Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ranc Tahunan Sns TH 5
Hochgeladen von
Marhaini MasngutOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Ranc Tahunan Sns TH 5
Hochgeladen von
Marhaini MasngutCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
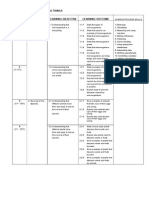
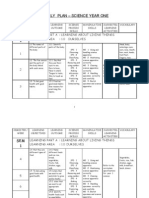
YEARLY PLAN SCIENCE YEAR 5 WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING PART A: Investigating Living Things.
LEARNING AREA : 1 Microorganism 1 1.1 Understanding that 1.1.1 Pupils state types of microorganism is a microorganisms. living thing. 1.1.2 Pupils state that yeast is an example of microorganism. 1.1.3 Pupils state that microorganism breathes. 1.1.4 Pupils state that microorganism grow. 1.1.5 Pupils state that microorganism moves. SPS/MS SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Controlling variable Making hypotheses Experimenting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Draw specimens and apparatus. Clean science apparatus. Store science apparatus. SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Controlling variable Making hypotheses Experimenting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Draw specimens and apparatus. Clean science apparatus. Store science apparatus. SPS/MS Pupils give examples of animals that take care of their eggs and young. Pupils explain how animals take care of their eggs and young. Pupils explain why animals take care of their eggs and young. SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Communicating Making hypotheses MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Draw specimens and apparatus. SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Controlling variable Making hypotheses Experimenting MS Use and handle VOCABULARY Yeast Harmful Magnifying glass Uses sprinkle
1.1.6
Pupils conclude that microorganism are living things and most of them cannot be seen naked eyes.
1.2
Understanding that some microorganisms are harmful and some are useful.
1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3
1.2.4
Pupils state examples of use of microorganism. Pupils state the harmful effects of microorganisms. Pupils describe that diseases caused by microorganisms can spread from one person to another. Pupils explain ways to prevent diseases cause by microorganisms.
Contagious Quarantine Measles Chicken pox Stomach upset Cough Harm Tooth decay Sneezing Scabies Flu Mumps Conjunctivitis
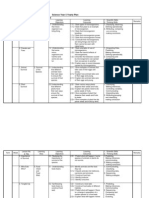
LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING OBJECTIVES WEEK LEARNING PART : 1. Investigating Living Things. LEARNING AREA: 2.0 Survival of the species. 3 2.1 Understanding that 2.1.1 different animals have their own ways to ensure the survival of 2.1.2 their species. 2.1.3
VOCABULARY Survival Adapt Take care Protect Young Slimy Pouch Herd Disturbed Plenty Attack Hide Ensure Feed Various Waxy Husk Shell Disperse Edible Flame of the forest Chestnut Balsam Okra Love grass
2.2
Understanding that different plants have their own ways to ensure the survival of their species.
2.2.1 2.2.2 2.2.3 2.2.4
Pupils state various ways plants disperse their seeds and fruits. Pupils explain why plants need to disperse seeds or fruits. Pupils give examples of plant that disperse seeds and fruit by water. Pupils give examples of plant that disperse seeds and fruits
by wind.
2.2.5
2.2.6
Pupils give example of plant that disperse seeds and fruits by animals. Pupils give example of plant that disperse seeds and fruits by explosive mechanism.
science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Draw specimens and apparatus. SPS/MS SPS Observing Making Inference Predicting Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting VOCABULARY Extinction Shortage
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING PART A: Investigating Living Things. LEARNING AREA : 2 Survival of The Species 5 2.3 Realizing the importance 2.3.1 Pupils predict what will of survival of the species. happen if some species of animals or plants do not survive.
LEARNING PART A: Investigating Living Things. LEARNING AREA : 3 Food Chain and Food Web 6 3.1 Understanding food 3.1.1 chains. 3.1.2 3.1.3 3.1.4 3.1.5
Pupils identify animals and the food they eat. Pupils classify animals into herbivore, carnivore and omnivore. Pupils construct food chain. Pupils identify producer. Pupils identify consumers.
SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Draw specimens and apparatus.
Food chain Producer Consumer
3.2
Synthesizing food chains to construct food web.
3.2.1
3.2.2
Pupils construct food web. Pupils construct food web of different habitats.
SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Communicating Making hypotheses
Food web Food chain
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING PART A: Investigating Living Things. LEARNING AREA : 3 Food Chain and Food Web 8 3.2 3.2.3 Pupils predict what will happen if there is a change in population of a certain species in a food web. 3.2.4 Pupils explain what will happen to a certain species of animals if they eat only one type of food. LEARNING PART B: Investigating Force and Energy. LEARNING AREA : 1 Energy 9 1.1 Understanding the 1.1.1 uses of energy. 1.1.2 1.1.3
SPS/MS SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Communicating Making hypotheses
VOCABULARY Food web Food chain
Pupils explain why energy is needed. Pupils give examples where and when energy is uses. Pupils state various sources of
SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Communicating
Sources Energy Bounce Fuel Boil
energy.
Making hypotheses
10
1.2
Understanding that energy can be transformed from one to another.
1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3
Pupils state the various forms of energy. Pupils state that energy can be transformed. Pupils give examples of appliances that make transformation.
SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully.
Transform Principle Whistle Appliances
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING PART B: Investigating Force and Energy LEARNING AREA : 1 Energy 11 1.3 Understanding 1.3.1 Pupils state what renewable renewable and nonenergy is. renewable energy. 1.3.2. Pupils state what nonrenewable energy is.
SPS/MS SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Store science apparatus. SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Store science apparatus.
VOCABULARY Transform Principle Whistle Appliances
1.3.3.
1.3.4.
Pupils list renewable energy resources. Pupils list non-renewable energy resources.
12
1.3
1.3.5 Pupils explain why we need to use energy wisely. 1.3.6 Pupils explain why renewable energy is batter than nonrenewable energy. 1.3.7 Pupils give examples on how to save energy. 1.3.8 Pupils practice saving energy.
Renewable energy Non-renewable energy Replenished Used up Coal Charcoal Wisely
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING PART B: Investigating Force and Energy LEARNING AREA : 2 Electricity 13 2.1 Knowing sources of 2.1.1 Pupils state the sources of electricity. electricity. 2.2 Understanding a series 2.2.1 Pupils identify the symbols of circuit and a parallel various components in a circuit. simple electric circuit. 2.2.2 Draw circuit diagrams.
SPS/MS SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting Controlling variable MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance.
VOCABULARY Dry cell Hydroelectric power Series circuit Parallel circuit Brightness Arrangement
2.2.3
Pupils identify difference in the arrangement of bulb in series and parallel circuits.
Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus. 14 2.2 2.2.4 Pupils build a series circuit. SPS Observing Classifying Making Inference Predicting Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting Controlling variable MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus. Series circuit Parallel circuit Brightness Arrangement Dry cell
2.2.5
2.2.6 2.2.7
Pupils build parallel circuit. Pupils compare the brightness of the bulbs in a series and parallels circuit. Pupils compare the effect on the bulb when various switches in a series circuit and a parallel circuit are off.
SEMESTER 2 WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING PART B: Investigating Force and Energy LEARNING AREA : 2 Electricity 15 2.3 Understanding the 2.3.1 Pupils describe the danger of safety precautions to mishandling electrical be taken when appliances. handling electrical 2.3.2 Pupils explain the safety appliances. precautions to be taken when using electrical appliances. SPS/MS SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting Predicting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus. LEARNING PART B: Investigating Force and Energy LEARNING AREA : 3 Light 16 3.1 Understanding that light 3.1.1 travels in a straight line. 3.1.2 3.1.3 VOCABULARY Series circuit Parallel circuit Brightness Arrangement Dry cell
Pupils state that light travels in a straight line. Pupils give examples to verify that light travels in a straight line. Pupils describe how shadow is formed.
SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting Predicting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus.
Beam Travel Opaque
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING PART B: Investigating Force and Energy LEARNING AREA : 3 Light 17 3.1 3.1.4 Pupils design a fair test to find out what cause the size of a shadow to change by deciding what to keep the same, what to change and what to observe.
SPS/MS SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting Controlling variable Predicting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus. SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Experimenting Controlling variable Predicting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus.
VOCABULARY Beam Travel Opaque
3.1.5
Pupils design a fair test to find out what factors cause the shape of a shadow to change by deciding what to keep the same, what to change and what to observe.
18
3.2
Understanding that light can be reflected.
3.2.1 3.2.2 3.2.3
Pupils state that light can be reflected. Pupils draw ray diagrams to show reflection of light. Pupils give examples of uses of reflections of light in every day life.
Reflections Sharp bend Ray diagram
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING PART B: Investigating Force and Energy LEARNING AREA : 4 Heat 19 4.1 Understanding that 4.1.1 Pupils state that when a temperature is an substance gains heat it will indicator of degree of become wormer. hotness. 4.1.2 Pupils state that when a substance loses heat it become cooler. 4.1.3 Pupils measure temperature using the correct technique. 4.1.4 Pupils state the metric unit for temperature.
SPS/MS SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting Controlling variable Predicting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus. SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting Controlling variable Predicting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance.
VOCABULARY Temperature Heat Metric unit Degree Hotness Cooler Wormer
20
4.1
4.1.5 4.1.6 4.1.7
Pupils state that temperature of an object or material increases as it gains heat. Pupils state that temperature of an object or material decreases as it loses heat. Pupils conclude that the temperature is an indicator to measure hotness.
Temperature Heat Metric unit Degree Hotness Cooler Wormer
Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus.
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING PART B: Investigating Force and Energy LEARNING AREA : 4 Heat 21 4.2 Understanding the 4.2.1 Pupils state that matter effects of heat on expands when heated. matter. 4.2.2 Pupils state that matter contracts when cooled.
SPS/MS SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting Controlling variable Predicting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus.
VOCABULARY Dent Expand Contract
4.2.3
Pupils give examples of the application of the principle of expansion and contraction in everyday life.
LEARNING PART C: Investigating Materials LEARNING AREA : 1 States of Matter 22 1.1 Understanding that matter exist in the form of solid, liquid or gas.
1.1.1
Pupils classify objects and materials into three states of matter. Pupils state the properties of solid. Pupils state the properties of liquid. Pupils state that some liquids flow faster than other. Pupils state the properties of gas.
1.1.2 1.1.3
1.1.4 1.1.5
SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting Controlling variable Predicting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus. SPS/MS SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting Controlling variable Predicting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus. SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Predicting
Solid Liquid Gas Water vapour Evaporation Condensation Water cycle Interchangeable Syringe
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING PART C: Investigating Materials LEARNING AREA : 1 States of Materials 23 1.2 Understanding that matter can change from one state to another.
LEARNING OUTCOMES 1.2.1 1.2.2 1.2.3 Pupils state that water can change its state. Pupils conclude that water can exist in any of the three states of matter. Pupils identify the processes involve when a matter changes from one state to another. Pupils identify factors that effect the rate of evaporation of water.
VOCABULARY Evaporation Condensation Freezing Melting
1.2.4
24
1.3
Understanding the water cycle.
1.3.1 1.3.2 1.3.3 1.3.4
Pupils describe how cloud are formed. Pupils describe how rain is formed. Pupils explain how water is circulated in the environment. Pupils explain the importance
Cloud Water cycle
of eater cycle. 25 1.4 Appreciating the importance of water resources. 1.4.1 1.4.2 Pupils give reasons why wee need to keep our water resources clean. Pupils describe ways to keep our water resources clean. SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Predicting Water resource
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING PART C: Investigating Materials LEARNING AREA : 2 Acid and Alkali 26 2.1 Understanding the properties of acidic, alkaline and neutral substances.
LEARNING OUTCOMES
SPS/MS SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Experimenting Controlling variable Predicting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus. Handle specimens correctly & carefully. Clean science apparatus.
VOCABULARY Litmus paper Sour Bitter Neutral Acidic Alkaline Property
2.1.1 2.1.2 2.1.3
Pupils identify acidic, alkaline and neutral substances using litmus paper. Pupils identify the taste of acidic and alkaline food. Pupils conclude the properties of acidic, alkaline and neutral substances.
LEARNING PART D: Investigating The Earth and The Universe LEARNING AREA : 1 Constellation 27 1.1 Understanding 1.1.1 Pupils state what constellation. constellation is. 1.1.2 Pupils identify constellation. 1.1.3 Pupils state the importance of constellations.
SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Predicting
Constellation Orion Scorpion Big Bipper Southern Cross Pattern Direction Season VOCABULARY Rotate Sundial Axis West East Movement Position Throughout Shadow
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING PART D: Investigating The Earth and The Universe LEARNING AREA : 2 The earth, The Moon and The Sun 27 2.1 Understanding the 2.1.1 Pupils state that the Earth movements of the rotates on its axis. Earth, The Moon and 2.1.2 Pupils state that the Earth The Sun rotates and at the same time moves round the Sun. 2.1.3 Pupils state that the Moon rotates on its axis. 2.1.4 Pupils state that the Moon rotates and at the same time moves round the Earth. 2.1.5 Pupils sate that the Moon and the Earth move round the Sun at the same time. 28 2.1 2.1.6 2.1.7 Pupils describe the changes in length and position of the shadow throughout the day. Pupils conclude that the Earth rotates on it axis from west to east.
SPS/MS SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Predicting
SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Predicting
Rotate Sundial Axis West East Movement Position Throughout Shadow
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING OUTCOMES LEARNING PART D: Investigating The Earth and The Universe LEARNING AREA : 2 The earth, The Moon and The Sun 29 2.2 Understanding the 2.2.1 Pupils state that it is day time occurrence of day and night. for the part of the Earth facing the Sun.
SPS/MS SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Predicting
VOCABULARY Illuminating Facing Rotating globe Day Night Occurrence
2.2.2 2.2.3
Pupils state that it is night time for the part of the Earth facing away from the Sun. Pupils explain that day and night occur due to the rotation of the Earth on its axis. Pupils state that the Moon does not emit light. Pupils explain that the Moon appears bright when it reflects sunlight. Pupils describe the phases of the Moon.
30
2.3
Understanding the phases of the Moon.
2.3.1
2.3.2 2.3.3
LEARNING PART E: Investigating Technology LEARNING AREA : 1 Strength and Stability 31 1.1 Knowing the shape of 1.1.1 objects in structure. 1.1.2
SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Predicting
New moon Crescent Half moon Full moon Reflect Phase Lunar calendar Emit
Pupils state the shape of the object. Pupils identify shape in structure.
SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Predicting MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus. SPS/MS SPS Observing Making Inference Communicating Making hypotheses Predicting Experimenting Controlling variable MS Use and handle science apparatus and substance. Store science apparatus. Draw specimens and apparatus.
Shape Cube Cuboid Sphere Cone Cylinder Pyramid Hemisphere Structure
WEEK LEARNING OBJECTIVES LEARNING PART E: Investigating Technology LEARNING AREA : 1 Strength and Stability 32 1.2.1 1.2 Understanding the strength and stability of a structure.
LEARNING OUTCOMES Pupils identify shape of objects that are stable. Pupils the factors that affects stability of objects. Pupils explain how base area affect stability. Pupils explain height affects stability
VOCABULARY Strength Stability Base area Effect Stand at ease Stand at attention
1.2.2 1.2.3 1.2.4
33
1.2
1.2.5
1.2.6
Pupils identify the factors that affect the strange of a structure. Pupils design a model that is strong and stable.
Strength Stability Base area Effect Stand at ease Stand at attention
SCIENCE YEARLY PLAN YEAR 6
PANITIA SAINS SK PASIR GUDANG 4
10
11
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Science Year 5-Yearly PlanDokument12 SeitenScience Year 5-Yearly PlanThevagi GovindasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Dokument8 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Muhammad FarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT SN Y5Dokument8 SeitenRPT SN Y5vargan_ramoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 5 Yearly PlanDokument14 SeitenScience 5 Yearly PlanSri GanggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT SN THN5Dokument10 SeitenRPT SN THN5Jhoster YulongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 10 First SemesterDokument10 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 10 First SemesterRaffie MuksinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Year 5 Yearly PlanDokument7 SeitenScience Year 5 Yearly Plan惠鑫Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 5 Science Sceme of WorkDokument30 SeitenYear 5 Science Sceme of WorkJc JoliatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ranc Peng Tahunan Sains Tahun 5 2014 JsuDokument8 SeitenRanc Peng Tahunan Sains Tahun 5 2014 Jsunanac_2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Tahunan Sains Tahun 5Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Tahunan Sains Tahun 5Som Mai EmaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Dokument9 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Annie GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomeDokument8 SeitenTheme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomewmpejonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.interaction Among Living ThingsDokument4 Seiten1.interaction Among Living ThingsRain KipliNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Term Science Year 5 Yearly Plan Themes A: Investigating Living ThingsDokument24 SeitenFirst Term Science Year 5 Yearly Plan Themes A: Investigating Living ThingsXgeniusXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan For Science Year 3: Theme: Learning About Living ThingsDokument13 SeitenYearly Plan For Science Year 3: Theme: Learning About Living ThingsMuhammad Azrieen SamsudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan For Science Year 5Dokument28 SeitenYearly Plan For Science Year 5siah.ameer5382Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Experiments English - STD3Dokument39 SeitenScience Experiments English - STD3pathmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theme A: Learning About Living Things: Yearly Plan Science Year 2Dokument7 SeitenTheme A: Learning About Living Things: Yearly Plan Science Year 2Zulkifli HamatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theme A: Learning About Living Things: Yearly Plan Science Year 2Dokument7 SeitenTheme A: Learning About Living Things: Yearly Plan Science Year 2hanujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SC Yearly 5 PlanDokument9 SeitenSC Yearly 5 PlanHani OsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Yr 1Dokument10 SeitenYearly Plan Science Yr 1Alif NasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit: Cell Structure and Function: Science 10Dokument8 SeitenUnit: Cell Structure and Function: Science 10Karen JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week C Stage 4 ScienceDokument30 SeitenWeek C Stage 4 ScienceVanjaSekulicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning About Living ThingsDokument16 SeitenLearning About Living ThingsSayid AdnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 6Dokument15 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 6Diana LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Plan For Year ThreeDokument11 SeitenScience Yearly Plan For Year Threefarizal_scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Plan Year 6,2015Dokument7 SeitenScience Yearly Plan Year 6,2015Kee Wei SamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 4 - 8 January: Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyDokument13 SeitenWeek 1 4 - 8 January: Learning Objectives Suggested Learning Activities Learning Outcomes Notes VocabularyFarid FazamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Sains Tahun 3-kbsrDokument18 SeitenRPT Sains Tahun 3-kbsrmine80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme of Work: ScienceDokument37 SeitenScheme of Work: ScienceMasitah ArNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 3 Science Scheme of WorkDokument15 SeitenYear 3 Science Scheme of WorkJhoster Yulong100% (2)
- Science Yearly Plan Year Five 2006Dokument13 SeitenScience Yearly Plan Year Five 2006Hikeri HarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Plan For Year TwoDokument11 SeitenScience Yearly Plan For Year TwoAziz AljaffariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 3Dokument12 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 3Awang Bakhtiar Awang SeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ms. Spence's Ms. Spence's Classroom Classroom Newsletter NewsletterDokument5 SeitenMs. Spence's Ms. Spence's Classroom Classroom Newsletter Newsletterapi-607129310Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year Three Science Scheme of Work 2007Dokument15 SeitenYear Three Science Scheme of Work 2007Gerald BenjaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 RdgardenpollinatorsDokument42 Seiten3 Rdgardenpollinatorsapi-276690423Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year Four Science Scheme of Work: Semester IDokument9 SeitenYear Four Science Scheme of Work: Semester IEzhilita EzhillNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Objectives 1. Animals Pupils Should LearnDokument6 SeitenLearning Objectives 1. Animals Pupils Should LearnSeashellcrabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capstone Unit PlanDokument20 SeitenCapstone Unit Planapi-336239478Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ubd Food ChainDokument5 SeitenUbd Food Chainapi-313687749Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 Chapter 1 SCIENTIFIC SKILLSDokument25 Seiten1.0 Chapter 1 SCIENTIFIC SKILLSJaswardi Anwar Bin Md Yaacob� IPGKKBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Dokument5 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 5wawa2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Science Year 3 Yearly Plan: A. Learning About Living ThingsDokument16 SeitenScience Year 3 Yearly Plan: A. Learning About Living Things272tamanmenteriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3Dokument7 SeitenLesson 3api-656655008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kontrak SC Yr 6Dokument9 SeitenKontrak SC Yr 6Shafinaz SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kecukupan Latihan YEAR 6Dokument23 SeitenKecukupan Latihan YEAR 6Asnal KamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Mengajar Tahunan 2012 YEAR 4Dokument20 SeitenRancangan Mengajar Tahunan 2012 YEAR 4Dilla FadillahNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Science Year 5 SJKT Ladang GulaDokument29 SeitenRPT Science Year 5 SJKT Ladang Gulavargan_ramoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 5 Investigations Yeast Lesson PlanDokument3 SeitenGrade 5 Investigations Yeast Lesson Planapi-691100008Noch keine Bewertungen
- SyllibusScience F2Dokument17 SeitenSyllibusScience F2206542Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Grade Animal Adaptations Final VersionDokument78 Seiten4th Grade Animal Adaptations Final VersionTGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yr5 Science Specification 2012Dokument17 SeitenYr5 Science Specification 2012Norazura ZuraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teacher Support Manual With Elective EnglishDokument260 SeitenTeacher Support Manual With Elective EnglishVal CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan (Year 5) 2012 SK Sentul Utama, Kuala LumpurDokument16 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan (Year 5) 2012 SK Sentul Utama, Kuala LumpursentulutamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science LessonPlan MicroOrganisms 8th 28-04-2015Dokument30 SeitenScience LessonPlan MicroOrganisms 8th 28-04-2015Ernesto GullodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Scheme of Work Science Year Three: First TermDokument14 SeitenYearly Scheme of Work Science Year Three: First TermZakaria SulaimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 8 BASIC SCIENCE - Finau A. Nanovo RepairedDokument185 SeitenYear 8 BASIC SCIENCE - Finau A. Nanovo RepairedDrSuesh Kumar Pandey69% (13)
- 2-Stability and Reliability Improvement in Solar Wind Hybrid Power System With Battery Energy Storage StationDokument9 Seiten2-Stability and Reliability Improvement in Solar Wind Hybrid Power System With Battery Energy Storage StationEngrImranKhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EME Unit 2 Turbines PPT by Kalyan ChakravarthyDokument64 SeitenEME Unit 2 Turbines PPT by Kalyan ChakravarthyvenkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation-3 - Exp - Flex Options - Tech WS - 181114 - V4Dokument65 SeitenPresentation-3 - Exp - Flex Options - Tech WS - 181114 - V4Juniko ParhusipNoch keine Bewertungen
- STIRPAT ModelDokument29 SeitenSTIRPAT ModelMohammadHas'sanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansi/Ashrae/Ies Standard 90.1-2016: Overview: Building Energy Codes ProgramDokument12 SeitenAnsi/Ashrae/Ies Standard 90.1-2016: Overview: Building Energy Codes ProgramDstormNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On Different Accessories of The Solar Power Plant 46-50Dokument5 SeitenReport On Different Accessories of The Solar Power Plant 46-50pagal noobNoch keine Bewertungen
- E7 - REVISION FOR THE SECOND TERM TEST- Nguyễn TrãiDokument3 SeitenE7 - REVISION FOR THE SECOND TERM TEST- Nguyễn Trãigia kiên phạm nguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Steam Power CycleDokument29 SeitenChapter 9 Steam Power CycleAmanRaghaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPRI Potential Effects of Climate Change On Electric UtilitiesDokument244 SeitenEPRI Potential Effects of Climate Change On Electric UtilitiesJait PosadasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Hydro Power LDokument76 Seiten4 Hydro Power LTibebu MerideNoch keine Bewertungen
- McQuay AWS User Manual EngDokument37 SeitenMcQuay AWS User Manual EngHermelindo Samuel Rabanales Cifuentes50% (2)
- The University of FaisalabadDokument10 SeitenThe University of FaisalabadAsim aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- SVB Pump Range Datasheet Crest Pumps v1Dokument6 SeitenSVB Pump Range Datasheet Crest Pumps v1Sham ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viewbill 02062019 080313Dokument1 SeiteViewbill 02062019 080313dinesh sharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Ect of Soiling in Bifacial PV Modules and Cleaning Schedule OptimizationDokument11 SeitenE Ect of Soiling in Bifacial PV Modules and Cleaning Schedule Optimizationrotarola100% (2)
- US Energy Efficiency Full ReportDokument165 SeitenUS Energy Efficiency Full Reportjosepmcdalena6542Noch keine Bewertungen
- ModuleDokument4 SeitenModuleChristine Abegail SambileNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dennis Miru Graphic Design PortfolioDokument9 SeitenDennis Miru Graphic Design PortfoliodenosciNoch keine Bewertungen
- JR CVDokument5 SeitenJR CVMostafa MohmmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vw.t4.Wd.79 - Climatronic - AES (Automatic Transmission) From Sep 98Dokument10 SeitenVw.t4.Wd.79 - Climatronic - AES (Automatic Transmission) From Sep 98Benjamin Barker100% (1)
- Mobile SubstationsDokument7 SeitenMobile SubstationsAnonymous EVFw59Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Proposal - Emdbedded GeneratorDokument10 SeitenThesis Proposal - Emdbedded GeneratorIvan KendrikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Nominal Operating Cell Temperature (NOCT)Dokument15 SeitenEvaluation of Nominal Operating Cell Temperature (NOCT)Efstathios MaliakisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renewable Energy Question BankDokument7 SeitenRenewable Energy Question BankLovleen GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 6057678804069908882Dokument184 Seiten5 6057678804069908882rajni raniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.KEPCO Annual ReportDokument32 Seiten1.KEPCO Annual ReportDipaDimposSitumeangNoch keine Bewertungen
- PFM Industrial LED Flood Light ROI CalculatorDokument3 SeitenPFM Industrial LED Flood Light ROI Calculatorrajbir_yadav6404Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pumping of LiquidsDokument20 SeitenPumping of Liquidsahmedyashar67% (3)
- AV6-R Spark Plug & Oil Filter PDFDokument28 SeitenAV6-R Spark Plug & Oil Filter PDFKamal Jit DhimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- C3 Series Low Voltage 4Dokument1 SeiteC3 Series Low Voltage 4khemrajmahadewNoch keine Bewertungen