Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
What Is A Web Browser
Hochgeladen von
Nomi OnniOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What Is A Web Browser
Hochgeladen von
Nomi OnniCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
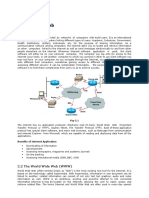
What is a Web Browser?
Browser, short for web browser, is a software application used to enable computers users to locate and access web pages. Browsers translates the basic HTML (Hypertext Mark Up Language) code that allows us to see images, text videos and listen to audios on websites, along with hyperlinks that let us travel to different web pages. The browser gets in contact with the web server and requests for information. The web server receives the information and displays it on the computer. There are different browsers for various things you do on the internet. There's a text based browser. With a text based browser you are only allowed to see text. Graphical material are not displayed. Hyperlinks are accessed by typing it in through the keyboard. An example of a text based browser is LYNX. There's a graphical browser and that allows the user to see all types of multimedia. There are several types of browsers but the one thing they have in common is that they carry out the same function; they transfer hypertext. Here are some familiar common web browsers:
Mozilla FireFox Netscape Navigator Microsoft Internet Explorer
Every browser features a toolbar that allows you to perform various functions like:
Go back to the first page you started on the internet which is called Home. Book your favorite websites Print content you find interesting on web pages Check your web history, like the websites you visited in the past You can go forward and backwards to see the previous sites you viewed
There are two basic ways that you can navigate through the browser:
You can click on links on different web pages. Those links will lead you to other web pages. If you know the URL or the address of the website you can type it in write in the browser's box all the way at the top. There's no need to type in the: http:// part when inserting the address because the browser automatically places it in. Then you have to click enter.
Once you click enter you have to wait for the page to load. While it's loading you will see the browser icon. Usually a little box will appear at the bottom with bars. It's called a status bar. When all the bars are filled you will know that the page has finished loading. So every time you click or a link or enter a URL your browser will request the information from the web server. If your browser returns to the page with a error message the address you typed in could be wrong on you may not be connected to the internet. Web pages can look different in various types of browser. It's always important to download the latest version of your browser. Today most web pages are designed to be viewed in updated browsers. By keeping up with the most up-to-date version of your web browser you will be able to get the best of the web for everything that you need.
Function
The primary purpose of a web browser is to bring information resources to the user ("retrieval" or "fetching"), allow them to view the information ("display", "rendering"), and then access other information ("navigation", "following links"). This process begins when the user inputs a Uniform Resource Locator (URL), for example http://en.wikipedia.org/, into the browser. The prefix of the URL, the Uniform Resource Identifier or URI, determines how the URL will be interpreted. The most commonly used kind of URI starts with http: and identifies a resource to be retrieved over the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).[10] Many browsers also support a variety of other prefixes, such as https: for HTTPS, ftp: for the File Transfer Protocol, and file: for local files. Prefixes that the web browser cannot directly handle are often handed off to another application entirely. For example, mailto: URIs are usually passed to the user's default e-mail application, and news: URIs are passed to the user's default newsgroup reader. In the case of http, https, file, and others, once the resource has been retrieved the web browser will display it. HTML and associated content (image files, formatting information such as CSS, etc.) is passed to the browser's layout engine to be transformed from markup to an interactive document, a process known as "rendering". Aside from HTML, web browsers can generally display any kind of content that can be part of a web page. Most browsers can display images, audio, video, and XML files, and often have plug-ins to support Flash applications and Java applets. Upon encountering a file of an unsupported type or a file that is set up to be downloaded rather than displayed, the browser prompts the user to save the file to disk. Information resources may contain hyperlinks to other information resources. Each link contains the URI of a resource to go to. When a link is clicked, the browser navigates to the resource indicated by the link's target URI, and the process of bringing content to the user begins again.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- UTS-Social Media Reaction PaperDokument2 SeitenUTS-Social Media Reaction PaperLeslieChang100% (1)
- Lab Report 8Dokument4 SeitenLab Report 8Stefan JenkinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vision and MissionDokument5 SeitenVision and MissionMadhu PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1.1 Activity Sheet Activity 1: Name: Date of SubmissionDokument4 SeitenModule 1.1 Activity Sheet Activity 1: Name: Date of SubmissionCHARLHYN GRACE BISNARNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Archimedes ١Dokument4 Seiten5 Archimedes ١Mohammed Yousif AbdualjabbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of ComputerDokument8 SeitenTypes of Computerapi-321074746Noch keine Bewertungen
- Archimedes PrincipleDokument2 SeitenArchimedes PrincipleRitson SolomonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business ProposalDokument2 SeitenBusiness ProposalNazifa100% (1)
- Folk DanceDokument3 SeitenFolk DanceShane Ambaked MagwilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is ConstitutionDokument2 SeitenWhat Is ConstitutionYanxs AlbiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarpDokument8 SeitenCarpRheinlander MusniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Activity 07 Autocad 3d Basics-Arce, KDokument13 SeitenLaboratory Activity 07 Autocad 3d Basics-Arce, KKalvinNoch keine Bewertungen
- DanceDokument2 SeitenDancevacinadNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Generations of ComputerDokument32 SeitenOn Generations of Computerd-fbuser-7880465380% (10)
- History of InternetDokument11 SeitenHistory of InternetusmannasrullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anthropometric MeasurementDokument2 SeitenAnthropometric MeasurementJames ClarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globalization and Its Impact On HealthDokument17 SeitenGlobalization and Its Impact On HealthAbdur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AppendixDokument30 SeitenAppendixDiosa Jamila Angsioco100% (1)
- Web BrowserDokument24 SeitenWeb BrowservanshikarockNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTML CourseDokument192 SeitenHTML CourseAshraf MazenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-11-2017 Lect I Web Page Designing (Refersher Course)Dokument74 Seiten4-11-2017 Lect I Web Page Designing (Refersher Course)shailesh shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Web BrowserDokument9 SeitenWhat Is A Web BrowserInnocent NoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- All About Internet BrowsersDokument6 SeitenAll About Internet BrowsersRaSShNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Hypertext Internet Web Browser Web Pages Multimedia Navigate HyperlinksDokument6 SeitenSystem Hypertext Internet Web Browser Web Pages Multimedia Navigate HyperlinksTanya KohliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information TechnologyDokument119 SeitenInformation TechnologyJessicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Internet Terminology StudentDokument31 SeitenBasic Internet Terminology Studentedwin tacdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Wide Web EditedDokument24 SeitenWorld Wide Web EditedJanice Agbuya TamondongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of InternetDokument15 SeitenFundamentals of Internetgowolo4077Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A BrowserDokument9 SeitenWhat Is A BrowserDdyash DayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEI004 LEC 8 WWW & Web BrowsingDokument32 SeitenGEI004 LEC 8 WWW & Web BrowsingAlvin ViajeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1 Introduction To Web - 231104 - 130108Dokument3 SeitenUnit-1 Introduction To Web - 231104 - 13010842z4bnwc4nNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Wide Web: Pages Are Hypertext Documents Formatted in Hypertext MarkupDokument20 SeitenWorld Wide Web: Pages Are Hypertext Documents Formatted in Hypertext MarkupFred PianistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 World Wide WebDokument25 SeitenUnit 5 World Wide WebDHAIRYAKUMAR MEHTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter (1) Fundamental of Web TechnologyDokument103 SeitenChapter (1) Fundamental of Web TechnologyPhone PyaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To WWWDokument36 SeitenIntroduction To WWWjohnhaile23Noch keine Bewertungen
- World Wide WebDokument1 SeiteWorld Wide WebJAYAVISHNU SNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTML Hypertext Markup LanguageDokument11 SeitenHTML Hypertext Markup LanguagePatriceTherriaultNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relationship Among Websites Webpages and Web BrowsersDokument8 SeitenRelationship Among Websites Webpages and Web Browsershantu malamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relationship Among Websites Webpages and Web BrowsersDokument8 SeitenRelationship Among Websites Webpages and Web Browsershantu malamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 7Dokument80 SeitenModule 7levu91Noch keine Bewertungen
- ALX Week 12Dokument10 SeitenALX Week 12akinnubimichael.maNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multimedia With Internet and Animation: Unit 4Dokument24 SeitenMultimedia With Internet and Animation: Unit 4Tanmay TawteNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Chepter 2Dokument40 Seiten2 Chepter 2pankajusbNoch keine Bewertungen
- M1 Ktunotes - inDokument37 SeitenM1 Ktunotes - insidhuskumar001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Hardware, Software and World Wide WebDokument18 SeitenComputer Hardware, Software and World Wide Webble23-mchirwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No 6: Aim: Getting Acquainted With Internet Connection, Browser, Website, URL, HTTP, WWW, Net BrowsingDokument3 SeitenExperiment No 6: Aim: Getting Acquainted With Internet Connection, Browser, Website, URL, HTTP, WWW, Net BrowsingSatya PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Features of Web BrowserDokument7 SeitenFeatures of Web Browsers.lakshmi narasimhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Wide WebDokument1 SeiteThe World Wide WebJosephine MinichiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- C# MaterilaDokument27 SeitenC# MaterilaRax RavNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is InternetDokument19 SeitenWhat Is InternetShashank SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- BROWSERDokument9 SeitenBROWSERMary Ann EscalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iwt Btech 6th CsDokument57 SeitenIwt Btech 6th CsAnusha DattiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chương 1 Giới thiệuDokument5 SeitenChương 1 Giới thiệuphuckhang33203Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IIIDokument12 SeitenUnit IIIAnuragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web Eng PDFDokument27 SeitenWeb Eng PDFsazzadsakir77Noch keine Bewertungen
- Information Sheet 5.1Dokument17 SeitenInformation Sheet 5.1bernadeth magtibayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Internet BrowsersDokument25 SeitenIntroduction To Internet BrowserssansarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Front End DevelopmentDokument179 SeitenFundamentals of Front End DevelopmentKhansa MueenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Web ServicesDokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Web ServicesMANAN GULATINoch keine Bewertungen
- From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument5 SeitenFrom Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMehar SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCCE RaptorDokument4 SeitenGCCE RaptorSayidina PanjaitanNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Truthland": Chesapeake S Rebuttal To GaslandDokument14 Seiten"Truthland": Chesapeake S Rebuttal To GaslandJames "Chip" NorthrupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Alternator and Generator Are Rated in KVA. Not in KW - 1Dokument2 SeitenWhy Alternator and Generator Are Rated in KVA. Not in KW - 1scribd0% (1)
- Operating Instructions Back Pressure Regulator Series: BPR: Holter RegelarmaturenDokument19 SeitenOperating Instructions Back Pressure Regulator Series: BPR: Holter Regelarmaturenamin100% (2)
- Manual Do Usuario de Automatizadores Deslizantes CE2017 InglesDokument2 SeitenManual Do Usuario de Automatizadores Deslizantes CE2017 InglesTasso ParteliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oil-Less Decal Transfer: Copyfun WhiteDokument1 SeiteOil-Less Decal Transfer: Copyfun WhiteIgor Cece GigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eletrical Motor OffshoreDokument38 SeitenEletrical Motor OffshoreandreisraelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment PlanDokument2 SeitenAssessment Planapi-282348214Noch keine Bewertungen
- National Convention National Convention On On Quality Concepts Quality ConceptsDokument9 SeitenNational Convention National Convention On On Quality Concepts Quality ConceptsMadhusudana ANoch keine Bewertungen
- HC110110007 Data Forwarding ScenarioDokument17 SeitenHC110110007 Data Forwarding ScenariojscansinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipason Product CatalogueDokument72 SeitenIpason Product CatalogueithacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 15462 2004 Modified Rubber BItumen PDFDokument16 SeitenIs 15462 2004 Modified Rubber BItumen PDFrajeshji_000100% (3)
- Practice Questions PneumaticsDokument13 SeitenPractice Questions Pneumaticssamer07hd100% (3)
- Angoca Db2 Cheat Sheet For DevelopmentDokument3 SeitenAngoca Db2 Cheat Sheet For DevelopmentTanveer AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spare Parts List: Hand-Held Gas Saw DS HS80-14"Dokument20 SeitenSpare Parts List: Hand-Held Gas Saw DS HS80-14"mayoo1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Litre Closed SamplersDokument3 Seiten4 Litre Closed Samplerslimhockkin3766Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Lanzar Web Optimized PDFDokument58 Seiten2015 Lanzar Web Optimized PDFrecursowebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naruto - NagareboshiDokument2 SeitenNaruto - NagareboshiOle HansenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pre-Disciplinary and Post-Disciplinary Perspectives: Bob Jessop & Ngai-Ling SumDokument13 SeitenPre-Disciplinary and Post-Disciplinary Perspectives: Bob Jessop & Ngai-Ling SumMc_RivNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cascaded Transformers:: Figure 1.basic 3 Stage Cascaded TransformerDokument3 SeitenCascaded Transformers:: Figure 1.basic 3 Stage Cascaded TransformeryugendraraoknNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Answer For Each Conversation. You Will Hear Each Conversation TwiceDokument4 SeitenBest Answer For Each Conversation. You Will Hear Each Conversation TwiceQuang Nam Ha0% (1)
- 07-GB Column BasesDokument14 Seiten07-GB Column BasesAUNGPSNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument2 SeitenPDFSalim AshorNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPv6 RoutingDokument27 SeitenIPv6 RoutingTtmManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patch Apply Instructions 19852360.HTMLDokument60 SeitenPatch Apply Instructions 19852360.HTMLdineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of Slab FormsDokument27 SeitenDesign of Slab FormsZevanyaRolandTualaka100% (1)
- Convention On Cybercrime BudafestDokument26 SeitenConvention On Cybercrime BudafestWinardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AVEVA VPRM Internationalisation SupportDokument25 SeitenAVEVA VPRM Internationalisation SupportShahfaraz Ahmad0% (1)
- Medium Voltage Application Guide en IECDokument224 SeitenMedium Voltage Application Guide en IECJag Jagdish0% (1)
- ChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveVon EverandChatGPT Side Hustles 2024 - Unlock the Digital Goldmine and Get AI Working for You Fast with More Than 85 Side Hustle Ideas to Boost Passive Income, Create New Cash Flow, and Get Ahead of the CurveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItVon EverandCyber War: The Next Threat to National Security and What to Do About ItBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (66)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindVon EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsVon EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (722)
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityVon EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Reality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyVon EverandReality+: Virtual Worlds and the Problems of PhilosophyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (24)
- Chaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyVon EverandChaos Monkeys: Obscene Fortune and Random Failure in Silicon ValleyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (111)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyVon EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (51)
- Generative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewVon EverandGenerative AI: The Insights You Need from Harvard Business ReviewBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- ChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessVon EverandChatGPT Millionaire 2024 - Bot-Driven Side Hustles, Prompt Engineering Shortcut Secrets, and Automated Income Streams that Print Money While You Sleep. The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide for AI BusinessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldVon EverandScary Smart: The Future of Artificial Intelligence and How You Can Save Our WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (55)
- AI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderVon EverandAI Superpowers: China, Silicon Valley, and the New World OrderBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (398)
- System Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootVon EverandSystem Error: Where Big Tech Went Wrong and How We Can RebootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesVon EverandSolutions Architect's Handbook: Kick-start your career as a solutions architect by learning architecture design principles and strategiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumVon EverandThe Infinite Machine: How an Army of Crypto-Hackers Is Building the Next Internet with EthereumBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (12)
- The Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldVon EverandThe Future of Geography: How the Competition in Space Will Change Our WorldBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- The Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyVon EverandThe Intel Trinity: How Robert Noyce, Gordon Moore, and Andy Grove Built the World's Most Important CompanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansVon EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Excel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceVon EverandExcel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyVon EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (227)
- The E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andVon EverandThe E-Myth Revisited: Why Most Small Businesses Don't Work andBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (709)