Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Musculoskeletal Bones Rheumatoid Arthritis PharmaPedia PharmaGates
Hochgeladen von
Islam FawzyOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Musculoskeletal Bones Rheumatoid Arthritis PharmaPedia PharmaGates
Hochgeladen von
Islam FawzyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
Rheumatoid Arthritis ()
Definition:
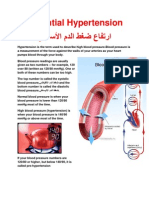
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)Is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that may affect many tissues and organs, but principally attacks synovial joints. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease. autoimmune diseases are illnesses that occur when the body's tissues are mistakenly attacked by their own immune system.
While rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic illness, meaning it can last for years, patients may experience long periods without symptoms. However, rheumatoid arthritis is typically a progressive illness that has the potential to cause joint destruction and functional disability.
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
The pathology of the disease process often leads to the destruction of articular cartilage and ankylosis of the joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis can also produce diffuse inflammation in the lungs, pericardium, pleura, and sclera, and also nodular lesions, most common in subcutaneous tissue. ==============================================================
Causes :
Although the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown
autoimmunity plays a pivotal role in both its chronicity and progression, and RA is considered a systemic autoimmune disease.
The disease involves abnormal B cellT cell interaction, with presentation of antigens by B
cells to T cells .
B-cells & T-cells Inflammation is then driven either by B cell or T cell products stimulating release of TNF and
other cytokines. If TNF release is stimulated by B cell products in the form of RF or ACPA -containing immune complexes, through activation of immunoglobulin Fc receptors, then RA can be seen as a form of Type III hypersensitivity. tareget Antigen ACPA tumor necrosis factor TNF reumatoid factor RF type III hypersensitivity B-cells Ag Antigen
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
If TNF release is stimulated by T cell products such as interleukin-17 it might be considered
closer to type IV hypersensitivity ) type V)delayed hypersensitivity T-cells
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
The debate on the relative roles of immune complexes and T cell products in inflammation in
RA has continued for 30 years. There is little doubt that both B and T cells are essential to the disease. 30 T-cells B-cells B-cells & T-cells As with most autoimmune diseases, it is important to distinguish between the cause(s) that trigger the process, and those that may permit it to persist and progress.
1-Possible infectious triggers:
Some infectious organisms suspected of triggering rheumatoid arthritis include: Mycoplasma, Erysipelothrix, parvovirus B19 and rubella, but these associations have never been supported in epidemiological studies. Nor has convincing evidence been presented for other types of triggers such as food allergies. Epidemiological studies have confirmed a potential association between RA and two herpesvirus infections: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and Human Herpes Virus 6 (HHV6). : RA .)6 - HHV(6 ) EBV( Individuals with RA are more likely to exhibit an abnormal immune response to the EpsteinBarr virus.
Psychological factors physical and emotional effects or stress could be a trigger for the disease. Continued abnormal immune response. ==============================================================
Propapility:
About 1% of the world's population is affected by rheumatoid arthritis. women three times more often than men.
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
Onset is most frequent between the ages of 40 and 50, but people of any age can be affected. ===============================================================
Symptoms:
Stiffness( :)The joint does not move as well as it once did. Its range of motion (the extent to which the appendage of the joint, such as the arm, leg, or finger, can move in different directions) may be reduced. Typically, stiffness is most noticeable in the morning and improves later in the day. . . Inflammation: Redness, tenderness, and warmth are the hallmarks of inflammation. Swelling: The area around the affected joint is swollen and puffy. Nodules: These are hard bumps that appear on or near the joint. They often are found near the elbows. .. They are most noticeable on the part of the joint that juts out when the joint is flexed. Pain: Pain in rheumatoid arthritis has several sources. Pain can come from inflammation or swelling of the joint and surrounding tissues or from working the joint too hard. The intensity of the pain varies by the individual. These symptoms may keep you from being able to carry out your normal activities. General symptoms include the following: malaise (a "blah" feeling), fever, fatigue, loss of appetite,
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
weight loss,
myalgias (muscle aches), and weakness or loss of energy.
Additional symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis include:
Eye problems
Nodules under the skin
Pale skin
Redness and inflammation of the skin
Swollen glands
==========================================================
Diagnosis:
1- Imaging X-Ray of the hand & feet .
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
2-Blood tests * Rheumatoid Factor :
When RA is clinically suspected, immunological studies are required, such as testing for the presence of rheumatoid factor (RF, a non-specific antibody) BUT about 15% of patients. During the first year of illness, rheumatoid factor is more likely to be negative.
* Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) :
when increased confirms the presence of an inflammatory condition .
* C-reactive protein (CRP) :
Increased when the disease is active but its not specific .
* Other tests :
Increased in : Alkaline phosphatase & Platelet count. Decreased in serum albumin . Normochromic,normocytic anaemia.
* The synovial fluid :
yellow, watery , turbid due to high white blood cell count & has low glucose content .
Treatment :
Lifestyle modification and analgesics are the mainstay of treatment. 1- Lifestyle modification : Exercise Physical therapy has been shown to significantly improve function, decrease pain, and delay need for surgical intervention in advanced cases. Exercise helps maintain joint and overall movement. Ask your health care provider to recommend an appropriate home exercise routine. Water exercises, such as swimming, are especially helpful. Exercise prescribed by a physical therapist has been shown to be more effective than medications in treating osteoarthritis of the knee.
Other lifestyle recommendations include:
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.* Applying heat and cold Eating a healthy, balanced diet Getting rest Losing weight if you are overweight Protecting the joints
2- Medication :
Analgesic Drugs : A- Paracetamol
Paracetamol is the first line treatment for OA. Mechanism of action: it exerts its analgesic action by raising the threshold of response to pain stimuli by interfering with their relay from the thalamus to the cortex, other forms of sensations however remain completely unaffected. Precautions: it should be given with care to patients with impaired kidney or liver & to patients with alcohol dependence. Dose: 1 tab. / 4-6 hours. N.B: 1) Can be safely used during pregnancy 2) Can be safely used with patients receiving anti-coagulants 3) Acetaminophen : is a metabolite of Paracetamol which has the same properties & action
N.B : Paracetamol ( Acetaminophen ) is not related to Non-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs but, its Analgesic Anti-pyretic Drug. Cetal Panadol Extra Paramol
* * *
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
Perfalgan
Abimol
Pyral
* * *
B- NSAIDs Mechanism of action: Most NSAIDs act as non-selective inhibitors of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), inhibiting both the cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) isoenzymes. COX catalyzes the formation of prostaglandins and thromboxane from arachidonic acid. Prostaglandins act as messenger molecules in the process of inflammation. If paracetamol does not control your pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, can be used instead. Common side effects of NSAIDs include: 1-indigestion 2-stomach ulcer N.B : PPIs help to prevent stomach ulcers and internal bleeding by reducing the production of stomach acid. N.B : Selective COX-2 inhibitors are not suitable for pregnant women or those with a history of heart problems. 1-Ibuprofen Brufen Marcofen Megafen (ibuprfen + Paracetamol)
10
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
* * *
2-Aceclofenac :
Amoflam
Bristaflam
Fenac
* *
3-Diclofenac :
11
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
Rheumafen (diclofenac Na)
Dolfin (diclofenac Na & K)
Voltareen (diclofenac Na)
* *
Cataflam (dicolfenac K)
Catafast (diclofenac K)
Neurofenac (diclofenac Na + Vit.B complex)
12
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
* * *
4-Indomethacin : Indomethacin
5-Ketoprofen :
Biprofenid
Ketofan
Ketolgin
13
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
* *
6-Naproxen : Naprofen 500
7-Piroxicam : Felden
14
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
8-Tolmetin :
Rumatol 200 , 400
Tolmet DS 400
9- Selective Cox II inhibitors : Arythrex (celecoxib) Celebrex (celecoxib) Mobic (meloxicam)
15
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
* *
Mobitil (meloxicam)
Rheuxicam (lornoxicam)
Xefo (lornoxicam)
* * *
10-Other Anti-inflamatory drugs : Diacerein (diacerein) Nimalox (nimesulide) Sulide (nimesulide)
16
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
* *
Ponstan fort (mefenamic acid)
Analfan (galfenine)
Nabutone (nabumetone)
* * *
Disease-modifyning antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) :
They are used to reduce signs & symptoms & retard structural damage of the joint ( erosions & joint space narrowing ).
17
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
1) Lefunamide Apetoid (leflunomide) Arthfree (leflunomide) Avara
N.B. : Leflunamide, has antiproliferative effect on B-cells
2) Sulphasalazine Salazopyrin 500
3)Methotrexate
18
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
Methotrexate
4) Penicillamine
It decreases RF & interfering with DNA synthesis .
Artamine
Retadel
Rheumaton
4) Cyclosporin 5) Hydroxychloroquine
Plaquenil
Hydroquine
19
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
6)Azathioprine Azathioprine Herceptin Immuless Imuran
9) Corticosteroids HydroCortisone Sigmacortin Solu-Cortef Hostacortin
20
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
Prednisolone Hostacortil-H Predilone Predsol Xilone
Methyl Prednisolone Depomedrol MPA Urbasone
Betamethasone Betasone Betafos Diprofos
21
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
Dexamethasone
Deltasone
Dexamethasone
Dexazone
Fortecortin
Epidron
Orazone
Oradexone
22
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
Triamicnolone & other CS
Kenacort-A
Ultralan
Synacthen
23
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
Dexamethasone & Chroropheniamine maleate Apidone Dexaphen Phenadone Vendexine
3- Complementary medicine : Many alternative medicines are purporting to decrease pain associated with arthritis.
Glucosamine & Chondroitin sulphate Combinations :
Glucosamine involved in the manufacture of glycosaminoglycan, which forms cartilage tissue in the body; also present in tendons & ligaments. Dose: one cap. 3 times daily. Dorofen Elasticin Genuphil
* *
24
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
Glucosamine
Glucosamine-Comp
Move Free
* *
Methyl Sulphonyl Methane (MSM) :
Natural source of sulphur needed by joints & muscle to gaurd against pain & cramps. It may relieve pain similar to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Joifit 500 MSM 1000 Nitora
* * *
Omega-3 fatty acid :
25
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
Essential fatty acids are molecules that cannot be synthesized by the human body but are vital for normal metabolism. One of the two families of these essential fatty acids is the omega-3 fatty acids. Omega 3
Anti-oxidants Vitamins ( Vit. A, C, E ) Acupuncture Mud Pack Therapy :
Mud pack therapy has been suggested to temporarily relieve pain in patients with osteoarthritis of the knees .According to researchers, treatment with mineral-rich mud compresses, can be used to augment conventional medical therapy in these patients. 4-Surgery : If the above management is ineffective, joint replacement surgery or resurfacing may be required in advanced cases. Severe cases of OA might need surgery to replace or repair damaged joints. Surgical options include:
Arthroscopic surgery to trim torn and damaged cartilage. Changing the alignment of a bone to relieve stress on the bone or joint. Surgical fusion of bones, usually in the spine ( arthrodesis ) Total or partial replacement of the damaged joint with an artificial joint ( knee replacement, hip replacement, shoulder replacement, ankle replacement, elbow replacement)
26
*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification.*
5-Braces & Splints : Splints and braces can sometimes support weakened joints . Some prevent the joint from moving; others allow some movement. You should use a brace only when your doctor recommends one. Using a brace the wrong way can cause joint damage, stiffness, and pain.
Complications :
Adverse reactions to drugs used for treatment
Anemia Bleeding gastric ulcers Chronic pain Immobility and disability Instability of neck bones Joint deformity and destruction Rheumatoid vasculitis, a type of inflammation of the blood vessels, which can lead to atherosclerosis, stroke, heart attack, and other cardiac conditions. Skin ulcerations and infections
Decreased ability to perform everyday activities, such as personal hygiene, or cooking Decreased ability to walk Surgical complications
Advices for patient :
1. . .
2. . 3. .
4. .
5. .
72
*.*this material is free to be used in any educational procedure, downloaded , copied or shared once used without any content modification
. .6
.7
. , , , .8
. ,, , , , , .9
. A, B .01 . ,, ,, .11
.21
: , .31 , ,
.41
:Refrences
ttp://www.bettermedicine.com/article/rheumatoid-arthritis/symptoms http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rheumatoid_arthritis http://www.bettermedicine.com/article/rheumatoid-arthritis/treatments
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- GENUS Clock Gating Timing CheckDokument17 SeitenGENUS Clock Gating Timing Checkwasimhassan100% (1)
- Automatic Coconut Dehusking MachineDokument12 SeitenAutomatic Coconut Dehusking MachineKumaresh Salem0% (1)
- Fundamentals of Marketing Presentation HandoutDokument488 SeitenFundamentals of Marketing Presentation HandoutIslam FawzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Urinary Diabetes Insipidus PharmaPedia PharmaGatesDokument7 SeitenUrinary Diabetes Insipidus PharmaPedia PharmaGatesIslam FawzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory UpperRT Tonsillitise PharmaPedia PharmaGatesDokument9 SeitenRespiratory UpperRT Tonsillitise PharmaPedia PharmaGatesIslam FawzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive Male Diseases Premature Ejaculation PharmaPedia PharmaGatesDokument12 SeitenReproductive Male Diseases Premature Ejaculation PharmaPedia PharmaGatesIslam FawzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Miscellaneous Vitamins Vitamin D Def. PharmaPedia PharmaGatesDokument21 SeitenMiscellaneous Vitamins Vitamin D Def. PharmaPedia PharmaGatesIslam Fawzy0% (1)
- GIT Anorexia PharmaPedia PharmaGatesDokument10 SeitenGIT Anorexia PharmaPedia PharmaGatesIslam FawzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye & Ear - Eye - Conjunctivitis - PharmaPedia - PharmaGatesDokument9 SeitenEye & Ear - Eye - Conjunctivitis - PharmaPedia - PharmaGatesIslam FawzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CVS Essential Hypertension PharmaPedia PharmaGatesDokument71 SeitenCVS Essential Hypertension PharmaPedia PharmaGatesIslam FawzyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Wid Awt Method 2Dokument7 SeitenLesson Plan Wid Awt Method 2Yan LianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Munchies BrochureDokument28 SeitenMunchies BrochureIbrahim Diaz LazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dphs Freshman Course List 2024-25Dokument1 SeiteDphs Freshman Course List 2024-25api-337771649Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hotel Voucher: Itinerary ID Hotel Santika Taman Mini Indonesia IndahDokument2 SeitenHotel Voucher: Itinerary ID Hotel Santika Taman Mini Indonesia IndahSyukron PribadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portfolio Eelco Maan - 06-2017Dokument25 SeitenPortfolio Eelco Maan - 06-2017tungaas20011Noch keine Bewertungen
- T10 - PointersDokument3 SeitenT10 - PointersGlory of Billy's Empire Jorton KnightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Market Challengers StrategiesDokument19 SeitenMarket Challengers Strategiestobbob007100% (20)
- Sample Engagement LetterDokument5 SeitenSample Engagement Letterprincess_camarilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Review A2-B1Dokument5 SeitenGrammar Review A2-B1Lena Silva SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Love Spells That WorkDokument14 SeitenSimple Love Spells That Workagg24ankitNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019q123.ev3-Descon Engro Level Gauges-QDokument7 Seiten2019q123.ev3-Descon Engro Level Gauges-Qengr_umer_01Noch keine Bewertungen
- THE Ketofeed Diet Book v2Dokument43 SeitenTHE Ketofeed Diet Book v2jacosta12100% (1)
- Review Problems On Gas TurbineDokument9 SeitenReview Problems On Gas TurbinejehadyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- L&T Motor CatalogDokument24 SeitenL&T Motor CatalogSanjeev DhariwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hybrid Neural-Network - Genetic Algorithm Technique For Aircraft Engine Performance Diagnostics Developed and DemonstratedDokument4 SeitenHybrid Neural-Network - Genetic Algorithm Technique For Aircraft Engine Performance Diagnostics Developed and Demonstratedmohamad theibechNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCG Damri SurabayaDokument11 SeitenGCG Damri SurabayaEndang SusilawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Architech 06-2016 Room AssignmentDokument4 SeitenArchitech 06-2016 Room AssignmentPRC Baguio100% (1)
- English Assignment - October 6, 2020 - Group AssignmentDokument3 SeitenEnglish Assignment - October 6, 2020 - Group AssignmentDaffa RaihanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSS SP 69pdfDokument18 SeitenMSS SP 69pdfLaura CaballeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Hum RepDokument21 SeitenSample Hum RepPritam PiyushNoch keine Bewertungen
- FE 208 Lab #4 - Profile Leveling: CrewDokument4 SeitenFE 208 Lab #4 - Profile Leveling: CrewJefferson Himson0% (1)
- 3S Why SandhyavandanDokument49 Seiten3S Why SandhyavandanvivektonapiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maven MCQDokument55 SeitenMaven MCQANNAPUREDDY ANIL KUMAR REDDY CSENoch keine Bewertungen
- Sorting Algorithms in Fortran: Dr. Ugur GUVENDokument10 SeitenSorting Algorithms in Fortran: Dr. Ugur GUVENDHWANIT MISENoch keine Bewertungen
- APS PresentationDokument32 SeitenAPS PresentationRozack Ya ZhackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cinnamon RollDokument1 SeiteCinnamon RollMaria Manoa GantalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductions and Basic Personal Information (In/Formal Communication)Dokument6 SeitenIntroductions and Basic Personal Information (In/Formal Communication)juan morenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Letter of Intent Date: 18-Feb-2019 Mr. Ravi Mishra,: For Multiplier Brand Solutions PVT LTDDokument2 SeitenLetter of Intent Date: 18-Feb-2019 Mr. Ravi Mishra,: For Multiplier Brand Solutions PVT LTDRavi MishraNoch keine Bewertungen