Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chemistry Vocabulary
Hochgeladen von
HueiSearsOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chemistry Vocabulary
Hochgeladen von
HueiSearsCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chemistry Vocabulary
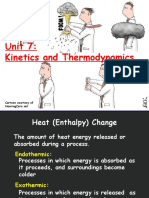
Reactant: One or more substances written to the left of the arrow Product: New substance(s) written to the right of the arrow Skeleton Equation: A chemical equation that does not indicate the relative amounts of the reactants and products involved in the reaction Coefficient: Tells the number of rep. Particles of each compound Subscript: Used to balance equations Ion: A charged particle Polyatomic ion: A tightly bound group of atoms that behave as a unit and carry a charge Atom: The representative particle for elements Molecule: The representative particle for covalent compounds Formula Unit: The representative particle for ionic compounds Empirical Formula: A chemical formula written in the lowest whole number ratio Molecular Formula: The chemical formula Limiting Reactant: Yields the least amount of product and is completely consumed Excess Reagent: The remaining reactant(s) after the L.R. is taken away Theoretical Yield: The maximum amount of product that could be formed from given amounts of reactants Actual Yield: The amount of product that actually forms when the reaction is carried out in the lab Percent Yield: The ratio of actual yield to the theoretical yield Activation Energy: The minimum amount of energy that particles must have in order to react; a barrier that reactants must cross to be converted into products Endothermic: When the heat change in a chemical reaction is written as a reactant; heat is being absorbed Exothermic: When the heat change in a chemical reaction is written as a product; heat is being released Catalyst: A substance that increases the rate of reaction without being used up Concentration: the number of reacting particles in a given volume; effects the rate at which reactions occur Le Chateliers Principle: If stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the system changes to relieve the stress Specific Heat: The amount of heat it takes to raise the temperature of 1g of the substance by 1C Heat Capacity: The amount of heat needed to increase the temperature of any object by exactly 1C Joule: The SI unit of heat and energy; slightly less than of a calorie Enthalpy: The heat content of a system; also change in heat Neutralization Reaction: Used to determine the concentration of an acid or a base in a solution Acid: A compound that produces hydrogen ions [H+] when dissolved in water Base: A compound that produces hydroxide ions [OH-] when dissolved in water Molarity: The number of moles of a solute dissolved per liter of solution Titration: The entire process of adding in the standard solution Buret: Adds in the standard solution; long glass tube Colligative Property: Properties of solutions that depend only upon the number of solute particles and NOT upon their identity
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Chemistry Revision Booklet PDFDokument397 SeitenChemistry Revision Booklet PDFlegal eagle100% (1)
- 2013 Guie of Student Kroes Aircraft Basic Science 8thDokument154 Seiten2013 Guie of Student Kroes Aircraft Basic Science 8thJose Tejeda100% (1)
- Grade 11 ChemistryDokument17 SeitenGrade 11 ChemistryKevin George100% (1)
- 2 the+Chemistry+of+LifeDokument107 Seiten2 the+Chemistry+of+Lifegabbs_123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo 12Dokument19 SeitenThermo 12Jess Ryan Olayon100% (2)
- G10 Chemistry RBDokument397 SeitenG10 Chemistry RBanupamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculations in Furnace TechnologyDokument277 SeitenCalculations in Furnace Technologysakthivel100% (2)
- Chemistry Form FiveDokument23 SeitenChemistry Form FiveNorazlin Ujang100% (1)
- Chemistry Cheat SheetDokument2 SeitenChemistry Cheat Sheetprincessrgl_112003705467% (3)
- Chemical ReactionDokument9 SeitenChemical Reactionapi-235404570Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alorimetry: D M, M M E, C E U P, D, Q C, PDokument2 SeitenAlorimetry: D M, M M E, C E U P, D, Q C, PJustine NacomelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Balance With Chemical ReactionDokument36 SeitenMaterial Balance With Chemical ReactionKuldeep Bhatt100% (1)
- AQA A Level Chemistry Unit 2 DefinitionsDokument2 SeitenAQA A Level Chemistry Unit 2 DefinitionsMuadh ChatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DJM MBA PCS CA 007 Deethanizer Reboiler E 1401 Rev BDokument37 SeitenDJM MBA PCS CA 007 Deethanizer Reboiler E 1401 Rev BDIANTORONoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Cooling SystemsDokument10 SeitenCambridge Cooling SystemsmalloryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 19Dokument3 SeitenChapter 19api-373649599Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sem 2 VocabularyDokument2 SeitenSem 2 VocabularyJeanne KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Science-Module 8 Chemical ReactionsDokument57 SeitenPhysical Science-Module 8 Chemical ReactionsJoana CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ib Notes SL 1Dokument6 SeitenIb Notes SL 1ANTONIOSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pnu Let ReviewDokument136 SeitenPnu Let ReviewVillafuerte Tayer JarnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics & ThermodynamicsDokument36 SeitenKinetics & ThermodynamicsHabibNoch keine Bewertungen
- A PDFDokument17 SeitenA PDFAhmed AlbaderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Lesson 2 Chemical Reactions G9Dokument18 SeitenUnit 1 Lesson 2 Chemical Reactions G9ftamyblooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Laws and Definitions 2021Dokument3 SeitenChemistry Laws and Definitions 2021MichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collision Theory and Reaction RatesDokument14 SeitenCollision Theory and Reaction RatesFira LalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Kinetics & Equilibrium: Froilan Aron S. Faraon, R.PHDokument34 SeitenChemical Kinetics & Equilibrium: Froilan Aron S. Faraon, R.PHKenneth TrogonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Midterm Study GuideDokument7 SeitenChemistry Midterm Study GuideTimajKalifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6.3 BetterDokument13 SeitenChapter 6.3 Betteradityayadav18julyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA Lesson 02 Chemical+ReactionsDokument21 SeitenCA Lesson 02 Chemical+ReactionsI Dont think you should knowNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Section 2 OutlineDokument4 SeitenChapter 6 Section 2 Outlineapi-263455052Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Chemical Reactors: Required Reading: Chapter 22 (Reactors) of Turton Et Al. (2018)Dokument61 SeitenDesign of Chemical Reactors: Required Reading: Chapter 22 (Reactors) of Turton Et Al. (2018)toofan shamssNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 30 Notes on Chemical EnergyDokument6 SeitenChem 30 Notes on Chemical Energystarryskies5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Section 2 OutlineDokument4 SeitenChapter 6 Section 2 Outlineapi-263455051Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 NewDokument40 SeitenChapter 4 NewhoiminhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 Stoichiometry PDFDokument16 SeitenChapter 11 Stoichiometry PDFapi-239855791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of equilibrium constant from calorimetric titration reaction heatDokument14 SeitenDetermination of equilibrium constant from calorimetric titration reaction heatJulian VelezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical change يئايزيف ريغت Chemical changeDokument4 SeitenPhysical change يئايزيف ريغت Chemical changeDebarshi SahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stoichiometry Calculations and ApplicationsDokument28 SeitenStoichiometry Calculations and Applicationskimberly bacaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 Equilibrium and Acid ReactionsDokument5 SeitenModule 5 Equilibrium and Acid Reactionsisaheqq12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 & 5 Chemistry Chapter SummaryDokument23 SeitenForm 4 & 5 Chemistry Chapter SummaryJs TeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ChemistryDokument49 SeitenChemistryAnam FNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - Everything About Chemical ReactionsDokument16 Seiten4 - Everything About Chemical ReactionsSagi IbiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calorimetry + Bond Energies Study NotesDokument9 SeitenCalorimetry + Bond Energies Study Noteszadinova.tereza16Noch keine Bewertungen
- cHEMICAL RECATIONSDokument2 SeitencHEMICAL RECATIONSAnam FNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 3 RATES AND REACTION-IRVANE ROVIC RAMOSDokument2 SeitenActivity 3 RATES AND REACTION-IRVANE ROVIC RAMOSkiara menesesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Concept OutlineDokument13 SeitenChemistry Concept OutlineZhengjie SituNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volumetric Analysis Definitions and Conditions Library by EljackDokument2 SeitenVolumetric Analysis Definitions and Conditions Library by EljackMohammed EljackNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Equilibria-23 - STDDokument65 Seiten7 Equilibria-23 - STDManh Doan DucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Chemical EquilibriumDokument17 SeitenPrinciples of Chemical EquilibriumkaditasookdeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Section 2 OutlineDokument4 SeitenChapter 6 Section 2 Outlineapi-263455076Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry EngineeringDokument31 SeitenChemistry EngineeringJesy TrinidadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rates of Chemical ReactionsDokument13 SeitenRates of Chemical ReactionsAshkan SharifiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry EnthalpyDokument3 SeitenChemistry EnthalpyAzariah GobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and EquilibriumVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and EquilibriumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 - Chemical EquilibriumDokument44 SeitenGrade 10 - Chemical EquilibriumVictoria LowmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical ReactionsDokument18 SeitenChemical Reactionsalexamanual0502Noch keine Bewertungen
- Secondary Chemistry Rate of ReactionDokument17 SeitenSecondary Chemistry Rate of ReactiondreamydamselNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 Section 2 OutlineDokument4 SeitenChapter 6 Section 2 Outlineapi-263455041Noch keine Bewertungen
- CATALYTIC REACTIONS ACCELERATE CHEMICAL PROCESSESDokument41 SeitenCATALYTIC REACTIONS ACCELERATE CHEMICAL PROCESSESKhuza EmahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Collision TheoryDokument46 SeitenCollision Theoryenero.rosasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 101 Exp3 Limiting Reagent Fall 2015Dokument6 SeitenChem 101 Exp3 Limiting Reagent Fall 2015Nahyan Akhtar MemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17 - Reaction RatesDokument3 SeitenChapter 17 - Reaction RatescaffeinewriterNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnergeticsDokument9 SeitenEnergeticsHadi AlnaherNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThermodynamicsDokument6 SeitenThermodynamicsajayyashpalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - Rates of Reaction & Chemical CalculationsDokument2 SeitenChemistry - Rates of Reaction & Chemical CalculationsMegan TaylorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report ChemistryDokument10 SeitenReport Chemistryjela rose camilonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plane Crash Survival Activity in Tropical ForestDokument3 SeitenPlane Crash Survival Activity in Tropical ForestDenialAlfonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 1 RefrigerationDokument18 SeitenExperiment 1 RefrigerationAdamu GinyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GT3Dokument14 SeitenGT3VenkateshPrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- On The Definition of Propellant Force: SciencedirectDokument4 SeitenOn The Definition of Propellant Force: SciencedirectMarcelo MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Animate and the InanimateDokument88 SeitenThe Animate and the InanimateAdriano CordeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECICDokument8 SeitenECICAndrew YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Specific Heat Ratio On Heat Release Analysis in A Spark IgnitionDokument6 SeitenEffect of Specific Heat Ratio On Heat Release Analysis in A Spark IgnitionRodrigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Temperature ModuleDokument22 SeitenHeat and Temperature Modulekiannatherese andradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conduction HMTDokument43 SeitenConduction HMTbalakaleesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bhanda Puta Valuka Puta Bhudhara PutaDokument19 SeitenBhanda Puta Valuka Puta Bhudhara PutaDr Debasis PanigrahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CompiledDokument114 SeitenCompiledRovic Jan Rafael RoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Impact of Design and Operating Parameters On Skull Formation in A Blast Furnace HearthDokument14 SeitenThe Impact of Design and Operating Parameters On Skull Formation in A Blast Furnace HearthmetalmasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eq o o o o Eq: ND RDDokument8 SeitenEq o o o o Eq: ND RDEl-Sayed MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics - Classes IX-X - NC 2006 - Latest Revision June 2012Dokument72 SeitenPhysics - Classes IX-X - NC 2006 - Latest Revision June 2012Mansoor AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Thermodynamics For Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDokument16 SeitenApplied Thermodynamics For Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurTommyVercettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concrete Engineering Properties. HW 2Dokument22 SeitenConcrete Engineering Properties. HW 2RawandAlbarodyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Optimization of Multipass Heat Exchangers: J.M. Ponce-Ortega, M. Serna-Gonz Alez, A. Jim Enez-Guti ErrezDokument8 SeitenDesign and Optimization of Multipass Heat Exchangers: J.M. Ponce-Ortega, M. Serna-Gonz Alez, A. Jim Enez-Guti ErrezPaulina Velandia LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamental Concepts and Definitions: Prepared By: EFREN A. DELA CRUZ E-Mail Address: Eadelacruz@clsu - Edu.phDokument16 SeitenFundamental Concepts and Definitions: Prepared By: EFREN A. DELA CRUZ E-Mail Address: Eadelacruz@clsu - Edu.phBilly Jake CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essar Sample QuestionsDokument3 SeitenEssar Sample Questionshgbv tttbNoch keine Bewertungen
- USCG ME Exam - General KnowledgeDokument262 SeitenUSCG ME Exam - General KnowledgeSai SarihadduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phs 105 Lecture Notes: by O.I. Olusola (PH.D.) Course ContentsDokument7 SeitenPhs 105 Lecture Notes: by O.I. Olusola (PH.D.) Course ContentsDorego TaofeeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Biomedical Engineering (Aait) : Work Sheet #3Dokument4 SeitenDepartment of Biomedical Engineering (Aait) : Work Sheet #3gfsfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet 836 PDFDokument2 SeitenDatasheet 836 PDFGIAS EUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics and Heat EnginesDokument7 SeitenThermodynamics and Heat EnginesWayne C.Noch keine Bewertungen