Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
EE 5231 HW 1 Linear Algebra and Vector Spaces
Hochgeladen von
honestcheaterOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EE 5231 HW 1 Linear Algebra and Vector Spaces
Hochgeladen von
honestcheaterCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EE 5231/AEM 8401 HW 1 Fall 2006
Due Friday 09/15/06
1. Reading Assignment: Chapters 48 of Brogan contain a very good coverage of linear algebra. Refer
to these chapters throughout the semester. For now, start by reading chapters 4 and 5 to follow the
lectures, and pick up what you need to do the homework.
2. Let H be a linear vector space on which we have the inner product , ) : H H C satisfying the
following axioms:
u, v) = v, u), where the bar denotes complex conjugation.
u,
1
v
1
+
2
v
2
) =
1
u, v
1
) +
2
u, v
2
) , for any
1
,
2
C.
v, v) 0 and v, v) = 0 if and only if v = 0.
For v H, let |v| = (v, v))
1
2
denote the norm of v. Verify that , ) satises the Cauchy-Schwarz
inequality and that | | satises the triangle inequality, i.e. [ u, v) [ |u||v|, and |u+v| |u|+|v|,
respectively, for all u, v H.
3. Consider the three vectors x
1
=
1 2 3
T
, x
2
=
1 2 3
T
, x
3
=
0 1 1
T
.
(a) Show that this set is linearly independent.
(b) Generate an orthonormal set using the Gram-Schmidt procedure.
(c) Express the vector z =
6 4 3
T
in terms of the orthonormal basis set obtained above.
4. Let H be a linear vector space consisting of all 2 2 matrices dened over the real eld. Let A, B be
any two elements of H.
(a) Show that A, B) = trace (A
T
B) is a valid inner product (you can actually prove this for n n
matrices with real entries).
(b) Show that a basis for the linear space H is the set of matrices
2 1
2 1
1 1
1 1
2 1
4 2
1 1
2 2
.
Is this an orthogonal set?
(c) Obtain a representation of the 2 2 identity matrix in terms of the basis given above.
5. Let / : R
3
R
3
be a linear operator. Consider the two sets B = b
1
, b
2
, b
3
and C = c
1
, c
2
, c
3
below
B =
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
, C =
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
.
It should be clear to you that these are bases for R
3
.
(a) Find the transformation P relating the two bases.
(b) Suppose the linear operator / maps
/b
1
=
2
1
0
, /b
2
=
0
0
0
, /b
3
=
0
4
2
.
Write down the matrix representation of / with respect to the basis B and also with respect to
the basis C.
Be careful with this one! You know that a similarity transformation is involved be sure to
carefully justify your choice for the required matrix.
1
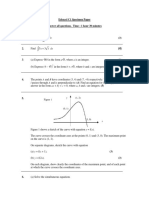
6. In Figure 1 a mass M slides over a frictionless wire and is connected to a spring with spring constant
k. The spring is in an unstretched position when it is at an angle of 45 degrees from the vertical. The
mass is subject to a force input u. The output of the system is the mass displacement z. Obtain a
state space description for this system.
Is this system
(a) causal,
(b) time-varying,
(c) linear,
(d) memoryless,
(e) nite-dimensional?
Explain.
Figure 1: Mass-spring system.
2
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Mooring Design AnalysisDokument41 SeitenMooring Design AnalysisRaghu Nath100% (1)
- A First Book of Quantum Field Theory (Amitabha Lahiri, Palash B. Pal) (Z-Library)Dokument400 SeitenA First Book of Quantum Field Theory (Amitabha Lahiri, Palash B. Pal) (Z-Library)Sudhanshu RanjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation SkillsDokument42 SeitenPresentation SkillsSaqib NawazNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Oliver Knill) Linear Algebra and Vector Calculus IDokument201 Seiten(Oliver Knill) Linear Algebra and Vector Calculus IptolmeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Sets ALL PDFDokument34 SeitenProblem Sets ALL PDFLeroy ChengNoch keine Bewertungen
- ISMS Policy ManualDokument93 SeitenISMS Policy Manualhonestcheater100% (3)
- ISMS Policy ManualDokument93 SeitenISMS Policy Manualhonestcheater100% (3)
- Curtis KS15 Series Part ListDokument102 SeitenCurtis KS15 Series Part ListrobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm A572-21Dokument4 SeitenAstm A572-21Jose Rueda100% (3)
- Real Variables with Basic Metric Space TopologyVon EverandReal Variables with Basic Metric Space TopologyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Marketing PlanDokument58 SeitenMarketing PlanhonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASI Design Guide 10 - Bolted Moment End Plate Beam Splice Connections 21Dokument1 SeiteASI Design Guide 10 - Bolted Moment End Plate Beam Splice Connections 21Anonymous 0x2pwMCWgjNoch keine Bewertungen
- BGP Failover Troubleshooting ManualDokument22 SeitenBGP Failover Troubleshooting ManualhonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nanotechnology in TextilesDokument14 SeitenNanotechnology in TextileshonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solu 7Dokument24 SeitenSolu 7engrs.umerNoch keine Bewertungen
- GP Na Aug2012Dokument2 SeitenGP Na Aug2012ashraf shalghoumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter+12+ReviewDokument13 SeitenChapter+12+Reviewmnvmk2h7xcNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2002 Cambridge ExamDokument22 Seiten2002 Cambridge ExamRoss WrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC-I Taller2Dokument4 SeitenMC-I Taller2Jhon Alexander Calderon SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument3 SeitenAssignment 2revanth ratna kireeti karriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors and CurvesDokument166 SeitenVectors and Curvesmat456Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 0Dokument2 SeitenProblem Set 0Toby ChengNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY321@2310@TD Chap2 MesureQuantiqueDokument3 SeitenPHY321@2310@TD Chap2 MesureQuantiqueEmmanuel BidiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super Boxer DogDokument11 SeitenSuper Boxer DogJack Ignacio NahmíasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Homework 2 Solutions and AnalysisDokument6 SeitenMath Homework 2 Solutions and AnalysisApam BenjaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Questions On Orthogonality and Least Squares and System of Linear EquationsDokument1 SeitePractice Questions On Orthogonality and Least Squares and System of Linear EquationsirfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Chemistry II Homework Problems ExplainedDokument4 SeitenQuantum Chemistry II Homework Problems ExplainedJulieth Moreno0% (1)
- STEP Paper 2 2014Dokument12 SeitenSTEP Paper 2 2014PatbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alg Exercises 3Dokument3 SeitenAlg Exercises 3Cayuss Andrei MihăițoaiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 1Dokument5 SeitenMath 1wissam sadiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set #1. Due Sept. 9 2020.: MAE 501 - Fall 2020. Luc Deike, Anastasia Bizyaeva, Jiarong Wu September 2, 2020Dokument3 SeitenProblem Set #1. Due Sept. 9 2020.: MAE 501 - Fall 2020. Luc Deike, Anastasia Bizyaeva, Jiarong Wu September 2, 2020Francisco SáenzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Population Growth: Flows O N The LineDokument6 SeitenPopulation Growth: Flows O N The LineRaúl Baigorri MartínezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial For Discrete MathematicsDokument2 SeitenTutorial For Discrete MathematicsMax ChiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exercise Sheet 06Dokument3 SeitenExercise Sheet 06timoiivulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ex 2Dokument2 SeitenEx 2Mkt SchrbrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Set 3Dokument3 SeitenTutorial Set 3poweder gunNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR COMPUTER SCIENCE PaperDokument2 SeitenMATHEMATICAL FOUNDATIONS FOR COMPUTER SCIENCE PaperAmrutha TarigopulaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 (MA512)Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1 (MA512)Ankit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete Mathematics 15 JDokument4 SeitenDiscrete Mathematics 15 JrapsjadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 - Vectors ExercisesDokument12 Seiten10 - Vectors ExercisesSebastian ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 4Dokument4 SeitenHomework 4tanay.s1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel C1 Specimen Paper Answer All Questions. Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesDokument3 SeitenEdexcel C1 Specimen Paper Answer All Questions. Time: 1 Hour 30 MinutesLaksh RameshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bmte 141Dokument16 SeitenBmte 141affaf faizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vidya College of Engineering, Meerut Sessional Exam: I (Odd Semester, 2010-2011) Discrete Math StructuresDokument1 SeiteVidya College of Engineering, Meerut Sessional Exam: I (Odd Semester, 2010-2011) Discrete Math StructuresVaibhav MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screenshot 2023-11-08 at 08.35.27Dokument5 SeitenScreenshot 2023-11-08 at 08.35.27alicejessicapreesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proving identities involving sets, numbers, and logicDokument5 SeitenProving identities involving sets, numbers, and logicM Nur RamadhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems Example Sectioned AllanswersDokument4 SeitenProblems Example Sectioned AllanswersRicardo MartínezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multivariate Calculus Worksheet SolutionsDokument13 SeitenMultivariate Calculus Worksheet SolutionsSaad MunawarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Btech Cs 3 Sem Discrete Mathematical Structures Ecs303 2020Dokument2 SeitenBtech Cs 3 Sem Discrete Mathematical Structures Ecs303 2020Vishal Kumar Sharma100% (1)
- Ugmath2021 SolutionsDokument12 SeitenUgmath2021 SolutionsGurkirat SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector Calc SummaryDokument7 SeitenVector Calc SummaryJedwin VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS 1Dokument1 SeiteWS 1Beth RankinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ps 10Dokument2 SeitenPs 10Mano Ranjith Kumar M 007684Noch keine Bewertungen
- Examples and Exercises - Module 2Dokument3 SeitenExamples and Exercises - Module 2UCHECHUKWU NGORKANoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 23b Final Review April 2008Dokument3 SeitenMath 23b Final Review April 2008Lishii Ðë Lä CallëNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vectors and Matrices, Problem Set 3: Scalar Products and DeterminantsDokument3 SeitenVectors and Matrices, Problem Set 3: Scalar Products and DeterminantsRoy VeseyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIDLANDS STATE UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS HMT109 SESSIONAL EXAMSDokument5 SeitenMIDLANDS STATE UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY DEPARTMENT OF APPLIED MATHEMATICS AND STATISTICS HMT109 SESSIONAL EXAMSGladmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- STA 414S Homework 1Dokument3 SeitenSTA 414S Homework 1何明涛Noch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Question 3 - Vector Spaces and Least SquaresDokument2 SeitenPractice Question 3 - Vector Spaces and Least SquaresirfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Tripos Part IADokument7 SeitenMathematical Tripos Part IAChristopher HitchensNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Tripos: Thursday, 7 June, 2018 1:30 PM To 4:30 PMDokument5 SeitenMathematical Tripos: Thursday, 7 June, 2018 1:30 PM To 4:30 PMKaustubhNoch keine Bewertungen
- B4 2-R3Dokument23 SeitenB4 2-R3api-37825190% (1)
- Inner Product SpaceDokument3 SeitenInner Product SpaceDharmendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NonlinearequationsDokument22 SeitenNonlinearequationsdeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- hw1 PDFDokument1 Seitehw1 PDFReinaldy MaslimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kms Mabrouk 2015Dokument9 SeitenKms Mabrouk 2015ismailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bisection methodDokument4 SeitenBisection methodKASHFI UDDINNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAP 2 Practice Paper A 2024Dokument6 SeitenCAP 2 Practice Paper A 2024Haz PlayzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Index notation problem sheetDokument2 SeitenIndex notation problem sheetsuman263947Noch keine Bewertungen
- MATA23 Midterm 2014WDokument2 SeitenMATA23 Midterm 2014WexamkillerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radioactivity: The Radioactive Decay ChainDokument8 SeitenRadioactivity: The Radioactive Decay ChainhonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Nanoparticles via Bottom-Up and Top-Down MethodsDokument68 SeitenSynthesis of Nanoparticles via Bottom-Up and Top-Down MethodshonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nanotechnology in TextilesDokument27 SeitenNanotechnology in TextileshonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9PostNotes PDFDokument8 Seiten9PostNotes PDFLanz de la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- EnterpreneureshipDokument25 SeitenEnterpreneureshiphonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 891 Series UpdatedDokument3 Seiten891 Series UpdatedhonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- These Problems Are Similar But Not Identical To The Actual Test. One or Two Parts Will Actually Show UpDokument5 SeitenThese Problems Are Similar But Not Identical To The Actual Test. One or Two Parts Will Actually Show UphonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- P8 10Dokument2 SeitenP8 10honestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- P8 10Dokument2 SeitenP8 10honestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Circular No.2017-173 Shifting of Location - Regional Office SargodhaDokument1 SeiteInformation Circular No.2017-173 Shifting of Location - Regional Office SargodhahonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY 137A (D. Budker) Midterm 2 SolutionsDokument3 SeitenPHY 137A (D. Budker) Midterm 2 SolutionshonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Ethics in Islam: Its Sources, Significance and DutiesDokument47 SeitenConcept of Ethics in Islam: Its Sources, Significance and DutieshonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- PTCL DC Rack ShiftingDokument1 SeitePTCL DC Rack ShiftinghonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- BatteriesDokument10 SeitenBatterieshonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social and Economic Development RussiaDokument22 SeitenSocial and Economic Development Russiahonestcheater100% (1)
- English Register Urdu Register Rs.50 Rs.50Dokument2 SeitenEnglish Register Urdu Register Rs.50 Rs.50honestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report WritingDokument17 SeitenReport WritingEdwin Wong50% (2)
- Global Crisis and Challenges For Russia PDFDokument26 SeitenGlobal Crisis and Challenges For Russia PDFhonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monetary PolicyDokument39 SeitenMonetary PolicyhonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Income AccountingDokument5 SeitenNational Income AccountinghonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesDokument33 SeitenCylindrical and Spherical CoordinatesAbraham ZawierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ag - sp01 - E1 - p1 h.248 Protocol v1.1 51pDokument51 SeitenAg - sp01 - E1 - p1 h.248 Protocol v1.1 51phonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 24 IP MSAN Maintenance Commands - 10Dokument10 Seiten24 IP MSAN Maintenance Commands - 10honestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- AM - SS03 - E2 - P1 ZXA10-MSAN Cabinet & Power Module Introduction (Malaysia) V1.1 19pDokument19 SeitenAM - SS03 - E2 - P1 ZXA10-MSAN Cabinet & Power Module Introduction (Malaysia) V1.1 19phonestcheaterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 - 254624-400-DS-INT-022 Ball Valve DSDokument8 Seiten4 - 254624-400-DS-INT-022 Ball Valve DSNerudaArarNoch keine Bewertungen
- HSLA Steel Specifications and PropertiesDokument3 SeitenHSLA Steel Specifications and Propertiesbaskaran ayyapparajNoch keine Bewertungen
- BC 640Dokument5 SeitenBC 640Miguel AngelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 7 Post Test Ratios and Proportions - QuizizzDokument7 SeitenGrade 7 Post Test Ratios and Proportions - QuizizzSadiah PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ficha Tecnica Cat 6a CableDokument3 SeitenFicha Tecnica Cat 6a CableVictor Guevara GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmic and Diagnostic Instruments: Ophthalmoscope / Retinoscope / OtoscopeDokument37 SeitenOphthalmic and Diagnostic Instruments: Ophthalmoscope / Retinoscope / OtoscopeKhelifa RadiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ETABS 19.1.0-Design Details4Dokument2 SeitenETABS 19.1.0-Design Details4Alejandro Tovar MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Owners Manual: 3000 SERIES Electric Hot Food Holding UnitsDokument15 SeitenOwners Manual: 3000 SERIES Electric Hot Food Holding UnitsAdeRorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter One Talking About The WeatherDokument6 SeitenChapter One Talking About The WeatherĐào Nguyễn Duy TùngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee Advanced 2 Paper 1Dokument13 SeitenJee Advanced 2 Paper 1egoistic dumboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual of M7000 Veterinary Monitor PDFDokument89 SeitenManual of M7000 Veterinary Monitor PDFbiomedicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CV 1Dokument1 SeiteCV 1Yousef JocmaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Srisudharshan Manikandan Register Number: 21BEC2104Dokument6 SeitenName: Srisudharshan Manikandan Register Number: 21BEC2104Srisudharshan Manikandan 21BEC2104Noch keine Bewertungen
- Positive Displacement Meter SpecificationsDokument3 SeitenPositive Displacement Meter SpecificationsYohanes AzzisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amb4519R0V06 2Mx-690-960-33-18.5I-M-R Easyret Dual-Beam Antenna With 2 Integrated Rcus - 2.0MDokument2 SeitenAmb4519R0V06 2Mx-690-960-33-18.5I-M-R Easyret Dual-Beam Antenna With 2 Integrated Rcus - 2.0MRobertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endsem QN PaperDokument2 SeitenEndsem QN Paper20EEE1004anjali yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predesign Pile Foundation EGYPT STERLING WILSON Draft v10.1 August 2018Dokument41 SeitenPredesign Pile Foundation EGYPT STERLING WILSON Draft v10.1 August 2018ramesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S1110093112000312 MainDokument11 Seiten1 s2.0 S1110093112000312 Maindanielafarmacie_1617Noch keine Bewertungen
- M&e 2Dokument2 SeitenM&e 2DODI02 deltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometry Worksheet on Shapes and AnglesDokument4 SeitenGeometry Worksheet on Shapes and AnglesairinputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soft Switching DC DC Converter With MPPT For Solar 2 PDFDokument56 SeitenSoft Switching DC DC Converter With MPPT For Solar 2 PDFAnonymous Z1RHn9ENoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY-433 04 KinematicsDokument39 SeitenPHY-433 04 KinematicsKim OpenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module3.Measurement of Vertical DistancesDokument25 SeitenModule3.Measurement of Vertical DistancesJohn Greg ChavezNoch keine Bewertungen
- FDS SheetDokument2 SeitenFDS SheetsunnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Notesm UuoiDokument72 SeitenUnit 2 Notesm UuoiTeacher JAY-AR LAGMANNoch keine Bewertungen