Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
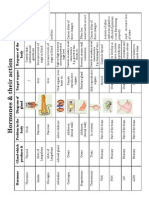
Hormone Target Tissue Effects
Hochgeladen von
Nathaniel SimOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hormone Target Tissue Effects
Hochgeladen von
Nathaniel SimCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
HORMONE
TARGET TISSUE
Growth hormone
Most tissue
OVER SECRETION Pituitary gland Anterior Giantism
UNDER SECRETION
Response
Dwarfism
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) Interstitial cellstimulating hormone (ICSH) Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
Thyroid gland
Hyperthyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Adrenal cortex
Darkening of the skin
No adverse symptoms
Melanocyte in skin
Darkening of the skin
No adverse symptoms
Ovaries(female) Testes (male)
Infertility, interfering with menstruation and ovulation
Delayed puberty, hypogonadism reproductive abnormalities
Follicles in ovaries (female) High fertility in women Seminiferous tubules (male)
Prolactin
Ovaries and mammary gland (female) Testes (male) Kidney
Over production of milk
Hypopituitarism, polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), Turner syndrome and Klinefelter syndrome Less production of milk
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Oxytoxin
Posterior No adverse symptoms
Diabetes insipidus
Uterus, Mammary gland
Can breastfeed due to high level of lactation
Women are unable to breastfeed
Thyroid hormone: Thyroxine Triiodothyronine Calcitonin
Most cell of the body
Thyroid gland Hypothyroidism
Hyperthyrodism
Primarily bone
No adverse symptoms
Medullary thyroid cancer
Parathyroid hormone
Bone, kidney
Parathyroid gland Hypoparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism
Epinephrine (adrenaline) mostly Norepinephrine some
Heart, blood vessel, liver, fat cells
Adrenal medulla insomnia, fatigue, depression, irritability, and digestive difficulties
poor circulation, low blood sugar level ,low blood pressure, low stamina, low self-esteem due to low energy output
Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) Glucocorticoids (cortisol)
Kidneys (lesser degree) Intestine, sweat glands Most tissue
Adrenal cortex Cushing Syndrome
Addison disease
Cushing Syndrome
Addison disease
Adrenal androgens
Most tissue
No adverse symptoms
adrenal virilism or precocious development of male sex characteristics Hyperglycemia High blood sugar Diabetes Mellitus Hypoglycemia Low blood sugar
Insulin
Liver, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue Liver
Pancreas Hypoglycemia Low blood sugar Hyperglycemia High blood sugar
Glucagon
Testosterone
Most tissues
Reproductive organs Testes hypogonadism
Hypergonadism
Estrogens Progesterone
Most tissues
Ovaries inability to conceive naturally hypogonadism
Endometrial Hyperplasia Hypergonadism
Uterus, ovaries, inflamed tissues Prostaglandins Most tissues
Thymus Thymosin Immune tissues
Melatonin
Hypothalamus
Pineal gland Treats sleeping problems
Insomnia, , high blood pressure, blood clots, heart attack
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Kuliah PituitariDokument48 SeitenKuliah PituitariLona Veronika HutajuluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pituitary Gland DisordersDokument80 SeitenPituitary Gland DisordersNang KhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Hormones - Hypersecretion and HyposecretionDokument11 SeitenList of Hormones - Hypersecretion and HyposecretionAngeli Jean Koreen Corpuz88% (48)
- HypopituitarismDokument2 SeitenHypopituitarismAnne de VeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amenorrhea, Hirsutism, VirilismDokument12 SeitenAmenorrhea, Hirsutism, VirilismAly MorganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zoology Notes: 018 Chapter 14Dokument3 SeitenZoology Notes: 018 Chapter 14humanupgrade100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Adults: Metabolic and Endocrine DisordersDokument134 SeitenNursing Care of Adults: Metabolic and Endocrine DisordersMary Ann Pardilla Alcober100% (4)
- Reproductive HormonesDokument43 SeitenReproductive HormonesMunchkin CelinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Hormone FunctionsDokument3 SeitenEndocrine Hormone FunctionsShashank AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypopituitarismDokument4 SeitenHypopituitarismissaiahnicolleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baluga, Basa, Ong: A concise guide to endocrine glands and hormonesDokument6 SeitenBaluga, Basa, Ong: A concise guide to endocrine glands and hormonesdave_1128Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Preconceptual Care, Normal PregnancyDokument233 SeitenManagement of Preconceptual Care, Normal PregnancyBritanny NelsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System Organ ActionsDokument4 SeitenEndocrine System Organ ActionsFlordeliza Santos MagalonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physio Bull BORRABLEDokument11 SeitenPhysio Bull BORRABLEfrhasseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- WorkshopBIO 12 CH. 50Dokument5 SeitenWorkshopBIO 12 CH. 50JISAS CLIMAXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amenorrhea: UNC School of Medicine Obstetrics and Gynecology Clerkship Case Based Seminar SeriesDokument20 SeitenAmenorrhea: UNC School of Medicine Obstetrics and Gynecology Clerkship Case Based Seminar Seriesbinadi vegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypopituitarismDokument6 SeitenHypopituitarismYasim MusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 PubertylectureDokument31 Seiten11 PubertylectureJust MeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine System OverviewDokument3 SeitenEndocrine System Overviewapi-320549212Noch keine Bewertungen
- S9 Q4 M2 Body Regulators and Reproduction and Development LectureDokument21 SeitenS9 Q4 M2 Body Regulators and Reproduction and Development LectureJermae DizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of Hormones Hypersecretion and Hyposecretion PDFDokument11 SeitenList of Hormones Hypersecretion and Hyposecretion PDFAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Bleeding in First Trimester - Miscarriage, Non-Obstetrical ReasonsDokument23 SeitenBleeding in First Trimester - Miscarriage, Non-Obstetrical ReasonsDiana TiganucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Menstruation and Bleeding Conditions in Women and AdolescentsDokument123 SeitenMenstruation and Bleeding Conditions in Women and AdolescentsBritanny NelsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (Pcos) : Mariann Jean Andrea C. Matalines Kenji Fatima L. PaderangaDokument12 SeitenPolycystic Ovarian Syndrome (Pcos) : Mariann Jean Andrea C. Matalines Kenji Fatima L. PaderangaMARIANN JEAN ANDREA CULANAG MATALINESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine DiseasesDokument170 SeitenEndocrine DiseasesJustin Ahorro-DionisioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Female Reproductive System: Central Nervous System Hypothalamus Pituitary Ovaries Uterus, Breasts, Skin, VaginaDokument44 SeitenFemale Reproductive System: Central Nervous System Hypothalamus Pituitary Ovaries Uterus, Breasts, Skin, VaginayeandunNoch keine Bewertungen
- HormonesDokument2 SeitenHormonesMario IstrefiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMENORRHEA CAUSES AND MANAGEMENTDokument41 SeitenAMENORRHEA CAUSES AND MANAGEMENTsridhaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- MENSTRUAL CYCLE GUIDEDokument77 SeitenMENSTRUAL CYCLE GUIDEAlivia SoerayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Hormonal ImbalanceDokument46 SeitenEffects of Hormonal Imbalancejademarco901Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Determination DX: LH Elevated E ElevatedDokument28 SeitenSexual Determination DX: LH Elevated E Elevatedsamantha_schnei9354Noch keine Bewertungen
- What To Know About Hormonal Imbalances?Dokument6 SeitenWhat To Know About Hormonal Imbalances?Tricia Claire BarraquioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Disorders GuideDokument73 SeitenEndocrine Disorders GuideSusie Rae FajardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pituitary Gland IntroDokument40 SeitenPituitary Gland IntroSaif AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine II Pituitary Gland Disorders 2006Dokument80 SeitenEndocrine II Pituitary Gland Disorders 2006Neha BhartiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology Review & Pituitary DisturbancesDokument27 SeitenWeek 2 Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology Review & Pituitary DisturbancesZiqri Dimas SandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Endocrine System: Glands and HormonesDokument213 SeitenThe Endocrine System: Glands and HormonesRosita Antiquina Elopre100% (1)
- Major Glands and Hormones ChartDokument2 SeitenMajor Glands and Hormones ChartKrizzel AlmazoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine SystemDokument3 SeitenEndocrine SystemAnne Jillian83% (6)
- Hormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniDokument21 SeitenHormones: Prof. Dr. V P SoniPadma VishwanathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of The Endocrine System. Violation of Hypophysis, Thyroid and Adrenal Glands. General Adaptation SyndromeDokument123 SeitenPathophysiology of The Endocrine System. Violation of Hypophysis, Thyroid and Adrenal Glands. General Adaptation SyndromeAyman RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HormonesDokument1 SeiteHormonesTang Tiong Min 郑中铭100% (1)
- Female HormonesDokument28 SeitenFemale HormonesmujahidalmakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PituartaryDokument3 SeitenPituartarynancy dasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ArainDokument71 SeitenArainAllah Bux KhosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine ChartDokument7 SeitenEndocrine Chartwjg2882Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anesthesia For Pituitary Lesions: Rialph Engel D. GuiaDokument57 SeitenAnesthesia For Pituitary Lesions: Rialph Engel D. GuiaDoc SabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disoreder Sex of DevelopmentDokument37 SeitenDisoreder Sex of DevelopmentBesth To Frynce HutabaratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Year ReproDokument4 SeitenPast Year ReproThulasi tootsieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sexual Differentiation Anomalies+Puberty - PPT Fara PozeDokument49 SeitenSexual Differentiation Anomalies+Puberty - PPT Fara PozeAmira AsaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marieb Endocrine System SummaryDokument8 SeitenMarieb Endocrine System SummaryLezahbef Neaj SollogonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheehan SyndromeDokument6 SeitenSheehan SyndromeArvie TagnongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endocrine Hormones and Their FunctionDokument1 SeiteEndocrine Hormones and Their FunctionDee RavalNoch keine Bewertungen
- HypopituitarismDokument19 SeitenHypopituitarismStudent FemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hormone Feedback LoopsDokument6 SeitenHormone Feedback LoopsSylheti BabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Janet R. Albers, M.D., Sharon K. Hull, M.D., and Robert M. Wesley, M.ADokument26 SeitenAbnormal Uterine Bleeding: Janet R. Albers, M.D., Sharon K. Hull, M.D., and Robert M. Wesley, M.ACecil-An DalanonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repro HormonesDokument3 SeitenRepro HormonesschmooshieNoch keine Bewertungen
- NeighboorhoodDokument2 SeitenNeighboorhoodNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 43 - Thrombocytopenia and ThrombocytosisDokument6 SeitenChapter 43 - Thrombocytopenia and ThrombocytosisNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Follicular Variant Papillary Thyroid CancerDokument11 SeitenFollicular Variant Papillary Thyroid CancerNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMGG 678Dokument1 SeiteCMGG 678Nathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytochemistry Chapter SummaryDokument3 SeitenCytochemistry Chapter SummaryNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 32 - Molecular Diagnosis in The Clinical LaboratoryDokument12 SeitenChapter 32 - Molecular Diagnosis in The Clinical LaboratoryNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- TriviaDokument10 SeitenTriviaNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro SGD4Dokument8 SeitenMicro SGD4Nathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- OrganizationDokument6 SeitenOrganizationNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 32 - Molecular Diagnosis in The Clinical LaboratoryDokument9 SeitenChapter 32 - Molecular Diagnosis in The Clinical LaboratoryNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hepatitis B, C, HIV and Syphilis Screening and DiagnosisDokument5 SeitenHepatitis B, C, HIV and Syphilis Screening and DiagnosisNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exfoliative CytologyDokument1 SeiteExfoliative CytologyNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- OrganizationDokument5 SeitenOrganizationNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 25 - Extrinsic Defects Leading To Increased Erythrocyte Destruction - Immune Causes Final DraftDokument2 SeitenChapter 25 - Extrinsic Defects Leading To Increased Erythrocyte Destruction - Immune Causes Final DraftNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 24 - Extrinsic Defects Leading To Increased Erythrocyte Destruction - Non Immune CausesDokument5 SeitenChapter 24 - Extrinsic Defects Leading To Increased Erythrocyte Destruction - Non Immune CausesNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 29 - Introduction To Leukocyte NeoplasmsDokument4 SeitenChapter 29 - Introduction To Leukocyte NeoplasmsNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin Rashes Seen After Eating in A Seafood RestaurantDokument2 SeitenSkin Rashes Seen After Eating in A Seafood RestaurantNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematology Laboratory TabulationsDokument6 SeitenHematology Laboratory TabulationsNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nobel Peace Prize Laureates 1901-2013Dokument2 SeitenNobel Peace Prize Laureates 1901-2013Nathaniel Sim100% (1)
- IgE SI Lab ReportDokument7 SeitenIgE SI Lab ReportNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exfoliative CytologyDokument2 SeitenExfoliative CytologyNathaniel Sim100% (2)
- Auto ImmunityDokument7 SeitenAuto ImmunityNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- CM Synovial FluidDokument42 SeitenCM Synovial FluidNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix A - Plasma Coagulation Factors PDFDokument1 SeiteAppendix A - Plasma Coagulation Factors PDFNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 38 - Pediatric and Geriatric HematologyDokument3 SeitenChapter 38 - Pediatric and Geriatric HematologyNathaniel Sim100% (2)
- HEMATOLOGY Cover PDFDokument10 SeitenHEMATOLOGY Cover PDFNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 15 - Examination of The Peripheral Blood Film and Correlation With The Complete Blood CountDokument7 SeitenChapter 15 - Examination of The Peripheral Blood Film and Correlation With The Complete Blood CountNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS ExcelDokument4 SeitenMS ExcelNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual and Semiautomatic Hematology TestingDokument10 SeitenManual and Semiautomatic Hematology TestingNathaniel Sim100% (1)
- BloodDokument2 SeitenBloodNathaniel SimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The German eID-Card by Jens BenderDokument42 SeitenThe German eID-Card by Jens BenderPoomjit SirawongprasertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Re: Laparoscopic Myomectomy: A Review of Alternatives, Techniques and ControversiesDokument1 SeiteRe: Laparoscopic Myomectomy: A Review of Alternatives, Techniques and ControversiesMayada OsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oreilly Design For Voice InterfacesDokument37 SeitenOreilly Design For Voice InterfacesHarmony JordenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Security Testing MatDokument9 SeitenSecurity Testing MatLias JassiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Clàsh The 0nly Band That MatteredDokument255 SeitenThe Clàsh The 0nly Band That MatteredNikos VaxevanidisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Security Training and Awareness Programs For OrganizationsDokument2 SeitenCloud Security Training and Awareness Programs For OrganizationsdeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 09 Chapter TeyyamDokument48 Seiten09 Chapter TeyyamABNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Seven Kings of Revelation 17Dokument9 SeitenThe Seven Kings of Revelation 17rojelio100% (1)
- Beyond VaR OfficialDokument76 SeitenBeyond VaR OfficialmaleckicoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- STS Syllabus 2020Dokument27 SeitenSTS Syllabus 2020AndreaDimaculangan100% (1)
- Frequently Asked Questions: Wiring RulesDokument21 SeitenFrequently Asked Questions: Wiring RulesRashdan HarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport in Plants: Test Yourself 9.1 (Page 178)Dokument3 SeitenTransport in Plants: Test Yourself 9.1 (Page 178)lee100% (3)
- Preparatory Lights and Perfections: Joseph Smith's Training with the Urim and ThummimDokument9 SeitenPreparatory Lights and Perfections: Joseph Smith's Training with the Urim and ThummimslightlyguiltyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symasym BBDokument37 SeitenSymasym BBChandraRizkyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dryers in Word FileDokument5 SeitenDryers in Word FileHaroon RahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nataraja Stotram - A Hymn Without 'CharaNa' and 'ShRi~NgaDokument8 SeitenNataraja Stotram - A Hymn Without 'CharaNa' and 'ShRi~NgaSiva Krishna100% (1)
- ComputerDokument26 SeitenComputer29.Kritika SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process of Producting High Carbon Ferro ChromeDokument5 SeitenProcess of Producting High Carbon Ferro ChromeSantosh Kumar MahtoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samuel Vizcaino: Professional ProfileDokument3 SeitenSamuel Vizcaino: Professional ProfileVizcaíno SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- BBRC4103 - Research MethodologyDokument14 SeitenBBRC4103 - Research MethodologySimon RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCM PPT (Supply Chain Management)Dokument19 SeitenSCM PPT (Supply Chain Management)Mairaj NaseemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 Ways To Balance MagicDokument11 Seiten50 Ways To Balance MagicRodolfo AlencarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education Doña Asuncion Lee Integrated School: Division of Mabalacat CityDokument2 SeitenDepartment of Education Doña Asuncion Lee Integrated School: Division of Mabalacat CityRica Tano50% (2)
- EINC ChecklistDokument3 SeitenEINC ChecklistMARK JEFTE BRIONESNoch keine Bewertungen
- J-Garlic in CheeseDokument12 SeitenJ-Garlic in CheeseMary GinetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disappearance of Madeleine McCannDokument36 SeitenDisappearance of Madeleine McCannCopernicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psalms Magick of The Old Testament PDFDokument129 SeitenPsalms Magick of The Old Testament PDFirrrs100% (1)
- 1 - Gear Seminar ManualDokument125 Seiten1 - Gear Seminar Manualgustool7100% (1)
- Digitrip 520Dokument40 SeitenDigitrip 520HACNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ce125-2500 Open FrameDokument48 SeitenCe125-2500 Open FrameRomão OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen