Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Browse& Retention POLICY
Hochgeladen von
Kanan NarayanaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Browse& Retention POLICY
Hochgeladen von
Kanan NarayanaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
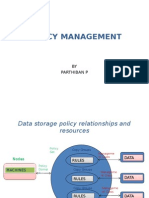
Determining Browse and Retention Policies (Index Policies)
When Worker starts a backup, it creates entries for the saved files in the online indexes . NetWorker maintains two types of indexes: a file index and a media index. The file index stores information about files backed up by NetWorker, and the media index maps the saved files to the backup volumes. NetWorker maintains one file index per client and one media index per NetWorker server. NetWorker uses the indexes as databases to locate the files that are marked for recovery. Each entry in the file index typically includes this information for a backed-up file: filename, number of blocks, access permissions, number of links, owner, group, size, last modified time, and backup time. The file index changes with each backup, as entries for the newly backed up files are inserted. As long as an entry for a file remains in the file index and the backup volume is not damaged, you can recover the file using the NetWorker Recover window. The media index maps each file to the backup volume or volumes where it is stored. NetWorker uses the media index to tell you or the jukebox which backup volume to mount during a recover. The media index is usually much smaller than the file index because each volume contains many saved files. The size of an index is proportional to the number of entries it contains. NetWorker determines which volume to mount for recovering a file by mapping the saved files to their backup volumes. In the NetWorker Policies, Indexes, and Volume Management windows, you create policies for automatic index management, monitor the contents of the indexes, select entries for removal, and mark backup volumes as recyclable. NetWorker uses browse and retention policies to manage and reduce the size of the online indexes:
The browse policy determines how long entries for your files remain in the online file index and thus browsable in the Recover window. Entries older than the browse policy are automatically removed from the online file index. The retention policy determines how long entries are retained in the media index and thus are recoverable. Entries older than the retention policy are marked as recyclable in the media index.
NetWorker performs four actions on both kinds of indexes: inserting entries, browsing, removing entries, and reclaiming space.
Inserting entries in the file index occurs during a backup. If the index has no free space, NetWorker acquires more space from the filesystem to hold the new entries. Browsing is looking through the index for information about your saved files or the contents of your backup volumes; thus, it neither increases nor decreases the size of an index. o The file index is browsed when you use the NetWorker Recover window to locate a file, or when you use the Indexes window to browse the save sets that contain the files you see in the Recover window.
The media index is browsed when you use the Volume Management window to view the save sets on the backup volume. Removing entries frees space in the index. NetWorker uses the free space to insert new entries. The browse and retention policies determine when entries should be removed from the index. You can also remove entries manually by selecting Remove oldest cycle in the Indexes window or by selecting Remove from the Volume pull-down menu in the Volume Management window. Reclaiming space returns empty space to the filesystem. The empty space is created when entries are removed from the index; you remove it by using the Reclaim space button in the Indexes wind
Comment - Any user defined description of this client or other explanatory remarks. Backup type - This attribute specifies the client backup type. Virtual client - This attribute indicates whether the client is a virtual machine. Physical host - This attribute specifies the physical hostname, if this resource is for a virtual client. The hostname does not need to be fully-qualified, and must be less than 64 bytes. All clients sharing the same physical host must use the identical name (don't mix name formats such as short, FQDN or IP address). Browse policy - The index policy this client will use to control how long entries are kept in the on-line file index. The choices are defined by the set of existing management policies. Retention policy - The index policy this client will use to control how long entries are kept in
the save set index. The choices are defined by the set of existing index policies. File inactivity threshold - The number of days a file has not been accessed before it is counted as inactive. A value of zero indicates that no inactivity statistics will be collected for this group. File inactivity alert threshold - Percentage of space occupied by inactive files, exceeding which will generate a notification. A value of zero indicates that no alert will be sent for this group. Scheduled backup - This attribute indicates if this client is enabled for scheduled backup Directive - Directives tell the client how to backup certain files. The choices are defined by the set of existing directives. Save set - A list of the save sets to be backed up for this client with this schedule. Group - The groups this client is part of for automatic backups. The choices are defined by the set of existing groups. Schedule - The schedule this client will use for backups. The choices are defined by the set of existing schedules. Backup renamed directories - This attribute enables the support of renamed directories during scheduled backups. The save program performs a lookup in the client file index to determine whether a directory has been renamed. If a directory has been renamed, all of the files and subdirectories under the directory will be backed up.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Deploying Secure Containers for Training and DevelopmentVon EverandDeploying Secure Containers for Training and DevelopmentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1. Introducing Tivoli Storage Manager: Server Server ProgramDokument24 SeitenChapter 1. Introducing Tivoli Storage Manager: Server Server Programjeetmajum007Noch keine Bewertungen
- MICROSOFT AZURE ADMINISTRATOR EXAM PREP(AZ-104) Part-3: AZ 104 EXAM STUDY GUIDEVon EverandMICROSOFT AZURE ADMINISTRATOR EXAM PREP(AZ-104) Part-3: AZ 104 EXAM STUDY GUIDENoch keine Bewertungen
- Commcell Logical Architecture: Logical Management of Production DataDokument6 SeitenCommcell Logical Architecture: Logical Management of Production DataRishabh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Recovery Appliance Handbook: An Insider’S InsightVon EverandOracle Recovery Appliance Handbook: An Insider’S InsightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step-By-Step Guide For File Server Resource Manager in Windows Server 2008Dokument44 SeitenStep-By-Step Guide For File Server Resource Manager in Windows Server 2008Awais Mirza100% (4)
- Chapter 13. Managing Data For Client Nodes: Validating A Node's DataDokument11 SeitenChapter 13. Managing Data For Client Nodes: Validating A Node's Datajeetmajum007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Visual SourceSafe 2005 Software Configuration Management in PracticeVon EverandVisual SourceSafe 2005 Software Configuration Management in PracticeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backup Recovery Best PracticesDokument44 SeitenBackup Recovery Best PracticesairjajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cache Backup and RestoreDokument32 SeitenCache Backup and RestoreMike PappasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active Directory Security Groups PDFDokument33 SeitenActive Directory Security Groups PDFRise UpNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSM Copy GroupDokument14 SeitenTSM Copy GroupKiran Kumar PeteruNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenText Archive and Storage Services 9.6.x and 9.7.x Retention HandlingDokument17 SeitenOpenText Archive and Storage Services 9.6.x and 9.7.x Retention HandlingTatra StarsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Data ArchivingDokument30 SeitenIntroduction To Data Archivingshambhu guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- File Integrity MonitoringDokument33 SeitenFile Integrity MonitoringNavaneeth KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Securing Windows 2000 Active DirectoryDokument6 SeitenSecuring Windows 2000 Active DirectoryEmraan KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DotnetDokument2 SeitenDotnetRamya Sasikala KNoch keine Bewertungen
- AD - Troubleshooting IssuesDokument104 SeitenAD - Troubleshooting IssuesasaravkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft System Administration - Windows Server 2003Dokument38 SeitenMicrosoft System Administration - Windows Server 2003Lacus ClyneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 POS 355 Tokla Xen Protection SchemeDokument7 SeitenWeek 2 POS 355 Tokla Xen Protection SchemeTokla XenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Websense Backup UtilityDokument3 SeitenWebsense Backup UtilityFabrizio RosinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Documentum Interview QuestionsDokument2 SeitenDocumentum Interview QuestionsSunandha V100% (1)
- 1.1 Organizational ProfileDokument31 Seiten1.1 Organizational ProfileAmir AmirthalingamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module3 Azure AdministrationDokument29 SeitenModule3 Azure AdministrationNithin krishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Native Cloud StorageDokument4 SeitenNative Cloud StorageDivya GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backup PolicyDokument2 SeitenBackup PolicyEdwin SemiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Azure Resource Group Management ModelDokument1 SeiteWhat Is Azure Resource Group Management ModelmicuNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Data ArchivingDokument29 SeitenSAP Data Archivinggowthamigamidi50% (2)
- Glossary 33Dokument23 SeitenGlossary 33vijay konduruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle Core DBA Interview QuestionsDokument8 SeitenOracle Core DBA Interview QuestionskarthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2275b - 07 (Compatibility Mode)Dokument53 Seiten2275b - 07 (Compatibility Mode)Hisham Al HalabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RmanDokument47 SeitenRmannewscop1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Backup Controls It6Dokument17 SeitenBackup Controls It6Kim JennieNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Restore Deleted User Accounts and Their Group Memberships in Active DirectoryDokument66 SeitenHow To Restore Deleted User Accounts and Their Group Memberships in Active DirectorykhyserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nexus Notes Session-01Dokument9 SeitenNexus Notes Session-01SUDHAN RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment of DbmsDokument10 SeitenAssignment of DbmsMOHD KASHIFNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Data ArchivingDokument12 SeitenIntroduction To Data ArchivingAmit GuglaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batch Processing in The Client:: OCLC Connexion Client GuidesDokument11 SeitenBatch Processing in The Client:: OCLC Connexion Client Guideskoushikghosh_pkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Contingency Planning and Disaster Recovery Best Practices Guide 7.2.xDokument10 SeitenContingency Planning and Disaster Recovery Best Practices Guide 7.2.xKamran BhattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Limitation of DFS (Contd.)Dokument2 SeitenLimitation of DFS (Contd.)Nitin DixitNoch keine Bewertungen
- File StructureDokument25 SeitenFile StructureSuriyakalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ClearCase Basics - CompleteDokument58 SeitenClearCase Basics - Completesxsund6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5. Verifying The Initial Configuration: Before Backing Up Remote ClientsDokument4 SeitenChapter 5. Verifying The Initial Configuration: Before Backing Up Remote Clientsjeetmajum007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Database Management System: Backup ControlsDokument17 SeitenDatabase Management System: Backup ControlsKim JennieNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReadDokument2 SeitenReadsaugata4589Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 8Dokument7 SeitenWeek 8Fakhri HafyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04-RMAN ConceptsDokument16 Seiten04-RMAN ConceptsFrances PatrickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 9Dokument51 SeitenUnit 9hesquiveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 3 - Oracle 8: Backup and Recovery (Exam # 1Z0-015) : Study Guide byDokument31 SeitenTest 3 - Oracle 8: Backup and Recovery (Exam # 1Z0-015) : Study Guide bysairam1980Noch keine Bewertungen
- How To Create, Copy, and Move, Resources in The KM Repository Using KM APIDokument11 SeitenHow To Create, Copy, and Move, Resources in The KM Repository Using KM APIMaximiliano MojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Backup All Email On Lotus NotesDokument23 SeitenHow To Backup All Email On Lotus NotesSrk KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Database NotesDokument12 SeitenChapter 1 - Introduction To Database NotesDibyeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backup Types and Methods in NetbackupDokument9 SeitenBackup Types and Methods in NetbackupSrinivas KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TSM Journal BackupDokument4 SeitenTSM Journal BackupsruthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Designing A Group Policy InfrastructureDokument49 Seiten3 Designing A Group Policy InfrastructureAlexandreAntunesNoch keine Bewertungen
- c9d3 4540 b6cb 9950ff4331ea - handout21030RestoringYourVaultHandoutDokument5 Seitenc9d3 4540 b6cb 9950ff4331ea - handout21030RestoringYourVaultHandoutdavinci1234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle - Content Writing - Chapter 1Dokument5 SeitenOracle - Content Writing - Chapter 1DolaDamaKrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Backup and RecoveryDokument6 SeitenBackup and RecoveryFaizan RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EV Data SheetDokument6 SeitenEV Data SheetTamer AdelNoch keine Bewertungen
- iPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsVon EverandiPhone 14 Guide for Seniors: Unlocking Seamless Simplicity for the Golden Generation with Step-by-Step ScreenshotsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Optimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesVon EverandOptimizing DAX: Improving DAX performance in Microsoft Power BI and Analysis ServicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Von EverandiPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Ultimate Snowflake Architecture for Cloud Data Warehousing: Architect, Manage, Secure, and Optimize Your Data Infrastructure Using Snowflake for Actionable Insights and Informed Decisions (English Edition)Von EverandUltimate Snowflake Architecture for Cloud Data Warehousing: Architect, Manage, Secure, and Optimize Your Data Infrastructure Using Snowflake for Actionable Insights and Informed Decisions (English Edition)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Linux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepVon EverandLinux: The Ultimate Beginner's Guide to Learn Linux Operating System, Command Line and Linux Programming Step by StepBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (9)
- RHCSA Exam Pass: Red Hat Certified System Administrator Study GuideVon EverandRHCSA Exam Pass: Red Hat Certified System Administrator Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleVon EverandGrokking Algorithms: An illustrated guide for programmers and other curious peopleBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (16)
- Dark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersVon EverandDark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Data Smart: Using Data Science to Transform Information into InsightVon EverandData Smart: Using Data Science to Transform Information into InsightBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- IPHONE 15 Pro Max: A Step by Step Comprehensive Guide, Tips, Tricks, With New Features For Seniors and Beginners.Von EverandIPHONE 15 Pro Max: A Step by Step Comprehensive Guide, Tips, Tricks, With New Features For Seniors and Beginners.Noch keine Bewertungen
- ITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideVon EverandITIL 4 : Drive Stakeholder Value: Reference and study guideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating iOS apps with Xcode: Learn how to develop your own app (English Edition)Von EverandCreating iOS apps with Xcode: Learn how to develop your own app (English Edition)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionVon EverandKali Linux - An Ethical Hacker's Cookbook - Second Edition: Practical recipes that combine strategies, attacks, and tools for advanced penetration testing, 2nd EditionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Dark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersVon EverandDark Data: Why What You Don’t Know MattersBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- The Future of Competitive Strategy: Unleashing the Power of Data and Digital Ecosystems (Management on the Cutting Edge)Von EverandThe Future of Competitive Strategy: Unleashing the Power of Data and Digital Ecosystems (Management on the Cutting Edge)Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)































































![iPhone Unlocked for the Non-Tech Savvy: Color Images & Illustrated Instructions to Simplify the Smartphone Use for Beginners & Seniors [COLOR EDITION]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/audiobook_square_badge/728318688/198x198/f3385cbfef/1715524978?v=1)



















