Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Euro Chapter 19 Study Guide
Hochgeladen von
Lili PengOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Euro Chapter 19 Study Guide
Hochgeladen von
Lili PengCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 19 Study Guide-Expansion of Europe in 18th c.
AP European History Agrarian economy
Name ________________________________
Famine foods Food substitutes when there were bad harvests chestnuts, dandelions, grass People sick influenze, small pox, starvation Open-field system Divdied land into large fields, each farmed afield as a community w/ the same pattern of plowing, sowing, harvesting Fallow fields Community planted every day, nitrogen in soil depleted Manure was limited, so allowed a field to lie fallow, alternated w/ year of cropping Three-year rotations: wheat, oats, fallow Common land Open meadows for hay and natural pasture for horses and oxen and pigs Allowed period for gleaning of grain Selfs in Eastern Europe peasants in Western Europe life is hard Agricultural revolution Coming of the French Revolution Mid17th century and on Secret in eliminating fallow was alternating grain w/ nitrogen storing crops Crop rotation New ways of organization Flanders 10 year rolation more scientific farming Effets: more feed for animals -> better diets -> more fertilizer -> better drops Enclosure Enclosed individual shares of the common Dutch low countries enclosed fields, continuous rotations, mauring, wide variety of crops helped make it more specialized and commuercialized Amsterdam grew Hard on poor b/c they eneded the common land Cornelius Vermuyden Drainage projects in Yorkshire and Cambridgeshire convered swamps to farm land in Dutch manner Charles Townsend found the secret was just to rotate the crops. This was done by planting a different crop each year. While wheat or corn would wear out the land, turnips or clover would restore the field turnip Townsend Jethro Tull Wanted touse horses for plowing; sowing seed w/ equipment; selective breeding of livestock Proletarianization Enclosure movement eliminated common rights and reduced access of poor to the land: 1) market oriented estate agriculture rose; 2) emergence of landless rural proletarial English leasing land to middle size farmers who had landless labrorers who lost common rights and were dependent on cash wages Large numbers of small peasant farmers in landless rural wage earners Grim reapers of demographic crisis Famine, epidemic disease, war
Economy based on the land agriculture In 16/17th centuries harvests were poor
18th century population grew rapidly b/c of fewer deaths
Asian brown rat Bubonic plague disappeared After 1600 asian rat drove out the black competitor and didnt carry fleas tat wanted blood Inoculation against small box, improvements in sewage, drainage of swamps, transportation, new foods from South America Cottage industry Poor needed to supplement their earnings started manufacturing w/ hand tools and work sheds, worked for lower wages Overwhelming artisans efforts to control industrial production Rural industrial development w/ wage works and hand tools that preceded to large scale factory industry Putting out system Key features of the 18th century rural industry: merchant capitalist and rural worker Merchant put out raw matierals to cottage workers who processed it and returned the finished product to merchant First in England spinning and weaving fo woolen cloth Louis XIV Colbert revived guilds but rural industries were then given free reign Germany and Low Countries gradually reduced power of guilds Competitive advantages labor plenty and poor would work for low wages; merchants could experiment and develop new methods Merchant capitalists Merchants needed capital held in the form of goods wanted to make profits and increase capital in businesses Textiles
Making of linen, woolen, cotton Rural worker worked in cottage, w/ looms and spinning wheels, work for everyone in the family work of four or five spinners to keep one weaver emplyed
spinster Widows and unmarried woman who spun for their living recruited by the wives Raw wool from merchant -> went to other cottages and picked up the thread and pay for spinning -> weaver -> merchant holy Monday Workers paid on Saturday, would relax for a few days Inactivity on Monday Cottage workers tended to work in spurts Atlantic economy Growth of world trade Great Brain formed from union of Eng and Scotland in 1707 Trade between NW European Netherlands, France, etc Mercantilism System of econ regulations to increase the power of the state balance of trade in order to increase gold holdings British Navigation Acts (do not answer a form of economic warfare) Cromwell 1651 extended by Charles II Colonies only allowed to buy Brit goods, and merchants only allowed to trade on Brit ships w/ Brit crews Biggest competitors France and Dutch Took Dutch colony of New Amsterdam Peace of Utrecht Louis XIV forced to give u pNewfoundland, Nova Scotia, and Hudson Bay to Britian Spain had to give Brirt control fo the West African slave trade asiento Treaty of Paris
Ended the Seven Years War France lost all possessions on the mainland of North America Canada and all French territory west of MI River = Brit; Louisiana = Spain; gave Brit most of holdings in India 1763
Atlantic Slave Trade Forced millions of Africans into slvary large scale production of commodities for sale b/c of the labor 4/5 of all produced in Americas like sugar, coffee, tobacco, rice Britain leader Wars between Africans to obtain salable captives, more guns ex Dahomey, Congo was undermined by search for slves from the monarchy England slaves mostly used as servants 1807 Parliament abolished Brit slave trade Philip V of Spain Spain defended themselves form Brit attacts, got Louisana from Spain Remorning ministers asserted royal authority, overhaulding state finances, and strengthening defense Creole elite People of Spanish blood born in America Silver mining encourage food production for large mining camps and gave Creols means to purchase more European goods controlled must of the land and used Native Americans Debt peonage Slavery and periodic forced labor gave way to debt peonage Planter would keep estates Indians in debt bondage by periodically advancing food, shelter, little money form of serfdom Mestizos Racially mixed Spanish men and Indian women Adam Smith, Wealth of Nations, invisible hand Basis for modern economics Free competition was mbetter than merchanilism would protect consumers from price gounging and give all a fair right Gov should limit itself to three duties: defense against invasion, maintain civil order, and sponsor certain public works Invisible hand of free competition Economic liberalism Smits work unregulated capitalism
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Economic SystemDokument8 SeitenEconomic SystemAparupa RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 6 History Peasants and FarmersDokument2 SeitenChapter - 6 History Peasants and Farmersbharath pachipentaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Economy During French Regime Part 2 Page 161Dokument32 Seiten15 Economy During French Regime Part 2 Page 161api-247532088Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Making of A Global WorldDokument21 SeitenThe Making of A Global WorldKeerthana AdarshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colonization in West IndiesDokument48 SeitenColonization in West IndiesYaashiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - The Colonies Come of AgeDokument27 SeitenChapter 3 - The Colonies Come of Ageapi-233545455Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 History Notes Chapter 3 - The Making of A Global WorldDokument8 SeitenCBSE Class 10 History Notes Chapter 3 - The Making of A Global WorldGitika DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- European Rule (1760AD - 1947AD)Dokument12 SeitenEuropean Rule (1760AD - 1947AD)Oyon Nur newazNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Short History of English AgricultureVon EverandA Short History of English AgricultureNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Making of A Global WorldDokument26 SeitenThe Making of A Global Worldatanush619Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Colonial Life COVIDDokument24 Seiten3 Colonial Life COVIDAllison HoyleNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMPERIALISM TITLEDokument47 SeitenIMPERIALISM TITLEKim HughesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Chapter 4 and 5Dokument46 Seiten2021 Chapter 4 and 5fo25804Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Making of A Global World Part 2Dokument18 SeitenThe Making of A Global World Part 2amulyajadhav119Noch keine Bewertungen
- Age of Exploration: Spain Claims An EmpireDokument50 SeitenAge of Exploration: Spain Claims An EmpireChristina BarsoumNoch keine Bewertungen
- European ImperialismDokument31 SeitenEuropean Imperialismapi-690086282Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 History PPT Grade 9 Term 1Dokument137 Seiten2020 History PPT Grade 9 Term 1Chloe van der MerweNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Did The World Go From That?Dokument76 SeitenHow Did The World Go From That?saxapilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation of Colonial Rule in Bengal: Was It Inevitable?Dokument53 SeitenFoundation of Colonial Rule in Bengal: Was It Inevitable?Siffat Bin AyubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Willian WordsworthDokument12 SeitenWillian Wordsworthchiara.laiolo00Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conquest and Colonies: Main IdeaDokument13 SeitenConquest and Colonies: Main IdeaLaMarius ThankMelater HuntNoch keine Bewertungen
- Starving the South: How the North Won the Civil WarVon EverandStarving the South: How the North Won the Civil WarBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (12)
- The High Middle Ages: Economic Growth and the Rise of CitiesDokument5 SeitenThe High Middle Ages: Economic Growth and the Rise of CitiesParsel BlehNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 British ColoniesDokument46 Seiten13 British ColoniesSarah SunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation of Colonial Rule in Bengal: Was It Inevitable?Dokument53 SeitenFoundation of Colonial Rule in Bengal: Was It Inevitable?SAM samNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - 38 They Complete The Next NightDokument93 Seiten1 - 38 They Complete The Next Nightapi-264216738Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wk2 - BritishColony and SlaveryDokument28 SeitenWk2 - BritishColony and SlaveryTempleton KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colonial Rule in Bengal: Decline of Mughal Power and Rise of British East India CompanyDokument53 SeitenColonial Rule in Bengal: Decline of Mughal Power and Rise of British East India CompanylerosadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP World History Cheat SheetDokument3 SeitenAP World History Cheat SheetTyler LitwickNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Industrial Revolution Notes 2022Dokument14 SeitenThe Industrial Revolution Notes 2022MichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation of Colonial Rule in Bengal: Was It Inevitable?Dokument53 SeitenFoundation of Colonial Rule in Bengal: Was It Inevitable?SyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Beginnings of African Slavery in The Americas - Middle PassageDokument17 SeitenThe Beginnings of African Slavery in The Americas - Middle Passagejordanf36Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3-History of BritainDokument42 Seiten3-History of BritainDELL 09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Colonization of North America: New England and Southern Colonies/TITLEDokument52 SeitenColonization of North America: New England and Southern Colonies/TITLEmarinusm100% (1)
- Industrial Revolution LectureDokument17 SeitenIndustrial Revolution LecturevikeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imperialism 1Dokument38 SeitenImperialism 1LucasNoch keine Bewertungen
- ImperialismDokument74 SeitenImperialismSajjad QaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 18 OutlineDokument5 SeitenChapter 18 OutlineFerrari94% (16)
- RevolutionDokument17 SeitenRevolutionAneta StejskalovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The French Revolution and NapoleonDokument16 SeitenThe French Revolution and NapoleonQdePatootieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading NotesDokument7 SeitenReading NotesZofia KowalskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AMH2010 Final Exam Study NotesDokument11 SeitenAMH2010 Final Exam Study NotesChristineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Science Class-XDokument22 SeitenSocial Science Class-Xdhdahanuwala100% (1)
- Agricultural Revolution Spreads from Netherlands to EnglandDokument5 SeitenAgricultural Revolution Spreads from Netherlands to EnglandJessica CottaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PresentationDokument24 SeitenPresentationDenisa StaicuNoch keine Bewertungen
- APUSH Key Concept 2.2: European Colonization and ConflictDokument30 SeitenAPUSH Key Concept 2.2: European Colonization and ConflictMoises Nava-LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 7 History RevisionDokument8 SeitenYear 7 History Revisionwildanomar51Noch keine Bewertungen
- Western CanadaDokument25 SeitenWestern Canadaapi-282338132Noch keine Bewertungen
- W5 - Atlantic TradeDokument19 SeitenW5 - Atlantic TradeFirst name Last nameNoch keine Bewertungen
- U.S. History Core Content and Key EventsDokument21 SeitenU.S. History Core Content and Key EventsMuneeb Ullah GandapurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 History Term 3Dokument20 SeitenGrade 10 History Term 3Owethu MkhwanaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agricultural RevolutionDokument23 SeitenAgricultural RevolutionCy MiolataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agricultural Revolution Notes and DrillsDokument6 SeitenAgricultural Revolution Notes and Drillsapi-245769776Noch keine Bewertungen
- Industrial Revolution 1750 1850Dokument25 SeitenIndustrial Revolution 1750 1850Ryan KeeneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fouberg CH 7Dokument4 SeitenFouberg CH 7Lili PengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fouberg CH 8Dokument3 SeitenFouberg CH 8Lili PengNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Scarlet Letter NotesDokument3 SeitenThe Scarlet Letter NotesLili PengNoch keine Bewertungen
- EuroChapter 19 Study GuideDokument3 SeitenEuroChapter 19 Study GuideLili PengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 5Dokument22 SeitenLec 5Abcdefgh EfghabcdNoch keine Bewertungen
- CGL Flame - Proof - MotorsDokument15 SeitenCGL Flame - Proof - MotorspriteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- © 2020 Lippincott Advisor Nursing Care Plans For Medical Diagnoses - Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID 19) PDFDokument7 Seiten© 2020 Lippincott Advisor Nursing Care Plans For Medical Diagnoses - Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID 19) PDFVette Angelikka Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parenteral NutritionDokument78 SeitenParenteral NutritionImen YunieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indra: Detail Pre-Commissioning Procedure For Service Test of Service Water For Unit 040/041/042/043Dokument28 SeitenIndra: Detail Pre-Commissioning Procedure For Service Test of Service Water For Unit 040/041/042/043AnhTuấnPhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50hz Sine PWM Using Tms320f2812 DSPDokument10 Seiten50hz Sine PWM Using Tms320f2812 DSPsivananda11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research of William Wells at HarvardDokument10 SeitenResearch of William Wells at HarvardARGHA MANNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Minimum Fees To Be Taken by CADokument8 SeitenMinimum Fees To Be Taken by CACA Sanjay BhatiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ford 30 V600Dokument7 SeitenFord 30 V60008088338Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan 12 Climate ChangeDokument5 SeitenLesson Plan 12 Climate ChangeRey Bello MalicayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matador - : Medical Advanced Training in An Artificial Distributed EnvironmentDokument25 SeitenMatador - : Medical Advanced Training in An Artificial Distributed EnvironmentNauman ChaudaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACM JournalDokument5 SeitenACM JournalThesisNoch keine Bewertungen
- p2 - Guerrero Ch13Dokument40 Seitenp2 - Guerrero Ch13JerichoPedragosa88% (17)
- John Williams - WikipediaDokument2 SeitenJohn Williams - Wikipedia三木和代Noch keine Bewertungen
- SMChap 018Dokument32 SeitenSMChap 018testbank100% (8)
- Windows Keyboard Shortcuts OverviewDokument3 SeitenWindows Keyboard Shortcuts OverviewShaik Arif100% (1)
- Benefits of Eating OkraDokument4 SeitenBenefits of Eating Okraama931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation of Kuttichira SettlementDokument145 SeitenConservation of Kuttichira SettlementSumayya Kareem100% (1)
- Evolution BrochureDokument4 SeitenEvolution Brochurelucas28031978Noch keine Bewertungen
- UK Commutator Maintenance CatalogueDokument9 SeitenUK Commutator Maintenance CatalogueCarlosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digestive System Song by MR ParrDokument2 SeitenDigestive System Song by MR ParrRanulfo MayolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Culinary Nutrition BasicsDokument28 SeitenCulinary Nutrition BasicsLIDYANoch keine Bewertungen
- B+V ELEVATOR SIDE DOOR Collar Type VS09 A4Dokument19 SeitenB+V ELEVATOR SIDE DOOR Collar Type VS09 A4Игорь ШиренинNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hollywood Game Plan 20 Page Sample PDFDokument20 SeitenHollywood Game Plan 20 Page Sample PDFMichael Wiese Productions0% (1)
- The Patient Self-Determination ActDokument2 SeitenThe Patient Self-Determination Actmarlon marlon JuniorNoch keine Bewertungen
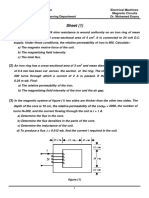
- Sheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMDokument2 SeitenSheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMKhalifa MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Sheet FC SIDokument2 SeitenData Sheet FC SIAndrea AtzeniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ace3 1122.03 GB PDFDokument16 SeitenAce3 1122.03 GB PDFArpit VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IBM Systems Journal PerspectivesDokument24 SeitenIBM Systems Journal PerspectivesSmitha MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- UTC awarded contracts with low competitionDokument2 SeitenUTC awarded contracts with low competitioncefuneslpezNoch keine Bewertungen