Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Natsci Ans
Hochgeladen von
Kathleen DamianOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Natsci Ans
Hochgeladen von
Kathleen DamianCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1. meteorology is the study of the atmosphere and its phenomena.
it is also the study of weather, climate, and the forces that cause change in our environment. 2. a meteorologist is a scientist that uses scientific principles to explain or forecast atmospheric phenomena.. Meteorologists are involved with research, teaching, consulting, and forecasting. 3. only small percentage, about 5% of the 9000 meteorologists and atmospheric scientists in the U.S do forecasts for radio and television stations(broadcast meteorologist). 4. Earth's Atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night. 5. a. 99% of dry air is composed of nitrogen (N2) and Oxygen(O2) b. they are not active ingredients for weather and climate. 6. the three reasons that water vapor is such a critical component of theatmosphere in regard to weather and climate are; a. source of precipitation (rain, snow, etc.) b. water is the only element that can exist as solid(ice), liquid(water), or gas(water vapor) at temperatures found in earth's environment. c. critical greenhouse gas. 7. we, humans, have upset the balamce created by the CO2 cycle by putting carbon dioxide into the air in minutes, through burning of fossil fuels, what took millions of years to create.
8. a. the vast majority of ozone (97%) of ozone is found in the stratosphere, above the layer of the atmosphere where weather occurs. b. it is critical to maintaining life on earth because, ozone absorbs harmful, high-energy ultraviolet rays from the sun so that they do not reach earth's surface. 9. a. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) is the atmosphere gas that is responsible for the ozone hole. b. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) is a manmade chemical used for propellants, refrigerants, and solvents. c. yes, because it releases chlorine atoms which facilitate chemical reactions that destroy ozone, particularly in cold stratospheric clouds that form in winter. 10. Atmospheric (Air) Pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth. 11. Air density and pressure always decrease with height above earth's surface. 12. The atmosphere is divided into different layers based upon these changing vertical temperature profiles. 13. a. Troposphere is the lowest level of the atmosphere where all weathers occur. b. troposphere extends up to 36,000 ft - 5 miles - 11 kilometers. temperature decreases with height above earth's surface. 14. a. The layer above the troposphere is called the Stratosphere. b. the temperature in stratosphere begins to increase with height.
c. this temperature profile is due to tha presence of ozone which absorbs ultraviolet rays from the sun, heating and surrounding air. 15. the transition zone between between troposphere and stratosphere is called Tropopause. 16. a. weather is the state of the atmosphere at any given time and place. b. climate is a weather "averaged" over a long period of time. 17. Temperature is how hot or cold the air is. 18. cold air is denser than hot air. 19. a. liquid water droplets. b. heat energy 20. a. 1. conduction - is the direct transfer of heat between adjacent molecules. 2. convection - is the transfer of heat by the mass movement of air. 3. radiation - is energy traveling through space in the form of waves. b. radiationis responsible for heating the earth. 21. a. cools b. warms 22. three important rules regarding radiation;
a. all substances emit radiation b. the wave lengths of radiation that an object emits depends on its temperature. c. the greater the temperature of an object, the greater amount (intensity) of radiation it emits. 23. a. 0.5 um much longer wavelength infrared radiation. 24. increases 25. a. acting like panes of glass b. solar radiation c. terrestrial radiation 26. a. insulating layers b. 0oF 27. water vapor and carbon dioxide 28. a. indirectly b. warmed from below by the earth's surface 29. scattering is when the light is deflected by molecules in all directions. 30. a. is a measure of the percent of radiation which is reflected by a given surface. b. snow and clouds have the highest albedo.
31. a. atmospheric b. oceanic c. storm d. poleward e. equatorward 32. we have seasons because the earth is not oriented straight up and down but is tilted on it's axis 23 1/2o 33. a. the angle at which sunlight strikes the surface b. how long the sun shines(daylight hours) 34. it is because the amount of heat energy provided has to spread over a much larger area when striking at an angle and therefore any given point will receive less heat. 35. a. first day of summer b. toward c. more than 12 hours of sunlight 36.
37. because this region never gets in the "shadow" zone as earth spins. 38. a. day b. night
39. a. warmest temperature b. june c. july d. august 40. exactly opposite
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pre Finals (Natsci)Dokument5 SeitenPre Finals (Natsci)Kathleen DamianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Natsci AnsDokument6 SeitenNatsci AnsKathleen DamianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre Finals (Natsci)Dokument5 SeitenPre Finals (Natsci)Kathleen DamianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Business ProposalDokument8 SeitenSample Business ProposalKathleen DamianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project in English: Business PlanDokument1 SeiteProject in English: Business PlanKathleen DamianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- lATTICE BOLTZMANN METHODDokument15 SeitenlATTICE BOLTZMANN METHODKrunal GangawaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRC Hand Book PDFDokument36 SeitenBRC Hand Book PDFYang W OngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fourier SeriesDokument16 SeitenFourier Seriesvolly666Noch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank AAIDokument4 SeitenQuestion Bank AAIANANYA VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automating commercial insurance data intake with a metamodel-driven solutionDokument5 SeitenAutomating commercial insurance data intake with a metamodel-driven solutionSachin ShingoteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Load Balancing Overview - Google CloudDokument1 SeiteCloud Load Balancing Overview - Google CloudnnaemekenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strength of Materials MarksDokument28 SeitenStrength of Materials Markslogeshboy007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Everything You Need to Know About Hino Truck Models FD, FE, FF and SGDokument4 SeitenEverything You Need to Know About Hino Truck Models FD, FE, FF and SGHS itNoch keine Bewertungen
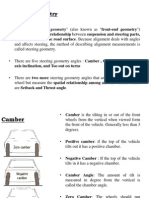
- Steering GeometryDokument23 SeitenSteering GeometryChetanPrasadSevana100% (1)
- Chapter 5 Review: 1 Writing Linear Equations: Slope-Intercept FormDokument2 SeitenChapter 5 Review: 1 Writing Linear Equations: Slope-Intercept FormmeanprNoch keine Bewertungen
- Webinar ZigBee 3-0 Launch FINAL PDFDokument54 SeitenWebinar ZigBee 3-0 Launch FINAL PDFHayadi HamudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Introduction To Computer Simulation Methods: Harvey Gould, Jan Tobochnik, and Wolfgang Christian July 31, 2005Dokument8 SeitenAn Introduction To Computer Simulation Methods: Harvey Gould, Jan Tobochnik, and Wolfgang Christian July 31, 2005Maria Juliana Ruiz MantillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- THE SAP® Business One Software Development Kit: SAP Functions in DetailDokument24 SeitenTHE SAP® Business One Software Development Kit: SAP Functions in DetailPaolo MinguzziNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB Image Processing Toolbox Basic IntroductionDokument10 SeitenMATLAB Image Processing Toolbox Basic IntroductionHilbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- NX2 To NX4 TransitionDokument536 SeitenNX2 To NX4 TransitionBogdan SocolescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Esteem 11 Brochure (24032023)Dokument9 SeitenEsteem 11 Brochure (24032023)TeaMeeNoch keine Bewertungen
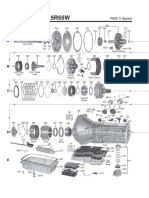
- RWD 5 Speed Transmission Technical DiagramDokument2 SeitenRWD 5 Speed Transmission Technical DiagramCarlos NogueiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Venturi Gas Scrubber WorkingDokument3 SeitenVenturi Gas Scrubber WorkingDonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDVT v140w Drn1 CabinDokument49 SeitenMDVT v140w Drn1 CabinambuenaflorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Einstein's Discoveries Paved the WayDokument3 SeitenEinstein's Discoveries Paved the WayAyman Ahmed CheemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlling Hole Angle - Vertical DrillingDokument15 SeitenControlling Hole Angle - Vertical DrillingImam PranadipaNoch keine Bewertungen
- P5 - Gate Estimate:-: Description L B D/H Quantity Unit Rate Amount For One Gate NosDokument3 SeitenP5 - Gate Estimate:-: Description L B D/H Quantity Unit Rate Amount For One Gate Nosanon_769074129Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Solutions Week 10Dokument3 SeitenTutorial Solutions Week 10Jaden EuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Fundamental IndiaBixDokument162 SeitenComputer Fundamental IndiaBixNa Thaka80% (5)
- Hardware Hacker: Don Lancaster'sDokument8 SeitenHardware Hacker: Don Lancaster'sRon_player8Noch keine Bewertungen
- II Year Civil Engineering Syllabus and Evaluation SchemeDokument12 SeitenII Year Civil Engineering Syllabus and Evaluation SchemeSheezan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 180.5Mbps-8Gbps DLL-based Clock and Data Recovery Circuit With Low Jitter PerformanceDokument4 Seiten180.5Mbps-8Gbps DLL-based Clock and Data Recovery Circuit With Low Jitter PerformanceMinh KhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Small Wind Turbine For Grid-Connected and Stand-Alone OperationDokument4 SeitenSmall Wind Turbine For Grid-Connected and Stand-Alone OperationPranav PiseNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1104decDokument414 Seiten1104decJose Lopez100% (1)
- Problem Set 4Dokument2 SeitenProblem Set 4chrisray39Noch keine Bewertungen