHari BabooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Therapeutic Modalities: Prepared By: John Patrick B. de JesusDokument22 SeitenTherapeutic Modalities: Prepared By: John Patrick B. de JesusChiee A. CentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP and Drug StudyDokument11 SeitenNCP and Drug StudyTonio PagaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrandolaprilDokument28 SeitenTrandolaprilYeyenJaejoongNoch keine Bewertungen