Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Brachial Plexus
Hochgeladen von
Coco GargaritaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Brachial Plexus
Hochgeladen von
Coco GargaritaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
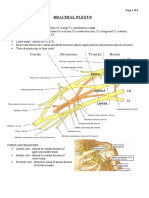
Brachial plexus
The brachial plexus is an arrangement of nerve fibres, running from the spine, specifically from above the fifth cervical vertebra to underneath the first thoracic vertebra (C5-T1). It proceeds through the neck, the axilla (armpit region) and into the arm. Function The brachial plexus is responsible for cutaneous and muscular innervation of the entire upper limb, with two exceptions: the trapezius muscle innervated by the spinal accessory nerve and an area of skin near the axilla innervated by the intercostobrachialis nerve. This function may be impaired by tumor growth of the Apical region of either Lung. Therefore, brachial plexus lesions can lead to severe functional impairment.
Anatomy
One can remember the order of brachial plexus elements by way of the mnemonic, "Read The Damn Cadaver Book" - Roots, Trunks, Divisions, Cords, Branches[1] or - Roots, Trunks, Divisions, Cords, Collateral/Pre-terminal Branches, and (Terminal) Branches.
The five roots are the five anterior rami of the spinal nerves, after they have given off their segmental supply to the muscles of the neck. These roots merge to form three trunks: o "superior"[2] or "upper" (C5-C6) o "middle"[3] (C7) o "inferior"[4] or "lower" (C8-T1) Each trunk then splits in two, to form six divisions: o anterior division[5] of the superior, middle, and inferior trunks o posterior division[6] of the superior, middle, and inferior trunks
These six divisions will regroup to become the three cords. The cords are named by their position in respect to the axillary artery. o The posterior cord is formed from the three posterior divisions of the trunks (C5-T1) o The lateral cord is the anterior divisions from the upper and middle trunks (C5-C7) o The medial cord is simply a continuation of the lower trunk (C8-T1) The branches are listed below. Most branch off of the cords, but a few branch (indicated in italics) directly off of earlier structures. The five in bold are considered "terminal branches".
Diagram
[edit] Specific branches
From roots roots superior trunk superior trunk lateral cord lateral cord lateral cord posterior cord posterior cord posterior cord Nerve dorsal scapular nerve long thoracic nerve Roots C5 C5, C6, C7 Muscles rhomboid muscles and levator scapulae serratus anterior subclavius muscle supraspinatus and infraspinatus Cutaneous -
nerve to the subclavius C5, C6 suprascapular nerve lateral pectoral nerve musculocutaneous nerve lateral root of the median nerve C5, C6 C5, C6, C7 C5, C6, C7 C5, C6, C7
pectoralis major (by communicating with the medial pectoral nerve) coracobrachialis, brachialis and biceps becomes the lateral cutaneous nerve of the brachii forearm fibres to the median nerve subscapularis (upper part) latissimus dorsi -
upper subscapular nerve C5, C6 thoracodorsal nerve C6, C7, C8
lower subscapular nerve C5, C6 C5, C6 C5, C6,
posterior axillary nerve cord posterior radial nerve
subscapularis (lower part) and teres major anterior branch: deltoid and a small area of overlying skin posterior branch becomes upper lateral posterior branch: teres minor and deltoid cutaneous nerve of the arm muscles triceps brachii, anconeus, the extensor skin of the posterior arm as the posterior
cord medial cord medial cord medial cord medial cord medial cord medial pectoral nerve
C7, C8, T1 C8, T1
muscles of the forearm, and brachioradialis pectoralis major and pectoralis minor fibres to the median nerve -
cutaneous nerve of the arm portions of hand not served by ulnar or radial front and medial skin of the arm medial skin of the forearm
medial root of the C8, T1 median nerve medial cutaneous nerve C8, T1 of the arm medial cutaneous nerve C8, T1 of the forearm ulnar nerve C8, T1
the skin of the medial side of the hand and flexor carpi ulnaris, the medial 2 bellies medial one and a half fingers on the palmar of flexor digitorum profundus, most of side and medial two and a half fingers on the the small muscles of the hand dorsal side
Additional images
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Brachial Plexus (Autosaved)Dokument19 SeitenBrachial Plexus (Autosaved)Muhamad SdeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexusDokument6 SeitenBrachial PlexusMuhamad SdeqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial Plexus Anatomy: Abdulaziz R. Alanzi Medical Student, Al-Imam University Riyadh, Saudi ArabiaDokument23 SeitenBrachial Plexus Anatomy: Abdulaziz R. Alanzi Medical Student, Al-Imam University Riyadh, Saudi ArabiaArybaa MeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Nerves of UL 2022Dokument45 SeitenAnatomy Nerves of UL 2022Malak AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nerves of Upper LimbDokument9 SeitenNerves of Upper LimbRaymond PosumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ana211 Brachial PlexusDokument8 SeitenAna211 Brachial PlexusKalu ComforterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexusDokument24 SeitenBrachial PlexusAamir ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Brachial PlexusDokument4 SeitenAnatomy Brachial PlexusMiracle For NursesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexusDokument2 SeitenBrachial Plexusc pavan kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMS UL5 Brachial PlexusDokument52 SeitenBMS UL5 Brachial PlexusStrive ShashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexusDokument10 SeitenBrachial PlexusPercy Jackson100% (1)
- Brachial PlexusDokument26 SeitenBrachial PlexustiiandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexusDokument24 SeitenBrachial Plexusfilza farheenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Brachial PlexusDokument5 SeitenThe Brachial PlexusEsther Marie SazonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handount Limbs CompleteDokument67 SeitenHandount Limbs CompletebigprogrammeramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexusDokument3 SeitenBrachial PlexusIshant SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexusDokument62 SeitenBrachial PlexusTutankhamoun Akhenatoun100% (2)
- Plexo BraquialDokument7 SeitenPlexo BraquialcataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 17 The Spinal Cord Somatic NervesDokument18 SeitenLab 17 The Spinal Cord Somatic Nervesrhycelayon304Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Lecture 3: (The Muscular System)Dokument35 SeitenAnatomy Lecture 3: (The Muscular System)Marikit2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cervical, Brachial PlexusDokument31 SeitenCervical, Brachial PlexusSophy AhdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial Plexus PresentationDokument143 SeitenBrachial Plexus Presentationkyomuhendobright4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Saraf Spinal: Neuroanatomy, Somatic Nervous SystemDokument10 SeitenSaraf Spinal: Neuroanatomy, Somatic Nervous SystemFitri SukmawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- P Brachialis 2Dokument2 SeitenP Brachialis 2jessgabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy 3 Upper LimbsDokument5 SeitenAnatomy 3 Upper LimbszahraaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexuseDokument58 SeitenBrachial PlexuseShekwolo LazarusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexusDokument9 SeitenBrachial Plexus林耿毅Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plexus BrachialisDokument18 SeitenPlexus BrachialisSpas ZmiycharovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discussion Topics IA1 AnatDokument9 SeitenDiscussion Topics IA1 AnatPhysics TutionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Syed Irfan Raza ArifDokument27 SeitenDr. Syed Irfan Raza ArifSyed Irfan ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Membrul Superior MGDokument118 SeitenMembrul Superior MGMihai OpreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of Brachial Plexus: DR - Sadiq Wadood Siddiqui JR3 Department of AnatomyDokument53 SeitenAnatomy of Brachial Plexus: DR - Sadiq Wadood Siddiqui JR3 Department of AnatomySadiq Wadood SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nazia SaifiDokument11 SeitenNazia Saifinaazu naazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexusDokument16 SeitenBrachial PlexusMedhat SabonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. AnanyaDokument55 SeitenDr. AnanyatarawifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of Axilla: Prof - Dr. Ahmed ZolfakarDokument61 SeitenAnatomy of Axilla: Prof - Dr. Ahmed ZolfakarْNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spinal Plexuses - Cervical, Brachial, Lumbar and Sacrococcygeal - Med School AnatomyDokument12 SeitenSpinal Plexuses - Cervical, Brachial, Lumbar and Sacrococcygeal - Med School AnatomyRomasha PurijjalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ana 211 The Brachial PlexusDokument10 SeitenAna 211 The Brachial PlexusAmadi CedarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arm AnatomyDokument66 SeitenArm AnatomyManaila AdrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spinal CordDokument27 SeitenSpinal Cordsiddharth.roy26587Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cervical PlexusDokument4 SeitenCervical PlexusIshant SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Limb, Brachial PlexusDokument28 SeitenUpper Limb, Brachial Plexusgtaha80Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arm and Back - TabulatedDokument5 SeitenArm and Back - TabulatedandiedeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomi Fossa AxillarisDokument56 SeitenAnatomi Fossa AxillarisdoktergigikoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Lecture 5 Brachial PlexusDokument66 SeitenAnatomy Lecture 5 Brachial PlexusSathvika ChallarapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Roots Value of Each Branch Is Given in BracketsDokument8 SeitenThe Roots Value of Each Branch Is Given in BracketsAneela PervezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Regional Anatomy of The Upper LimbDokument37 SeitenThe Regional Anatomy of The Upper LimbAdelin GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRACHIAL PLEXUS (Autosaved)Dokument51 SeitenBRACHIAL PLEXUS (Autosaved)Coy EnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexusDokument4 SeitenBrachial PlexussaluniasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Brachial PlexusDokument22 SeitenThe Brachial PlexusMusonda LumbweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial Plexus Block: "Dr. Sami Ur Rehman" House OfficerDokument65 SeitenBrachial Plexus Block: "Dr. Sami Ur Rehman" House OfficerSami Ur RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertebrae and Muscles of The Back: Lecturer: Dr. M. Samsam Univ. of Central FloridaDokument39 SeitenVertebrae and Muscles of The Back: Lecturer: Dr. M. Samsam Univ. of Central FloridaT CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cervical Nerves.: Tural Rajabov. TSMU. Medicine Faculitiy. 7 GroupDokument22 SeitenCervical Nerves.: Tural Rajabov. TSMU. Medicine Faculitiy. 7 GroupManisanthosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Axilla 13 DR - Gun ANA227 For DT2Dokument37 SeitenAxilla 13 DR - Gun ANA227 For DT2julesarojineeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoulder Anatomy SummaryDokument4 SeitenShoulder Anatomy Summaryapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Axilla, Brachial Plexus, Subscapular RegionsDokument28 SeitenAxilla, Brachial Plexus, Subscapular RegionsSerenaNg2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument60 SeitenNervous SystemFiraol DiribaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial Plexus InjuriesDokument46 SeitenBrachial Plexus Injuriesnams orthoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Way of Thinking in Brachial Plexus InjuryDokument48 SeitenThe Way of Thinking in Brachial Plexus InjuryYoonHeeNyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoulder MuscleDokument52 SeitenShoulder Muscleshahirah770% (1)
- Blood Vessels of Upper LimbDokument23 SeitenBlood Vessels of Upper Limbkhalid_shinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial PlexusDokument42 SeitenBrachial PlexusPrince DuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carcinoma BreastDokument47 SeitenCarcinoma BreastMayank YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lambou Delto PectoralDokument9 SeitenLambou Delto PectoralalexNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07.lymphatic Sysytem 18Dokument24 Seiten07.lymphatic Sysytem 18driraja9999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acland's DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Vol-1-TranscriptDokument36 SeitenAcland's DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Vol-1-TranscriptJaime Quimbayo EdogawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pilates For The Treatment Fo Postural Hyper Kyphosis PDFDokument17 SeitenPilates For The Treatment Fo Postural Hyper Kyphosis PDFbrunoduartefrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Checklist For Breast ExamDokument5 SeitenChecklist For Breast ExamKaira Denise BilaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 22 Post-Lab - The Muscular System (New Ver.)Dokument33 SeitenBio 22 Post-Lab - The Muscular System (New Ver.)Arah Sacdalan92% (12)
- Serdev Suture Techniques Breast Lift - Prof Nikolay P Serdev MD PHDDokument4 SeitenSerdev Suture Techniques Breast Lift - Prof Nikolay P Serdev MD PHDjobetobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Three Stretches For The Pectoralis Minor Muscle PDFDokument7 SeitenComparison of Three Stretches For The Pectoralis Minor Muscle PDFsebafigueroa94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gregory I. Bain, Eiji Itoi, Giovanni Di Giacomo, Hiroyuki Sugaya Eds. Normal and Pathological Anatomy of The ShoulderDokument410 SeitenGregory I. Bain, Eiji Itoi, Giovanni Di Giacomo, Hiroyuki Sugaya Eds. Normal and Pathological Anatomy of The ShoulderNikolaos Anastasopoulos100% (3)
- Mink Dissection PracticalDokument84 SeitenMink Dissection PracticalKimiko GriffinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brachial Plexus PowerpointDokument37 SeitenBrachial Plexus PowerpointMuhammad Naqiuddin JalaluddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benefits of The Costoclavicular Space For.15Dokument2 SeitenBenefits of The Costoclavicular Space For.15andrew herringNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 10 Lecture Presentation CDokument48 SeitenCH 10 Lecture Presentation CLindseyRae ParkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Touch For Health Level IDokument2 SeitenTouch For Health Level ISilvia De AlejandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro Handbook (SUNY)Dokument100 SeitenNeuro Handbook (SUNY)Serge KhelemsKy100% (3)
- SinulDokument86 SeitenSinulCucos NataliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drawing ChildrenDokument94 SeitenDrawing Childrenaleah100% (2)
- 4) Mammary Gland 220413 Upnm2Dokument22 Seiten4) Mammary Gland 220413 Upnm2AaronMaroonFive100% (1)
- Anatomy MCQsDokument41 SeitenAnatomy MCQsAzim Arif Hashmi100% (1)
- Cervical RadiculopathyDokument7 SeitenCervical Radiculopathyrhymescsf100% (1)
- Anatomy Mnemonics 2Dokument50 SeitenAnatomy Mnemonics 2Nourhan JamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flaps in Head & Neck ReconstructionDokument78 SeitenFlaps in Head & Neck Reconstructionkatnev100% (3)
- Flaps in Head & Neck Reconstruction: Moderator: DR - Arun Kumar .K.V Presenter: DR - Ananth Kumar.G.BDokument78 SeitenFlaps in Head & Neck Reconstruction: Moderator: DR - Arun Kumar .K.V Presenter: DR - Ananth Kumar.G.BisabelNoch keine Bewertungen
- SyllabusDokument344 SeitenSyllabusabugehad2100% (1)
- 2014-10-17 Trail Guide To The Body CH 2Dokument4 Seiten2014-10-17 Trail Guide To The Body CH 2Ben WisherNoch keine Bewertungen