Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Dynamics of Machines 4 Units New Question Bank
Hochgeladen von
gbharathreddysOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dynamics of Machines 4 Units New Question Bank
Hochgeladen von
gbharathreddysCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONS
UNIT-I 1
A flywheel of mass 10 kg and radius of gyration 200 mm is spinning about its axis, which is horizontal and is suspended at a point distant 150mm from the plane of rotation of the flywheel. Determine the angular velocity of precession of the flywheel. The spin speed of flywheel is 900rpm. What will be the effect of the gyroscopic couple on a disc fixed at certain angle to a rotating shaft? The rotor of the turbine of a ship makes 1500 rpm clockwise when viewed from the stern. The rotor has a mass of 800 kg and its radius of gyration is 300 mm. Find the maximum gyro- couple transmitted to the hull when the ship pitches with maximum angular velocity of 1 rad/s. How do the effects of gyroscopic couple and of centrifugal force make the rider of a two wheeler tilt on one side? Derive a relation for the limiting speed of the vehicle. June 2010 A flywheel having a mass of 20 kg and a radius of gyration of 300mm is given a spin of 500 rpm about its axis which is horizontal. The flywheel is suspended at a point that is 250mm from the plane of rotation of the flywheel. Find the rate of precession of the wheel Explain the gyroscopic effect on four wheeled vehicles. What do you mean by spin, precession and gyroscopic planes? Explain.
UNIT -II
6 7 1 2 3 4
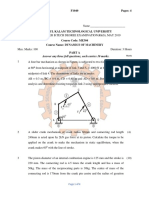
Explain static and dynamic force analysis of a planar mechanism. Explain static equilibrium. What is free body diagram? Explain the free body diagrams of four bar mechanism and slider crank mechanism. Discuss the conditions for equilibrium of two and three force members. In a four link mechanism the dimensions of the links are given below. Fixed link AD=500mm. Driving link AB=500 mm, Coupler BC=1000 mm, Driven link DC=750 mm, and DE=350 mm. The driving link is making an angle 120 with AD. The driven link is acted upon by a force of 80 N at 150 on link DC at E. Determine the input torque T on the link AB for the static equilibrium of the mechanism. In a slider crank mechanism the crank is making an angle of 45 with IDC. The crank and connecting rod lengths are 100 mm and 300 mm respectively. The driving moment on the crank is 50N-m. Determine the force on the slider that is necessary to be applied for the equilibrium of the linkages. In a slider crank mechanism the crank is making an angle of 120 with IDC. The crank and connecting rod lengths are 100 mm and 450mm respectively. If the force applied on the slider is 2 kN. Determine the input torque on the crank for the equilibrium of the linkages.
8 9 10 1 2 3
State and explain DAlemberts principle. What do you mean by dynamical equivalent system? Explain. Discuss the effect of inertia force on the reciprocating engine mechanism by drawing the free body diagram of each link.
UNIT -III
Explain the three position synthesis of a slider crank mechanism. Describe the three position synthesis of a four bar mechanism. Write a short note on: i. Precision positions ii. Structural error iii. Chebychev spacing
UNIT -IV
1 2 3 4
Describe with a neat sketch the working of a single plate friction clutch. Derive the expression for the torque transmitting capacity of single plate clutch by considering uniform pressure. Derive the expression for the torque transmitting capacity of single plate clutch by considering uniform wear. Which of the two assumptions, uniform intensity of pressure or uniform rate of wear, would you make use of in designing a friction clutch and why? A single plate clutch having both sides effective is required to transmit 30 kW at 1500 rpm. The outer diameter of the plate is limited to 300 mm, and the intensity of pressure between the plates is not to exceed 0.07 MPa. Assuming uniform wear and a coefficient of friction 0.35, determine the inside diameter of the plate. The engine of an automobile is rated to give 80 kW at 1800 r.p.m. and maximum torque 550 N-m. Design a dry single plate clutch assuming the outer radius of friction plate is 20% more than the inner radius. The intensity of pressure between the plates is not to exceed 80 KN/m. The coefficient of friction may be assumed equal to 0.25. The helical springs required by this clutch to provide axial force necessary to engage the clutch are six. If each spring has stiffness equal to 50 N /mm, Determine the initial compression in the springs and dimensions of the friction plate. A multi disc clutch has 5 plates having four pairs of active friction surfaces. If the intensity of pressure is not to exceed 127 KN/m. Find the power in KW transmitted at 500 rpm. If the outer and inner radii of friction surfaces are 125 mm and 75 mm respectively. Assume uniform wear and take coefficient of friction as 0.3 Derive the expression for the torque transmitting capacity of cone clutch by considering uniform wear. Determine the axial force required to engage a cone clutch transmitting 25 kW of power at 750 rpm. Average friction diameter of the cone is 400 mm, and average pressure intensity is 60 KN/m2. Semi cone angle is 100 and coefficient of friction is 0.25. Also find the width of the friction cone.
10
11
12
13
14
An effective diameter of cone clutch is 75 mm. The semi-angle of the cone is 18. Find the torque required to produce slipping of the clutch if an axial force applied is 200 N. This clutch is employed to connect an electric motor running uniformly at 100 r.p.m. with a flywheel which is initially stationary. The flywheel has a mass of 13.5 kg and its radius of gyration is 150 mm. Calculate the time required for the flywheel to attain full speed and also the energy lost in the slipping of the clutch. Take coefficient of friction is 0.3. A centrifugal clutch has four shoes which slide radially in a spider keyed to a driving shaft and make contact with the internal cylindrical surface of a rim keyed to driven shaft. When the clutch is at rest, each shoe is pulled against a stop by a spring so as to leave a radial clearance of 5 mm between the shoe and the rim. The pull exerted by the spring is then 500 N. The mass centre of shoe is 160mm from the axis of the clutch. If the internal diameter of rim is 400 mm, the mass of each shoe is 8 kg, the stiffness of each spring is 50N/mm and coefficient of friction between the shoe and rim is 0.3.Find the power transmitted by the clutch at 500rpm. Find an expression for the braking torque for single shoe brake when the brake drum is rotating anti clockwise and the friction force is at a distance b above the fulcrum. a) A bicycle and rider of mass 100 kg are travelling at the rate of 16 km/h on a level road. A brake is applied to the rear wheel which is 0.9 m in diameter and this is the only resistance acting. How far will the bicycle travel and how many turns will it make before it comes to rest? The pressure applied on the brake is 100 N and = 0.05. b) Can a block brake become self locking? If so derive the condition for self locking. What do you understand by self-locking brake and self-energized brake? Should we have self-locking brake or self-energized brake? Justify your answer. The brake drum of a single block brake of diameter is 600 mm is rotating at 400 r.p.m as shown in fig. The operating force of 300 N is applied at the end of a lever. The angle of contact is 90and the coefficient of friction between the drum and the lining is 0.3. Determine the torque that may be transmitted by the block brake. Take a=60 mm, x=375 mm and l=825mm.
15
16
A simple band brake is operated by a lever of length 450 mm. The brake drum has a diameter of 600 mm, and the brake band embraces 5/8th of the circumference. One end of the band is attached to the fulcrum of the lever while the other end is attached to a pin on the lever 120 mm from the fulcrum. The effort applied to the end of the lever is 2 KN, and the coefficient of friction is 0.30. Find the maximum braking torque on the drum
17
18
19
20
21
A band and block brake, having 14 blocks each of which subtends an angle of 15 at the centre, is applied to a drum of 1 m effective diameter. The drum and flywheel mounted on the same shaft has a mass of 2000 kg and a combined radius of gyration of 500 mm. The two ends of the band are attached to pins on opposite sides of the brake lever at distances of 30 mm and 120 mm from the fulcrum. If a force of 200 N is applied at a distance of 750 mm from the fulcrum. Calculate 1. The maximum braking torque, 2. The angular retardation of the drum, and 3. The time taken by the system to come to rest from the rated speed of 360 r.p.m. The coefficient of friction between blocks and drum may be taken as 0.25. A car moving on a level road at a speed 50 km/h has a wheel base 2.8 meters, distance of C.G. from ground level 600 mm, and the distance of C.G. from rear wheels 1.2 meters. Find the distance travelled by the car before coming to rest when brakes are applied, 1. to the rear wheels, 2. to the front wheels, and 3. to all the four wheels. The coefficient of friction between the tyres and the road may be taken as 0.6. The following data refers to a car in which brakes are applied to the front wheels. Wheel base=2.8 m Centre of mass from rear axle=1.3 m Centre of mass above ground level=0.96 m Coefficient of friction between roads and tires=0.4 If the speed of the car to be 40km/hr, find the distance travelled by the car before coming to rest. When the car i. Moves up an incline 1 in 16 ii. Moves down an incline 1 in 16 iii. Moves on a level track. a) Classify dynamometers and explain function of one transmission type dynamometer. b) Distinguish between brakes and dynamometers. a) Distinguish between absorption dynamometer and transmission dynamometer. b) In a vertical belt transmission dynamometer the diameter of the driving pulley rotating at 1500 rpm is 80 mm. The centre distance of the intermediate pulleys from the fulcrum is also 80 mm each. The weighing pan on the lever is at a distance as 250 mm. Find the power transmitted when a mass of 20 kg is required in the pan.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Cave Rescue ActivityDokument6 SeitenCave Rescue Activityshweta bambuwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysVon EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and Transformers and Other EssaysBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- A New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersVon EverandA New System of Alternating Current Motors and TransformersBewertung: 1 von 5 Sternen1/5 (1)
- Vocabulary Booster 1bDokument3 SeitenVocabulary Booster 1btrinskie100% (1)
- A Strategic Management PaperDokument7 SeitenA Strategic Management PaperKarll Brendon SalubreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Time and Labor - Data SheetDokument5 SeitenOracle Time and Labor - Data Sheetbilaltanoli@gmail.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- HOW To Use Jmeter To Load Test T24Dokument27 SeitenHOW To Use Jmeter To Load Test T24Hiếu KoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- FinallDokument175 SeitenFinallremeceldo dagamac100% (1)
- Caribbean Studies - Lesson 8 - Concept and Indicator of Development PDFDokument37 SeitenCaribbean Studies - Lesson 8 - Concept and Indicator of Development PDFDarrion BruceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study No. 11 - Hydroelectric Power Plant in The PhilippinesDokument26 SeitenCase Study No. 11 - Hydroelectric Power Plant in The PhilippinespicefeatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of The Renaissance: Silk RoadDokument6 SeitenCauses of The Renaissance: Silk RoadCyryhl GutlayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural AnalysisDokument51 SeitenStructural AnalysisgbharathreddysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analog To Digital Conversion (ADC)Dokument62 SeitenAnalog To Digital Conversion (ADC)Asin PillaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A03502 Dynamics of MachineryDokument4 Seiten9A03502 Dynamics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IDokument3 SeitenUnit Imahendra babu mekalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dom Questions For Mid1Dokument4 SeitenDom Questions For Mid1Sai SmartNoch keine Bewertungen
- PBR VISVODAYA ENGINEERING COLLEGE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING UNIT-IDokument7 SeitenPBR VISVODAYA ENGINEERING COLLEGE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING UNIT-Ihod mechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Questions Dom Me 5004Dokument5 SeitenAssignment Questions Dom Me 5004sharmasweeta927Noch keine Bewertungen
- R7310303 Dynamics of MachineryDokument1 SeiteR7310303 Dynamics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnitDokument6 SeitenUnitPreethi SharmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- rr320304 Dynamics of MachinesDokument8 Seitenrr320304 Dynamics of MachinesSRINIVASA RAO GANTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Anna University Exams April / May 2019 – Mechanics of Machines QuestionsDokument3 SeitenAnna University Exams April / May 2019 – Mechanics of Machines QuestionsShobiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOM AssignmentDokument2 SeitenDOM AssignmentBharath NNoch keine Bewertungen
- PVP Siddhartha Mech Engineering III Sem HomeworkDokument2 SeitenPVP Siddhartha Mech Engineering III Sem HomeworkNarayanarao PalagaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- KomDokument2 SeitenKomPartha SarathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- University QuestionsDokument4 SeitenUniversity QuestionsMartin De Boras PragashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromDokument3 SeitenOur Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromAjay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Chassis DesignDokument4 SeitenAutomotive Chassis DesigndressfeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Theory NumericalsDokument5 SeitenMachine Theory NumericalsSaad FarooqNoch keine Bewertungen
- MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY MODEL QUESTION PAPERDokument4 SeitenMECHANICAL ENGINEERING DYNAMICS OF MACHINERY MODEL QUESTION PAPERNirman ParasharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment - IIDokument3 SeitenAssignment - IIRamaswamy SubbiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.assignment QuestionsDokument10 Seiten6.assignment QuestionsideepujNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Machinery Jntua Previous PapersDokument20 SeitenDesign of Machinery Jntua Previous PapersHimadhar SaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- S6 QB MeDokument18 SeitenS6 QB MevenkiteshksNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOM Some Problems 1Dokument21 SeitenDOM Some Problems 1NagarajuRbNoch keine Bewertungen
- DYNAMICS OF MACHINES Anna University Exams Nov/Dec 2019 QuestionsDokument5 SeitenDYNAMICS OF MACHINES Anna University Exams Nov/Dec 2019 QuestionsSai KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism MechanicsDokument5 SeitenMechanism MechanicsEzmel KazimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 01Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 01Ratan Sadanandan O MNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A03502 Dynamics of MachineryDokument2 Seiten9A03502 Dynamics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOM2Dokument7 SeitenDOM2ds_shivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Dokument4 SeitenQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Iyyappan SubramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOM Unit 4 & 5 QBDokument6 SeitenDOM Unit 4 & 5 QBRayleighNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis OF Mechanisms GTU IMPDokument5 SeitenAnalysis OF Mechanisms GTU IMPSwastik PanchalNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME4001D Assign 1Dokument3 SeitenME4001D Assign 1vivek geddamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rr320304 Dynamics of MachinesDokument8 SeitenRr320304 Dynamics of MachinesSrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB For Mid-IiDokument3 SeitenQB For Mid-Iihod mechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jntu Question PaperDokument3 SeitenJntu Question Paperrohitchanakya76Noch keine Bewertungen
- At 6602 ACCD Imp Qns 2by2resultsDokument3 SeitenAt 6602 ACCD Imp Qns 2by2resultsKarthickNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTME-402 – THEORY OF MACHINES TWO MARKS QUESTIONSDokument6 SeitenBTME-402 – THEORY OF MACHINES TWO MARKS QUESTIONSNavneet Singh DhamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- NR-310304 - Dynamics of MachineryDokument8 SeitenNR-310304 - Dynamics of MachinerySrinivasa Rao GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dom 16 MarksDokument2 SeitenDom 16 MarksKarthikn AltocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dom Unit I Imp QuestionsDokument1 SeiteDom Unit I Imp QuestionsSree MurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics of MachineryDokument8 SeitenDynamics of MachineryNORIMAR24Noch keine Bewertungen
- DOM Model PaperDokument2 SeitenDOM Model PaperRambabuDaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Au Qp-Me8594 PDFDokument18 SeitenAu Qp-Me8594 PDFMariappan VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 TOM2 YBKDokument2 SeitenAssignment 3 TOM2 YBKyogesh_b_kNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME2302 Dynamics of Machinery Question Bank Part A and BDokument14 SeitenME2302 Dynamics of Machinery Question Bank Part A and BNagendar SelvakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mom T2 QPDokument1 SeiteMom T2 QPsutha_me20098282Noch keine Bewertungen
- Model Question BankDokument4 SeitenModel Question BankVinod BalakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Mech Me8594 Dom QBDokument29 Seiten3 Mech Me8594 Dom QBSurya SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokument - Pub Dom Assignment Flipbook PDFDokument22 SeitenDokument - Pub Dom Assignment Flipbook PDFMuhammad SaboorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics Question Bank PDFDokument21 SeitenDynamics Question Bank PDFbejumohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics of Machinery Question BankDokument8 SeitenDynamics of Machinery Question BankArun ShawnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2MID EXAMS ENGINE MODEL QUESTIONSDokument4 Seiten2MID EXAMS ENGINE MODEL QUESTIONSSrimanthula SrikanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Dynamics Question Bank1Dokument16 SeitenMachine Dynamics Question Bank1ashoku2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics of Machinery Exam: Torque and Force AnalysisDokument8 SeitenDynamics of Machinery Exam: Torque and Force AnalysisAkhil C KNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOM Model QuestionDokument2 SeitenDOM Model QuestionSenthilkumar SubbiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Crank and Connecting Rod of A Steam Engine Are 0Dokument7 SeitenThe Crank and Connecting Rod of A Steam Engine Are 0ANBU RAJ ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics of Machinery 4Dokument2 SeitenDynamics of Machinery 4prasaad08Noch keine Bewertungen
- HMT Lab 2Dokument36 SeitenHMT Lab 2Rahul TripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DrillingDokument14 SeitenDrillinggbharathreddysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volume I 200 Word Definitions PDFDokument6 SeitenVolume I 200 Word Definitions PDFleviboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dom Question BankDokument3 SeitenDom Question BankgbharathreddysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nontraditional MachiningDokument22 SeitenNontraditional MachiningSagar WakankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDM and Other NTMDokument15 SeitenEDM and Other NTMSyed Basith MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nontraditional MachiningDokument22 SeitenNontraditional MachiningSagar WakankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Generators 2Dokument33 SeitenSteam Generators 2gbharathreddysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ump Question BankDokument1 SeiteUmp Question BankgbharathreddysNoch keine Bewertungen
- PIEZOELECTRIC CRYSTALS AND POLYMERSDokument14 SeitenPIEZOELECTRIC CRYSTALS AND POLYMERSgbharathreddysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Materials For Powder Based Rapid Prototyping With DateDokument8 SeitenAdvances in Materials For Powder Based Rapid Prototyping With DateNeo MechatronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Spray ProcessDokument18 SeitenThermal Spray ProcessgbharathreddysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Theory of Matter and Inter Molecular ForcesDokument10 SeitenMolecular Theory of Matter and Inter Molecular ForcesgbharathreddysNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 1 1 108Dokument8 Seiten10 1 1 108gbharathreddysNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIACRYL VSC 6250w/65MP: Technical DatasheetDokument2 SeitenVIACRYL VSC 6250w/65MP: Technical DatasheetPratik MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Science & Engineering A: Alena Kreitcberg, Vladimir Brailovski, Sylvain TurenneDokument10 SeitenMaterials Science & Engineering A: Alena Kreitcberg, Vladimir Brailovski, Sylvain TurenneVikrant Saumitra mm20d401Noch keine Bewertungen
- MarasiNews Issue 12Dokument47 SeitenMarasiNews Issue 12Sunil Kumar P GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Range of Muscle Work.Dokument54 SeitenRange of Muscle Work.Salman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- E TN SWD Csa A23 3 94 001 PDFDokument9 SeitenE TN SWD Csa A23 3 94 001 PDFRazvan RobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultra Slimpak G448-0002: Bridge Input Field Configurable IsolatorDokument4 SeitenUltra Slimpak G448-0002: Bridge Input Field Configurable IsolatorVladimirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Proposal For SGF - BomDokument2 SeitenSolution Proposal For SGF - BomABHISHEK ADHIKARYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Film set safety rules for COVIDDokument12 SeitenFilm set safety rules for COVIDTanveer HossainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquid Air Energy Storage Systems A - 2021 - Renewable and Sustainable EnergyDokument12 SeitenLiquid Air Energy Storage Systems A - 2021 - Renewable and Sustainable EnergyJosePPMolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Camp ApplianceDokument1 SeiteCamp ApplianceflyzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Avance Collection Mixer Grinder SpecsDokument3 SeitenAvance Collection Mixer Grinder SpecsfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PremiumpaymentReceipt 10663358Dokument1 SeitePremiumpaymentReceipt 10663358Kartheek ChandraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Provisional List of Institutes1652433727Dokument27 SeitenProvisional List of Institutes1652433727qwerty qwertyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.9 Bernoulli's Equation: GZ V P GZ V PDokument1 Seite1.9 Bernoulli's Equation: GZ V P GZ V PTruong NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vikash Kumar: 1. Aunico India May 2018Dokument4 SeitenVikash Kumar: 1. Aunico India May 2018Rama Krishna PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comparison of Fuel Cell Testing Protocols PDFDokument7 SeitenA Comparison of Fuel Cell Testing Protocols PDFDimitrios TsiplakidesNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCMEDokument9 SeitenBCMEVenkateshwaran VenkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Physics KPN MurthyDokument151 SeitenThermal Physics KPN MurthyRithish BarathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam IN Sample QuestionsDokument27 SeitenFinal Exam IN Sample QuestionsJI TEN100% (1)
- A. Rationale: Paulin Tomasuow, Cross Cultural Understanding, (Jakarta: Karunika, 1986), First Edition, p.1Dokument12 SeitenA. Rationale: Paulin Tomasuow, Cross Cultural Understanding, (Jakarta: Karunika, 1986), First Edition, p.1Nur HaeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIL (Second Quarter)Dokument13 SeitenMIL (Second Quarter)Menma ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- RCC Lintel and Slab PlanDokument3 SeitenRCC Lintel and Slab PlanSaurabh Parmar 28Noch keine Bewertungen