Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chemistry Paper 3 Sample
Hochgeladen von
rihdus2Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chemistry Paper 3 Sample
Hochgeladen von
rihdus2Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
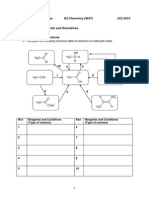
EXAMPLE 1 (SPM 2012 Paper3/Question 3)
Diagram 1 shows spirit lamps that contain different types of alcohols.
Ethanol, propanol, butanol, water, [metal] Apparatus Copper container, spirit lamp, thermometer, electronic balance, wooden block, tripod stand, wind shield and measuring cylinder.
[3 marks] f. Procedure of the experiment
Diagram 1 Different types of alcohols produce different heat of combustions. When the number of carbon per molecule of the alcohol increases the heat of combustion increases. Table 1 shows the heat of combustion of ethanol, propanol and butanol.
Table 1 Plan an experiment to compare the heat combustion of the alcohols. Your planning should include the following aspects: a. Aim:
To determine the heat of combustion of various alcohol
[2 marks] b. Statement of the problem
How does the number of carbon per molecule of alcohol affect the heat of combustion?
[2 marks] c. All the variables
Manipulated variable: Types of alcohols Responding variable: Heat of combustion Fixed variable: Volume of water, type of container, size of container and spirit lamp
[3 marks] d. Statement of the hypothesis
1. 250 cm3 of water is poured into a copper container as shown in the diagram above. 2. Initial temperature of the water is recorded. 3. A spirit lamp is half filled with ethanol. 4. Initial mass of the spirit lamp is recorded. 5. The spirit lamp under the copper beaker and ignite the wick immediately. 6. Stir the water and the flame is put off after the temperature has increased by 30C. 7. The highest temperature of the water is recorded 8. Immediately the final mass of the spirit lamp is recorded. 9. Repeat the experiment by replacing ethanol with propanol and butanol.
[3 marks] g. Tabulating data
When the number of carbon per molecule of alcohol increases, the heat of combustion increases.
[3 marks]
[3 marks]
e.
List of substance/materials and apparatus
Substance/materials
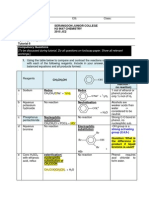
EXAMPLE 2 (SPM 2012 Paper3/Question 3)
Diagram 2 shows two methods of dissolving sugar cubes to make sugar solution.
Substances Sodium thiosulphate solution 0.5 mol dm-3, sulphuric acid 1.0 mol dm-3 Apparatus Conical flask 250 cm3, measuring cylinder, thermometer, Bunsen burner, filter paper, tripod stand, wire gauze, stopwatch
e. Procedure
Diagram 2 A group of students discovered that it is faster to dissolve the sugar cubes to make sugar solution by using hot water rather than cold water. This is due to the difference in the temperature of the water. Referring to the situation above, plan a laboratory experiment to investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction between sulphuric acid and sodium thiosulphate solution . Your planning should include the following aspects. a. Statement of the problem
How does temperature effect the rate of reaction between sulphuric acid and sodium thiosulphate solution?
b. All the variables
Manipulated variable Temperature of sodium thiosulphate solution Responding variable Time taken for the mark X to disappear from sight Constant variable Volume and concentration of sulphuric acid/ sodium thiosulphate solution// volume of conical flask.
c. Statement of the hypothesis
1) 50 cm3 of sodium thiosulphate solution is poured into a conical flask. 2) The temperature of the solution is recorded. 3) The conical flask is placed on top of a piece of white paper with a mark X at the centre. 4) 5 cm3 of sulphuric acid is added into the conical flask and the stopwatch is started immediately. 5) Swirl the conical flask and record the time taken for the mark X to disappear from sight. 6) Repeat steps 1 to 5 by heating the sodium thiosulphate solution at temperatures of 40C, 50C and 60C
f. Tabulation of data
The higher the temperature of sodium thiosulphate solution the higher the rate of reaction/time taken for the mark X to disappear from sight
d. Lists of substances and apparatus
The fruits in Figure 2 produce natural esters which have various tastes and scents.
Methanol is added to butanoic acid. The mixture is stirred. Several drops of concentrated sulphuric acid are added into the mixture using dropper. The mixture is warmed/heated. The scent produced is recorded. Repeat steps 1 to 5 using ethanol to replace methanol.
e. Tabulation of data
Figure 2 Esters can be produced in the laboratory when an alcohol reacts with a carboxylic acid. Table 2 shows types of alcohol and carboxylic acid used to produce various esters. These esters have a similar scent to the esters in fruits.
[17 marks]
Table 2 You are required to prepare two different types of ester using the same carboxylic acid with different alcohols. The two esters must be chosen from those shown in Table 2. Use the information in Table 2 to plan a laboratory experiment to prepare the esters and describe their scents. Your explanation should include all the followings: a. Aim of the experiment
Producing two esters using the same carboxylic acid and describe its scents.
b. Statement of hypothesis
Different alcohol produces ester with different scents.
c. List of substances and apparatus
Butanoic acid, ethanol, methanol, concentrated sulphuric acid/Ethanoic acid, octanol, pentanol, concentrated sulphuric acid. Apparatus: Test tubes, beakers, dropper/condenser, Bunsen burner, test tube holder/retort stand.
d. Procedures of the experiment
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- H2 Chemistry Prelims 2011 (Planning)Dokument12 SeitenH2 Chemistry Prelims 2011 (Planning)iuhihzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 8 Reaction Kinetics 1415FARRADokument129 SeitenChap 8 Reaction Kinetics 1415FARRA黄麒安Noch keine Bewertungen
- Relative Oxidising Powers of Chlorine and Iodine Measured Using an Electrochemical CellDokument7 SeitenRelative Oxidising Powers of Chlorine and Iodine Measured Using an Electrochemical CellkitoniumNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Chemical Kinetics and EnergeticsDokument12 SeitenH2 Chemical Kinetics and EnergeticskitoniumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem G-9 Lesson 7 IGCSE Qs - Rates of ReactionDokument24 SeitenChem G-9 Lesson 7 IGCSE Qs - Rates of ReactionKarim WaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Molecules To Metabolism WorksheetDokument3 Seiten2.1 Molecules To Metabolism WorksheetSayedMuhammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS Chemistry Unit 1 Class Test Jan 2015 QuestionsDokument26 SeitenAS Chemistry Unit 1 Class Test Jan 2015 Questionsecs90603Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Bases Chapter SummaryDokument3 SeitenAcids and Bases Chapter SummaryjihuhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxidation Reduction Reactions ExplainedDokument21 SeitenOxidation Reduction Reactions ExplainedKaroline UhlemannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redox MCQ Cie + AnswersDokument1 SeiteRedox MCQ Cie + Answersby7777Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes from Vanasthali Public SchoolDokument8 SeitenChemical Reactions and Equations Notes from Vanasthali Public SchoolPlatinum Gaming Warrior100% (1)
- Electron Affinity and Ionization EnergiesDokument251 SeitenElectron Affinity and Ionization Energiesgkawsar22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationDokument22 SeitenForm 4 Biology Chapter 7 - RespirationChew Han Hoong0% (2)
- Molar Volumes of Hydrogen Gas LabDokument4 SeitenMolar Volumes of Hydrogen Gas LabHannah Lee100% (3)
- CAIE Chemistry A-Level: 24: ElectrochemistryDokument8 SeitenCAIE Chemistry A-Level: 24: ElectrochemistryahumanbeinginearthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundDokument24 SeitenChemistry Form 5 Module Organic CompoundTiviya Tarini ManiamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Matter & The Atomic Structure ModulDokument43 Seiten1 Matter & The Atomic Structure Modulryder1man6433100% (1)
- H2 Atomic Structure, Stiochiometry QuestionsDokument8 SeitenH2 Atomic Structure, Stiochiometry QuestionskitoniumNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 Chem PackDokument5 Seiten6 Chem PackCody YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Mock Unit 4 4 To 4 11 A2 Organic Chemistry and Structure DeterminationDokument15 SeitenMini Mock Unit 4 4 To 4 11 A2 Organic Chemistry and Structure DeterminationSahanNivanthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sDokument10 SeitenPractice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sjeffrey XiaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of Solubility Product: (I) Purification of Common SaltDokument6 SeitenApplications of Solubility Product: (I) Purification of Common SaltSiddhartha GautamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic ChemistryDokument60 SeitenOrganic ChemistryddddddffdfdfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Module Form 4Dokument30 SeitenChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (1)
- Chem U5 A2 EdexcelDokument48 SeitenChem U5 A2 EdexcelReez SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empirical and Molecular Formulae WorksheetDokument3 SeitenEmpirical and Molecular Formulae WorksheetJohnclyde Ferry100% (1)
- Limiting Reagents and Percentage Yield WorksheetDokument1 SeiteLimiting Reagents and Percentage Yield WorksheetFandy ArdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 5Dokument386 SeitenEdexcel A2 Chemistry Paper 5AbdulRahman Mustafa100% (1)
- Gas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Dokument3 SeitenGas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Nikhil Singh100% (1)
- CHM 101 Complete - LNDokument80 SeitenCHM 101 Complete - LNSimon AdediranNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2016 QP - Unit 1 OCR Chemistry A-LevelDokument16 SeitenJune 2016 QP - Unit 1 OCR Chemistry A-Levelmark sjsieuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrocarbons: K. Atkins IB Chemistry Pensacola High SchoolDokument31 SeitenHydrocarbons: K. Atkins IB Chemistry Pensacola High Schoollianchen251110Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Development of The Periodic TableDokument95 SeitenThe Development of The Periodic TableSherren NalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Naming Alkanes Worksheet 1 & 2Dokument4 SeitenNaming Alkanes Worksheet 1 & 2cheryl retioNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Equilibrium and Ideal GasDokument9 SeitenH2 Equilibrium and Ideal GaskitoniumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebraic Method To Balance Chemical EquationDokument3 SeitenAlgebraic Method To Balance Chemical EquationBruce WalkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate of Reaction NotesDokument27 SeitenRate of Reaction NotesYong SiewkuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid State-1Dokument31 SeitenSolid State-1ChirAgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Derivatives TutorialDokument18 SeitenAcids and Derivatives TutorialChen ZhihaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BT2 Revision Package 2013 - AnsDokument70 SeitenBT2 Revision Package 2013 - AnsSean Ng Jun JieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Dokument27 SeitenStructured Question: Analysis of Past Year Questions From 2003 - 2008Nazreen NashruddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Chem Bond - Modul - ChemistryDokument11 Seiten05 Chem Bond - Modul - Chemistryrudi_z100% (1)
- Chemistry Form 6 Sem 3 07Dokument65 SeitenChemistry Form 6 Sem 3 07Ng Swee Loong StevenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydroxyl Compounds Tutorial 6 Key ConceptsDokument21 SeitenHydroxyl Compounds Tutorial 6 Key ConceptsJohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibrium Lab ReportDokument3 SeitenEquilibrium Lab ReportJustin G-Hood Jung100% (2)
- AP Thermodynamics Problems and Standard Heat of FormationDokument4 SeitenAP Thermodynamics Problems and Standard Heat of FormationHasantha PereraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrochemistry UnitDokument14 SeitenElectrochemistry UnitOGEGA KERUBONoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Atomic Structure?: ProtonsDokument5 SeitenWhat Is Atomic Structure?: Protonsjohn mwambuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predicting Redox Reactions (No MS)Dokument1 SeitePredicting Redox Reactions (No MS)AsadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 3 EnergeticsDokument47 SeitenSection 3 Energeticsapi-3734333Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryDokument102 SeitenChapter 1 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryMELVINDO JACOBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoms, Molecules and IonsDokument58 SeitenAtoms, Molecules and IonsJunaid Alam100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry NomenclatureDokument8 SeitenOrganic Chemistry NomenclaturetasneemNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Chem Notes 9729 PDFDokument78 SeitenH2 Chem Notes 9729 PDFBobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photochemical ReactionDokument16 SeitenPhotochemical ReactionChandra ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Kinetics Part - IDokument43 SeitenChemical Kinetics Part - ISanskar BhattacharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions and Balancing Chemical Equations Web Quest 3Dokument6 SeitenChemical Reactions and Balancing Chemical Equations Web Quest 3api-262586446Noch keine Bewertungen
- Allison Transmission-1K 2K Mechanic's Tips 4th GenDokument60 SeitenAllison Transmission-1K 2K Mechanic's Tips 4th GenCarlos Cornejo80% (5)
- A Practical Handbook of Seawater AnalysisDokument328 SeitenA Practical Handbook of Seawater Analysisfdlab100% (2)
- TM Rev PDFDokument18 SeitenTM Rev PDFHarshavardhan KutalNoch keine Bewertungen
- FormulaDokument6 SeitenFormulaLars RembrandtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Chapter 2 QuestionsDokument19 SeitenAtomic Structure and Chemical Bonding Chapter 2 QuestionsAhmed ZiadNoch keine Bewertungen
- LirioDokument220 SeitenLirioAntonio MeseguerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Development of Light Weight ConcreteDokument14 SeitenDevelopment of Light Weight ConcreteAmit ChouguleNoch keine Bewertungen
- SymmetryDokument43 SeitenSymmetryDeepa Kapadia0% (1)
- Powder Coating at HomeDokument9 SeitenPowder Coating at Homepakde jongko100% (1)
- Starline VALVESDokument16 SeitenStarline VALVESmanmohansingh1999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inclusion Compounds & Cyclodextrins: Presented By: Kunal Goyal Pt.B.D. Sharma Univ. Health Sci. RohtakDokument23 SeitenInclusion Compounds & Cyclodextrins: Presented By: Kunal Goyal Pt.B.D. Sharma Univ. Health Sci. Rohtakgkunal991Noch keine Bewertungen
- Surface Prepairation STD For PC ASTM D6386Dokument4 SeitenSurface Prepairation STD For PC ASTM D6386Rohit SangwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- KITZ DJ Series Ductile Iron Butterfly Valves E-231-06 PDFDokument16 SeitenKITZ DJ Series Ductile Iron Butterfly Valves E-231-06 PDFYulita Ika PawestriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab - Properties of Carboxylic AcidsDokument2 SeitenLab - Properties of Carboxylic Acidsapi-209270909Noch keine Bewertungen
- Problem Set 3 Simulation ActivityDokument12 SeitenProblem Set 3 Simulation Activityapi-182809945Noch keine Bewertungen
- V. Divakar Botcha Et al-MRX-2016Dokument14 SeitenV. Divakar Botcha Et al-MRX-2016divakar botchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COBB SIZING TESTER Quick Clamping CT-05 modelDokument1 SeiteCOBB SIZING TESTER Quick Clamping CT-05 modelNguyễn Tá TriệuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A10VO Regulator Teory PDFDokument45 SeitenA10VO Regulator Teory PDFmohammad100% (2)
- 1577-Research Results-2795-1-10-20191023Dokument13 Seiten1577-Research Results-2795-1-10-20191023Nadia fadlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paint Failures Library - PPT (Read-Only)Dokument75 SeitenPaint Failures Library - PPT (Read-Only)Elhusseiny FoudaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOA DKK Water Quality Sensor Xseries PreDokument12 SeitenTOA DKK Water Quality Sensor Xseries PrealdiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm e 518Dokument5 SeitenAstm e 518Pao Dela Cruz100% (1)
- Ujian RemediDokument1 SeiteUjian RemediJokoSuswonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pit and Fissure SealantsDokument35 SeitenPit and Fissure SealantsshrutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Institute of Public Health and The Environment, PO Box 1, 3720 BA Bilthoven, The Netherlands. Tel. 31-30-2749111, Fax. 31-30-2742971Dokument23 SeitenNational Institute of Public Health and The Environment, PO Box 1, 3720 BA Bilthoven, The Netherlands. Tel. 31-30-2749111, Fax. 31-30-2742971Saras Unggul UtamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Is 2190.2010 Selection, Installation & Maintenance of Portable Fire ExtinguishersDokument26 SeitenIs 2190.2010 Selection, Installation & Maintenance of Portable Fire ExtinguishersShivakumara ArehalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Chip FormingDokument33 SeitenNon Chip FormingNur AmirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iesc 103Dokument12 SeitenIesc 103Debasish DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical Balance Procedure For The Unbalanced Diode Error On The G1362A Refractive Index DetectorDokument4 SeitenOptical Balance Procedure For The Unbalanced Diode Error On The G1362A Refractive Index DetectorAhmad IbrahemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2Dokument8 SeitenPaper 2Prateek MalhotraNoch keine Bewertungen