Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Drug Study
Hochgeladen von
Joan AbardoOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Drug Study
Hochgeladen von
Joan AbardoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Drug Study: Drug 1.
Cefuroxime Dosage 750mg IV q8 Indication As for the other cephalosporins, although as a secondgeneration it is less susceptible to Beta-lactamase and so may have greater activity against Haemophilus influenzae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Lyme disease Contraindications Hypersensitivity to cephalosporins. Side Effects >Allergic reaction: hives; difficulty breathing; swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat. >Serious Side effects: diarrhea that is watery or bloody; fever, sore throat, and head ache with a severe blistering, peeling, and red skin rash; seizure (black-out or convulsions);or jaundice(yellowing of the eyes or skin). >Less Serious Side Effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, stomach pain; headache, dizziness; fussiness of crying (in children);sleep problems(insomnia); or vaginal itching or discharge.
2. Tramadol
50mg IV q6
Moderate to severe pain
Acute alcohol intoxication. Hypnotics, centrally-acting analgesics, opioids or psychotropic drugs. Treatment with MAOI's or within 2wk from withdrawal. Children <12yr. Patients with active peptic ulcer disease, in patients with recent gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation, and in patients with a history of
Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation. Tiredness, drowsiness, dizziness, headache, confusion, hallucinations,. Skin rashes, tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia, flushing, allergic reactions
3. Ketorolac
30mg IV q6
Short-term management of moderate to severe post op pain
G.I. ulceration, bleeding and perforation, postoperative bleeding, acute renal failure, anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions, and liver failure
peptic ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. 4. Paracetamol 300mg IV q6 Reduces fever and relieves the muscular pain characteristic of influenza. This is a nontoxic drug that has excellent gastric tolerance and is increasingly accepted and used. Contraindicated in patients Hypersensitive to the drug. Use cautiously in patients with long term alcohol use because therapeutic doses cause hepatotoxicity in these patients. Hematologic: hemolytic anemia, neutropenia, leucopenia, pancytopenia. Hepatic: Jaundice Metabolic: Hypoglycemia Skin: rash, urticaria. Hypersensitivity to omeprazole or to any of its components. When taken at the recommended dose, side-effects of paracetamol are rare. Skin rashes, blood disorders and a swollen pancreas have occasionally happened in people taking the drug on a regular basis for a long time. One advantage of paracetamol over aspirin and similar drugs (eg ibuprofen
5. Omeprazole
40mg IV
-As an alternative for patients who cannot tolerate oral therapy in the following conditions: benign gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, gastroesophageal reflux disease. -Acid aspiration prophylaxis
Generally mild and reversible. Dermatologic: skin rash, urticaria, pruritus Gastrointestinal: constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting, acid regurgitation, abdominal pain, Others: asthenia, headache, photosensitivity, dizziness, lightheadedness, arthritic and myalgic symptoms, paraesthesia.
Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Objective: -dressing dry and intact Diagnosis Risk for infection related to inadequate defense to surgical incision Planning After 2 hours of nursing intervention, patient will be able to understand causative factors, identify signs of infection and report them to health care provider accordingly. Implementation Independent: -Monitor vital signs -Inspect dressing and perform wound care -Monitor elevated temperature, redness, swelling, increased pain, or purulent drainage at incisions -Wash hands and teach other caregivers to wash hands before contact with patient and between procedures with patient. -Encourage fluid intake of 2000 ml to 3000 ml of water per day(unless contraindicated).Encourage coughing and deep breathing Independent: Administer antibiotics Rationale -To establish a baseline data -Moist from drainage can be a source of infection -these are signs of infection -Friction and running water effectively remove microorganisms from hands. Washing between procedures reduces the risk of transmitting pathogens from one area of the body to another -Fluids promote diluted urine and frequent emptying of bladder -Antibiotics have bactericidal effect that combats pathogens Evaluation Patient is expected to be free of infection, as evidenced by normal vital signs and absence of purulent drainage from wounds, incisions, and tubes.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- CH 14 Digestive-SystemDokument179 SeitenCH 14 Digestive-SystemAntonio Calleja IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Plan Gerontologic NursingDokument3 SeitenTeaching Plan Gerontologic NursingJoan AbardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discontinuing IvDokument2 SeitenDiscontinuing IvJamaica Leslie NovenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 & Unit 4Dokument8 SeitenUnit 3 & Unit 4Melania Arliana MeoNoch keine Bewertungen
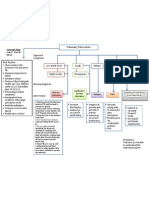
- Concept Map PTBDokument1 SeiteConcept Map PTBJoan Abardo100% (2)
- Animal Environmental EthicsDokument9 SeitenAnimal Environmental EthicsJoan AbardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bipolar DisorderDokument11 SeitenBipolar DisorderJoan AbardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of The Bone Marrow and Blood Conditions That Can Occur When The Blood-Forming Cells in The Bone Marrow Become AbnormalDokument4 SeitenDiseases of The Bone Marrow and Blood Conditions That Can Occur When The Blood-Forming Cells in The Bone Marrow Become AbnormalLuqman QadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory AcidosisDokument5 SeitenRespiratory Acidosisapi-376421583% (6)
- UntitledDokument16 SeitenUntitledAstriUtamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suxamethonium Apnoea Update 2003Dokument2 SeitenSuxamethonium Apnoea Update 2003jira neaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rds NRP 2021Dokument33 SeitenRds NRP 2021Aiwi Goddard MurilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical use of plasma lactate concentration: Understanding its physiology and pathophysiologyDokument21 SeitenClinical use of plasma lactate concentration: Understanding its physiology and pathophysiologyJeaneth SamaniegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04.02 Assignment FinishedDokument5 Seiten04.02 Assignment Finishedjazzmine andesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Health - Emerging and Re-Emerging Infectious Disease Program - 2011-10-17Dokument3 SeitenDepartment of Health - Emerging and Re-Emerging Infectious Disease Program - 2011-10-17John Oliver Y. MatuguinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trauma: HX and PE (Adults) : For The EMS Providers, (Prior To Patient'sDokument3 SeitenTrauma: HX and PE (Adults) : For The EMS Providers, (Prior To Patient'sJustine CastilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Intraocular Foreign BodiesDokument7 SeitenManagement of Intraocular Foreign BodiesdebbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan Kasus BronkopneumoniaDokument30 SeitenLaporan Kasus BronkopneumoniaShifa Ali JannatinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indisposition & Their CauseDokument13 SeitenIndisposition & Their Causenaazsaheba448Noch keine Bewertungen
- JNatlComprCancNetw 2015 Nabors 1191 202Dokument13 SeitenJNatlComprCancNetw 2015 Nabors 1191 202Reyhan AristoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahir Dar University College of Medicine and Health SciencesDokument21 SeitenBahir Dar University College of Medicine and Health SciencesMegbaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Insulin For Diabetes TreatmentDokument2 SeitenTypes of Insulin For Diabetes TreatmentKrystale Mae ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- TETRASODIUM EDTA - National Library of Medicine HSDB DatabaseDokument21 SeitenTETRASODIUM EDTA - National Library of Medicine HSDB DatabaseElena TrofinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Power Conditioner 25 LTRDokument17 SeitenFuel Power Conditioner 25 LTRVijayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal Air Leak Syndrome and The Role Of.3Dokument9 SeitenNeonatal Air Leak Syndrome and The Role Of.3Claudia KosztelnikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preoperative Skin AntisepsisDokument1 SeitePreoperative Skin AntisepsisKatherine GanzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSEBTDokument17 SeitenTSEBTcornejo1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Doctors Specialties Qualifications Timings Saddique HospitalDokument2 SeitenDoctors Specialties Qualifications Timings Saddique HospitalZahid MushtaqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Structure and FunctionsDokument3 SeitenHeart Structure and FunctionsChristella KateNoch keine Bewertungen
- BREAST CANCER CLINICAL PHARMACY PRESENTATIONDokument21 SeitenBREAST CANCER CLINICAL PHARMACY PRESENTATIONfrankNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 LIT208RevH BrainPath-Product-Info FINAL 181003Dokument2 Seiten3 LIT208RevH BrainPath-Product-Info FINAL 181003Carlos Minino P.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cheatsheet PDFDokument2 SeitenCheatsheet PDFJudaeo SandovalNoch keine Bewertungen
- GI Polyps DR OdzeDokument30 SeitenGI Polyps DR OdzeJuliana Do CoutoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 228-Article Text-823-1-10-20210201Dokument6 Seiten228-Article Text-823-1-10-20210201maya chandra ditaNoch keine Bewertungen