Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Neonatal Goals
Hochgeladen von
Jehanie LukmanOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Neonatal Goals
Hochgeladen von
Jehanie LukmanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
NEONATAL INTENSIVE CARE UNIT GOALS, OBJECTIVES AND TEACHING The rotation in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
is intended to promote the compassionate, effective, and developmentally appropriate assessment and treatment of critically ill newborns by enhancing the residents knowledge of physiology, pharmacology and evidence based medicine.
PART I: PATIENT CARE AND MEDICAL KNOWLEDGE GOAL: The ongoing acquisition of knowledge regarding established and evolving biomedical, clinical and cognate sciences, with the resultant application of that knowledge to the compassionate, age appropriate, and effective treatment of critically ill newborns. OBJECTIVES: 1. Resuscitation and Stabilization: Understand the basic principles and perform appropriate steps in resuscitation and stabilization, with particular reference to airway management and pharmacology. Function appropriately in newborn resuscitation and stabilization in the delivery suite as a member of the critical care team. 2. Information Gathering: Gather essential and accurate maternal history. Obtain a labor and delivery history. Conduct a congenital defects screen Perform an appropriate prenatal assessment of growth status (pre-term, AGA, etc) by history of the mother. Perform an appropriate physical examination Explain the indications and limitations of laboratory and radiologic study abnormalities in the context of disease-specific pathophysiology and formulate a plan for therapeutic intervention, when appropriate 3. Common signs and symptoms: ( see table 1): Rapidly recognize sings and symptoms indicating the onset of lifethreatening events in preterm and term newborns. Formulate a gestational age-appropriate differential diagnosis with appropriate prioritization. Discuss the indications for admission to, and discharge diagnosis from, the NICU, including indications for emergent intervention and stabilization prior to transport to the NICU.
Formulate and execute a plan of assessment and management based on physiology, pathophysiology, pharmacology and evidence based guideline. 4. Common conditions: (see table 2): Discuss the pathophysiologic basis of the disease process or injury Discuss disease specific considerations for resuscitation, stabilization , continued evaluation and management Understand the potential complications and consequences of the disease and various treatment options; evaluate prognosis. 5. Monitoring and therapeutic modalities: Integrate physiologic and pathophysiologic principles to determine appropriate use of common therapies (oxygen administration, positive pressure ventilation, analgesia, sedation, enteral and parenteral nutrition, blood product transfusions, vasoactive medications), monitor their effects and describe potential complications 6. Management and decision making: Develop and maintain a detailed list of tasks with accurate prioritization Coordinate with multiple consultants involved in the care of the patient Coordinate orderly transfer of care under another provider when NICU care is no longer required Recognize the limits of ones knowledge, skills, and tolerance for stress levels. 7. Medical ethics and legal issues; Discuss concepts of futility, withdrawal and withholding of care. Define brain death. Describe hospital policy on Do not resuscitate order.
PART II: INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNCIATIN SKILLS GOAL: Understand and demonstrate effective communication and interpersonal skills with parents, patients and professional associates. OBJECTIVES: 1. Develop and maintain a therapeutic and ethically sound relationship with patients and their families. 2. Listen effectively 3. Elicit and provide information using effective nonverbal, informative, interrogative, and writing skills
4. Communicate and work effectively with other residents, attendings, consultants, nurses and ancillary staff as part of the critical care team. 5. Communicate effectively with surgeons and subspecialists whose patients are being managed in the NICU. 6. Communicate frequently and effectively with referring and primary care physicians 7. Consistently maintain accurate, timely and legally appropriate medical records.
PART III: PROFESSIONALISM GOAL: Understand and demonstrate commitment to carrying out professional responsibilities, adherence to ethical principles and sensitivity to a diverse patient population. OBJECTIVES: 1. Demonstrate respect, compassion, and integrity; a responsiveness to the needs of patients and society that supersedes self-interest; accountability to patients, society and the profession and a commitment to excellence and on-going professional development 2. Demonstrate a commitment to ethical principles pertaining to provision or withholding of clinical care, confidentiality of patient information, informed consent and clinical practices 3. . PART IV: TEACHING METHODS
To achieve the objectives of the Neonatal Critical Care rotation, the resident physician will participate in the following educational activities: 1. Teaching rounds: a. Prior to the start of daily teaching rounds, it is expected that the resident will: i. Examine each patient ii. Collect and review all bedside data iii. Review all radiographic studies iv. Develop a concise, system-based treatment plan. b. Teaching rounds will start at 0930 am daily and will continue until all patients have been discussed.
2. Neonatal Critical Care teaching conference: a. Formal didactic teaching conferences will be held as part of the core curriculum schedule of the pediatric residency program and will include the following topics: i. Mechanical ventilation ii. Nutrition
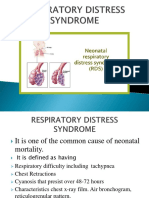
Table 2: Common conditions: General: Congenital abnormalities Prematurity Cardiovascular: Persistent pulmonary hypertension of the Newborn Congenital heart disease Patent ductus arteriosus Respiratory: Respiratory Distress Syndrome Hyaline Membrane disease Pneumothorax Meconium aspiration Congenital Pneumonia Neurologic: Hydrocephalus
Hypoxic-ischemic injury Intraventricular hemorrhage Neonatal asphyxia Hematologic: Neonatal coagulopathy ABO incompatability Hemolytic disease Anemia/polycythemia Neutropenia Thrombocytopenia Gastrointestinal: Necrotizing enterocolitis Bowel obstruction Abdominal wall defects Infectious Diseases: Neonatal infections caused by bacteria, virus and parasites Congenital acquired infections (HIV, CMV, toxoplasmosis, syphilis, and rubella) Fluids, electrolytes and metabolic: Hypoglycemia Inborn errors of metabolism
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Emergency Nursing Care GuideDokument14 SeitenEmergency Nursing Care GuideJehanie LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEDI GENITOURINARYDokument7 SeitenPEDI GENITOURINARYcayla mae carlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 H q1 l1.2 The Concept of Community HealthDokument16 Seiten9 H q1 l1.2 The Concept of Community HealthRegine Rellores BaliatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newborn Assessment, Apgar & Ballard Scoring NotesDokument3 SeitenNewborn Assessment, Apgar & Ballard Scoring NotesAshitakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Surgical InstrumentsDokument37 SeitenBasic Surgical Instrumentsapi-2658787991% (33)
- Essential Intrapartum Newborn Care 181120082158 PDFDokument19 SeitenEssential Intrapartum Newborn Care 181120082158 PDFDorinna Rizada BagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Resuscitation. Advances in Training and PracticeDokument10 SeitenNeonatal Resuscitation. Advances in Training and PracticeFer45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bubble Nasal CPAPDokument83 SeitenBubble Nasal CPAPJunior763Noch keine Bewertungen
- Newborn Respiratory Disorders PDFDokument10 SeitenNewborn Respiratory Disorders PDFMax RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NRPDokument10 SeitenNRPNovi BaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentDokument11 SeitenNeonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) Causes, Symptoms & TreatmentHina MasoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Transition: Training of The Trainers Neonatal ResuscitationDokument36 SeitenNeonatal Transition: Training of The Trainers Neonatal ResuscitationmitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AHA Guidelines On Neonatal ResuscitationDokument17 SeitenAHA Guidelines On Neonatal ResuscitationVillia Damayantie100% (1)
- Low Birth Weight Baby and HyalineDokument42 SeitenLow Birth Weight Baby and Hyalineakhmad rizky subkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonates Maternal Drugs Which May Adversely Affect The Newborn BabyDokument9 SeitenNeonates Maternal Drugs Which May Adversely Affect The Newborn BabyAnonymousNoch keine Bewertungen
- NRP HandoutDokument10 SeitenNRP HandoutElisabeth F. OjhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Newborn Intensive Care Unit Environment of CareDokument6 SeitenThe Newborn Intensive Care Unit Environment of CareSteph FergusonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Golden Hours Management of High Risk Newborns - 2019Dokument10 SeitenGolden Hours Management of High Risk Newborns - 2019Suryadi LimardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing High Risk NewbornsDokument42 SeitenAssessing High Risk NewbornsKiran KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competency1. Patient Care: The Neonatal Intensive Care UnitDokument8 SeitenCompetency1. Patient Care: The Neonatal Intensive Care UnitChristopher TibuleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Levothyroxine (Synthroid)Dokument1 SeiteLevothyroxine (Synthroid)E50% (2)
- High Risk Newborn Conditions Present at BirthDokument47 SeitenHigh Risk Newborn Conditions Present at BirthChinchu ChinchuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recommended Standards For Newborn ICU DesignDokument18 SeitenRecommended Standards For Newborn ICU DesignYayang Andayani100% (1)
- Neonatal Emergencies FinalDokument90 SeitenNeonatal Emergencies FinalDr Raseena VattamkandathilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newborn CareDokument49 SeitenNewborn CareJohn Mark PocsidioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resuscitation of New Born: SBA - Presentation 5 (B)Dokument27 SeitenResuscitation of New Born: SBA - Presentation 5 (B)Dr-Nikhil Goswami100% (1)
- Evidence Based Guidelines For Prevention of Infection in NicuDokument50 SeitenEvidence Based Guidelines For Prevention of Infection in NicuBahaa Gamal100% (2)
- Nursing the NeonateVon EverandNursing the NeonateMaggie MeeksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment and Management of High Risk NewbornsDokument45 SeitenAssessment and Management of High Risk NewbornsShiva KarthikeyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plan de Nutritie in HipotiroidismDokument48 SeitenPlan de Nutritie in Hipotiroidismalbinuta100% (1)
- Expanding Designed Exercise Awareness and Produced by Gregory Petrovich GrabovoiDokument5 SeitenExpanding Designed Exercise Awareness and Produced by Gregory Petrovich GrabovoiManojkumar NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Breast FeedingDokument17 SeitenManagement of Breast FeedingUday KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal ResuscitationDokument5 SeitenNeonatal Resuscitationabdirahiim ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Ventilation of The Neonate Principles and StrategiesDokument6 SeitenMechanical Ventilation of The Neonate Principles and StrategiesKelly HoffmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birth asphyxia causes and neonatal resuscitationDokument20 SeitenBirth asphyxia causes and neonatal resuscitationinne_fNoch keine Bewertungen
- NRP 2011 SummaryDokument6 SeitenNRP 2011 Summaryvanstar7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Systems Checklist for Pediatric Physical ExamDokument2 SeitenReview of Systems Checklist for Pediatric Physical ExamteuuuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergic Rhinitis in Children: Diagnosis and TreatmentDokument39 SeitenAllergic Rhinitis in Children: Diagnosis and Treatmentrinajacky100% (2)
- Neonatal SubgalealDokument6 SeitenNeonatal SubgalealIrenLayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Allergic Rhinitis in Children: A Common but Treatable ConditionDokument7 SeitenAllergic Rhinitis in Children: A Common but Treatable ConditionTina MorleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newborn Resuscitation GuidelinesDokument7 SeitenNewborn Resuscitation GuidelinesYwagar YwagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Congenital AnomaliesDokument22 SeitenCongenital Anomaliesjessy100% (1)
- Febrile Convulsions in ChildrenDokument2 SeitenFebrile Convulsions in ChildrenMagdalena Dwiyani HutajuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care For NewbornDokument33 SeitenNursing Care For NewbornDarla Quiballo100% (1)
- Mechanical Ventilation Practice Guidelines: 1. 2. Initial Settings - ModeDokument12 SeitenMechanical Ventilation Practice Guidelines: 1. 2. Initial Settings - ModeGayathri RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Neonatal HypoglycemiaDokument14 SeitenManagement of Neonatal Hypoglycemiaece142Noch keine Bewertungen
- NICU Equipment Guide for Premature BabiesDokument7 SeitenNICU Equipment Guide for Premature BabiesGheDine PeracionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundal Height ScreeningDokument10 SeitenFundal Height ScreeningDr_Soranus100% (1)
- Pedia Concepts 2:: From Respiratory Problems To HematologicDokument119 SeitenPedia Concepts 2:: From Respiratory Problems To HematologicarudarbmeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Problems in NeonatesDokument73 SeitenCommon Problems in NeonatesWan FaizuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- HYPERBILIRUBINEMIADokument30 SeitenHYPERBILIRUBINEMIAAlexisRoyE100% (1)
- 9, Procedure of PICCDokument9 Seiten9, Procedure of PICCputriseptinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps in Essential Newborn CareDokument12 SeitenSteps in Essential Newborn CareCedy L. CieloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sept 22 Neonatal HypothermiaDokument23 SeitenSept 22 Neonatal Hypothermiaf.abrahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PP Bag TechniqueDokument74 SeitenPP Bag TechniqueAngelika BacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn (TTNDokument6 SeitenTransient Tachypnea of the Newborn (TTNWivan Havilian DjohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birth AsphyxiaDokument10 SeitenBirth Asphyxiasarita Singh MaharjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case 7 - Newborn With Respiratory DistressDokument10 SeitenCase 7 - Newborn With Respiratory DistressSue HuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermoregulation in NewbornDokument14 SeitenThermoregulation in NewbornSamsiah ChaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal JaundiceDokument63 SeitenNeonatal JaundiceMade Oka HeryanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Newborn Medicine Clinical Practice GuidelinesDokument15 SeitenPediatric Newborn Medicine Clinical Practice GuidelinesJosselle Sempio CalientaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric TracheostomyDokument13 SeitenPaediatric TracheostomyYwagar YwagarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report "Febrile Seizures": Betsheba E. S. 123307018Dokument37 SeitenCase Report "Febrile Seizures": Betsheba E. S. 123307018AmandaRizkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NicuDokument6 SeitenNicuassadhhmohammed assadh100% (1)
- Nicu Discharge GuidelinesDokument8 SeitenNicu Discharge Guidelinessophia mendiolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ideal Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Super Diet Guide To Replenish Overall Health For A Vibrant Lifestyle With Nourishing RecipesVon EverandThe Ideal Neutropenic Diet Cookbook; The Super Diet Guide To Replenish Overall Health For A Vibrant Lifestyle With Nourishing RecipesNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Emergency Room Skills HecklistDokument5 SeitenAll Emergency Room Skills HecklistJehanie LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNLE Nursing Licensure Exam OutlineDokument11 SeitenPNLE Nursing Licensure Exam OutlineJehanie LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeroDokument7 SeitenGeroJehanie LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNLE Nursing Licensure Exam OutlineDokument11 SeitenPNLE Nursing Licensure Exam OutlineJehanie LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing care of burnsDokument2 SeitenNursing care of burnsRadz Lyn LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing care of burnsDokument2 SeitenNursing care of burnsRadz Lyn LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNLE Nursing Licensure Exam OutlineDokument11 SeitenPNLE Nursing Licensure Exam OutlineJehanie LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing care of burnsDokument2 SeitenNursing care of burnsRadz Lyn LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing care of burnsDokument2 SeitenNursing care of burnsRadz Lyn LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing care of burnsDokument2 SeitenNursing care of burnsRadz Lyn LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRC FormatDokument5 SeitenPRC FormatJehanie LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRC FormatDokument5 SeitenPRC FormatJehanie LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final PRC Evaluation ToolDokument8 SeitenFinal PRC Evaluation ToolJehanie LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRC FormatDokument5 SeitenPRC FormatJehanie LukmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions PneumoniaDokument8 SeitenQuestions PneumoniaMeliza BancolitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Questions To Be Answered. Each Question To Be Answered in A Separate Book (Or Books If More Than One Is Required For The One Answer)Dokument3 SeitenAll Questions To Be Answered. Each Question To Be Answered in A Separate Book (Or Books If More Than One Is Required For The One Answer)matentenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Puskesmas PDFDokument24 SeitenPuskesmas PDFChristopher AdhisasmitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eastern Connecticut State University Informed Consent Form: Participant's Printed NameDokument4 SeitenEastern Connecticut State University Informed Consent Form: Participant's Printed NameKisu Hive GamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- CindyDokument4 SeitenCindyUsama QayyumNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEDIATRIC AUDIOLOGY WEEKLY TOPICSDokument3 SeitenPEDIATRIC AUDIOLOGY WEEKLY TOPICSAhiawortor KplorlaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autism DisorderDokument5 SeitenAutism DisorderAndreeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HER2 Targeted Therapy For Early and Locally Advanced Breast CancerDokument58 SeitenHER2 Targeted Therapy For Early and Locally Advanced Breast Cancerreny hartikasariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uncovering A Curricular Model of Self Care in Pediatric Physical TherapyDokument17 SeitenUncovering A Curricular Model of Self Care in Pediatric Physical TherapyAnnette WillgensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Study Between Swiss Ball and Theraband Exercises On Overweight IndividualsDokument42 SeitenComparative Study Between Swiss Ball and Theraband Exercises On Overweight Individualssundar_kumar0Noch keine Bewertungen
- DNP - Doctor-Nursing-Practice-Brochure - 0Dokument8 SeitenDNP - Doctor-Nursing-Practice-Brochure - 0martynbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Philips issues urgent field safety notice for ventilator touchscreensDokument3 SeitenPhilips issues urgent field safety notice for ventilator touchscreensChris SilerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kumpulan Journal Kompartemen SindromDokument6 SeitenKumpulan Journal Kompartemen SindromBrinna Anindita SatriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health and Safety CultureDokument2 SeitenHealth and Safety CultureAbdul WahabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education School Nutritional Status RecordDokument17 SeitenDepartment of Education School Nutritional Status RecordSwitkizzes SwitkizzesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Project 3Dokument35 SeitenFinal Project 3api-666429985Noch keine Bewertungen
- Revised FAQs for HDB Employees on Covid19 Leave, Medical AssistanceDokument3 SeitenRevised FAQs for HDB Employees on Covid19 Leave, Medical AssistanceMulukallavinay ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Postpartum HemorrhageDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Postpartum HemorrhageroxaynnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Cervical Lymphadenopathy GuideDokument11 SeitenPediatric Cervical Lymphadenopathy GuideAMENDBENoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes of Mortality and MorbidityDokument8 SeitenCauses of Mortality and MorbiditypurletpunkNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Hudson, Hall & Harkness (2019)Dokument11 SeitenA-Hudson, Hall & Harkness (2019)Jordanitha BhsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.11 SEPTIC ABORTION AND SEPTIC SHOCK. M. Botes PDFDokument4 Seiten2.11 SEPTIC ABORTION AND SEPTIC SHOCK. M. Botes PDFteteh_thikeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Giant Ovarian Cyst Mimicking AscitesDokument3 SeitenGiant Ovarian Cyst Mimicking AscitesbellastracyNoch keine Bewertungen
- EU Digital COVID Vaccine CertificateDokument2 SeitenEU Digital COVID Vaccine Certificatekrasota izdorovieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Factors in Dental ErosionDokument6 SeitenRisk Factors in Dental ErosionMuftihat IsrarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 WinterDokument48 Seiten10 WintercontinentdriftNoch keine Bewertungen