Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Air Conditioning System For Your Car
Hochgeladen von
Sanjeev GuptaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Air Conditioning System For Your Car
Hochgeladen von
Sanjeev GuptaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Air Conditioning System For Your Car
How an Air Conditioner Works
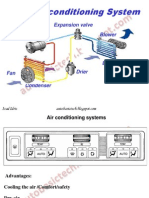
Air conditioning facilitates the removal of heat from inside the vehicle. The principle applied is that heat is removed by conduction and convection. An evaporator which is cold absorbs the heat from the air that is passed through it and then cold air is forced out through the vents inside the car by the blower motor. This is done by pressurizing refrigerant (134a) with a compressor and then releasing refrigerant (134a) inside the air conditioner evaporator.
Some automobiles are equipped with an automatic climate control system to regulate the temperature inside the car automatically. The climate control module is a computer which monitors and adjusts to a temperature set by the user. The temperature is controlled by a combination of cold air from the air conditioner, and hot air from the heater to achieve a desired temperature. The blower motor speed is controlled by a solid state speed controller. This controller electrically controls the speed of the blower motor and replaces the conventional blower motor resistor system.
Typical Air Conditioner System Configuration The air conditioning and heating unit provides thermal comfort to passengers inside no matter what the temperature is outside. The air inside can be heated, cooled, filtered or ventilated. The climate control feature helps to maintain the desired temperature. The system that provides cooling, heating and climate control is known as the HVAC (heating, ventilation, air conditioning) system. Basic principles of fluid mechanics, thermodynamics and heat transfer provide cold and heat for the particular system. Your climate control settings allow all three to work together to achieve good indoor air quality, thermal comfort and optimal pressure.
Climate Control Panel
The climate control system can store trouble codes when a problem is detected in the system. You can retrieve codes by pressing two or more buttons on the control panel at the same time. To find out how to retrieve trouble codes for you vehicle check your owner's manual or consult a repair manual. When the code retrieval system is enabled a trouble code will appear on the temperature control head. After repairs have been made the system will need to be re-enabled this is done by disconnecting the battery for 45 seconds and reconnecting the battery. Testing can be aborted at anytime by turning the key to the off position. Basic Maintenance
Automotive charging kits are available at any auto parts store and it is recommended to buy can with fluorescent refrigerant dye which can help to point out the location of any refrigerant leaks. The kit will have instructions to add the refrigerant safely. Protective eyewear should be used when handling pressurized refrigerant cans. Sometimes bugs, leaves and dust particles can get stuck in the condenser fins. Foreign objects and dirt can be cleaned with the help of a garden hose or compressed air forced through the radiator and condenser backwards until clean
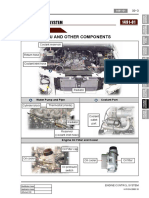
Car Air Conditioner | The part of Automotive Air Conditioning System
The automotive air conditioning system comprises seven major parts. These parts are:
1. Compressor Commonly referred to as the heart of the system, the compressor is a belt driven pump that is fastened to the engine. It is responsible for compressing and transferring refrigerant gas. It is basically a pump connected to the engine whose chief function is to compress the refrigerant from the evaporator coils and the compressor, or the heart of the system, is a pump that is attached to the engine. Its purpose is to compress and transfer refrigerant gas. The compressor has both an intake and a discharge side. 2. Condenser This is the area in which heat dissipation occurs. The condenser, in many cases, will have much the same appearance as the radiator in you car as the two have very similar functions. The condenser is designed to radiate heat. Its location is usually in front of the radiator, but in some cases, due to aerodynamic improvements to the body of a vehicle, its location may differ. Condensers must have good air flow anytime the system is in operation. On rear wheel drive vehicles, this is usually accomplished by taking advantage of your existing
engines cooling fan. On front wheel drive vehicles, condenser air flow is supplemented with one or more electric cooling fan(s). 3. Evaporator Located inside the vehicle, the evaporator serves as the heat absorption component. The evaporator provides several functions. Its primary duty is to remove heat from the inside of your vehicle. Its chief duty is to absorb heat. Besides getting rid of heat from inside your vehicle, it is also responsible for dehumidifying the car. In order to regulate the temperature of the evaporator, pressure introducing pressure regulating devices like orifice tube is necessary 4. Orifice Tube The orifice tube, probably the most commonly used, can be found in most GM and Ford models. It is located in the inlet tube of the evaporator, or in the liquid line, somewhere between the outlet of the condenser and the inlet of the evaporator. 5. Thermal Expansion Valve Another common refrigerant regulator is the thermal expansion valve, or TXV. Commonly used on import and aftermarket systems. This type of valve can sense both temperature and pressure, and is very efficient at regulating refrigerant flow to the evaporator. Several variations of this valve are commonly found. Another example of a thermal expansion valve is Chryslers H block type. 6. The receiver-Drier The receiver-drier is used in automotive air conditioning systems that employ thermal expansion valves as pressure regulating devices to ensure that this pressure regulating device receives the liquid refrigerant that it needs in order to function. In order to do so, it must separate gas and liquid. 7. The accumulator Accumalators are used only on automotive air conditioning systems that have the orifice tube as the pressure regulating device, and its main function is to store surplus liquid refrigerant. It is connected directly to the evaporator outlet and stores excess liquid refrigerant. Introduction of liquid refrigerant into a compressor can do serious damage. In doing so, it prevents any liquid from entering the compressor, which could be detrimental to the system.
What are the benefits of air conditioning?
Efficient cool air in summer Warm dehumidified air in winter easily demists steamed up windows Filters pollutants / airborne particles inc pollen helping allergy sufferers Pleasant and odour free vehicle atmosphere at all times.
Why does a car need an air conditioning recharge? Your air conditioning system can lose up to 15% of it's coolant every year, so a 3 year old car may have lost almost half it's coolant seriously impacting on the performance of the system and damaging the components involved. You should regularly have the air conditioning systems serviced to reduce wear and tear on the components and help avoid potentially big repair bills.
How an Alternator Works
A battery is needed to power the operating system of your car. Once the vehicle is running an alternator that is driven by the engine charges the battery. While in operation the alternator creates electricity, about 13.6 to 14.3 volts, and recharges the battery to its original state of charge. The alternator is one of the hardest working electrical components in your vehicle. When your vehicle is running the alternator is busy creating electricity to provide the engine and the car accessories with needed power. When the car is not running and your battery is severely discharged some electrical components such as alarms or other memory retaining items may still operate or operate poorly. Typically, these components are designed to operate properly at 12 volts; if the system voltage is low it can cause erratic symptoms
An alternator, battery and voltage regulator are the three major components of an automotive charging system. See how the alternator works.
The alternator consists of:
A stationary winding assembly, called the stator. A rotating electro-magnet, the rotor. A slip-ring and brush assembly. A rectifier assembly. Two end-frames. And a cooling fan.
A voltage regulator monitors battery voltage and varies current flow through the rotor field circuit, and thus controls the strength of the rotating magnetic field. This keeps system voltage to a safe level.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Career as an Air Conditioning TechnicanVon EverandCareer as an Air Conditioning TechnicanBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Auto Air ConditioningDokument23 SeitenAuto Air ConditioningAbdul Qadeer Siddiqui80% (5)
- INSPECT AND SERVICE COOLING SYSTEMS - QuizDokument8 SeitenINSPECT AND SERVICE COOLING SYSTEMS - QuizbalalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Air Conditioning SystemDokument17 SeitenAutomotive Air Conditioning SystemVivek Prasad100% (3)
- Automotive Aircnditioning Training ManualDokument102 SeitenAutomotive Aircnditioning Training ManualMarinela-Victor Dobre100% (1)
- Car Cooling SystemDokument42 SeitenCar Cooling Systemymessaoud100% (1)
- Vehicle Air ConditioningDokument32 SeitenVehicle Air ConditioningAkshay Chandel100% (2)
- Automotive Transmission: Be Skilled Be SmartDokument55 SeitenAutomotive Transmission: Be Skilled Be SmartgvnagamaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Conditioning PDFDokument113 SeitenAir Conditioning PDFAndrey Gladyshev100% (3)
- Waeco Car Air Conditioning PDFDokument51 SeitenWaeco Car Air Conditioning PDFsaka ja100% (1)
- UNIT-6: Emission Control Sensors: Knock Sensor Lambda SensorDokument42 SeitenUNIT-6: Emission Control Sensors: Knock Sensor Lambda SensorAnkur SachdevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Brake System: Presented By: T Pravalika 19D45A0307 Presented By: T Pravalika 19D45A0307Dokument24 SeitenAir Brake System: Presented By: T Pravalika 19D45A0307 Presented By: T Pravalika 19D45A0307priyanka priya100% (1)
- Engine System ComponentsDokument33 SeitenEngine System Componentsgatul denaenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ac Compressor Oil CheckingDokument3 SeitenAc Compressor Oil CheckingToua YajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4-AEEDokument92 SeitenUnit 4-AEEMrs G Hemalatha PSG-PTCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Techtip Eng 2007Dokument76 SeitenAutomotive Techtip Eng 2007Veronica Reyes100% (6)
- Compresor AC SanDen Service Guide Rev.2Dokument30 SeitenCompresor AC SanDen Service Guide Rev.2MArco Zaragoza100% (2)
- Automotive Air Conditioning Training Manual PDFDokument88 SeitenAutomotive Air Conditioning Training Manual PDFSamiYousif100% (12)
- Auto Shop SafetyDokument10 SeitenAuto Shop Safetykumawatml100% (2)
- Air CondDokument50 SeitenAir CondIzad Bin Idris100% (2)
- The Theory Behind The Engine BrakeDokument3 SeitenThe Theory Behind The Engine BrakeJoseGarzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part-Iv: Drive ShaftDokument32 SeitenPart-Iv: Drive Shaftgebremariam birkieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Conditioner in The Motor Vehicle: Self-Study Programme 208Dokument37 SeitenAir Conditioner in The Motor Vehicle: Self-Study Programme 208Cristian IfrimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Component CarDokument12 SeitenBasic Component CarFery Budi SatriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel System For Gasoline Engines 1Dokument57 SeitenFuel System For Gasoline Engines 1smithworkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02-Engine Mechanical SystemDokument96 Seiten02-Engine Mechanical Systemsalvador341100% (1)
- 4 Automotive Engine MaintenanceDokument22 Seiten4 Automotive Engine MaintenanceThiruselvan Ayyadorai100% (1)
- 1) Introduction To Cooling System in IC Engine 2) Types of Cooling System A) Air Cooling System B) Water Cooling SystemDokument21 Seiten1) Introduction To Cooling System in IC Engine 2) Types of Cooling System A) Air Cooling System B) Water Cooling SystemRahul PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 74 Sliding Roof ConvertibleDokument16 Seiten74 Sliding Roof ConvertibleTung NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Injectors - and Further MoreDokument4 SeitenFuel Injectors - and Further MoreFabricio LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gearbox Components and Parts Everything You Need To KnowDokument9 SeitenGearbox Components and Parts Everything You Need To KnowSulafa yoga AimanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel System of Conventional EFI-dieselDokument27 SeitenFuel System of Conventional EFI-dieselnahomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emission Control SystemDokument26 SeitenEmission Control SystemnahomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heater & Air Conditioning Control System: SectionDokument230 SeitenHeater & Air Conditioning Control System: SectionАндрей НадточийNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2AZ FE IntakeDokument7 Seiten2AZ FE IntakeLuks Fernandez100% (2)
- Service Electrical Fuel Injection System and Its ComponentsDokument50 SeitenService Electrical Fuel Injection System and Its ComponentsBiruk TilahunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diesel Engine Operation and DiagDokument76 SeitenDiesel Engine Operation and DiagHafiezul Hassan100% (3)
- Air Conditioning SystemDokument48 SeitenAir Conditioning SystemST100% (1)
- Finding Problems in HVAC R Refrigeration CycleDokument4 SeitenFinding Problems in HVAC R Refrigeration CyclejotalopecincoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refrigeration in AutomobilesDokument11 SeitenRefrigeration in Automobilesanswer1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engine Efi System PDFDokument66 SeitenEngine Efi System PDFJesus Teodoro Mendoza Guerra100% (4)
- Refrigerant Charging ProcedureDokument3 SeitenRefrigerant Charging ProcedureRiyas UdheenNoch keine Bewertungen
- LuK TecBr Failure Disgnosis en New 0217Dokument48 SeitenLuK TecBr Failure Disgnosis en New 0217Cata100% (1)
- Air ConditionerDokument79 SeitenAir ConditionerMuch Abdulah NurhidayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Troubleshoot Air ConditioningDokument15 SeitenTroubleshoot Air ConditioningLeonel RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starting SystemDokument21 SeitenStarting SystemNikunj Yagnik100% (1)
- Egine Control System: GeneralDokument18 SeitenEgine Control System: GeneralAnh Tu NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternador Honda LineasDokument2 SeitenAlternador Honda LineasJames JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steering SystemDokument15 SeitenSteering SystemSatya NarayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Air Conditioning Training Manual 1Dokument49 SeitenAutomotive Air Conditioning Training Manual 1Intan Risky100% (1)
- Engine Cooling SystemsDokument31 SeitenEngine Cooling SystemsPujara Manish100% (1)
- Industrial Visit Maruti Suzuki in GurgaonDokument20 SeitenIndustrial Visit Maruti Suzuki in Gurgaonnitin garg100% (1)
- SD Compressor Service ManualDokument33 SeitenSD Compressor Service Manualapi-19789368100% (2)
- Four-Stroke Diesel EngineDokument18 SeitenFour-Stroke Diesel Enginebs esliye me aap ka fan ho gya100% (2)
- Car Air Condition CycleDokument34 SeitenCar Air Condition CycleMubarek TeshomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Air Conditioning SystemsDokument14 SeitenAutomotive Air Conditioning SystemsBekalu DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imi Ae06kDokument4 SeitenImi Ae06kpawel ras100% (2)
- Fundamentals of The Automotive Cabin Climate Control SystemDokument6 SeitenFundamentals of The Automotive Cabin Climate Control SystemSeddik MaarfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Conditioning SystemDokument9 SeitenAir Conditioning SystemRafique PiraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricalor SystemDokument5 SeitenElectricalor SystemyonasNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS en 12516-3 2002 Industrial Valves - Experimental MethodDokument16 SeitenBS en 12516-3 2002 Industrial Valves - Experimental MethodKarthik Raman100% (2)
- ACC20 Engine Safety UnitDokument2 SeitenACC20 Engine Safety UnitVictor EugenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bsi Bs en 1366-8 Smoke Extraction DuctsDokument40 SeitenBsi Bs en 1366-8 Smoke Extraction DuctsMUSTAFA OKSUZNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Mains (2024) AprilDokument129 SeitenJEE Mains (2024) Aprilsophos408Noch keine Bewertungen
- AC Resistance and Impedance in An AC Circuit PDFDokument20 SeitenAC Resistance and Impedance in An AC Circuit PDFKamal CharbelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SortDokument174 SeitenSortPeter CampellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Industrial BiotechnologyDokument29 SeitenBasic Industrial BiotechnologyBharathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion 2000 Hydraulic v8 42-02-1P20 B7Dokument248 SeitenMotion 2000 Hydraulic v8 42-02-1P20 B7ElputoAmo XD100% (1)
- Powernel1500 TDS EN 02152006Dokument1 SeitePowernel1500 TDS EN 02152006Magoge NgoashengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 5 Section 5: Weight and Balance Weight and BalanceDokument36 SeitenSection 5 Section 5: Weight and Balance Weight and Balanceandres felipe sandoval porrasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010-12 600 800 Rush Switchback RMK Service Manual PDFDokument430 Seiten2010-12 600 800 Rush Switchback RMK Service Manual PDFBrianCook73% (11)
- ISO 3384 2005-Stress RelaxationDokument18 SeitenISO 3384 2005-Stress RelaxationshashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skewed Bridges: Effect of SkewDokument2 SeitenSkewed Bridges: Effect of SkewArun K RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seatex DPS 132 User's ManualDokument96 SeitenSeatex DPS 132 User's ManualilgarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RC2 22873Dokument2 SeitenRC2 22873Henok AlemayehuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISODRAFT Reference ManualDokument248 SeitenISODRAFT Reference Manualgabi_nanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thanh Huyen - Week 5 - Final Test AnswerDokument3 SeitenThanh Huyen - Week 5 - Final Test AnswerNguyễn Sapphire Thanh HuyềnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer For Art AppreciationDokument10 SeitenReviewer For Art AppreciationSharmaine FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis - AN Fertiliser Properties Applic and Safety FinlandDokument256 SeitenThesis - AN Fertiliser Properties Applic and Safety FinlandGonzalo O'ortiz Araneda's IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- MNED G12MNEDMockP22017MemoDokument11 SeitenMNED G12MNEDMockP22017MemoChey1242Noch keine Bewertungen
- Price Sheet - Alta Construction Equipment Florida, LLCDokument663 SeitenPrice Sheet - Alta Construction Equipment Florida, LLCeduardo automotrizcpNoch keine Bewertungen
- MPLS PDLDokument47 SeitenMPLS PDLSandro R. S. MacielNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATRA GM 4L60-4L60E (700R4) Rebuild ProceduresDokument0 SeitenATRA GM 4L60-4L60E (700R4) Rebuild ProceduresJuan Manuel Aguero Diaz83% (12)
- Solution To Q9 (Vii) Tut-Sheet 3 (By Professor Santanu Dey)Dokument1 SeiteSolution To Q9 (Vii) Tut-Sheet 3 (By Professor Santanu Dey)Prayas JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exam Syllabus For Genius20Dokument2 SeitenExam Syllabus For Genius20Vaishali PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automatic Power Factor Detection and CorDokument53 SeitenAutomatic Power Factor Detection and CorAshritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Binomial Distribution ProblemsDokument7 SeitenWorksheet Binomial Distribution Problemsonek1ed50% (2)
- Theoretical FrameworkDokument5 SeitenTheoretical FrameworkPatziedawn GonzalvoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solow Model Extension-Human CapitalDokument16 SeitenSolow Model Extension-Human CapitalQusay Falah Al-dalaienNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sachin BiradarDokument2 SeitenSachin Biradardecoo.cocooNoch keine Bewertungen