Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Dilatation and Curettage
Hochgeladen von
mervin342Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dilatation and Curettage
Hochgeladen von
mervin342Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Dilatation and Curettage
Dilation (dilatation) and curettage literally refers to the dilation (opening) of the cervix and surgical removal of the contents of the uterus. It is a therapeutic gynecological procedure as well as a rarely used method of first trimester abortion. It is commonly referred to as a D&C. D&C normally refers to a procedure involving a curette, also called sharp curettage. However, some sources use the term D&C to refer more generally to any procedure that involves the processes of dilation and removal of uterine contents, which includes the more common suction curettage procedures of manual and electric vacuum aspiration. Procedure The first step in a D&C is to dilate the cervix, usually done a few hours before the surgery. The woman is usually put under general anesthesia before the procedure begins. A curette, a metal rod with a handle on one end and a sharp loop on the other, is inserted into the uterus through the dilated cervix. The curette is used to gently scrape the lining of the uterus and remove the tissue in the uterus. This tissue is examined for completeness (in the case of abortion or miscarriage treatment) or pathologically for abnormalities (in the case of treatment for abnormal bleeding). Clinical uses D&Cs are commonly performed to resolve abnormal uterine bleeding (too much, too often or too heavy a menstrual flow); to remove the excess uterine lining in women who have conditions such as PCOS (which cause a prolonged buildup of tissue with no natural period to remove it);[citation needed] to remove tissue in the uterus that may be causing abnormal vaginal bleeding; to remove retained tissue (also known as retained POC or retained products of conception) in the case of an incomplete miscarriage; and historically, as a method of abortion that is now uncommon. Abortion Because medical and non-invasive methods of abortion now exist, and because D&C requires heavy sedation or general anesthesia and has higher risks of complication, the procedure has been declining as a method of abortion. The World Health Organization recommends D&C as a method of abortion only when manual vacuum aspiration is unavailable. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, D&C only accounted for 2.4% of abortions in the United States in the year 2002, down from 23.4% in 1972.
Complications If the procedure is performed too roughly, scar tissue may form and seal the uterus shut (Asherman's syndrome), resulting in infertility. Another consequence of excessively forceful technique is uterine perforation. Although normally no treatment is required for uterine perforation, a laparoscopy may be done to verify that bleeding has stopped on its own. Infection of the uterus or fallopian tubes is also a possible complication, especially if the woman has an untreated sexually transmitted infection. Having two or more sharp curettage procedures may increase the risk of complications in future pregnancies, such as ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, and placenta previa.
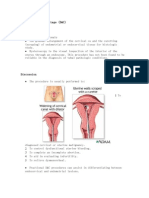
Normal Anatomy - Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
The uterus is located inside of the abdomen, and is the site of fetal development during pregnancy. The lower and narrow end of the uterus forms the cervix. The cervix opens into the vagina.
Indications - Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
A D&C or dilatation and curettage is a procedure to scrape and collect the tissue (endometrium) from inside the uterus. D&C or uterine scraping may be done to: diagnose conditions using the tissue samples collected (biopsies) treat irregular bleeding remove fetal or placental tissue ( used for some elective or therapeutic abortions and to remove any remaining tissue after a spontaneous abortion (miscarriage)) D&C or uterine scraping may be recommended for: bleeding between periods heavy menstrual bleeding bleeding after intercourse investigation of infertility uterine fibroids endometrial polyps uterine cancer (early diagnosis) cervical cancer (early diagnosis) thickening of the uterus (endometrial hyperplasia ) an embedded IUD (intrauterine device) therapeutic or elective abortion miscarriage
Procedure - Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
The procedure may be performed in the hospital or in a clinic using general or local anesthesia. The vaginal canal is held open by a speculum and the opening to the uterus (cervix) is anesthetized (not always). The cervical canal is widened (dilated) using a metal rod and a curette (a metal loop on the end of a long thin handle) is then passed through the canal into the uterine cavity. The inner layer of the uterus (endometrium) is scraped away and the tissue is collected for examination.
Aftercare - Dilation and Curettage (D&C)
Uterine scraping (D&C) has relatively few risks, can provide relief from bleeding, and can help diagnose problems including infection, cancer, infertility and other disease. Normal activities may be resumed as soon as the patient feels well, even the same day. There may be vaginal bleeding, as well as pelvic cramps and back pain for a few days after the procedure. Pain can usually be managed well with medications. Tampon use is not recommended for a few weeks and sexual intercourse is not recommended for a few days.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- DNC 2Dokument6 SeitenDNC 2Maria VisitacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dilation and CurettageDokument4 SeitenDilation and CurettageMary Grace MasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dilation and CurettageDokument2 SeitenDilation and CurettageElisse GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incomplete Abortion 1Dokument40 SeitenIncomplete Abortion 1Denise FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dilation and Curettage Janelle ReforDokument4 SeitenDilation and Curettage Janelle ReforCjay HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dilation and Curettage PreparationDokument2 SeitenDilation and Curettage PreparationKaren ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal Problems With PowerDokument2 SeitenMaternal Problems With PowerAlex CvgNoch keine Bewertungen
- O o o o o O: Hydatidiform MoleDokument5 SeitenO o o o o O: Hydatidiform MoleArniefah RegaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 1: Camposano, Lynn Cielo, Divina Gracia Edem, Katrine Tricia Ibalin, Jasmin Rodriguez, April RoseDokument66 SeitenGroup 1: Camposano, Lynn Cielo, Divina Gracia Edem, Katrine Tricia Ibalin, Jasmin Rodriguez, April RoseDivina Gracia Vibal Cielo100% (1)
- Uterine Bleeding-A Case StudyDokument4 SeitenUterine Bleeding-A Case StudyRoanne Lagua0% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta FullDokument10 SeitenAbruptio Placenta FullChester ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incompetent Cervix Case Analysis Subgroup 2Dokument44 SeitenIncompetent Cervix Case Analysis Subgroup 2bunso padillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HMOLEDokument34 SeitenHMOLEZuellen Mae Garapan BedañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - Incomplete Abortion Related To APSDokument8 SeitenCase Study - Incomplete Abortion Related To APSRomeo ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abruptio Placenta Mini Case StudyDokument20 SeitenAbruptio Placenta Mini Case StudyAira AlaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment in PregnancyDokument15 SeitenAssessment in PregnancyAna75% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Myoma and EndometriosisDokument15 SeitenPathophysiology of Myoma and EndometriosisEarle Jimenez Niervo RNNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study H MOLEDokument11 SeitenCase Study H MOLEHomework PingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cervical IncompetenceDokument30 SeitenCervical IncompetenceSignor ArasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentDokument4 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentTed Cipriano VistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GTD Case StudyDokument9 SeitenGTD Case StudyZnarf Izlah Sadanreb100% (1)
- Introduction HmoleDokument32 SeitenIntroduction HmoleBrian Montales BaggayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydatidiform Mole/ Molar Pregnancy: College of Health SciencesDokument11 SeitenHydatidiform Mole/ Molar Pregnancy: College of Health SciencesAngelu Gabrielle CastroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molar Pregnancy: November 2018 Jis Dungca, Delos Santos, CrisostomoDokument99 SeitenMolar Pregnancy: November 2018 Jis Dungca, Delos Santos, CrisostomoDarnell DelgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abruptio PlacentaDokument8 SeitenAbruptio PlacentaNutz TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Pres AutosavedDokument21 SeitenCase Pres AutosavedJaysellePuguonTabijeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leiomyoma UteriDokument81 SeitenLeiomyoma UteriLea Rose Dictaran Aronza100% (2)
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDokument4 SeitenBenign Prostatic Hyperplasiaエド パジャロンNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discharge PlanDokument4 SeitenDischarge PlanPaul Loujin LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Missed Miscarriage Dilation and CurettageDokument48 SeitenCase Study Missed Miscarriage Dilation and CurettageEsther Ellise AbundoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partial Mole or Complete Mole: Pathophysiology of Molar PregnancyDokument1 SeitePartial Mole or Complete Mole: Pathophysiology of Molar PregnancyKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cord ProlapseDokument22 SeitenCord ProlapseJoyjet Evangelista-murilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- H MoleDokument7 SeitenH MoleRaymond Christopher LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- H Mole Case StudyDokument7 SeitenH Mole Case StudyReznak0% (1)
- NCP Drug Study Group 1Dokument21 SeitenNCP Drug Study Group 1Cassandra Grace Muerong Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Placenta Abruptio - Topic OverviewDokument8 SeitenPlacenta Abruptio - Topic OverviewLei AbellarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uterine AtonyDokument33 SeitenUterine AtonyNonie 'Erni' HastiriniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Placenta PreviaDokument87 SeitenPlacenta PreviaKaye Cueto100% (1)
- CS Case PresentationDokument16 SeitenCS Case PresentationjisooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cervical InsufficiencyDokument39 SeitenCervical InsufficiencyMaczimilianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uterine ProlapseDokument21 SeitenUterine ProlapseFau Fau DheoboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of OvaryDokument2 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of OvaryFrancez Anne GuanzonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim Examination MaternalDokument23 SeitenPrelim Examination MaternalAaron ConstantinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care of Client With HypospadiaDokument21 SeitenNursing Care of Client With HypospadiaancoursNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endometriosis PresentationDokument58 SeitenEndometriosis PresentationBRI KUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Incompetent NCPDokument1 SeiteIncompetent NCPMina RacadioNoch keine Bewertungen
- RLE 109 Group 4 Case Analysis in MastitisDokument20 SeitenRLE 109 Group 4 Case Analysis in MastitisEugene MananganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydatifor M Mole: By: Namita Arya Asst. Lecturer PDMSNCDokument27 SeitenHydatifor M Mole: By: Namita Arya Asst. Lecturer PDMSNCnamitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imperforate Anus: Preoperative CareDokument2 SeitenImperforate Anus: Preoperative CareLalisaM ActivityNoch keine Bewertungen
- And Vaginal Bleeding (In Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy)Dokument9 SeitenAnd Vaginal Bleeding (In Ruptured Ectopic Pregnancy)Clareen JuanicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uterine RuptureDokument19 SeitenUterine RuptureAna Denise Quinajon0% (1)
- Case Study Castillo H MoleDokument52 SeitenCase Study Castillo H MoleGodfrey Bag-ao100% (1)
- Indirect Inguinal HerniaDokument54 SeitenIndirect Inguinal HerniaYlamher Bufi Imperial100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta: Prepared By: Claire Alvarez Ongchua, RNDokument42 SeitenAbruptio Placenta: Prepared By: Claire Alvarez Ongchua, RNclaireaongchua1275100% (2)
- PLacenta PreviaDokument10 SeitenPLacenta Previaeyestrain_ajpn5001Noch keine Bewertungen
- 5b - NCPDokument7 Seiten5b - NCPKelly Camero ÜNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cesarean Section and Surgical InstrumentsDokument35 SeitenCesarean Section and Surgical InstrumentsHarry Cloth100% (1)
- Dilation and CurettageDokument8 SeitenDilation and CurettageMelody B. Miguel100% (1)
- What Is Dilation and Curettage (D&C) ?Dokument3 SeitenWhat Is Dilation and Curettage (D&C) ?jaroh_20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dilation and Curettage (D&C)Dokument13 SeitenDilation and Curettage (D&C)KADIZA ARABINoch keine Bewertungen
- Valzlegit Nude Picture - Google SearchDokument1 SeiteValzlegit Nude Picture - Google Searchamberrihanna38Noch keine Bewertungen
- The First Cry of The Revolution AugustDokument17 SeitenThe First Cry of The Revolution AugustElern AsombradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feminist Film TheoryDokument3 SeitenFeminist Film Theoryapi-270166735Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genesis - RipplesDokument2 SeitenGenesis - Ripplesaggram840% (1)
- A Beginner Guide To Dominating HerDokument4 SeitenA Beginner Guide To Dominating HerRohith Kumar Venna100% (2)
- August 7, 2011Dokument12 SeitenAugust 7, 2011Christ the KingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Reading Assignment News Item Text: LecturerDokument4 SeitenAdvanced Reading Assignment News Item Text: LecturerShabira FirdelinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 556 l6 Breach of TrustDokument18 Seiten556 l6 Breach of TrustAttyynHazwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysing Gender in "Araby"Dokument2 SeitenAnalysing Gender in "Araby"james joyceNoch keine Bewertungen
- United States Ex Rel. Willie Richardson v. Daniel McMann Warden, Clinton Prison, Dannemora, New York, 408 F.2d 48, 2d Cir. (1969)Dokument8 SeitenUnited States Ex Rel. Willie Richardson v. Daniel McMann Warden, Clinton Prison, Dannemora, New York, 408 F.2d 48, 2d Cir. (1969)Scribd Government DocsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ulek Mayang ScriptDokument3 SeitenUlek Mayang ScriptMartinLukeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes For Prelim Theo 12Dokument61 SeitenNotes For Prelim Theo 12Paolo VariasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conflict in Indochina EssayDokument2 SeitenConflict in Indochina Essayisabella RepoleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arca vs. JavierDokument1 SeiteArca vs. Javierjm bernalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cebu Country Club, Inc. vs. ElizagaqueDokument2 SeitenCebu Country Club, Inc. vs. ElizagaquejaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEOPLE VS. RIBADAJO 142 SCRA 637 (1986) FactsDokument2 SeitenPEOPLE VS. RIBADAJO 142 SCRA 637 (1986) FactsSyed Almendras IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Tele BRANCHES 01.06.2021Dokument23 SeitenTele BRANCHES 01.06.2021Abhishek BarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIR vs. DOJ DigestDokument2 SeitenCIR vs. DOJ DigestKing BadongNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceDokument4 SeitenA Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in ScienceSheyn Benito81% (31)
- Filipinas Investment V Sps RidadDokument2 SeitenFilipinas Investment V Sps Ridadk santosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Black Power Movement Through TheDokument29 SeitenThe Black Power Movement Through Theeliyahy100% (3)
- West Yorkshire Police Chief Faces Outside Force InvestigationDokument5 SeitenWest Yorkshire Police Chief Faces Outside Force InvestigationPoliceCorruptionNoch keine Bewertungen
- As We Gather at Your TableDokument2 SeitenAs We Gather at Your TableRegine GarabilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prayer: According To SunnahDokument32 SeitenPrayer: According To SunnahSZHUSSAINI100% (3)
- Easystart, Marcel and The Mona Lisa AWDokument2 SeitenEasystart, Marcel and The Mona Lisa AWVlad-NicolaeAchimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Person: A Filipino Christian Perspective: "Madaling Maging TAO, Mahirap MAGPAKATAO."Dokument31 SeitenThe Human Person: A Filipino Christian Perspective: "Madaling Maging TAO, Mahirap MAGPAKATAO."IvyJoyceNoch keine Bewertungen
- EF4e Beg Quicktest 12Dokument3 SeitenEF4e Beg Quicktest 12irene100% (1)
- Sting OperationsDokument54 SeitenSting Operationsm_vishnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asufrin - Jr. - v. - San - Miguel - Corp PDFDokument6 SeitenAsufrin - Jr. - v. - San - Miguel - Corp PDFMonica FerilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Chapter 4Dokument19 SeitenFinal Chapter 4Jhanelyn V. InopiaNoch keine Bewertungen