Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Piduca FINAL Syllabus Outcomes Based NCM103FINAL1
Hochgeladen von
mj CanilangOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Piduca FINAL Syllabus Outcomes Based NCM103FINAL1
Hochgeladen von
mj CanilangCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
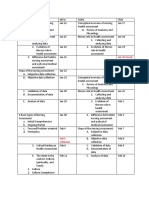
University of the Cordilleras Baguio City College of Nursing Course Syllabus I. COURSE CODE: II.
COURSE NAME: NCM 103 Care of Clients with Problems in Oxygenation, Fluid and Electrolyte Balance, Nutrition and Metabolism and Endocrine
III. COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course deals with the principles and techniques of nursing care management of sick clients across lifespan with emphasis on the adult and the older person, population group in any setting with alterations/problems in oxygenation, fluid and electrolyte balance, nutrition and metabolism and endocrine function. PLACEMENT: CREDIT: PRE-REQUISITE: 3rd year, 1st semester 8 units lecture; 6 units RLE (1 unit skills lab, 5 units Clinical); 144 lecture hours; 306 RLE hours NCM 102
IV.UC-PVMO
PHILOSOPHY : UC believes that education is the foundation of a progressive nation in the rearing of the youth towards civil efficiency and the development of moral character that the benefits of higher education should be made accessible to everyone who deserves it. UC envisions itself as a community of scholars aggressively involved in the pursuit of knowledge who help preserve Filipino culture and values to act positively by training them to think critically and creatively. UCs mission is to provide functional knowledge and skills, dynamic interaction and leadership in various disciplines for a better quality of life.
VISION :
MISSION :
OBJECTIVES: 1. Develop an environment conducive to inquiry. 2. Empower constituents in the quest for progress. 3. Contribute to appreciation of historical and cultural heritage. 4. Actively involve in the molding of a national identity. 5. Deeper sense of moral and spiritual values.
6. Expand scholarship to a wider segment. 7. Update curricula to keep abreast of change. 8. Community involvement and research intensified.
V.
COURSE OUTCOMES Description Utilize the nursing process in the care of individuals, families in community and hospital settings. Assess with client/s his/her/their condition/health status through interview, physical examination, interpretation of laboratory findings. Identify actual and at-risk nursing diagnosis Plan appropriate nursing interventions with client/s and family for identified nursing diagnosis Implement plan of care with client/s and family. Evaluate the progress of his/her/their clients condition and outcomes of care. 2. Ensure a well organized and accurate documentation system; 3. Relate with client/s and their family and the health team appropriately; 4. Observe bioethical concepts/principles, core values and nursing standards in the care of clients; and, 5. Promote personal and professional growth of self and others. PO1 3 PO2 2 P03 3 PO4 3 PO5 3 PO6 3 PO7 3 PO8 3 PO9 3 PO10 3 PO11 3 PO12 3
Course Outcomes CO1
CO2 CO3 CO4 CO5
3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3
3 3 3 2
3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3
3 3 3 3
VI.
COURSE CONTENT
OBJECTIVES
INTERMEDIATE COMPETENCIES
COURSE CONTENT The different risk factors among clients that contribute to the development of problems in oxygenation: Current respiratory problems History of respiratory disease Lifestyle (smoking, alcoholism, exercise patterns) Presence of cough Presence of Chest Pain Lung Cancer Cardiovascular disease Stroke Tuberculosis Obesity Dietary assessment Medication history a.Chief complaints b. Relevant information, to include eleven functional patterns Health perception management pattern Nutritional/metabolic pattern Elimination pattern Activity/exercise patterns Cognitive/perceptual pattern Sleep-rest pattern Self-perception-self-concept pattern Role relationship pattern Sexuality-reproductive
TEACHING-LEARNING ACTIVITIES
TIME FRAM E 2.5 hours
GRADING PERIOD
ASSESSMENT TOOL
At the end of the 1. Identify risk lecture discussion, factors among the students will be clients that able to: contribute to the 1. Utilize the development of nursing process problems in in the care of Oxygenationindividuals, cardiovascular risk families with factors (modifiable problems in and nonoxygenation in modifiable). community and hospital 2. Identify significant settings; subjective data 2. Ensure a from client history well organized related to and accurate problems in documentation oxygenation. system;
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
PRELIM
Quiz (Objective) Case Analysis Presentation
Role Analysis
Play
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Postl test
2 hours
Group Discussion
Group Presentation/ Report
3. Relate with client/s and their family and the health team appropriately; 4. Observe bioethical concepts/princi ples, core values and nursing standards in the care of clients; and, 5. Promote personal and professional growth of self and others.
pattern Coping-stress tolerance pattern Value-belief pattern 3. Enumerate the principles and techniques of physical examination in assessing the oxygenation status in newborn, children, adults. 4. Identify results and implications of diagnostic/laborat ory examinations of clients with reference to problems in Oxygenation. a. Inspection- gas exchange, perfusion b. Palpation- gas exchange, perfusion c. Percussion- gas exchange d. Auscultation- gas exchangeheart sound, breath sounds, deviations, fluid transport Screening procedure- peak flow meter Diagnostic Procedures Non-invasive: Pulmonary: e.g. sputum microscopy, chest x-ray, pulmonary function tests, smoke analyzer Fagerstrom test standardized degree of nicotine dependence Cardiac: ultrasound, ECG, 2D echo, stress test Vascular: Doppler ultrasonography Blood: pulse oximeter Invasive: Pulmonary: bronchoscopy, ABG, 4horacentesis, pulmonary angiography Cardiac: CO determination, cardiac catheterization, CVP, hemodynamics monitoring, enzyme levels, Serum, Cholesterol Vascular: angiography Demonstration Return Demonstration Lecture Discussion Post test 3 hours Output Presentation
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
2.5 hours
Oral Graded Recitation
5. Determine the Patho-physiologic mechanisms of the Alterations in oxygenation
6. Enumerate Nursing diagnoses taxonomy pertinent to problems/alteratio n in Oxygenation.
Blood: CBC and bone marrow biopsy a.Alteration in gas exchange ventilator dysfunction, impaired perfusion b.Alteration in cardiac performance heart rate problems, impaired stroke volume secondary to altered preload, afterload, myocardial contractility c. Alteration in vascular integrity transport network impairment d.Alteration in oxygen carrying capacity of the blood- decreased circulating erythrocytes (anemia), increased circulating erythrocytes (polycythemia) a. Ineffective breathing pattern b. Ineffective airway clearance c. Impaired gas exchange d. Inability to sustain spontaneous ventilation e. Dysfunctional 5entilatory weaning response f. Decreased cardiac output (CO) g. Altered tissue perfusion systemic h. Impaired gas exchange related to altered O2 carrying capacity of blood due to decreased erythrocytes/hemoglobi n i. Activity intolerance
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
16 hours
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
2 hours
Prioritization of Nursing Diagnosis NCP Analysis Presentation
Reaction Paper
7. Identify principles of various modalities of management of clients with problems in oxygenation taking into consideration the following levels of care: 1. Health promotive 2. Disease preventive 3. Curative and restorative
related to malnutrition tissue hypoxia a. For altered pulmonary function: Airway patency Oxygen therapy Adequate ventilation Drug therapy Hydration Removal of secretion Prevention of infection Prevention of complications Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation b. For cardiac function Hemodynamics monitoring O2 therapy Drug therapy Hydration Prevention of infection Prevention of complications Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation c. Oxygen carrying capacity of the blood Blood component replacement O2 therapy Drug therapy Hydration Prevention of infection
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
4 hours
8. Enumerate Pharmacologic actions, therapeutic uses, side effects, indications, contraindications, and nursing responsibilities in administering medications clients with oxygenation problems.
Prevention of complications a. Pulmonary Bronchodilators Expectorants Antitussives Antihistamines b. Cardiac Sympathomymetic agents Sympatholytic agents Anti-anginal agents Anti- arrhythmic agents Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors Antilipemic agents Anticoagulant agents Thrombolytics Peripheral vascular agents c. Blood Hematinics Vitamin supplements 1. Safe and comprehensive perioperative nursing care 1.1Assessment and care during the perioperative period 1.2Techniques in assisting the surgical team during the operation 1.3Principles of safety, comfort and privacy during the perioperative period 1.4Nursing responsibilities during the perioperative period Preoperative physical, psychological, spiritual preparation Intraoperative
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
2 hours
9. List the purposes, indications, nursing responsibilities for the surgical and special procedures in alterations in oxygenation.
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
2 hours
Group Presentation
Case Analysis
circulating nurse functions, scrub nurse functions Postoperative airway, breathings, circulation priorities. Meeting the physical, psychological and spiritual needs of the cliet. 2. Pulmonary a. Surgical procedures tracheostomy, thoracostomy, lung resection, lobectomy, pneumonectomy, thoracoplasty, decortications b. Special procedures endotrcheal/tracheal suctioning and care, humidication, IPPB, ventilator assist 3. Cardiac a. Surgical procedures coronary aretery bypass, pacemaker insertion, valve replacement, repair of congenital abnormality, insertion of ventricular assist device, heart plansplant b. Special procedures laser therapy, basic life support, advance life support 3.1 Vascular a. Surgical procedures endarterectomy, aneurysmectomy, insertion of intravascular stents b. Special procedures application of antiembolic stockings 3.2 Blood forming organs
Prelim Exam Quiz (Objective)
Role
Play
At the end of the 10. Identify risk lecture discussion, factors among the students will be clients that able to: contribute to the 1. Utilize the development of nursing process problems in Fluid in the care of and Electrolytes. individuals, 11. Enumerate the families with principles and problems in techniques of Fluids and physical electrolyte examination in imbalances in newborn, children, community and adults, deviations hospital settings. from normal. 2. Ensure a well organized and accurate 12. Identify results documentation and implications system; of 3. Relate with diagnostic/laborat client/s and their ory examinations family and the of clients with health team reference to appropriately; problems in 4. Observe bioethical 13. Determine the concepts/principl Patho-physiologic es, core values Mechanisms of and nursing Fluid and standards in the electrolyte care of clients; imbalances. and, 5. Promote personal and
a. Surgical procedures bone marrow aspiration, bone marrow transplant b. Special procedures blood component transfusion, reverse isolation Potential factors for exceeding renal reserve capacity, dietary habits to include salt intake, hypertension, infection, diabetes. Inspection- signs of dehydration, overhydration Palpation- edema, ascites, neck vein filling, hand vein filling, neuromuscular irritability, characteristic of pulse Percussion- abdomen for presence of air, fluid Auscultation- rates a. Diagnostic tests Non-invasive: electrolyte determination, intake and output, KUB-IVP and ultrasound Invasive biopsy b. Weight c. Vital Signs a. Volume impairment fluid volume deficit, fluid volume excess, third space fluid shift b. Osmotic imbalances hyponatremia, hypernatremia c. Ionic concentration problems hypo- and hyperkalemia; hypo and hyperchloremia; hypo- and
Analysis
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test Demonstration Return Demonstration Lecture Discussion Post test
1.5 hours
MIDTERM
Group Discussion
2 hours
Group Presentation/ Report
Output Presentation
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
1.5 hours
12 hours Prioritization of Nursing Diagnosis NCP Analysis Presentation
professional growth of self and others.
hypermagnesemia; hypo- and hyperphosphatemia d. Acid and base imbalances metabolic acidosis and alkalosis; respiratory acidosis and alkalosis 14. Enumerate Nursing diagnoses taxonomy pertinent to problems/alteratio n in Fluid and electrolyte imbalance. 15. Identify principles of various modalities of management of clients with problems in fluid and electrolyte imbalances taking into consideration the following levels of care: a. Health promotive b. Disease preventive c. Curative and restorative a. Risk for fluid volume deficit b. Fluid volume excess c. Fluid volume deficit d. High risk for injury related to electrolyte deficit/excess e. High risk for injury related to acid/base imbalance f. Altered urinary elimination g. Impaired integumentary integrity a. Fluid Volume Deficit Determination and management of cause Hydration Blood transfusion as needed Drug therapy electrolyte Supportive management Prevention of infection Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation b. Fluid Volume Excess Determination and management of cause Drug therapy diuretics, electrolytes Dietary restriction Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test 2 hours
Oral Graded Recitation
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
12 hours
sodium Supportive management Prevention of infection Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation c. Electrolyte Deficit hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, hypophosphatemia Determination and management of cause Drug therapy electrolyte replacement Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation d. Electrolyte Excess hyperkalemia, 11ypercalcaemia, hypermagnesemia, hyperphosphatemia Determination and management of cause Drug therapy electrolyte replacement Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of complication
Reaction Paper
Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation e. Metabolic Alkalosis Base bicarbonate exces Determination and management of cause Drug therapy Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation a. Metabolic Acidosisbase bicarbonate deficit Determination and management of cause Drug therapy Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation f. Respiratory Alkalosis carbonic and acid deficit Determination and management of cause Drug therapy Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation
Group
Presentation Case Analysis
16. Enumerate Pharmacologic actions, therapeutic uses, side effects, indications, contraindications, and nursing responsibilities in administering medications clients in fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
17. List the purposes, indications, nursing responsibilities for the surgical and special procedures in alterations in fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
g. Respiratory Acidosis carbonic acid excess Determination and management of cause Drug therapy Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation a. Fluid Parenteral fluids Hypotonic Hypertonic Isotonic b. Electrolyte Sodium Potassium Calcium Magnesium Phosphate c. diuretics Potassium-sparing Potasium-losing Osmotic diuretics d. Vitamin D supplements Renal dysfunction a. Major surgical procedures nephrectomy, nephrostomy, cystectomy, uterostomy, renal transplants, urinary diversion b. Special proceduresperitoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, bladder training,
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
2.5 hours
Midterm Exam Quiz (Objective)
Role Analysis
Play
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
2.5 hours
Group Discussion
Group Presentation/ Report
At the end of the 18. Identify risk lecture discussion, factors among the students will be clients that able to: contribute to the 1. Utilize the development of nursing process problems in in the care of Nutrition and individuals, Metabolism. families with 19. Identify problems in significant nutrition and subjective data metabolism in from client history community and related to hospital settings. problems in 2. Ensure a well nutrition and organized and metabolism. accurate documentation system; 3. Relate with client/s and their family and the health team appropriately; 4. Observe bioethical concepts/principl es, core values and nursing standards in the care of clients; and, 20. Enumerate the 5. Promote principles and personal and techniques of professional physical growth of self examination in and others. newborn, children, adults, deviations from normal.
cystoclysis/bladder irrigation Risk factors related to malnutrition, obesity.
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
1 hour
FINALS
Prioritization Nursing Diagnosis
of
NCP Analysis Presentation
a. Chief complaints b. Relevant information, to include eleven functional patterns Health perception management pattern Nutritional/metabolic pattern Elimination pattern Activity/exercise patterns Cognitive/perceptual pattern Sleep-rest pattern Self-perception-self-concept pattern Role relationship pattern Sexuality-reproductive pattern Coping-stress tolerance pattern Value-belief pattern 3.3Gastrointestinal function IPPA Inspection- color, texture of skin, mucous membrane, growth patterns, scars, masses Auscultation- bowel sounds, bruits
2 hours
Demonstration Return Demonstration Lecture Discussion Post test
1.5 hours
21. Identify results and implications of diagnostic/laborat ory examinations of clients with reference to problems in Nutrition and Metabolism. 22. Determine the Patho-physiologic mechanisms of the Alterations in Nutrition and Metabolism.
Palpation focus on GIT for presence of masses, ascites, rebound tenderness, distention Percussion liver span, masses a. Non-invasive: ultrasound of the abdomen, stool culture b. Invasive: to include: barium swallow, esophagoscopy, biopsy, cytology examination, gastric secretion analysis, endoscopy (gastroscopy, duodenoscopy), proctosigmoidoscopy and rectal examination a. Disturbances in ingestion problems in buccal cavity and esophagus b. Disturbances in digestion peptic acid disease, gastritis and gastric cancer c. Disturbances in absorption malnutrition, malabsorption syndrome and inflammatory bowel conditions d. Disturbances in elimination bowel obstruction, hemorrhoids, diarrhea and constipation. Alteration in nutrition less than body requirement Alteration in nutrition more than body requirement Alteration in oral mucous membrane integrity Alteration in comfort: epigastric pain/abdominal pain Fluid volume deficit A. Disturbances in ingestion
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
1.5 hours
Reaction Paper
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
12 hours
23. Enumer ate Nursing diagnoses taxonomy pertinent to problems/alteratio n in Nutrition and Metabolism. 24. Identify
a. b. c. d. e.
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test Pre-tests
1.5 hours
12
principles of various modalities of management of clients with problems in Nutrition and Metabolism taking into consideration the following levels of care: 4. Health promotive 5. Disease preventive 6. Curative and restorative
Determination and management of cause Drug therapy Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation B. Disturbances in digestion Determination and management of cause Drug therapy Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation C. Disturbances in absorption Determination and management of cause Drug therapy Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation D. Disturbances in elimination Determination and management of cause Drug therapy Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of
Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
hours
Group Presentation
25. Enumerate Pharmacologic actions, therapeutic uses, side effects, indications, contraindications, and nursing responsibilities in administering medications clients with Nutrition and Metabolism problems. 26. List the purposes, indications, nursing responsibilities for the surgical and special procedures in alterations in Nutrition and Metabolism.
complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation E. Disturbances in hepatic, biliary and pancreatic functions Determination and management of cause Drug therapy Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation Antiemetics Anticoagulants Hematinics agents Laxatives and stool softeners Antipruritus Vitamin supplement Antacids Antihyperlipidemics Antispasmodics Antidiarrheal a. Surgical procedures gastrostomy, gastrectomy, colostomy, hemorrhoidectomy, gastrointestinal bypass, ileostomy b. Special procedures parenteral hyperalimentation; feeding per nasogastric, jejunostomy, gastrostomy tubes; colostomy care and
Case Analysis
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
2 hours
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
2.5 hours
At the end of the 27. Identify risk lecture discussion, factors among the students will be clients that able to: contribute to the 1. Utilize the development of nursing process problems in in the care of Endocrine individuals, Function. families with 28. Identify problems in significant endocrine subjective data functioning in from client history community and related to hospital settings. problems in 2. Ensure a well endocrine organized and functioning. accurate documentation system; 3. Relate with client/s and their family and the health team appropriately; 4. Observe bioethical concepts/principl es, core values and nursing standards in the care of clients; and, 29.Enumerate the 5. Promote principles and personal and techniques of professional physical growth of self examination in
irrigation, dietary planning for common GT and endocrine problems; administering medications via NGT, J tube, G tube; hot sitz bath Risk factors related to endocrine hypo or hyperfunctioning.
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
1.5 hours
A. Chief complaints B. Relevant information, to include eleven functional patterns Health perception management pattern Nutritional/metabolic pattern Elimination pattern Activity/exercise patterns Cognitive/perceptual pattern Sleep-rest pattern Self-perception-self-concept pattern Role relationship pattern Sexuality-reproductive pattern Coping-stress tolerance pattern Value-belief pattern Inspection- color, texture of skin, mucous membrane, growth patterns, obesity Auscultation bruit, heart sounds, breath sounds
2 hours
Demonstration Return Demonstration Lecture Discussion
1.5 hours
and others.
newborn, children, adults, deviations from normal in the endocrine system. 30. Identify results and implications of diagnostic/laborat ory examinations of clients with reference to problems in endocrine functioning.
Palpation- organ-thyroid enlargement, masses, edema Percussion- fluid, edema Others weight, delayed healing of wounds
Post test
31. Determine the Patho-physiologic mechanisms of the Alterations in endocrine functioning.
a. Screening: glucose tolerance test Non-invasive: e.g. GI x-ray, ultrasound abdomen, Radioiodine assay (RAI), protein bound iodine (PBI), thyroid scan, free thyroxin level, basal metabolic rate (BMR), thyroxine stimulating hormone (TSH) test, OGTT (Glucose tolerance test) urinalysis (glycosuria, ketonuria) Invasive: e.g. percutaneous transhepatic cholangiogram, liver function test, serum thyroxine and triiodothyronine test, iodine 131 uptake, blood sugar tests (fasting blood sugar FBS), random blood sugar (RBS), glycosylated hemoglobin (Hgb), two-hour post prandial blood glucose, endocrine assay. a. Hypo- and Hyperfunction of the pituitary organ b. Hypo- and Hyperfunction of the hypothalamus c. Hypo- and Hyperfunction of the thyroid organ d. Hypo- and Hyperfunction of the parathyroid organ e. Hypo- and Hyperfunction of the
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
2.5 hours
Final Exam
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
10 hours
32. Enumer ate Nursing diagnoses taxonomy pertinent to problems/alteratio n in endocrine functioning. 33. Enumerate Pharmacologic actions, therapeutic uses, side effects, indications, contraindications, and nursing responsibilities in administering medications clients with endocrine problems.
adrenal organ f. Hypo- and Hyperfunction of the gonads g. Problems in glucose metabolism hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia (IDM, NIDDM) a. Alterations in nutrition less than body requirement b. Fluid volume deficit c. Activity intolerance
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
1.5 hours
Corticosteroids Alpha-adrenergic blocking agents Beta-adrenergic blocking agents Tyrosine inhibitors Dopamine receptor antagonists Glucocorticoids Parathyroid hormone agents Thyroid hormone agents Insulin Oral hypoglycemic agents Determination and management of cause Drug therapy - diuretics, electrolytes Dietary management Supportive management Prevention of complication Prevention of psychosocial problems Rehabilitation
2.5 hours
34. Identify principles of various modalities of management of clients with problems in endocrine functioning taking into consideration the following levels
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
12 hours
of care: a. Health promotive b. Disease preventive c. Curative and restorative 35. List the purposes, indications, nursing responsibilities for the surgical and special procedures in alterations in endocrine functioning.
a. Surgical procedures thyroidectomy, parathyroidectomy b. Special procedures monitoring of blood glucose levels; maintenance of blood glucose diet, exercise, drugs
Pre-tests Case Analysis Small Group Learning Lecture Discussion Post test
2.5 hours
VII. TEACHING-LEARNING ACTIVITIES (TLA) TLA Lecture/ Discussion Group Work Case Analysis/Study Film Viewing Total CO 1 50% 25% 230% 2% 100% CO2 50% 25% 23% 2% 100% CO3 50% 25% 23% 2% 100% CO4 50% 25% 23% 2% 100%
VIII. ASSESSMENT TOOLS (AT) AT Quiz(Essay and Recall) Group Presentation Case Study Presentation Film Analysis/Reaction Total CO 1 50% 25% 230% 2% 100% CO2 50% 25% 23% 2% 100% CO3 50% 25% 23% 2% 100% CO4 50% 25% 23% 2% 100%
IX. COMPUTATION OF SCORES NCM 103 A Grade: Prelims: PG = 60% CS + 40% Exam Midterms RMG = 60% CS+40% Exam MG = 50% PG +50% RMG Finals: RFG = 40%CS +60% Exam FG= 25% PG +25 % RMG +50% RFG NCM 103-B Prelims: PG= 60% CS +40% Exam (CS= 30% Rotational Grade+ 20% Skills Lab +10% E-Learning) (CS= 30% Rotational Grade+ 20% Skills Lab +10% E-Learning) Midterms: RMG =60% CS+40% Exam MG = 50% PG +50% RMG
Finals: RFG= 40% CS + 60% Compre (CS= 15% Rotational Grade+ 15% Skills Lab +10% E-Learning) FG = 25% PG +25 % RMG +50% RFG NCM 103 Grade: (NCM 103 Lecture Final Grade x 8) + ((NCM 103 RLE x6) 14
X. REFERENCES: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Commission on Higher Education Memorandum No. 14 Series of 2009 Nettina S.,(2001), The Lippincotts Pocket Manual of Nursing Practice, New York: Lippincott Marieb, E., (2006), Essentials of Human Anatomy and Physiology, Pearson Education South Asia PTE. LTD. Brunner, L. and Suddarth, D., (2008), Textbook of Medical-Surgical Nursing, Philadelphia: Lippincott Black, J and Hawks, J., (2008), Medical Surgical Nursing: Clinical Management for Positive Outcomes, Philadelphia: Lippincott Lemone, P. and Burke, K., (2004) Medical Surgical Nursing: Critical Thinking in Client Care, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall Sharon Lewis, (2007) Medical Surgical Nursing: Assessment and Management of Clinical Problems, Mosby
Prepared by: Mr. Michael Joel C. Piduca, RN, MAN BASAEN Instructor
Evaluated by: Eddieson Pasay-an,Ph.D,RN Area Head
Approved by: Dr. Marian Grace Gascon Dean
Noted by: Dr. CLEOFAS VPAA
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pharmacology MCQDokument1 SeitePharmacology MCQmj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grading System For NCM 103 - 103A - Funda SL and RDDokument2 SeitenGrading System For NCM 103 - 103A - Funda SL and RDmj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prelim Exam PharmaDokument2 SeitenPrelim Exam Pharmamj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHO Core Nurse Educator CompetenciesDokument1 SeiteWHO Core Nurse Educator Competenciesmj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 46 Chest AssessmentDokument12 SeitenChapter 46 Chest Assessmentmj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Funda RLE RD Time TableDokument4 SeitenFunda RLE RD Time Tablemj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soliman SchedDokument1 SeiteSoliman Schedmj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wifi HackingDokument3 SeitenWifi Hackingmj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alignment Matrix For PLOs Health AssessmentDokument4 SeitenAlignment Matrix For PLOs Health Assessmentmj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- School of Nursing Level 1 Time Table of RD Activities MTW Day Dates Hrs. Schedule of RD Skills Schedule of Seatwork/ActivityDokument4 SeitenSchool of Nursing Level 1 Time Table of RD Activities MTW Day Dates Hrs. Schedule of RD Skills Schedule of Seatwork/Activitymj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDokument1 SeiteTime Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturdaymj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDokument1 SeiteTime Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturdaymj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- PA Lec SchedDokument5 SeitenPA Lec Schedmj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grading System For NCM 100 - Skills Lectute and RDDokument2 SeitenGrading System For NCM 100 - Skills Lectute and RDmj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schedule For Faculty Use - DHDokument1 SeiteSchedule For Faculty Use - DHmj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grading System For NCM 100 - Skills Lectute and RDDokument2 SeitenGrading System For NCM 100 - Skills Lectute and RDmj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Problem Solving in Large Introductory Classes: The View From PhysicsDokument48 SeitenTeaching Problem Solving in Large Introductory Classes: The View From PhysicsAlvaro H GalvisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wound CareDokument3 SeitenWound Caremj CanilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Learner Notes 0411Dokument14 SeitenLearner Notes 0411Mohamed AbdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be Healthy Be Happy at Georgia and MaltaDokument9 SeitenBe Healthy Be Happy at Georgia and MaltaProutist Universal MaltaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research SipDokument9 SeitenResearch SipSHeen100% (4)
- Vitamin D An Old Vitamin With New Health Implications (PDF 208k)Dokument4 SeitenVitamin D An Old Vitamin With New Health Implications (PDF 208k)ytreffalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity IntoleranceDokument4 SeitenActivity IntoleranceShermane Criszen F. SallanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ascorbic Acid ExperimentDokument10 SeitenAscorbic Acid ExperimentJoa YupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health EducationDokument23 SeitenHealth EducationdinirajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nclex ChartsDokument39 SeitenNclex ChartsDuvu99100% (6)
- Exams Firstcert Prog1-4Dokument5 SeitenExams Firstcert Prog1-4Anonymous 0PRCsW6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vegetarian Nutrition and Wellness PDFDokument345 SeitenVegetarian Nutrition and Wellness PDFSanchit GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 10 Tips From ZOE Science and NutritionDokument5 SeitenTop 10 Tips From ZOE Science and NutritionGabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pepti Junior Aptamil - Recipe - Booklet 1Dokument27 SeitenPepti Junior Aptamil - Recipe - Booklet 1sorinsoareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Approach To Metabolic Bone DiseaseDokument12 SeitenClinical Approach To Metabolic Bone DiseaseRamez Nagi NicolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBI - Contoh Soal LabelDokument4 SeitenDBI - Contoh Soal Labelahmad darmawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Healthy Food in Pregnancy and Mediterain Type of Food PyramidDokument14 SeitenHealthy Food in Pregnancy and Mediterain Type of Food Pyramidfawzia rashediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quick Bread 1Dokument36 SeitenQuick Bread 1atanacia100% (1)
- Evaluating A Self Developed Physical Wellness Self Care PlanDokument12 SeitenEvaluating A Self Developed Physical Wellness Self Care Planscience pathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nutrition Month Talking PointsDokument35 SeitenNutrition Month Talking PointsTheSummitExpress100% (8)
- SF8 Nutritional Status ReportDokument1 SeiteSF8 Nutritional Status ReportRubelyn PatiñoNoch keine Bewertungen
- APIDokument17 SeitenAPIShakil LangahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme For Paper 1 2016Dokument3 SeitenMark Scheme For Paper 1 2016Suhaila Nik Ismail AzlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Benefits of Drinking Hot Water - How Can It Help Your Health - PDFDokument15 Seiten10 Benefits of Drinking Hot Water - How Can It Help Your Health - PDFMisgun SamuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ag Science Final Study GuideDokument2 SeitenAg Science Final Study GuideLiz HarfstNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lactose Intolerance: C2 - Group 3Dokument29 SeitenLactose Intolerance: C2 - Group 3Mark PadulloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Latihan Soal SNMPTN 2011 B. Inggris 336Dokument0 SeitenLatihan Soal SNMPTN 2011 B. Inggris 336Gina GiovaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organifi Green Juice The Best Organic Health Supplement For The MoneyDokument3 SeitenOrganifi Green Juice The Best Organic Health Supplement For The MoneyHasan TareqNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Dolce Diet - 3 Weeks To Shredded - Dolce, M.Dokument225 SeitenThe Dolce Diet - 3 Weeks To Shredded - Dolce, M.freddyrocks100% (9)
- Dr. Rio Herdyanto - Presentasi SCU 2018 Background - Update Template - SENT PDFDokument32 SeitenDr. Rio Herdyanto - Presentasi SCU 2018 Background - Update Template - SENT PDFanon_701937590Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 NuHemp Brand Information PackageDokument41 Seiten2009 NuHemp Brand Information PackageNuHemp100% (1)
- Hatchery Guide Layout R4 MinDokument90 SeitenHatchery Guide Layout R4 Minnasih hamadNoch keine Bewertungen