Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Tour of The Cell With Pictures
Hochgeladen von
stcgtdOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Tour of The Cell With Pictures
Hochgeladen von
stcgtdCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
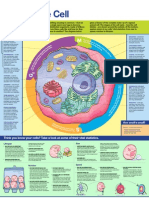
TOUR OF THE CELL
CELLS
Simplest collection of matter than can live Cell Theory: all living things are composed of cells & all cells come from other cells
CELL STRUCTURE
Surface area is important for carrying out cells functions (acquiring adequate nutrients & oxygen, etc.). Small cell has more surface area relative to its cell volume and is therefore more efficient. 2 types of cell structure: both have plasma membrane & 1 or more chromosomes & ribosomes Prokaryotic (bacteria & archaea): nucleoid and no true organelles Eukaryotic (all other forms of life): membrane-bound nucleus & organelles; life processes in eukaryotic cells depend on structure & organelles
EUKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE
4 life processes in eukaryotic cells that depend on structures/organelles Manufacturing: involves nucleus, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus (manufacture of a protein, perhaps an
enzyme, involves all of these)
Breakdown of molecules: involves lysosomes, vacuoles, peroxisomes (breakdown of an internalized bacterium by a phagocytic cell
would involve all of these)
Energy processing: involves mitochondria in animal cells, and chloroplasts in plant cells (generation of energy-containing
molecules, such as adenosine triphosphate, occurs in mitochondria and chloroplasts)
Structural support, movement, communication: involve cytoskeleton, plasma membrane, cell walls (example of importance of
these is the response and movement of phagocytic cells to an infected area)
Many similarities between animal & plant cells, but differences exist Plant cells dont have lysosomes & centrioles Plant cells have rigid cell wall, chloroplasts, and a central vacuole not found in animal cells
CELL MEMBRANES
Plasma membrane controls movement of molecules in/out of cell (selective permeability) Structure of membrane with its component molecules is responsible for this characteristic Membranes are made of lipids (mostly phospholipids), proteins, some carbohydrates Phospholipids form 2-layer sheet (phospholipid bilayer) Hydrophilic head faces outward (exposed to water) Hydrophobic tail points inward (shielded from ater) Proteins are attached to the surface, some are embedded into phospholipid bilayer
NUCLEUS
Controls cells activities and is responsible for inheritance Chromatin: complex of proteins & DNA inside nucleus which makes up the cells chromosomes DNA is copied within nucleus prior to cell division Nuclear envelope is double membrane with pores that allow material to flow in/out of nucleus Its attached to network of cellular membranes called endoplasmic reticulum
RIBOSOMES
Involved in cells protein synthesis Synthesized in nucleolus, which is found in nucleus Cells that must synthesize large amounts of protein have large number of ribosomes Some ribosomes are free, others are bound Free ribosomes are suspended in cytoplasm Bound ribosomes are attached to endoplasmic reticulum associated with the nuclear envelope
ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
Membranes within eukaryotic cell are physically connected and compose the endomembrane system Includes: nuclear envelope, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, plasma membrane Important function is synthesis, storage, export of molecules
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM
Biosynthetic factories, 2 kinds of ER (differ in structure/function, but are connected) Smooth ER (lacks attached ribosomes) is involved in diverse metabolic processes (ex. enzymes produced by smooth ER are involved in synthesis of lipids, oils, phospholipids, steroids) Rough ER (lines outer surface of membranes) makes proteins destined for secretion Once proteins are synthesized, theyre transported in vesicles to other parts of endomembrane system
GOLGI APPARATUS
Functions in conjunction with the ER by modifying products of the ER Products travel in transport vesicles from ER to Golgi apparatus One side of GA functions as receiving dock for the product, other is shipping dock Products are modified as they go from one side of GA to the other and travel to vesicles to other sites
LYSOSOMES
Membranous sac containing digestive enzymes Enzymes & membrane are produced by ER and transferred to the Golgi apparatus for processing The membrane serves to safely isolate these potent enzymes from rest of cell One of several functions of lysosomes is to remove/recycle damaged parts of cell Damaged organelle is first enclosed in membrane vesicle Then a lysosome fuses with vesicle, dismantling its contents and breaking down damaged organelle
VACUOLES
Membranous sacs that are found in variety of cells and possess assortment of functions Examples are central vacuole in plants with hydrolytic functions, pigment vacuoles in plants to provide color to flowers, contractile vacuoles in some protists to expel water from cell
MITOCHONDRIA
Cellular respiration is accomplished in mitochondria of eukaryotic cells Conversion of chemical energy in foods to chemical energy in ATP Mitochondria have 2 internal compartments separated by folded inner membrane (cristae) Intermembrane space & mitochondrial matrix (energy)
CHLOROPLASTS
Photosynthesizing organelles of plants Photosynthesis: conversion of light energy to chemical energy in sugar molecules Chloroplasts are partitioned into compartments Important parts: stroma, thylakoids, grana
ENDOSYMBIOSIS
Hypothesis of endosymbiosis proposes that mitrochrondria and chloroplasts were formerly small prokaryotes that began living within larger cells (symbiosis benefited both cell types) Mitochondria and chloroplasts have DNA and ribosomes Structure of DNA and ribosomes is very similar to that found in prokaryotic cells, and mitochondria and chloroplasts replicate much like prokaryotes
CYTOSKELETON
Network of protein fibers that functions in cell structural support and motility Scientists believe that motility and cellular regulation results when cytoskeleton interacts with proteins called motor proteins Cytoskeleton is composed of 3 kinds of fibers Microfilaments (actin filaments) support the cells shape and are involved in motility Intermediate filaments reinforce cell shape and anchor organelles Microtubules (made of tubulin) shape the cell and act as tracks for motor protein
CILIA & FLAGELLA
Both are made of microtubules wrapped in an extension of plasma membrane Ring of 9 microtubule doublets surrounds central pair of microtubules Arrangement is called 9 + 2 pattern and is anchored in basal body with 9 microtubule triplets arranged in ring While some protists have flagella and cilia that are important in locomotion, some cells of multicellular organisms have them for different reasons Cells that sweep mucus out of lungs have cilia Animal sperm are flagellated
EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX (ECM)
Cells synthesize and secrete the ECM that is essential to cell function ECM is composed of strong fibers of collagen, which holds cells together and protests plasma membrane ECM attaches through connecting proteins that bind to membrane proteins called integrins Integrins span plasma membrane and connect to microfilaments of the cytoskeleton
CELL JUNCTIONS
Adjacent cells communicate, interact, adhere through specialized junctions between them Tight junctions prevent leakage of extracellular fluid across layer of epithelial cells Anchoring junctions fasten cells together into sheets Gap junctions are channels that allow molecules to flow between cells
CELL WALL
Plant cells have rigid cell wall It protects and provide skeletal support that helps keep plant upright against gravity Composed primarily of cellulose Plant cells have cell junctions called plasmodesmata that serve in communication between cells
EUKARYOTIC CELL STRUCTURE & FUNCTIONS (SUMMARY)
MANUFACTURING
Nucleus (Central Office): DNA/RNA synthesis; Assembly of ribosomal subunits (in nucleoli) Ribosomes (Assembly Line): Polypeptide (protein) synthesis Rough ER (Conveyor Belt): Synthesis of membrane lipids & proteins, secretory proteins, hydrolytic enzymes; Formation of transport vesicles Smooth ER (Conveyor Belt): Lipid synthesis; Detoxification in liver cells; Calcium ion storage Golgi apparatus (Packaging/Shipping): Modification/transport of macromolecules; Formation of lysosomes & transport vesicles
BREAKDOWN
Lysosomes (animal cells/some protists) (Collection Center): Digestion of ingested food/bacteria/cells damaged organelles/macromolecules for recycling Vacuoles (Storage): Digestion (like lysosomes); Storage of chemicals; Cell enlargement; Water balance Peroxisomes (not part of endomembrane system): Diverse metabolic processes, with breakdown of H2O2 by-product
ENERGY PROCESSING
Mitochondria (Generator): conversion of chemical energy of food to chemical energy of ATP Chloroplasts (plants/some protists): Conversion of light energy to chemical energy of sugars
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT, COMMUNICATION BETWEEN CELLS
Cytoskeleton (cilia, flagella, centrioles in animal cells) (Bricks/Steel): Maintenance of cell shape; Anchorage for organelles; Movement of organelles within cells; Cell movement; Mechanical transmission of signals from exterior of cell to interior Extracellular matrix (animals): Binding of cells in tissues; Surface protection; Regulation of cellular activities Cell junctions: Communication between cells; Binding of cells in tissues Cell walls (plants/fungi/some protists): Maintenance of cell shape & skeletal support; Surface protection; Binding of cells in tissues Plasma membrane (Door): Controls movement of molecules in/out of cell (selective permeability)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- ILGM Marijuana Grow BibleDokument58 SeitenILGM Marijuana Grow BibleRemy Spring100% (3)
- Herbal MedicineDokument6 SeitenHerbal MedicineBashu PoudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Magical and Ritual Use of Aphrodisiacs (Richard Alan Miller) (Z-Library)Dokument180 SeitenThe Magical and Ritual Use of Aphrodisiacs (Richard Alan Miller) (Z-Library)Walter Sobchak100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Instant Notes in Physical ChemistryDokument399 SeitenInstant Notes in Physical Chemistrymjarteza92% (12)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Book of Orchids (1923) PDFDokument141 SeitenThe Book of Orchids (1923) PDFluitoz05Noch keine Bewertungen
- Stress PhysiologyDokument2 SeitenStress PhysiologySmitha AsokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Potted Ornamental PlantsDokument83 SeitenPotted Ornamental PlantsDR V S PATIL50% (2)
- CAIE Biology 9700 Topic 4 Cell Membrane and Transport 2012 To 2018Dokument51 SeitenCAIE Biology 9700 Topic 4 Cell Membrane and Transport 2012 To 2018ADEEL AHMAD100% (2)
- Maturity and Harvest IndicesDokument10 SeitenMaturity and Harvest IndicesKavita MohiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract Algebra Cheat Sheet PDFDokument5 SeitenAbstract Algebra Cheat Sheet PDFZsofia PopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abstract Algebra Cheat Sheet PDFDokument5 SeitenAbstract Algebra Cheat Sheet PDFZsofia PopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Libro 3º BásicoDokument98 SeitenLibro 3º BásicoCheveux du Feu83% (6)
- Promoter RegionDokument3 SeitenPromoter RegionstcgtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular GeometryDokument1 SeiteMolecular GeometrystcgtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry & Biochemistry MnemonicsDokument5 SeitenChemistry & Biochemistry MnemonicsPRONOY.V.UNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trig SummaryDokument1 SeiteTrig SummarystcgtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integral SummaryDokument1 SeiteIntegral SummaryChih Tien Fan100% (3)
- Chemistry - A Self Teaching GuideDokument306 SeitenChemistry - A Self Teaching GuidestcgtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trig SummaryDokument1 SeiteTrig SummarystcgtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Picture On The Cell PosterDokument1 SeiteBig Picture On The Cell PosterWellcome Trust100% (1)
- Cell Biology NotesDokument8 SeitenCell Biology NotesstcgtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- CB CS07 CellCommunicationDokument1 SeiteCB CS07 CellCommunicationstcgtdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adoption of Agricultural Innovations by Smallholders in KenyaDokument226 SeitenAdoption of Agricultural Innovations by Smallholders in KenyadatateamNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSC SabryAbdallahDokument276 SeitenMSC SabryAbdallahDr-SabryAbdelmonemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 26Dokument14 SeitenChapter 26Mhmad MokdadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corn Pest and Diseasses PDFDokument23 SeitenCorn Pest and Diseasses PDFCarleen Camacho-CalimponNoch keine Bewertungen
- Of Important Diseases in Dragon Fruit (Hylocereus SP.)Dokument4 SeitenOf Important Diseases in Dragon Fruit (Hylocereus SP.)Potor Aan IsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsDokument49 SeitenBiology Notes Form Two: Transport in Plants and AnimalsPeter Osundwa Kiteki100% (2)
- Plant Growth Factors: Light: Colorado State University ExtensionDokument4 SeitenPlant Growth Factors: Light: Colorado State University ExtensionMehdi MaataouiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolation and Identification of Fungi Associated With Different Species of Stored GrainesDokument9 SeitenIsolation and Identification of Fungi Associated With Different Species of Stored GrainesabondancejosemariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Denr Plants Urban ForestryDokument21 SeitenDenr Plants Urban ForestryPatricia Nicole BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of 10 Abiotic Factors Causing Plant DiseaseDokument3 SeitenList of 10 Abiotic Factors Causing Plant DiseaseFrances Jay FerrerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banana ResearchDokument14 SeitenBanana ResearchJas TeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Arsitektur PohonDokument6 SeitenJurnal Arsitektur PohonNovi Rizal UmamNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Born March 1, 1929) : Angel C. AlcalaDokument5 Seiten(Born March 1, 1929) : Angel C. AlcalaRica GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stingless bees: from obscurity to insect ambassadorsDokument34 SeitenStingless bees: from obscurity to insect ambassadorsMOHD FAISALNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Honey ReportDokument11 SeitenNational Honey ReportManikanta Sai KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics midterm exam questionsDokument3 SeitenGenetics midterm exam questionsMa.Janice GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Choanephora PDFDokument4 SeitenChoanephora PDFAnael Ruiz100% (1)
- RRL 2 Peanut AutosavedDokument8 SeitenRRL 2 Peanut AutosavedDivina Labuguen TurquezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thrips UCARDokument8 SeitenThrips UCARSergio Luís Fernandes PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Inoculation On Euterpe Oleracea Mart. SeedlingsDokument6 SeitenThe Effects of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Inoculation On Euterpe Oleracea Mart. SeedlingsManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- DENR Recommends Mass Propagation MethodsDokument11 SeitenDENR Recommends Mass Propagation MethodsRod AlboresNoch keine Bewertungen