Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Unit 2 Newsletter
Hochgeladen von
mrslsarnoldOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Unit 2 Newsletter
Hochgeladen von
mrslsarnoldCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UNIT 2: Exponents
COMMON CORE GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARD
MCC8.EE.1
Work with radical and integer exponents.
Know and apply the properties of integer exponents to generate equivalent numerical expressions. Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x2 = p and x3 = p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that 2 is irrational. Use numbers expressed in the form of a single digit times an integer power of 10 to estimate very large or very small quantities, and to express how many times as much one is than the other. Perform operations with numbers expressed in scientific notation, including problems where both decimal and scientific notation are used. Use scientific notation and choose units of appropriate size for measurements of very large or very small quantities (e.g., use millimeters per year for seafloor spreading). Interpret scientific notation that has been generated by technology. Understand informally that every number has a decimal expansion; the rational numbers are those with decimal expansions that terminate in Os or eventually repeat. Know that other numbers are called irrational. Use rational approximations of irrational numbers to compare the size of irrational numbers, locate them approximately on a number line diagram, and estimate the value of expressions (e.g., 2). For example, by truncating the decimal expansion of 2, show that the 2 is between 1 and 2, then between 1.4 and 1.5, and explain how to continue on to get better approximations.
MCC8.EE.2
MCC8.EE.3
MCC8.EE.4
MCC8.NS.1
MCC8.NS.2
COMMON CORE GEORGIA PERFORMANCE STANDARD
Analyze and solve linear equations and pairs of simultaneous linear equations
Solve linear equations in one variable. MCC8.EE.7a Give examples of linear equations in one variable with one solution, infinitely many solutions, or no solutions. Show which of these possibilities is the case by successively transforming the given equation into simpler forms, until an equivalent equation of the form , =, or = = results (where and are different numbers). MCC8.EE.7b Solve linear equations with rational number coefficients, including equations whose solutions require expanding expressions using the distributive property and
MCC8.EE.7
Key Topics to be Covered this Unit
Real Numbers- Rational vs Irrational Numbers Laws of Exponents Perfect Square and Cubes Square Roots and Cube Roots Understanding Scientific Notation Operations with Scientific Notation
Real Numbers Irrational Numbers Integers Whole numbers Radical radicand Perfect squares cube roots Repeating decimals truncate Power perfect cubes
Solving One-variable equations variables on both side of the equation Understand Unique solutions, no solutions and infinite solutions Write and solve equations from descriptions
Rational Numbers Natural Numbers square roots terminating decimals law of exponents scientific notation
Math Language to be used
Coefficient distributive property Standard form of a number
like terms
- - - - - - --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Math 7 Unit 1 Operations With Rational NumbersDokument2 SeitenMath 7 Unit 1 Operations With Rational NumbersmrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Meeting - FlyerDokument1 SeiteAnnual Meeting - FlyermrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Part 2 Review SheetDokument4 SeitenUnit 1 Part 2 Review SheetmrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Learning Night November 12Dokument1 SeiteFamily Learning Night November 12mrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Holiday Lunch FlyerDokument1 SeiteHoliday Lunch FlyermrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 17 16 Barber Weekly UpdateDokument1 Seite5 17 16 Barber Weekly UpdatemrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 NCHS Summer Sports CampsDokument1 Seite2016 NCHS Summer Sports CampsmrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- August 17 15 FlyerDokument1 SeiteAugust 17 15 FlyermrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- EOG Parent Letter - EnglishDokument2 SeitenEOG Parent Letter - EnglishmrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Review Sheet Part I Answer KeyDokument3 SeitenUnit 1 Review Sheet Part I Answer KeymrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- End of Grade Assessment Schedule: Test Date Content AreaDokument1 SeiteEnd of Grade Assessment Schedule: Test Date Content AreamrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Food Drive FlyerDokument1 SeiteFood Drive FlyermrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nov 9 15 FlyerDokument1 SeiteNov 9 15 FlyermrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- August 6 15 FlyerDokument1 SeiteAugust 6 15 FlyermrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Summit FlyerDokument1 SeiteDrug Summit FlyermrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra 1: Slope Review Multiple Choice: Use Graphs of Lines A-D To Answer Question 1-6Dokument2 SeitenAlgebra 1: Slope Review Multiple Choice: Use Graphs of Lines A-D To Answer Question 1-6mrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Road To Graduation FlyerDokument1 SeiteRoad To Graduation FlyermrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication 3Dokument1 SeitePublication 3mrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pass To Learn in Mrs. Arnold'S Class Pass To Learn in Mrs - Arnold'S ClassDokument2 SeitenPass To Learn in Mrs. Arnold'S Class Pass To Learn in Mrs - Arnold'S ClassmrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
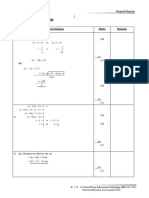
- Solution:: Esolutions Manual - Powered by CogneroDokument11 SeitenSolution:: Esolutions Manual - Powered by Cogneromrslsarnold0% (1)
- Saturday Success Academy Registration Form 2014Dokument2 SeitenSaturday Success Academy Registration Form 2014mrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
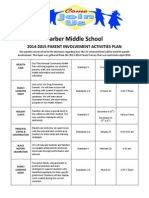
- 2014-2015 Parent Involvement Activites Plan 2Dokument1 Seite2014-2015 Parent Involvement Activites Plan 2mrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- February FlyerDokument1 SeiteFebruary FlyermrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE.7 Graphic OrganizerDokument1 SeiteEE.7 Graphic OrganizermrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Input Meeting InviteDokument1 SeiteInput Meeting InvitemrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Travel Budget: Breakdown of Expenses TotalDokument1 SeiteTravel Budget: Breakdown of Expenses TotalmrslsarnoldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Calc 3-Exam 2 ReviewDokument3 SeitenCalc 3-Exam 2 ReviewLance MeyersNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Knapsack Problem: Lecture 16 - Greedy AlgorithmsDokument6 SeitenThe Knapsack Problem: Lecture 16 - Greedy AlgorithmsTigabu YayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diophantine Equations and Its Applications in Real LifeDokument6 SeitenDiophantine Equations and Its Applications in Real LifePokko PokkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 1 Studyguide360Dokument13 SeitenClass 10 Maths Notes Chapter 1 Studyguide360Magesh wariNoch keine Bewertungen
- C3L4 Tangent Planes and Normal LinesDokument17 SeitenC3L4 Tangent Planes and Normal LinesSabrina MajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheduling With RMADokument8 SeitenScheduling With RMAAnusha KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic Equation PDFDokument54 SeitenQuadratic Equation PDFHāřśh Đīxīţ HđNoch keine Bewertungen
- Average ProblemsDokument2 SeitenAverage ProblemsMadhu Mahesh RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- HKDSE MIA 3E 4A IntExerciseSol EDokument33 SeitenHKDSE MIA 3E 4A IntExerciseSol Ewuheihei2008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Project in deDokument5 SeitenProject in deWelbert Cuanan LumapguidNoch keine Bewertungen
- No de FunctionsDokument26 SeitenNo de FunctionsRAMESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22mat31c QBDokument5 Seiten22mat31c QBU-36 Le0nelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Calculus Grade 11 Quarter 4Dokument4 SeitenBasic Calculus Grade 11 Quarter 4Kazandra Cassidy Garcia100% (1)
- HCF & LCM BasicsDokument11 SeitenHCF & LCM BasicschaostheoristNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Linear Differential Equations With Constants & Variable Coefficients.Dokument63 Seiten06 Linear Differential Equations With Constants & Variable Coefficients.G.M.Tasnimul KarimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology: Algebra (BIC10303)Dokument4 SeitenFaculty of Computer Science and Information Technology: Algebra (BIC10303)HuayszeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minimum Diameter Spanning Trees and Related ProblemsDokument21 SeitenMinimum Diameter Spanning Trees and Related ProblemsThomas RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Worksheets 6th Grade Worksheet 4Dokument7 SeitenAlgebra Worksheets 6th Grade Worksheet 4guptadevesh200Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter1 ALA-handoutDokument88 SeitenChapter1 ALA-handouthong thaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips - Algebra 2 and Trigonometry HonorsDokument43 SeitenDokumen - Tips - Algebra 2 and Trigonometry HonorsgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths GRADE 12 Investigation Sequenses and Series and MemoDokument10 SeitenMaths GRADE 12 Investigation Sequenses and Series and Memotshegomatsididi0505Noch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of MathematicsDokument148 SeitenFoundations of MathematicsAhmad Alhour100% (2)
- SMA 1216 Course OutlineDokument2 SeitenSMA 1216 Course OutlinecharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ed Excel SchemeDokument144 SeitenEd Excel SchemeBaka NitroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application of Gauss Jordan On Matlab Computation in Civil EngineeringDokument5 SeitenApplication of Gauss Jordan On Matlab Computation in Civil EngineeringMaizan Rin DalwainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signal Flow Graph of Control System - Electrical4uDokument10 SeitenSignal Flow Graph of Control System - Electrical4udhineshpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lim F (X) L X C: AP Calculus AB Course Study Guide Limits and ContinuityDokument6 SeitenLim F (X) L X C: AP Calculus AB Course Study Guide Limits and ContinuityPinkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 254 - Algebraic Function Fields and Codes - 2ed - Henning Stichtenoth 3540768777 PDFDokument363 Seiten254 - Algebraic Function Fields and Codes - 2ed - Henning Stichtenoth 3540768777 PDFVishakh Kumar100% (2)
- Quasi Newton MethodsDokument17 SeitenQuasi Newton Methodsm_k_aminNoch keine Bewertungen