Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ideal Gas
Hochgeladen von
Muhammad UzairOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ideal Gas
Hochgeladen von
Muhammad UzairCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
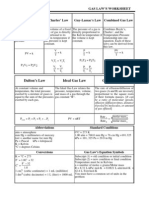
IDEAL GAS: 1- Under what conditions is the ideal-gas assumption suitable for real gases?
2- What is the difference between R and Ru? How are these two related? 3- What is the difference between mass and molar mass? How are these two related? 4- A spherical balloon with a diameter of 6 m is filled with helium at 20C and 200 kPa. Determine the mole number and the mass of the helium in the balloon. Ans (9.28 kmol, 37.15 kg) 5- The pressure in an automobile tire depends on the temperature of the air in the tire. When the air temperature is 25C, the pressure gage reads 210 kPa. If the volume of the tire is 0.025 m3, determine the pressure rise in the tire when the air temperature in the tire rises to 50C. Also, determine the amount of air that must be bled off to restore pressure to its original value at this temperature. Assume the atmospheric pressure to be 100 kPa. 6- The pressure gage on a 1.3-m3 oxygen tank reads 500 kPa. Determine the amount of oxygen in the tank if the temperature is 24C and the atmospheric pressure is 97 kPa 7- A800-L rigid tank contains 10 kg of air at 25C. Determine the reading on the pressure gage if the atmospheric pressure is 97 kPa. COMPRESSIBILITY FACTOR: 1- What is the physical significance of the compressibility factor Z? 2- What is the principle of corresponding states? 3- How are the reduced pressure and reduced temperature defined? 4- Determine the specific volume of superheated water vapor at 10 MPa and 400C, using (a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the generalized compressibility chart, and (c) the steam tables. Also determine the error involved in the first two cases. Answers: (a) 0.03106 m3/kg, 17.6 percent; (b) 0.02609 m3/kg, 1.2 percent; (c) 0.02641 m3/kg 5- Determine the specific volume of refrigerant-134a vapor at 1.4 MPa and 140C based on (a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the generalized compressibility chart, and (c) the experimental data from tables. Also, determine the error involved in the first two cases. 6- Somebody claims that oxygen gas at 160 K and 3 MPa can be treated as an ideal gas with an error of less than 10 percent. Is this claim valid? 7- What is the percentage of error involved in treating carbon dioxide at 3 MPa and 10C as an ideal gas? 8- A 3.27-m3 tank contains 100 kg of nitrogen at 225 K. Determine the pressure in the tank, using (a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the van der Waals equation, and (c) the Beattie- Bridgeman equation. Compare your results with the actual value of 2000 kPa.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Tutorial 4 PDFDokument2 SeitenTutorial 4 PDFAnonymous hxyDxxcoJNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18 Tugas Sifat Sifat Gas CH 1Dokument19 Seiten18 Tugas Sifat Sifat Gas CH 1Fadhillah AnsyariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo Sheet 1Dokument2 SeitenThermo Sheet 1Kerro MankoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbon Dioxide Thermodynamic Properties Handbook: Covering Temperatures from -20° to 250°C and Pressures up to 1000 BarVon EverandCarbon Dioxide Thermodynamic Properties Handbook: Covering Temperatures from -20° to 250°C and Pressures up to 1000 BarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Laws Review WS ANSWERSDokument3 SeitenGas Laws Review WS ANSWERSAlyssa ColeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions to Problem Set 1 for Physical Chemistry I (Chem 331) - Fall 2011Dokument5 SeitenSolutions to Problem Set 1 for Physical Chemistry I (Chem 331) - Fall 2011Feredun AzariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument5 SeitenAssignment 2SouravNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding GasesDokument30 SeitenUnderstanding GasesMohammad Amjad KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Questions 1111Dokument6 SeitenTutorial Questions 1111Fahmy Muhd100% (1)
- Gas Laws Packet Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRTDokument5 SeitenGas Laws Packet Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRTJose Barrera GaleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Soal GasDokument1 SeiteLatihan Soal GasnajmahsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 59-240 Physical Chemistry - Question Set #4 - Lecture 4 - v. 1.1 - Updated Sep. 17, 2015Dokument3 Seiten59-240 Physical Chemistry - Question Set #4 - Lecture 4 - v. 1.1 - Updated Sep. 17, 2015honey joy ZambasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise On Properties of Pure Substances and The Ideal Gas (Teves)Dokument4 SeitenExercise On Properties of Pure Substances and The Ideal Gas (Teves)Fria Lelaine TevesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Dokument3 SeitenGas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Nikhil Singh100% (1)
- Science Quest Reviewer Gas LawsDokument5 SeitenScience Quest Reviewer Gas LawsEva esperaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 8 Test Review Study Guide Hon-18Dokument2 SeitenUnit 8 Test Review Study Guide Hon-18api-368121935Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cpp-Gaseous State - RGVDokument2 SeitenCpp-Gaseous State - RGVGauri KabraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Problems 1 (Pressure, Gas Laws)Dokument3 SeitenPractice Problems 1 (Pressure, Gas Laws)Jose Ruben SortoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHYCHEMDokument12 SeitenPHYCHEM22-00248Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Laws Packet 2 ANSWERSDokument5 SeitenGas Laws Packet 2 ANSWERSCenando BodanioNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME2202 Question BankDokument5 SeitenME2202 Question BankStanly ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Homework 3 11th Gas LawDokument5 SeitenKey Homework 3 11th Gas LawTai PanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solucionario Maron Capítulo 1Dokument8 SeitenSolucionario Maron Capítulo 1anon_788159847Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Laws Worksheetsand SolutionsDokument9 SeitenGas Laws Worksheetsand SolutionskjgfsogkpsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ideal Gas Law and Gas Stoichiometry Hon)Dokument3 SeitenThe Ideal Gas Law and Gas Stoichiometry Hon)Camilo RosasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Laws Practice Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRT: R 0.0821 (L Atm) / (K Mol) or R 8.31 L Kpa / (K Mole)Dokument5 SeitenGas Laws Practice Ideal Gas Law Worksheet PV NRT: R 0.0821 (L Atm) / (K Mol) or R 8.31 L Kpa / (K Mole)Alyssa ColeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MI-106 Tut ThermoDokument37 SeitenMI-106 Tut ThermoDhananjayLekshmiNarayan100% (7)
- Chapter 1 Questions 8th Ed.Dokument4 SeitenChapter 1 Questions 8th Ed.Samya SoaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- MA2003 Thermo-Fluids Tutorial ProblemsDokument6 SeitenMA2003 Thermo-Fluids Tutorial ProblemsLadnilrebNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS Practice W GraphsDokument4 SeitenWS Practice W GraphsgiyagirlsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Engineering Calculations for Gases and VaporsDokument2 SeitenChemical Engineering Calculations for Gases and VaporsKhristel PenoliarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phat (Necro) Ho - 5-00 Gases Unit Pack - 2021Dokument8 SeitenPhat (Necro) Ho - 5-00 Gases Unit Pack - 2021Just an Abnormal SIMPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Thermodynamics - Department of Mechanical EngineeringDokument5 SeitenEngineering Thermodynamics - Department of Mechanical EngineeringKarthik P MuraliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Gas Mixture ExerciseDokument6 Seiten2 Gas Mixture ExerciseSurenderan LoganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set - Real GasesDokument1 SeiteProblem Set - Real GasesLorhen Yap SiembreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics II - EngineeringG PDFDokument110 SeitenPhysics II - EngineeringG PDFRami JarrarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry SheetsDokument10 SeitenChemistry Sheetshebaneyar74Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problems On Unit IV and V - PDFDokument2 SeitenProblems On Unit IV and V - PDFchristo_nitinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9A03302 ThermodynamicsDokument5 Seiten9A03302 ThermodynamicssivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Laws 201314 Review Sheet W Answers 2Dokument4 SeitenGas Laws 201314 Review Sheet W Answers 2Leighton RowlandNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTD QuestionsDokument5 SeitenBTD Questionsjeffreysingh jdNoch keine Bewertungen
- KF 1Dokument19 SeitenKF 1Diana Fitriani SurtikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 38 1 THE PROPERTIES OF GASES Discussion PDFDokument3 Seiten38 1 THE PROPERTIES OF GASES Discussion PDFZakirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Laws Practice SheetDokument4 SeitenGas Laws Practice SheetJensen Ryan LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Chemistry 1 Prob SetDokument8 SeitenPhysical Chemistry 1 Prob SetArrianne Jaye MataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems Analysis and EOS 2011-1Dokument2 SeitenProblems Analysis and EOS 2011-1Jenny CórdobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gases Practice Quest 2013 AnswersDokument5 SeitenGases Practice Quest 2013 Answersethanwong3412Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Laws PracticeDokument3 SeitenGas Laws Practiceapi-280439402Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHEM 2820 Problem Set 1Dokument3 SeitenCHEM 2820 Problem Set 1Vicente JonathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HWDokument6 SeitenHWapi-248733530Noch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Bab IDokument6 SeitenSoal Bab IMia Herlina NasutionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Chapter 1 - 0 ThermodynamicDokument2 SeitenTutorial Chapter 1 - 0 ThermodynamicSufferedMuchNoch keine Bewertungen
- GLWS9Dokument6 SeitenGLWS9Vince HernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChE 323 Prob Set 1 11 - 30-13Dokument2 SeitenChE 323 Prob Set 1 11 - 30-13Stephanie JainarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Thermodynamics Nov2004 NR 21030Dokument8 Seiten4 Thermodynamics Nov2004 NR 21030Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Our Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromDokument2 SeitenOur Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromPradeep KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 1201Dokument5 SeitenMe 1201Navaneethakrishnan RangaswamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Uzair's Lecture on Renewable Energy SourcesDokument71 SeitenDr. Uzair's Lecture on Renewable Energy SourcesMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- PV NumericalsDokument30 SeitenPV NumericalsMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Engineering, Auckland University of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand E-Mail: Timothy - Anderson@aut - Ac.nzDokument8 SeitenSchool of Engineering, Auckland University of Technology, Auckland, New Zealand E-Mail: Timothy - Anderson@aut - Ac.nzMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 08Dokument32 SeitenLesson 08Muhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Geometrical Aspect On PerformanceDokument13 SeitenEffect of Geometrical Aspect On PerformanceMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Fluid Statics - Fluid PropertiesDokument23 Seiten1 Fluid Statics - Fluid PropertiesMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- SandiaDokument140 SeitenSandiaMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of SCIE Journals PDFDokument150 SeitenList of SCIE Journals PDFvivekvs1987Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Fluid Statics - Submerged SurfacesDokument24 Seiten2 Fluid Statics - Submerged SurfacesMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- MaterialDokument1 SeiteMaterialMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) : Tao Xing and Fred SternDokument52 SeitenIntroduction To Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) : Tao Xing and Fred Sternknaidu_1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metal HydridesDokument18 SeitenMetal HydridesMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Properties of Pure Substances Phase DiagramDokument12 SeitenProperties of Pure Substances Phase DiagramMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- IrfanDokument2 SeitenIrfanMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moment of Inertia of Mass, or The Angular Mass, (SI Units KG M ) Is A Measure of An Object's Resistance ToDokument5 SeitenMoment of Inertia of Mass, or The Angular Mass, (SI Units KG M ) Is A Measure of An Object's Resistance ToMuhammad UzairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of Kill Method: Well ControlDokument17 SeitenPrinciple of Kill Method: Well ControlfarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elsanhouty Pharma Hold Time Study NotesDokument6 SeitenElsanhouty Pharma Hold Time Study NotesHuỳnh Ngọc SángNoch keine Bewertungen
- Juventas New Catalogue PDFDokument6 SeitenJuventas New Catalogue PDFboona mNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Studies of The EntrepreneursDokument14 SeitenCase Studies of The EntrepreneursSneha DobariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HOSTAFORM® C 27021 - POM - Unfilled: DescriptionDokument5 SeitenHOSTAFORM® C 27021 - POM - Unfilled: Descriptionrahul vermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLANS SCOUTCHEL: 100 Euros: Available PartsDokument2 SeitenPLANS SCOUTCHEL: 100 Euros: Available PartsIdris IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- API Standard 614 - Lubrication, Shaft-Sealing, and Control-Oil Systems For Special-Purpose ApplicationDokument4 SeitenAPI Standard 614 - Lubrication, Shaft-Sealing, and Control-Oil Systems For Special-Purpose ApplicationFabioSalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paediatric Doses of DrugsDokument2 SeitenPaediatric Doses of DrugsumapathisivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- About The Dyes: Dyes For Cellulose FibersDokument4 SeitenAbout The Dyes: Dyes For Cellulose FibersmanqabatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Davey XS250HG ManualDokument2 SeitenDavey XS250HG Manualcoolestkiwi100% (1)
- Himani Bansal Jayant Negi Ritesh Kumar Uday PratapDokument7 SeitenHimani Bansal Jayant Negi Ritesh Kumar Uday PratapJayant NegiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To GFRCDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To GFRCFred VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiochemistryDokument410 SeitenBiochemistryCaptainReeham79% (14)
- Volumetric Analysis 7Dokument3 SeitenVolumetric Analysis 7vijay kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety: ArticleinfoDokument7 SeitenEcotoxicology and Environmental Safety: ArticleinfoEswin Hernandez ObregonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Report: Noida Testing Laboratories, Noida G T - 20, SECTOR - 117, NOIDA, G. B. NAGAR, U.P., 201 316Dokument1 SeiteTest Report: Noida Testing Laboratories, Noida G T - 20, SECTOR - 117, NOIDA, G. B. NAGAR, U.P., 201 316Kushal Sharma0% (1)
- Comparing antioxidant assays for estimating activity in guava extractsDokument7 SeitenComparing antioxidant assays for estimating activity in guava extractsFira KuswandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 RevaDokument20 SeitenChapter 8 RevaanildhakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Wise QuestionsDokument6 SeitenChapter Wise QuestionsDr. B. Sree Giri Prasad100% (2)
- Uniz Resin Spec PDFDokument11 SeitenUniz Resin Spec PDFYerayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Noble Gases 20 Aug 2022Dokument2 SeitenNoble Gases 20 Aug 2022PLABAN DASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 03 AnnotDokument4 SeitenChapter 03 AnnotNur Amira Mardiana ZulkifliNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASME B31.3 Process Piping Code GuideDokument7 SeitenASME B31.3 Process Piping Code Guideshreyash bhadirkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecological Effects Test Guidelines: OPPTS 850.3020 Honey Bee Acute Contact ToxicityDokument8 SeitenEcological Effects Test Guidelines: OPPTS 850.3020 Honey Bee Acute Contact ToxicityNatalie Torres AnguloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1995Dokument283 Seiten1995Robert BataraNoch keine Bewertungen
- DelAgua Portable Water Testing Kit User ManualDokument70 SeitenDelAgua Portable Water Testing Kit User ManualMayra Gabriela100% (1)
- Building electricity vocabularyDokument9 SeitenBuilding electricity vocabularyChan PhakkdeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative Report For Environmental Protection Awareness ProgramDokument3 SeitenNarrative Report For Environmental Protection Awareness ProgramFam ValerianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SafetyDataSheet (SDS) 31 Liquid en 03122020Dokument14 SeitenSafetyDataSheet (SDS) 31 Liquid en 03122020Harry VandermeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Revision NotesDokument2 SeitenClass 8 Science Chapter 1 Revision NotesShwetabh Aman SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonVon EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (103)
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldVon EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (57)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidVon EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1395)
- The Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaVon EverandThe Beekeeper's Lament: How One Man and Half a Billion Honey Bees Help Feed AmericaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastVon EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (31)
- Highest Duty: My Search for What Really MattersVon EverandHighest Duty: My Search for What Really MattersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarVon EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (19)
- Faster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestVon EverandFaster: How a Jewish Driver, an American Heiress, and a Legendary Car Beat Hitler's BestBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (28)
- Transformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelVon EverandTransformed: Moving to the Product Operating ModelBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellVon EverandThe End of Craving: Recovering the Lost Wisdom of Eating WellBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (80)
- 35 Miles From Shore: The Ditching and Rescue of ALM Flight 980Von Everand35 Miles From Shore: The Ditching and Rescue of ALM Flight 980Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (21)
- A Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsVon EverandA Place of My Own: The Architecture of DaydreamsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (241)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldVon EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)
- Dirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureVon EverandDirt to Soil: One Family’s Journey into Regenerative AgricultureBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (124)
- Pale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceVon EverandPale Blue Dot: A Vision of the Human Future in SpaceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (586)
- Across the Airless Wilds: The Lunar Rover and the Triumph of the Final Moon LandingsVon EverandAcross the Airless Wilds: The Lunar Rover and the Triumph of the Final Moon LandingsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseVon EverandData-ism: The Revolution Transforming Decision Making, Consumer Behavior, and Almost Everything ElseBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (12)
- Recording Unhinged: Creative and Unconventional Music Recording TechniquesVon EverandRecording Unhinged: Creative and Unconventional Music Recording TechniquesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseVon EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (50)
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyVon EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (24)
- The Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationVon EverandThe Technology Trap: Capital, Labor, and Power in the Age of AutomationBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (46)
- Broken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterVon EverandBroken Money: Why Our Financial System is Failing Us and How We Can Make it BetterBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Fallout: The Hiroshima Cover-up and the Reporter Who Revealed It to the WorldVon EverandFallout: The Hiroshima Cover-up and the Reporter Who Revealed It to the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (82)
- The Path Between the Seas: The Creation of the Panama Canal, 1870-1914Von EverandThe Path Between the Seas: The Creation of the Panama Canal, 1870-1914Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (124)