Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
87 Technical Sheet - Tig Welding
Hochgeladen von
Zeu AressOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
87 Technical Sheet - Tig Welding
Hochgeladen von
Zeu AressCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
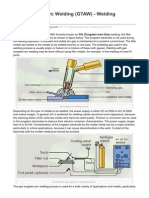
Tungsten Inert Gas Welding (TIG)
Tungsten Inert Gas Welding, also known by its acronym as TIG welding, is a welding process that uses the heat produced bby an electric arc created between nonconsumable tungsten electrode and the e weld pool. This electric arc is produced by the passage of current trough aa conductive ionized inert gas that also provides shielding of the electrode, mmolten weld pool and solidifying weld metal from contamination by the atmo osphere. The process may be used with or without the addition of filler metal us sing metal rods. Electric arc: The process can be used with eeither direct o alternating current, the choice is depending largely on the metal to be welded. Direct current with electrode negative offers the advantage of de eep penetration and faster welding speeds. Direct current with electrode possitive I highly unrecommended because causes electrode overheating and is s rarely used. Alternating current provides cathodic cleaning which removes refractory oxides on materials like aluminum and magnesium allowing superior quality welds. Other types of welding current are avaailable for particular applications like sine-wave or sq quare-wave alternating current and pulsed direct current.
Electrode: In TIG welding, tungsten refers t to the element used on the electrode. The function of tthe electrode is to serve as one of the electric terminals which supplies the heat t required to the weld, for this reason tungsten is chose en because, as a pure element, it as the highest melting point in close to whic ch it gets thermionic becoming a ready source of electrons. Great care mu ust be taken so that the tungsten electrode does not contact the weld pool inn any way or the gas flow rate is sufficient to protect it, in order to avoid its contamination resulting on faulty weld. Some other elements may be add ded to the tungsten, like cerium, lanthanum, thorium and zirconium creating g electrode alloys that improve arc stability, emissivity and bring higher mellting points. Tungsten electrodes may be uses with a variety of tip configurat tions and finishings depending on its welding applications. Shielding gases: Argon and helium or mixtures of both are the most common inert gases used for shielding, allthough argon is more extendedly used providing excellent arc stability and h having a cleaning action in certain materials. Helium, unlike argon, as a high t thermal conductivity which results in a deeper penetrating arc, however beca ause helium is a light gas it is less higher than argon in order to provide the same shieldi ing, adding the fact helium cost is considerably more higher then argon, heliu um welding becomes more expensive and as to be weighed against the penetration increase and increased travel speeds, makin ng it more suitable for thick materials, metals with h high thermal conductivity or high speed mechanized welding. Mixtures of both h gases are used when is useful to balance the two gase es characteristics. Applications
TIG welding has become indispensible as a tool for many industries because of the high quality welds produced at relativ vely low equipment cost. It is used extensively in the aerospace and nuclear indu ustries, also often used for small jobs, maintenance and repair work because of its flexibility and ease of control, however requiring great care and skill from thhe welder. It provides precise control of heat input, for that reason it is preferred for joining thin gage metal and to produce weld close to heat sensitive components. Furthermore then the manual welding techniique TIG welding can be applied on semiautomatic , automatic and machine weldding, it can be also be used for spot welding in sheet metal applications. The pro ocess can be used to weld almost all metals, it is specially used for joining alum minum and magnesium which form refractory oxides, and for reactive metals liike titanium and zirconium that can become embrittled. The mains process limitations are the low de eposits rates provided by this method, also it requires high skill welding tec chnique where tungsten electrode contamination may occur and shielding becommes difficult on drafty environments.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Art Of Saw-Filing, Scientifically Treated And Explained On Philosophical Principles.Von EverandThe Art Of Saw-Filing, Scientifically Treated And Explained On Philosophical Principles.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Welding Process SeminarDokument14 SeitenWelding Process Seminartemporary hNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard dimensions and data for steel and stainless steel pipe sizesDokument7 SeitenStandard dimensions and data for steel and stainless steel pipe sizesRSGatesNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIG Welding Class NotesDokument21 SeitenMIG Welding Class NotesRaju SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing Technology: Tig Welding - Process AnalysisDokument8 SeitenManufacturing Technology: Tig Welding - Process AnalysisshubhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Piercing and PunchingDokument41 SeitenDesign of Piercing and Punchingjacky hansdahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deisel EngineDokument11 SeitenDeisel EngineSaravanaKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Metal Arc Welding (MIG) Presented by N.Sankar/Ap /mechDokument50 SeitenGas Metal Arc Welding (MIG) Presented by N.Sankar/Ap /mechlastjohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide to basic welding techniquesDokument7 SeitenGuide to basic welding techniquesJaveed A. KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 X 7 Guernsey ShedDokument4 Seiten10 X 7 Guernsey ShedDavid Brown100% (1)
- (Metalworking) Welding and MachiningDokument1.767 Seiten(Metalworking) Welding and MachiningEugeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mig Gmaw Welding 1Dokument26 SeitenMig Gmaw Welding 1HAZEL BELLONoch keine Bewertungen
- Equivalent ASTM MaterialDokument34 SeitenEquivalent ASTM Materialgolf0910251891% (45)
- 555 Timer ICDokument13 Seiten555 Timer ICRitu KashyapNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDM Series: Power Driven Medium Duty Lift Truck Serial Number 374575 and HigherDokument156 SeitenPDM Series: Power Driven Medium Duty Lift Truck Serial Number 374575 and HigherDmitryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Tig WeldingDokument11 SeitenStudy of Tig WeldingChandan Srivastava100% (1)
- 20-Min BBQ RecipeDokument1 Seite20-Min BBQ RecipeKate JensenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arc Welding Process PDFDokument12 SeitenArc Welding Process PDFBiswanath RoulNoch keine Bewertungen
- 70 Triumph Repair Manual 63 70Dokument236 Seiten70 Triumph Repair Manual 63 70Swapnil PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honda H3013Dokument77 SeitenHonda H3013Kung KleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric WeldingDokument28 SeitenElectric WeldingmayankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jigs Fixtures MainDokument30 SeitenJigs Fixtures MainPrashanth RamakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications For Jigs and FixturesDokument10 SeitenApplications For Jigs and FixturesAntay Korakot100% (1)
- 2 1 4 PDFDokument7 Seiten2 1 4 PDFAndre STANoch keine Bewertungen
- Welder's Handbook (Air Products Co.)Dokument48 SeitenWelder's Handbook (Air Products Co.)Patrick DominguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIG Welding Guide Under 40 CharactersDokument21 SeitenMIG Welding Guide Under 40 Charactersvishnu0751Noch keine Bewertungen
- Soot and Liquid-Phase Fuel Distributions in A Newly Designed Optically AccessibleDokument20 SeitenSoot and Liquid-Phase Fuel Distributions in A Newly Designed Optically AccessibleHERMAWANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welder HandbookDokument7 SeitenWelder Handbooksandeepkumar63Noch keine Bewertungen
- TIG Welding Seminar ReportDokument13 SeitenTIG Welding Seminar ReportRahul ShawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Jigs and FixturesDokument10 SeitenIntroduction To Jigs and Fixturesabhilash karanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suzuki Tuning GuideDokument7 SeitenSuzuki Tuning GuideHazimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Tungsten-Arc Welding GTAW - Welding TechnologyDokument2 SeitenGas Tungsten-Arc Welding GTAW - Welding TechnologyMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applying TIG Welding TechniquesDokument104 SeitenApplying TIG Welding Techniqueshema_avraoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elec 9714Dokument68 SeitenElec 9714David Vang100% (1)
- PTW-40 SERIES SELF-PROPELLED PALLET LIFT TRUCK MANUALDokument116 SeitenPTW-40 SERIES SELF-PROPELLED PALLET LIFT TRUCK MANUALDmitryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 99924-2094-01 FS600V FS541V FS481V English-EbookDokument167 Seiten99924-2094-01 FS600V FS541V FS481V English-EbookJeff Comfort100% (1)
- Amarex KRT8041eDokument36 SeitenAmarex KRT8041eRui Alves da Silva100% (1)
- Aircraft Materials and Hardware: BoltsDokument27 SeitenAircraft Materials and Hardware: BoltsPakistaniTalent cover songsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carb 2Dokument29 SeitenCarb 2Selva RamNoch keine Bewertungen
- QUERCETANUSDokument64 SeitenQUERCETANUSganyesod100% (2)
- Instructions For Use: 5801H0056 EN Rev.02Dokument181 SeitenInstructions For Use: 5801H0056 EN Rev.02HUY HOANG100% (1)
- Photos of Defects Found in RadiographyDokument14 SeitenPhotos of Defects Found in RadiographyKavipriyan KaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nelson Stud Welding 2009Dokument110 SeitenNelson Stud Welding 2009LhenzMorrizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pioneer SX 45 Service ManualDokument12 SeitenPioneer SX 45 Service Manualel_lujoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSCM Series Stock Selector Counterbalanced Lift Truck Troubleshooting and Maintenance ManualDokument172 SeitenSSCM Series Stock Selector Counterbalanced Lift Truck Troubleshooting and Maintenance ManualDmitryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonVon EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Mig & Mag WeldingDokument24 Seiten13 Mig & Mag WeldingMohamed BencharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sans 10137 2011Dokument107 SeitenSans 10137 2011Pamps Mangampo50% (2)
- 2017 Standard CatalogDokument116 Seiten2017 Standard CatalogpicottNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dumg060d Omniscan MX (En)Dokument98 SeitenDumg060d Omniscan MX (En)Zeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- TP 7052Dokument284 SeitenTP 7052Nelson MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test For Cations, Anions and Gases (QA) NotesDokument10 SeitenTest For Cations, Anions and Gases (QA) Noteschong56100% (2)
- Steam Turbine ConstructionDokument14 SeitenSteam Turbine ConstructionKamal Arab100% (4)
- Cracking of Inconel 800H - SMRDokument8 SeitenCracking of Inconel 800H - SMRkoyasrujanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant tissue culture techniques for plant transformationDokument19 SeitenPlant tissue culture techniques for plant transformationPayal Chauhan57% (7)
- Analiza PESTDokument23 SeitenAnaliza PESTstifler_new100% (2)
- Keystone Better Mann CatalogDokument12 SeitenKeystone Better Mann CatalogSpencer100% (1)
- Clarke Angle Grinder - Manual BooksDokument14 SeitenClarke Angle Grinder - Manual BooksPramzNoch keine Bewertungen
- BN 901467 Pte30 PDFDokument96 SeitenBN 901467 Pte30 PDFDmitryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nelson Stud Welding - Standard FerruleDokument3 SeitenNelson Stud Welding - Standard FerruleStefan Ionita0% (1)
- Arc Welding GuideDokument29 SeitenArc Welding GuideManojKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDS 20/25 Operation and Maintenance ManualDokument152 SeitenPDS 20/25 Operation and Maintenance ManualBladimir GuerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7) PhilProut Final PDFDokument44 Seiten7) PhilProut Final PDFAndrés FelipeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 108 Metal Forming Systems PDFDokument3 Seiten108 Metal Forming Systems PDFNatarajan BalajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Die Blocks PDFDokument26 Seiten01 Die Blocks PDFLibardo Cardenas PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buddyarc400i Usuario En-UsDokument16 SeitenBuddyarc400i Usuario En-UsShivam SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broaching NotesDokument5 SeitenBroaching NotesfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Dynamics Ultra-Cut 200 Eng-OmDokument168 SeitenThermal Dynamics Ultra-Cut 200 Eng-OmsajsigalomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 555 TimerDokument7 Seiten555 TimerHERMAWAN100% (1)
- Halderman AutoTec ch29Dokument37 SeitenHalderman AutoTec ch29PardeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stalwart Technosource Shear Stud WeldingDokument4 SeitenStalwart Technosource Shear Stud WeldingVinicius Geraldini PiantolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ag-900 GunDokument24 SeitenAg-900 GunROMERJOSENoch keine Bewertungen
- 64 TechSupport Static Strength in Joints of Strenx Grades en PDFDokument5 Seiten64 TechSupport Static Strength in Joints of Strenx Grades en PDFZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model ChitantaDokument1 SeiteModel ChitantaZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tehnical Sheets For HardoxxDokument2 SeitenTehnical Sheets For HardoxxZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8942Dokument2 Seiten8942Zeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bebe PressDokument221 SeitenBebe PressZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScriptingDokument10 SeitenScriptingZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- InfoDokument1 SeiteInfoZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zbot CommandDokument1 SeiteZbot CommandDaniil TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutor DataDokument24 SeitenTutor DataMonikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixari Chimice 01 PDFDokument1 SeiteFixari Chimice 01 PDFZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commands NoteDokument1 SeiteCommands NoteZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 CatalogDokument50 Seiten3 CatalogZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web ServerDokument1 SeiteWeb ServerZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- 25multi Plus Olympus NDT - TestingDokument2 Seiten25multi Plus Olympus NDT - TestingZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 TV Firmware Upgrade Instruction T-MST14DEUCDokument5 Seiten2014 TV Firmware Upgrade Instruction T-MST14DEUCRafa MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Change Auto Equip Armors-Weapons (Absolutepower)Dokument7 SeitenChange Auto Equip Armors-Weapons (Absolutepower)Zeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Glow in 1 WepDokument1 Seite2 Glow in 1 WepZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Hack A Website GuideeDokument5 SeitenHow To Hack A Website GuideeZeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coduri Starcraft 2Dokument1 SeiteCoduri Starcraft 2Zeu AressNoch keine Bewertungen
- Square Duct Board Installation ManualDokument4 SeitenSquare Duct Board Installation ManualApurv GoyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urea MsdsDokument5 SeitenUrea MsdsVinnyVidichiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cosmetics 09 00063 v2Dokument44 SeitenCosmetics 09 00063 v2maizhafiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS en 12396-2-1999Dokument10 SeitenBS en 12396-2-1999DoicielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidDokument18 SeitenAldehyde, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidPRADEEP CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry SBA7 ReportDokument6 SeitenChemistry SBA7 ReportSam ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sansico Top Access Floor Trap - S3Dokument20 SeitenSansico Top Access Floor Trap - S3Biggie ColdAngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Triode and Diode Ion PumpDokument7 SeitenComparison of Triode and Diode Ion PumpAarkayChandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ceilcote 242 Flakeline coating specification for concreteDokument2 SeitenCeilcote 242 Flakeline coating specification for concretenoto.sugiartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computational Models For Drug Design and DelivDokument235 SeitenComputational Models For Drug Design and DelivIbrahim Al SharabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improved Conductivity and Mechanism of Carrier Transport in Zinc Oxide With Embedded Silver LayerDokument8 SeitenImproved Conductivity and Mechanism of Carrier Transport in Zinc Oxide With Embedded Silver LayerAbdul BasitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Chem. Lab. M6 ACTIVITY SHEET PCCH103L Santos Ronzel ANgelo M.Dokument3 SeitenOrganic Chem. Lab. M6 ACTIVITY SHEET PCCH103L Santos Ronzel ANgelo M.Akira SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Auxilliary Equipment - US PricingDokument132 Seiten1 Auxilliary Equipment - US PricingOscar EspitiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flashing CalculationsDokument8 SeitenFlashing CalculationsjcmarabouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid Waste Management Not FinishDokument32 SeitenSolid Waste Management Not FinishMans LaderaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NanotechnologyDokument28 SeitenNanotechnologyCordelia Marisse ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 10585 2002 PDFDokument9 SeitenIs 10585 2002 PDFmsreerajvarmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Filter Elements, Parts for Compressors and EnginesDokument2 SeitenFilter Elements, Parts for Compressors and Enginespgm900Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power Distribution at NFC EeeDokument70 SeitenPower Distribution at NFC EeeTeEbhan ChAnthira SeEkaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commiphora Myrrh A Phytochemical and Pharmacologic PDFDokument17 SeitenCommiphora Myrrh A Phytochemical and Pharmacologic PDFWaterfall ShapelessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volcanic Eruptions NotesDokument24 SeitenVolcanic Eruptions NotesKarthikesan MakNoch keine Bewertungen