Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
964 Biology (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
Josh, LRTOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
964 Biology (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-Syllabus
Hochgeladen von
Josh, LRTCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
[PPU] Semester 2 Topics-Syllabus
964
BIOLOGY
Sources from:
Share Agent: LRT Documents
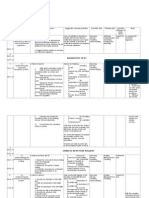
SECONDTERM: PHYSIOLOGY Topic 7 Gas Exchange 7.1 Gaseous exchange in humans Teaching Period 12 7 Candidates should be able to: (a) outline the structure of human respiratory system, including the microscopic structure of the wall of an alveolus; (b) describe the structure of haemoglobin; (c) explain the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in blood; (d) explain the oxygen dissociation curves of haemoglobin, myoglobin and foetal haemoglobin; (e) explain the Bohr effect and relate it to the oxygen dissociation curve. 7.2 Breathing cycle 3 Candidates should be able to: (a) explain the control of breathing mechanism, including the role of chemoreceptor; (b) define tidal volume, vital capacity, total lung capacity, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume and residual volume. 7.3 Gaseous exchange in plants 2 Candidates should be able to: (a) describe the structure and functions of stomata; (b) describe the mechanism of opening and closing of stomata based on potassium ion accumulation hypothesis. 8 Transport in Animals and Plants 8.1 Transport system in mammals 16 Learning Outcome
Candidates should be able to: (a) describe the structure of a mammalian heart; (b) define systole and diastole, and explain the sequence of events in a cardiac cycle including changes in pressure and volume in aorta, left atrium and left ventricle; (c) describe the initiation and regulation of heart beat;
Share Agent: LRT Documents
Page 1 of 7
Topic
Teaching Period
Learning Outcome (d) explain hypertension, atherosclerosis, arteriosclerosis and myocardial infarction, and state their causes and preventions; (e) describe the lymphatic system in relation to the blood circulatory system; (f) determine the direction of fluid movement at the arterial and venous ends of the capillaries by calculating the differences between osmotic pressure/solute potential and hydrostatic pressure.
8.2
Transport system in vascular plants
Candidates should be able to: (a) explain the uptake of water and mineral ions from the soil by the root hairs involving water potential; (b) describe the apoplast, symplast and vacuolar pathway of water movement through the root tissues; (c) describe the root pressure, cohesion-tension theory and transpiration pull in relation to water movement from the roots to leaves; (d) explain translocation using the mass flow, electro-osmosis, cytoplasmic streaming and peristaltic waves hypotheses; (e) explain the concept of source and sink, and phloem loading and unloading in translocation according to pressure flow hypothesis.
Control and Regulation 9.1 Nervous system
22 16 Candidates should be able to: (a) describe the organisation of the nervous system in humans; (b) explain the formation of resting and action potentials; (c) describe the characteristics of nerve impulse; (d) describe the structure of synapse, and explain the role of neurotransmitters (acetylcholine and norepinephrine); (e) explain and compare the mechanisms of impulse transmission along the axon and across the synapse;
Share Agent: LRT Documents
Page 2 of 7
Topic
Teaching Period (f)
Learning Outcome describe the structure of neuromuscular junction and sarcomere;
(g) explain the role of sarcoplasmic reticulum, calcium ions, myofibril and T tubules in muscle contraction; (h) explain the mechanism of muscle contraction according to the sliding filament hypothesis; (i) (j) compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems; explain the mechanisms of drug action on nervous system and neuromuscular junction (cocaine and curare).
9.2
Hormones
Candidates should be able to: (a) explain the mechanisms of action of steroid hormone and non-steroid hormones; (b) explain the roles of plant hormones in growth and development; (c) explain the mechanism of phytochrome action and their roles in photoperiodism and flowering; (d) outline the application of plant growth regulators (synthetic auxin, synthetic gibberellins, and synthetic ethylene) in agriculture.
10 Reproduction, Development and Growth 10.1 Sexual reproduction in humans
13
Candidates should be able to: (a) outline spermatogenesis and oogenesis; (b) describe the passage and development of sperms from the testis to the oviduct for fertilisation; (c) describe the process of fertilisation and implantation; (d) describe the roles of hormones in menstrual cycle and pregnancy; (e) describe briefly the stages in embryonic development;
Share Agent: LRT Documents
Page 3 of 7
Topic
Teaching Period (f)
Learning Outcome explain the roles of placenta, chorion, amniotic fluid and allantois in foetal development;
(g) explain the process of parturition. 10.2 Sexual reproduction in flowering plants 2 Candidates should be able to: (a) outline double fertilisation; (b) describe the embryonic development in seed and formation of fruit. 10.3 Seed germination 1 Candidates should be able to: (a) explain the mobilisation of nutrients after imbibition in seed germination; (b) state the external factors affecting germination. 10.4 Growth curves and patterns of growth 4 Candidates should be able to: (a) explain the types of growth curves (absolute growth curve, absolute growth rate curve and relative growth rate curve); (b) explain with examples the patterns of growth (limited growth in humans, unlimited growth in perennial plant, allometric growth in humans, isometric growth in fish and intermittent growth in insect); (c) explain the processes of ecdysis and metamorphosis in insects, and relate the role of hormones (neurosecretory hormone, juvenile hormone and ecdysone) in these processes. 11 Homeostasis 11.1 Importance of homeostasis 10 2 Candidates should be able to: (a) explain the importance of homeostasis; (b) describe the homeostatic control system in mammals; (c) explain the physiological and behavioural control in thermoregulation of endotherms.
Share Agent: LRT Documents
Page 4 of 7
Topic 11.2 Liver
Teaching Period 4
Learning Outcome Candidates should be able to: (a) describe the structure of liver, and explain the roles of its components; (b) describe carbohydrate metabolism in the liver (glycogenesis, glycogenolysis, gluconeogenesis); (c) describe protein metabolism (transamination, deamination and urea formation) in the liver.
11.3 Osmoregulation in mammals
Candidates should be able to: (a) explain the process of ultrafiltration, reabsorption and secretion in the formation of urine; (b) explain the role of ADH and aldosterone, and the related hormones in regulating water, sodium and potassium ions of urine; (c) explain the regulation of pH of tissue fluid.
11.4 Osmoregulation in plants
Candidates should be able to: (a) describe the role of stomata in regulation of water loss, and explain the importance of transpiration; (b) describe the various types of plant adaptations to prevent water loss (halophytes and xerophytes).
12 Immunity 12.1 Immune system
10 3 Candidates should be able to: (a) describe human lymphatic system, and explain its function in relation to immunity; (b) describe antibody (structure and function), antigen, epitope, and the development of B and T cells; (c) describe the roles of macrophages, B cells and T cells.
Share Agent: LRT Documents
Page 5 of 7
Topic 12.2 Development of immunity
Teaching Period 3
Learning Outcome Candidates should be able to: (a) explain cell-mediated and humoral immune responses; (b) outline the antigen-antibody reactions (precipitation, agglutination, neutralisation, complement fixation).
12.3 Concept of self and non-self
Candidates should be able to: (a) explain the concept of self and non-self and relate this to tissue rejection in organ transplant; (b) explain the mechanism of immune suppression (HIV infection).
12.4 Immune disorder
Candidates should be able to: (a) describe autoimmune disorder (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)).
13 Infectious Diseases 13.1 Infectious disease
13 1 Candidates should be able to: (a) explain what is meant by an infection and an infectious disease; (b) outline the types of infectious agents.
13.2 Dengue
Candidates should be able to: (a) describe the causes and symptoms of dengue; (b) explain the transmission of dengue; (c) discuss the roles of social, economical and biological factors in the prevention of dengue.
13.3 Cholera
Candidates should be able to: (a) describe the causes and symptoms of cholera; (b) explain the transmission of cholera; (c) discuss the roles of social, economical and biological factors in the prevention of cholera.
Share Agent: LRT Documents
Page 6 of 7
Topic 13.4 Tuberculosis (TB)
Teaching Period 3
Learning Outcome Candidates should be able to: (a) describe the causes and symptoms of tuberculosis (TB); (b) explain the transmission of TB; (c) discuss the roles of social, economical and biological factors in the prevention of TB.
13.5 Malaria
Candidates should be able to: (a) describe the causes and symptoms of malaria; (b) explain the transmission of malaria; (c) discuss the roles of social, economical and biological factors in the prevention of malaria.
Share Agent: LRT Documents
Page 7 of 7
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Yearly Plan Form 6 Term 2 & 3Dokument7 SeitenYearly Plan Form 6 Term 2 & 3Mohamad Sahimi Bin MahatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology SloDokument9 SeitenBiology SloBilal Rizvi SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomrsmbetong: Biology SPM Learning Objective: Form 5Dokument1 SeiteBiomrsmbetong: Biology SPM Learning Objective: Form 5Nureen IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Bio Form5Dokument30 SeitenYearly Plan Bio Form5maieyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan 2007Dokument13 SeitenYearly Plan 2007Masitah AmzalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Form TwoDokument7 SeitenBiology Form TwoteramindgreatnessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Pocket Biology May-22 O'level: Chapter: Movement of Substances Into and Out of CellsDokument7 SeitenFinal Pocket Biology May-22 O'level: Chapter: Movement of Substances Into and Out of CellszareenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 964 Biology (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusDokument7 Seiten964 Biology (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRT100% (2)
- Email.: by Foozi SilagiDokument9 SeitenEmail.: by Foozi SilagiHasifa KonsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Paper 1Dokument3 SeitenBiology Paper 1TubocurareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Institute of Technology Tralee: Semester 1 Examinations A/Y 2009/2010 Biology 1 BIOL 61000 (CRN 45419) (CRN 43186)Dokument4 SeitenInstitute of Technology Tralee: Semester 1 Examinations A/Y 2009/2010 Biology 1 BIOL 61000 (CRN 45419) (CRN 43186)Mohmmad Alhazmi AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology StudyDokument4 SeitenBiology StudyWinndell DupresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maple Leaf International School Syllabus of Session 2016-17 2 Monthly Examination Class: VIII Subject: Human BiologyDokument5 SeitenMaple Leaf International School Syllabus of Session 2016-17 2 Monthly Examination Class: VIII Subject: Human BiologyMd A RAZZAKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2 OCR Biology ChecklistDokument8 SeitenYear 2 OCR Biology Checklistjamal jackNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biol 0200 SyllabusDokument18 SeitenBiol 0200 SyllabusShandev IndoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UG022524 International GCSE in Human Biology 4HB0 For PrintDokument42 SeitenUG022524 International GCSE in Human Biology 4HB0 For PrintHosni ShowikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 2 Only - StatementsDokument2 SeitenPaper 2 Only - Statementsnvadhri066Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment DPS BIO Practice Paper-01 Class-X 0110Dokument2 SeitenAssignment DPS BIO Practice Paper-01 Class-X 0110amartyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pengajaran Penggal 2 2015Dokument7 SeitenRancangan Pengajaran Penggal 2 2015Theresa IzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Past QuestionsDokument37 Seiten100 Past QuestionsNasif Basher0% (1)
- University Entrance Examination Biology SyllabusDokument17 SeitenUniversity Entrance Examination Biology Syllabusss44kkuurraa8888Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 Xe Biology WorksheetDokument5 Seiten2023 Xe Biology Worksheetsomeonehalp12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Directions (As You Will See On The AP Biology Exam) Answers Must Be in EssayDokument5 SeitenDirections (As You Will See On The AP Biology Exam) Answers Must Be in Essaybetaman99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mdcat PDFDokument47 SeitenMdcat PDFsajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Old A. P. Biology Essay QuestionsDokument17 SeitenOld A. P. Biology Essay QuestionszaynsmirrorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Tahunan BIO T5Dokument38 SeitenRancangan Tahunan BIO T5riyashreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCR A Level Biology Content Year 2 Checklist 2016Dokument11 SeitenOCR A Level Biology Content Year 2 Checklist 2016Billy thorntonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio GR 10Dokument4 SeitenBio GR 10api-253466750Noch keine Bewertungen
- AP Biology QuestionsDokument37 SeitenAP Biology QuestionsRaci DesovskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Sb0014Dokument16 SeitenTutorial Sb0014ezamNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOLOGY (Theory) : Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsDokument21 SeitenBIOLOGY (Theory) : Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70 General InstructionsWajahat AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- JandaranaDokument2 SeitenJandaranaMalieh MaximeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPE Biology Syllabus With Specimen Papers - Split - 2Dokument5 SeitenCAPE Biology Syllabus With Specimen Papers - Split - 2Enz JosephNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Biology Form 5: Diagnostic TestDokument18 SeitenYearly Plan Biology Form 5: Diagnostic TestShahida Salwa MohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- NIH Public Access: Bacterial Swarming: A Model System For Studying Dynamic Self-AssemblyDokument31 SeitenNIH Public Access: Bacterial Swarming: A Model System For Studying Dynamic Self-AssemblyverdosNoch keine Bewertungen
- HBIO POCKET BIOLOGY May-22Dokument6 SeitenHBIO POCKET BIOLOGY May-22lisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper - I Section A: C.S.E-Mains 1994 BotanyDokument3 SeitenPaper - I Section A: C.S.E-Mains 1994 BotanyhimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HY XI Bio QP Nov 2022Dokument6 SeitenHY XI Bio QP Nov 2022Biswajit BeheraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12 Cbse Biology Sample Paper 2012-13 Model 1Dokument13 SeitenClass 12 Cbse Biology Sample Paper 2012-13 Model 1Sunaina RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nnu 3112 Medical Physiology I 1Dokument6 SeitenNnu 3112 Medical Physiology I 1bosco kiuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double Blaster Pro V1Dokument3 SeitenDouble Blaster Pro V1kunihirabyaruhangqNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Bio Syll 2017Dokument15 SeitenO Level Bio Syll 2017helloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kibuli SS A Level Biology Seminar September 2022 FinalDokument15 SeitenKibuli SS A Level Biology Seminar September 2022 Finalmins.succesorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Scheme of Work-Biology (Form5) Theme: Physiology of Living Things Learning Area: 1.0 TransportDokument52 SeitenYearly Scheme of Work-Biology (Form5) Theme: Physiology of Living Things Learning Area: 1.0 TransportSyakirah Abdullah100% (1)
- Biology Essay QuestionsDokument6 SeitenBiology Essay Questionsintothelight2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology B1 Characteristics of Living OrganismsDokument28 SeitenBiology B1 Characteristics of Living OrganismsShamini Segari GunasakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12th Biology 2008-2013-Final (For Web) 1Dokument353 Seiten12th Biology 2008-2013-Final (For Web) 1Sandeep100% (1)
- Biology: Previous Year QuestionsDokument12 SeitenBiology: Previous Year QuestionsMayank PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set-3 BiologyXIDokument6 SeitenSet-3 BiologyXIavishank584Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem Learning ObjectiveDokument7 SeitenBiochem Learning Objectivepetemaravich333Noch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Cells Practice TestDokument6 SeitenBiology Cells Practice TestcamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BDokument2 Seiten964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BSeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Biology CurriculumDokument13 SeitenThe Biology CurriculumFatin Liyana AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Markscheme HL Paper3Dokument8 SeitenMarkscheme HL Paper3Jane ChangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periphyton: Functions and Application in Environmental RemediationVon EverandPeriphyton: Functions and Application in Environmental RemediationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanobiology: Exploitation for Medical BenefitVon EverandMechanobiology: Exploitation for Medical BenefitSimon C. F. RawlinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology of Elasmobranch Fishes: Internal ProcessesVon EverandPhysiology of Elasmobranch Fishes: Internal ProcessesNoch keine Bewertungen
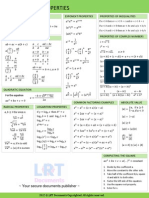
- QUICK Reference Mathematics FormularDokument4 SeitenQUICK Reference Mathematics FormularJosh, LRT100% (1)
- EAMS - Epicurean Apartment Management System (WEB BASED SYSTEM)Dokument87 SeitenEAMS - Epicurean Apartment Management System (WEB BASED SYSTEM)Josh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- IoT SMART BUS WITH LoRaDokument11 SeitenIoT SMART BUS WITH LoRaJosh, LRT100% (1)
- STPM SBA Chemistry Presentation 2013Dokument94 SeitenSTPM SBA Chemistry Presentation 2013Josh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM SBA Chemistry Report 2013Dokument31 SeitenSTPM SBA Chemistry Report 2013Josh, LRT90% (10)
- Qualitative Inorganic Analysis (QIA) Chart On CationsDokument1 SeiteQualitative Inorganic Analysis (QIA) Chart On CationsJosh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM SBA Physics Presentation 2013Dokument56 SeitenSTPM SBA Physics Presentation 2013Josh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- 962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusDokument13 Seiten962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Math T 954 Coursework 2013 (Sem 2) QUESTION 5Dokument15 SeitenSTPM Math T 954 Coursework 2013 (Sem 2) QUESTION 5Josh, LRT100% (1)
- PBS/SBA Chemistry Scheme 12-13Dokument20 SeitenPBS/SBA Chemistry Scheme 12-13Josh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Mathematics Project Work 2013 WPKLDokument20 SeitenAdditional Mathematics Project Work 2013 WPKLJosh, LRT0% (3)
- STPM 954 Math T Coursework 2013 (Sem 1)Dokument3 SeitenSTPM 954 Math T Coursework 2013 (Sem 1)Josh, LRT67% (6)
- STPM 954 Math T Coursework 2013 (Sem 3)Dokument30 SeitenSTPM 954 Math T Coursework 2013 (Sem 3)Josh, LRT100% (5)
- PIC Programming Module USB and Traffic Light System ControllerDokument26 SeitenPIC Programming Module USB and Traffic Light System ControllerJosh, LRT100% (1)
- 962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusDokument13 Seiten962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- 954 Math T (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusDokument5 Seiten954 Math T (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRT67% (3)
- 960 Physics (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusDokument8 Seiten960 Physics (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- 950 Math M (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusDokument4 Seiten950 Math M (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPU 960 Physics Note (Sem 2 Chapter 13 - Capacitors)Dokument13 SeitenPPU 960 Physics Note (Sem 2 Chapter 13 - Capacitors)Josh, LRT100% (3)
- STPM 954 Math T Coursework 2013 (Sem 2)Dokument23 SeitenSTPM 954 Math T Coursework 2013 (Sem 2)Josh, LRT100% (12)
- 964 Biology (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusDokument7 Seiten964 Biology (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRT100% (2)
- 962 Chemistry (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusDokument9 Seiten962 Chemistry (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRT100% (1)
- 960 Physics (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusDokument7 Seiten960 Physics (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRT0% (1)
- PPU 960 Physics Note (Sem 2 Chapter 12 - Electrostatics)Dokument11 SeitenPPU 960 Physics Note (Sem 2 Chapter 12 - Electrostatics)Josh, LRT100% (6)
- SMK Cochrane Us1 2013 Time TableDokument1 SeiteSMK Cochrane Us1 2013 Time TableJosh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- 954 Math T (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusDokument4 Seiten954 Math T (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- 950 Math M (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusDokument4 Seiten950 Math M (PPU) Semester 2 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article 254. Discharge of Firearms. - Any Person Who Shall Shoot at Another With Any Firearm Shall Suffer The PenaltyDokument8 SeitenArticle 254. Discharge of Firearms. - Any Person Who Shall Shoot at Another With Any Firearm Shall Suffer The PenaltyReyes BeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protozoa and PoriferaDokument2 SeitenProtozoa and Poriferatezpur123Noch keine Bewertungen
- HistologyDokument3 SeitenHistologyUsama KhawajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12.4 Voluntary & Involuntary Action, 12.6 Endocrine System - Google FormsDokument7 Seiten12.4 Voluntary & Involuntary Action, 12.6 Endocrine System - Google FormsHAJAR LENNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gynecology MnemonicsDokument5 SeitenGynecology MnemonicsJared Khoo Er HauNoch keine Bewertungen
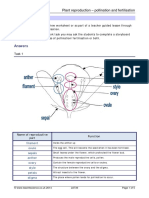
- Answers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesDokument5 SeitenAnswers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesKhoo Ying WeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics & Inheritance: Questions: Test Duration: Reading TimeDokument14 SeitenGenetics & Inheritance: Questions: Test Duration: Reading Timeincognitus940% (1)
- 2 - Growth and Development (I)Dokument99 Seiten2 - Growth and Development (I)Hosny M IsseNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Family Health SurveyDokument21 SeitenNational Family Health SurveyNamita Goyal100% (1)
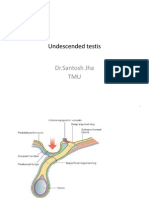
- Undescended Testis: DR - Santosh Jha TMUDokument33 SeitenUndescended Testis: DR - Santosh Jha TMUYamir Fernando Monroy MartínNoch keine Bewertungen
- Job AidcdDokument3 SeitenJob AidcdNicole PramonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malpresentation and Malposition - ShoulderDokument5 SeitenMalpresentation and Malposition - ShoulderNishaThakuri100% (1)
- The Boys of WinterDokument1 SeiteThe Boys of WinterKristen HendersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 10Dokument7 Seiten8 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 10Raj Anand100% (1)
- Delivery Room RecordDokument1 SeiteDelivery Room RecordalabenoryvieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample To SendDokument6 SeitenSample To SendRica Ehlaine CañetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pig Embryo Production byDokument18 SeitenPig Embryo Production byJaylord AgpuldoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Placenta ChecklistDokument2 SeitenPlacenta ChecklistNidhi Shivam Ahlawat100% (3)
- Suchita Srivastava Chandigarh Case - 35395Dokument31 SeitenSuchita Srivastava Chandigarh Case - 35395Disability Rights AllianceNoch keine Bewertungen
- IOL LaborDokument22 SeitenIOL LaborSingey LhendupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thesis Chapter 1Dokument8 SeitenThesis Chapter 1Chrisly Guadayo100% (2)
- Transvaginal MorcellationDokument8 SeitenTransvaginal Morcellationsanjayb1976gmailcomNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDokument27 SeitenNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentRafika SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yellow Bellied Slider TurtleDokument6 SeitenYellow Bellied Slider TurtleSky Kristen DrerupNoch keine Bewertungen
- Safe MotherhoodDokument27 SeitenSafe MotherhoodEsory BasnetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical ParasitologyDokument64 SeitenMedical ParasitologymulatumeleseNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument18 SeitenUntitledstuffednurseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 008Dokument11 SeitenChapter 008api-281340024Noch keine Bewertungen
- Antenatal CareDokument19 SeitenAntenatal CareSaima KanwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 10 External and Internal Anatomy of A FrogDokument11 SeitenExperiment 10 External and Internal Anatomy of A FrogJhasper ManagyoNoch keine Bewertungen