Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Web 2 Business Proposal For Brisbane Airport
Hochgeladen von
Alex LimOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Web 2 Business Proposal For Brisbane Airport
Hochgeladen von
Alex LimCopyright:
Web 2.
0 Business Improvement Proposal
Web 2.0 Business Proposal for Brisbane Airport
by Alex Y Lim
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
Executive Summary
Few businesses are as diversified in scope and far-flung in reach as an airport or air terminal service provider (Dreiling, 2012), whether managed as a government-run operation or by a privately-held management team. The Brisbane Airport exemplifies the latter and faces vast opportunity to achieve a wider market patronage through a more intensive Web 2.0 or Enterprise 2.0 presence. Web 2.0 started out as social online experience at the individual level in the early part of the 21st century and has become a staging platform for promoting business objectives to a global market that has embraced Web 2.0 as integral to how commerce is undertaken today. A privately managed international airport that servers more than 20 million arriving, departing and transiting air travelers is a diverse business concern that can benefit from being close to its stakeholders through the social wonders of Web 2.0 online experience. With no more than an $60,000 investment as proposed herein, the Brisbane Airport can tap into the Web 2.0 social media powers to achieve greater economies of marketing, closer relationships with its customers, and achieve wider brand awareness that traditional marketing can only dream about. Over a 12-month period, the proposal will strengthen the airports social media presence with a second social networking site, a presence in blogosphere and a stab at YouTube marketing all of which can provide not only a more intimate relationship with its stakeholders, customers and business partners, but open up the potential to have added revenue streams from business referrals made from these social sites.
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
Table of Contents
Executive Summary .............................................................................................................. 2 1 Introduction ................................................................................................................... 4 2 Current Situation ........................................................................................................... 5 2.1 The Brisbane Airport Corporation (BAC) .............................................................. 5 Ownership ......................................................................................................................... 6 2.2 Web 2.0 Business Implications .............................................................................. 6 2.3. Web 2.0 in BAC ..................................................................................................... 8 2.4 Business Needs Analysis ...................................................................................... 10 3. Web 2.0 Solution Proposal.......................................................................................... 15 3.1 Description ........................................................................................................... 15 3.1.1 Identified Business Drivers ........................................................................... 17 3.1.2 Objectives ...................................................................................................... 18 3.2 Cash Flow Analysis .............................................................................................. 19 3.2.1 Projected Benefits ......................................................................................... 19 3.2.2 Anticipated Project Implementation Costs ................................................... 20 3.2.3 Cash Flow Analysis ...................................................................................... 21 4 Proposed Project Management .................................................................................... 22 4.1 Statement of Work................................................................................................ 22 4.2 Key Project Assumptions and Constraints ........................................................... 23 4.3 Project team composition and organization ...................................................... 23 4.4 Work Breakdown Structure and deliverables per milestone ................................ 24 4.4.1 Activity duration ........................................................................................... 25 4.5 General Project performance metrics ................................................................... 26 4.5.1 Project Milestone Metrics ............................................................................. 27 4.5 Communication Plan ............................................................................................ 28 References ........................................................................................................................... 30 Appendices .......................................................................................................................... 33 Annex A: Statement on Collaborative Efforts in the Developing the Proposal............. 33 Annex B: Work Breakdown Structure elements ............................................................ 36
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
Introduction
Web 2.0 is the term that defines a broad range of computing experience for the consumer that is revolves around the social dimension of online users. It is not a specific update to browsing the World Wide Web such as what IP 6.0 does to the internet networking protocol. Rather, it describes a 21st century online experience that goes beyond mere web browsing. The internet is not more than just a mere source of information but has taken on a computing platform that harnesses broadband telecommunications and several online technologies to bring a level of interactivity and collaboration between users online, broadening the implications of online computing into the business and socio-political landscape (Swabey, 2008). Dale Dougherty of ORielly Media is credited for having coined the Web 2.0 term back in 2004 to simply put a title that would best describe an OReilly media conference (Musser & OReilly, 2008). Since then, the term has stuck to describe an online experience that transcended a mere trend for social networking in Facebook and Twitter, blogging with Tumblr and Googles BlogSpot, and media content sharing in YouTube, Picasa and Flickr, into a defining online computing landscape from which there is no turning back. It is precisely this ease with which content can become viral, reaching a potential global market as well as the marketing potential of the experience that has not escaped entrepreneurs who realized early on that Web 2.0 has not only revolutionized the way people use the internet, but also created a valuable channel to enhancing brand awareness and reach that traditional advertising could only dream about at tremendous cost to the business. This proposal looks at improving the operations of a major international airport the Brisbane International by optimizing its use of a few major Web 2.0 technologies that can make a profound difference to its business.
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
2
2.1
Current Situation
The Brisbane Airport Corporation (BAC) Considered the 3rd busiest airport in Australia after Sidney and Melbourne airports, Brisbane Airport (BNE in IATA code) is the only major passenger air terminal serving the residents and tourists of Brisbane and suburbs. It has two runways and two passenger terminals - a domestic terminal with flights to and from around 46 destinations in the Australian states and territories, and an international terminal serving 32 foreign destinations. The 12 months ending in May 2011 saw it serving more than 20 million passengers. The airport is a one of the major hubs of Virgin Australia where it
has a maintenance facility, and a secondary hub for Qantas and its budget affiliate Jetstar. Awards Since the dawn of the 21st century, the Brisbane airport has been the recipient of various awards starting in 2001 when the Australian Airports Association named it the Major Airport of the Year. In in the current year, the Australian Competition and Consumer Association (ACCC) honoured it as the top Australian airport for quality of service for the 8th consecutive year while Skytrax bestowed on it the Best Regional Airport Award, following the same awards it got in 2008 and 2009. In 2010, its international terminal wing received the Queensland architecture award and entered the 18th position in the list of the worlds top 25 airports while once again being voted by Skytrax as the "Best Australian Airport (Brisbane Airport, 2012). In 2005, the airport
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
earned the IATA Eagle Award, the second of only two airports in Australia to be so awarded (IATA, 2005), Ownership The Australian federal government has privatized several airports and the Brisbane airport was acquired from the Federal Airports Corporation by a private consortium consisting of private financial and government interests under the Brisbane Airport Corporation (BAC) led by Amsterdam Schiphol Airport which currently holds a management contract for airport on a 99-year lease of the facility.
2.2
Web 2.0 Business Implications Web 2.0 replaces the traditional view of a website as a channel for disseminating
digital information to browsed and consumed by the user, with one that sees websites as engaging tools for structured interaction between people and between organizations and people. Social media is a common, more meaningful alternative term that aggregates a panoply of Web 2.0 technologies behind blogs, wikis, social networks, social bookmarking, media file sharing, and news aggregation sites that are constantly evolving and recombining. The implications for business are numerous and have spawned the term Enterprise 2.0 for corporations as a counterpart to the consumer-centric Web 2.0. For starters, Web 2.0 changes the way customers interact with one another and that demands a change in the way businesses communicate and interact with their markets. A company website simply used an online product brochure is a wasted opportunity. More progressive companies are using Web 2.0/Enterprise 2.0 to stimulate discussion and community awareness around their brand, products and services, and are harvesting invaluable customer insight as a result.
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
The key implication of social media to the business in promoting a closer relationship between the business and its publics customers, government, other businesses, media, and the general public. For the Brisbane Airport, communication between these segments of society and the business is made more convneient by the fact that travel related information (flight arrivals and departures, airport weather and traffic condition, potential and actual delays, boarding routines, things to do while at the airport, etc.) can now be accessed from anywhere and at any time, using PCs at home and mobile devices such as smartphones and laptops with internet access. The same communication channel can be harnessed using social media marketing over wider market reach advertising but minus the regular advertising costs. Brisbane Airport can promote cost effective deals on behalf of airport business concessionaires and airlines with an active and far-reaching social media presence. These could result in added revenues to its business partners open up the option for the airport to earn sales commission from online bookings and online sales generated from a redirection of website traffic from its social media pages. User Awareness once in the airport Using Wi-Fi technology at the airport premises that can access a cloud database, passengers arriving thereat can be prompted to check on their travel requirements such as visas, the rules of what can be brought with them while on board or their destination, and provide them the easy channels to post feedback in regards to their travels via mobile gadgets. This creates a sense on interaction between the organization and the public the airport serves. Equally significant as the impact of Web 2.0 on consumers and customers are the implications for internal collaboration. That workhorse of internal communication email is looking decidedly tired as more effective and more efficient communication and
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
collaboration tools devised in the consumer realm work their way into corporate life., Because an airport is a mecca for airlines and their businesses (catering, aircraft maintenance, etc.), along with airport business concessionaires (car hire firms, restaurants, trade and cultural exhibitors, duty free shops and even health and recreational establishments), harnessing the social interactive power of Web 2,0 can bring these internal elements into a more cohesive and productive group acting towards a shared commitment with airport management as if they as employees of the airport itself. But some companies appreciate the business value of Web 2.0/Enterprise 2.0 than others. Companies like Dell and PlusNet use it to learn more about how they can serve their customers better. Others, like Wachovia Bank and Best Buy use Web 2.0 tools to help their companies and business partners work together more synergistically with improved social cohesion (Swabey, 2008). Every Web 2.0 application shows why it is imperative for the company, particularly its information technology departments to understand and harness Web 2.0 from a technical and social perspective. By enabling collaboration and fostering closer relationships with their stakeholders (markets and publics as well as governments and business partners), Web 2.0 empowers the business to bring its marketing, customer service and business development activities to better economies and cost efficiencies.
2.3.
Web 2.0 in BAC The company is open to adapting emerging new technologies in its business
operations. In a press release issued by Cisco (2012), the Brisbane Airport Corporation has implemented virtualization technology from network solutions provider Cisco, storage solutions provider EMC and virtualization software provider VMware to strengthen the company ability to enhance economies of airport operations and customer responsiveness
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
through strategies harnessing emergent technologies information and communications technologies (ICT). But along with this, just exactly how far Brisbane Airport has arrived in harnessing Web 2.0 or Enterprise 2.0 as a means to further the ends of its business imperatives is seen by its current social media activities (Abady, 2012). The BAC has established a relatively wide social media presence with the following: Mobile version of official website enabling mobile users to check flight details using smartphones with internet access; Official Facebook page in standard format and linked to the corporate website Official Twitter account; and Official Pinterest account Having said that, the airports social media presence can stand significant improvements in the way it interact with its customers and airport concessionaires. For instance, their mobile website version displays flight arrival and departure details. However, given the fact that over 20 million foreign passengers have used or passed through the terminal in 2011/12, it should not be that difficult to incorporate a language selection options for passengers on the existing mobile phone application (see Figure 1). This is more of a feature enrichment rather than an innovation as most online services catering to several nationalities generally have some form of language transcription that can cater to people that do not use English as their first language. There is currently a gap in marketing infrastructure of Brisbane Airport Corporation that social networking platforms such as Facebook, blogging and social media
Figure 1: Mobile apps accessing BAC flight information
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
10
sharing could help close. Facebook can essentially be used like a live wiki for thousands travellers who are Facebook users who may want to be remain updated by simply clicking one button and getting linked to the official Brisbane Airport page. The type of information that the Airport can share on Facebook can be extremely broad, ranging from quick facts about the airport and say its baggage procedures and limitations to Updates on the Traffic and congestion troubling the primary routes in and out of the facility. There is great room for improvement within the relationship and closeness that the consumers feel towards the airport. Brisbane Airport is a large multi-faced business that needs to leverage communicative competence in bringing together the disparate business concession operating within the pre-departure, post-departure and transit experience of passengers. Using social media to enable the Brisbane Airports marketing strategy could aid in helping establish a better relationship with the thousands of travellers who use social networks as well as employees working in the airport. Social networks are all about crating and sustaining a feeling of connection that keeps users logging in every day or several times in a day and while the Brisbane Airport has already gained a foothold into the social media bandwagon, there is ample room to make this presence grow to its optimum potential.
2.4
Business Needs Analysis An exhaustive analysis or assessment of business needs is a fundamental
diagnostic process to determine root causes of current problems and situations that can prepare the company in exploring and evaluating various alternatives in solving these problems, filling in proficiency or competency gaps or market expectation and real-world service quality gaps, and addressing the needs that can enable the company to better achieve its business objectives. For the Brisbane Airport Corporation, the current
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
11
situational analysis using a Strengths, Weakness, Opportunities and Threats (SWOT)) analytical framework has been used to identify the major areas when Web 2.0 can be harnessed to maximize the companys business potential in its target markets (Weihrich, 1982). In addition, the PESTLE framework which explores in more detail the external factors can feed right into the opportunities and threats in the SWOT analysis (JISC, 2012). These are the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal and Environmental factors that may be missed if only the SWOT was used (Thomas et al, 2007).
Table 1: SWOT Analysis
SWOT Areas Strengths
Assessment The Airport is a major domestic and international hub for several airlines in the Brisbane metropolis serving as a gateway to Queensland, the region and the world. BNE is seeing an increase in visitor arrivals going through the airport totalling 1.8 million or an increase in 2.7% year on year as of September 2012 (BNE, 2012). The company has a relatively strong but static online presence through its corporate website at www.bne.com.au where BNE customers can check on flight information, travel news in Brisbane, and access information on various travel related topics while in the airport The airport has been at the forefront of social media as it recently became the first Australian airport to use Pinterest which has a reported 8.9 million views in the country in February 2012. This was it third social network after Facebook and Twitter.
Weaknesses
There is no effective internal communication that can link airport management to its business concessionaires (car rentals, duty free shops, restaurants and lounge operators, airlines booking offices)
Opportunities
Web 2.0 technologies have yet to be fully harnessed;
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
12
A stable and growing national economy that portends a sustained recovery from the global recession as evidenced by recent increases in passenger arrivals in the airport
Threats
The airport has little competition in the area other than those that function as alternate or feeder airports such as Sunshine Coast. Gold Coast, Toowoomba, Ballina/Byron Gateway and Lismore airports.
Table 2: PESTLE Analysis
PESTLE elements Political
Factors Healthy business relationships exist between the company and local Brisbane authorities as well as commercial firms engaged in concessionary business within the airport premises.
Economic
Strong macroeconomic fundamentals with rising GDP and improving unemployment rate ensure a local economy slowly recovering from the onslaught of the global recession over the last three years.
5.1% unemployment rate as of 2011, improving slightly from the 5.2% registered in 2010. But among the youth sector (aged 15-24) unemployed stood at 11.6% during the same period. (Index Mundi 2012).
Brisbane is experiencing modest but stable growth in visitor arrivals which totalled 1.8 million for a year on year increase of 2.7% year as of September 2012 (BNE, 2012a).
Social
The airport has a thriving list of business concessions such as car rentals, restaurants and shops that together serve passengers while going through the airport.
It has a growing involvement in social networking groups such as Facebook, Twitter and recently joined Pinterest dedicated for online users who love or enjoy air travel (BNE, 2012b).
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
13
Technological
Strong internal IT infrastructure and development support for inhouse application systems using existing computing and database platforms
There is a growing social media penetration rate among internet users and this can be harnessed more fully by the company Cloud computing which is a form of IT outsourcing when used from a 3rd party provider is emerging as the new way of supporting the business for improved economies of scale that effectively makes unnecessary the traditional continuous investments in hardware and software during system upgrades (Hogan, 2008).
Legal
Copyright violations increase with user-generated content in Web 2.0 (Ingram. 2010). The issues revolve around managing userdeveloped or collaborated content and ensuring that the copyright of others is not infringed in the process. This often requires a more conscientious monitoring of critical social media content like images, music and video whose owners are known to enforce copyright ownership rights.
Social media often comes with personal information as in the case of user profiles and photos in social networks and face the potential risk that such information are used without securing explicit permission from their owners. Web 2.0 implementors will have to exercise more diligence and care about protecting the privacy of individuals. (Thomson, 2008).
Web 2.0 content risks being compromised by malicious users who may post pornographic, licentious, hateful or racially derogatory materials. Constant monitoring of the site can prevent such materials from defacing the site.
Environmental
The company has not highlighted its greening or eco-friendly efforts to general more support from greening enthusiasts among its passengers. Further studies will be conducted in this area to identify areas for improvement and inclusion as an airport feature for its social media marketing efforts.
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
14
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
15
3.
3.1 Description
Web 2.0 Solution Proposal
The online experience generated by the Web 2.0 phenomenon for consumers and Enterprise 2.0 for business takes advantage of several technologies that have emerged over the last decade most prominent of which is the increasing affordability of broadband internet telecommunications, and the ease with which online media content can be generated by ordinary users. This has effectively transformed cyberspace from merely a static browsing experience into a media-rich collaborative computing experience that truly empowers its users (Blue Coat, 2011; McAfee, 2010). The technologies behind the Web 2.0 trend covers social networking (Facebook, Google+, MySpace, etc. where interaction between friends, colleagues and acquaintances create a social dimension to the online experience), Wikis (collaborative engagement online allowing users to share and edit content), blogs (participative engagement that allows users to assess and appraise content presented by individuals or groups online for specific focused topics), and media content sharing such as YouTube where user can share multimedia content (Thomson, 2008) that has made YouTube a search engine second only to Google in terms of being the most frequently visited site for online search purposes (Stokes, 2012). Other technologies include podcasting, news alerts, and social bookmarking but for purposes of this proposal, not all technologies are proposed as being suitable for a company that is just starting to create a social media presence. The business proposal recommends the following: 1. Blogging is proposed as a complement to social networks and its website extend the interactive communication reach of social media, enabling companies to benefit from market feedback and insights that take the place of commissioned
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
16
expensive market research works to improve their merchandise and services. , and widen the brand awareness of the company and potentially convert online traffic into more sales revenues (KISSmetrics, 2012). Blogs create a venue for real-world experiences on products and services that companies can capture freely and has grown to become a global pastime among online users with more than 110 million blogs as of 2008 and growing (Mayfield, 2008). 2. YouTube marketing using short videos about the company and its accomplishments, news and ongoing projects that can immensely improve the online search presence of the company. YouTube is the 2nd largest search engine on the internet with an estimated 100 million videos viewed each day (Mayfield, 2008; Skwire & Teppema, 2012). Half of YouTubes 300 million worldwide users access the site at least once a week making 2.8 billion searches monthly (Stokes, 2012). Posting videos about Brisbane Airport and its role in the tourism and business travel industry as well as related news can take advantage of this reach as a more cost effective advertising model 3. Enhance and fine-tune the companys social networking presence by creating and developing a Google+ social networking presence to complement its Facebook account. With the Google BlogSpot/Blogger presence incorporated into it, this social media presence is expected to promote and further widen the brand awareness of the services provided by the airport. Over the last 10 months after its inception in June 2011, Google+ has shown phenomenal growth outpacing that of Facebook and twitter with 170 million active users (Gonzales, Cuevas, Rejale & Cuevas, 2012), and as of reaching its first birthday in July, Google announced the site has 250 million users (Olander, 2012).
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
17
4. Harness the revenue earning potential of social media marketing by taking advantage of the social behaviour of users. For instance, every Facebook user brings with him an estimated 120 friends and colleagues on average (KISSmetrics, 2012). This potential information cascading opportunity for a product or service endorsement has not escaped savvy marketers to generate a positive down line awareness that fosters the marketing potential of advertising in social networks (Leskovec, Adamic, and Huberman, 2006). 78% of consumers prefer the recommendations in social networks which gives social media a significant advantage over traditional advertising models (KISSmetrics, 2012), making social media the darling among advertisers and marketers. In this regard, the BAC can harness this social behaviour to make product and service endorsements for its business concessionaires and airline operators in the airport premises. 3.1.1 Identified Business Drivers
The following factors have been identified as key drivers in further enhancing the BAC social media presence by harnessing popular and innovative Web 2.0 technologies for both its external and internal stakeholders (passengers or commuters, and employee / consignees). Harness the communicative powers of social media and its reach in creating and sustaining and wider awareness about the role of Brisbane Airport to its passengers, surrounding communities, the government and to the countrys tourism programs. The business concessionaires at the Brisbane Airport can benefit from have a shared access to a common communication platform with which they can access information that can benefit them, the airport and the passenger going through the terminal. For instance, coordination can be made between airlines and airport managers to ensure flight times and passenger turnout are communicated
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
18
through alerts on smartphones and laptops of concerned parties to ensure that enough manpower can man car rentals, food concessionaires and baggage handlers. In times of emergencies, coordination can be instant as information can be updated and immediately accessible to every stakeholder. While the current social media presence is not meant to generate additional revenue streams directly, but more as a tool to improve communication between the company and its publics, there is the potential for social media to generate direct income through commissions in the sale of products and services that have a presence in the airport premises. 3.1.2 Objectives
The project aims to establish a more robust and active Web 2.0 computing environment for the Brisbane Airport Corporation with the following specific objectives: Objective Optimize marketing communications potential through a wider social media presence Outcome Use of Google+ for a wider social networking presence that can be harnessed for marketing and PR purposes Creation of blog sites to engage the public to actively share comments and suggestions on company products and services Creation of a more intense YouTube marketing presence that can replace advertising spend on tradition print and broadcast media Measure User base to exceed 30,000 within the first 6-8 months from launch At least 12 active blog feedback per day after the 4th month of implementation Generate no less than 20,000 aggregate views for the corporate video materials posted in YouTube within the 6 months of launch; and Reduce advertising placement spend on TV and print by 40 % within the same period. Incremental sales of $100,000 for the first year of operation with a conservative 15% increase every year thereafter.
Augment revenue stream through online sales commissions from
Signed contract with business concessionaires to provide a 2%5% commission on sales generated from local and
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
19
airport concessionaires
international traffic to their websites directed from any social media site of Brisbane Airport
3.2
Cash Flow Analysis 3.2.1 Projected Benefits
The proposed Web 2.0 enhancement to the business is expected to generate benefits that are qualitative and quantitative n natures with primary and secondary benefits in each as shown in Table
Table 3: Project benefits
Qualitative Quantitative Enhancing social media presence Primary Wider reach of information about Fewer passenger inquiries at the the airport, local aviation news, its airport on flight schedules, airport plans and project and other matters taxes, documentation that concern the passengers going requirements, etc. since these are through the airport. now available online Secondary Better market perception about the Increased user base for social company, further boosting the networking sites for the airport goodwill of the airport name driven by its constant communication with its passengers and stakeholders, Augment revenue stream through online sales commissions Primary Enhanced e-commerce value for Generate commission sales the website and social media revenues of at least $100,000 with presence a 15% annual increase Secondary Foster better business relationships Retention of high value business with airport concessionaires concessionaires with no more at least 10% increase in their aggregate sales the airports social media referrals.
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
20
3.2.2
Anticipated Project Implementation Costs Assumptions
No additional manpower is needed for the project or in the implementation itself; current staff handling the social medial activities will be involved in the project and additional internal users will be harnessed to ensure that market feedback from social media sites are responded do even outside of office hours. To these end, several units of iPads will be provided to them as initial equipment that will enable them to engage in social media concerns even at home.
Technical specifications for PC Tablet (Apple iPad2) purchases will be valid within 6 months from submission of this proposal. Hence immediate purchase is recommended as soon as possible considering the high obsolescence rate of these
Table 4: Estimated project cost components
Project Cash Out (Year 0) Web 2.0 Project Tablets for key personnel to maintain the proposed social media presence 24x7 (30 units of iPad2 units at $530 each (1) Allowance for Software licences for standard Apple iOS and apps (at an estimated $300 per iPad2 unit) Social media upkeep 3 Party Consultancy Service Project Management Project Manager Training (allocation) Collaborative Online Service Total Contngency (20%)
rd
Hardware
Software licensing
People
Consultant
Planned Budget ($)
15,900
15,900
devices in the
9,000 sunk cost 12,000 9,000 0 12,000
sunk cost 10,000 freeware
0 10,000 0 46,900 9,380
Total Year 1 Cash Out
(1) Reduced Apple iPad2 prices as of March 2012, based on Engadget site at http://www.engadget.com/2012/03/07/apple-drops-ipad-2-price-to-399/
56,280
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
21
market, usually in 8-14 months. Exchange rates and inflation rates will remain relatively stable throughout the project duration with no more than 5% fluctuation. Purchase prices are valid within three months of this proposal. 3.2.3 Cash Flow Analysis
This proposal assumes an incremental increase of 15% of commissions revenues resulting from online purchases of items from visits directed or emanating from a visit to any of the Brisbane Airport social media sites. The current base income is also assumed to be $100,000 which has been conservatively estimated. In the absence of a company
Table 5: Cash flow
Cash Flow Analysis Years Investment Cost of Capital Incremental Revenue over previous year Sales (15% annual increase from base year's incremental commission income of $100,000 ) Cash Flows Discounted Cash flows Cumulative Net Cash Flow Discounted Payback Period Net Present value (NPV) Internal Rate of Return (IRR) Modified IRR (MIRR) Profitability Index (PI) Current Year 0 56,280.0 7.1% 10.0% 1 2 3 4 5
15,000.0
16,500.0
18,150.0
19,965.0
21,961.5
15.0% 100,000.0 -56,280.0 -56,280.0
15,000.0 17,250.0 19,837.5 15,000.0 16,500.0 18,150.0 14,012.1 14,398.3 14,795.1 -42,267.9 -27,869.6 -13,074.5 N/A N/A N/A N/A
22,813.1 19,965.0 15,202.8 2,128.2 3.9
26,235.1 21,961.5 15,621.7 17,750.0 N/A
16,581.0 17.43% 13% 0.74
preferred a weighted average cost of capital (WACC), the cash flow analysis used the prevailing average of 7.05% for several markets as calculated by Damodaran (2012). From this assumption, a cash flow analysis on Table 5 clearly shows that the project will pay for itself in less than for years based on a discounted payback period computation. It has positive NPV and its IRR exceeds the current cost of capital (7.05% rounded out in the table presentation), both indicative of project that has acceptable business value for the company. The revenue assumption will have to be validated after the first year, but this quantitative assessment can be insignificant compared with the
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
22
qualitative value of achieving a wider communication reach among the companys stakeholders that the proposed Web 2.0 technologies promise.
4
4.1 Statement of Work
Proposed Project Management
Over a period of 12 months, the project team will implement the various webbased technologies to enable the company to harness the Web 2.0 or Enterprise 2.0 computing platform and create the application web experience for its customers. The Web 2.0 umbrella project covers the following: (1) Blogging: Using Googles BlogSpot/Blogger, create blog sites to provide closer interaction between customers and the company. (2) Improve Facebook presence: Fine-tune the corporate Facebook presence to present the company products and services, news and industry developments, as well as customer feedbacks to create a positive impression that the company values its markets. (3) Create Google+ social networking presence that incorporates its blogosphere presence for optimum market reach and ability to extract passenger feedback and reaction to airport services provided by the company (4) Implement YouTube Marketing. Develop short 10-30 second advertising and advertorial content about the company products and services, history and programs, people profiles, and other relevant materials that can be used to promote the company name and thus create branding preference.
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
23
4.2
Key Project Assumptions and Constraints The project will have the following assumptions and constraints or limitations: The project team members are stakeholders in the organization and will be directly involved in operating and using the proposed Web 2.0 computing technologies as proposed for at least 3 years from the successful implementation of the project The system vendor (s) in the supply chain for the project will cease to operate during the system implementation. The implementation will result in the decommissioning of the various existing computing systems that are replaced throughout the companys operations. Project funding may be increased within 20% as approved by the project sponsor The project has a 12-month timeframe, ending on or before 10 December 2013. The project deliverable will comply with approved policies of the company where applicable unless otherwise rescinded for purposes of accommodating any new procedural requirement as may arise from its implementation.
4.3
Project team composition and organization It is recommended that the project team be constituted as multi-disciplinary multi-
departmental team with members coming from marketing, public relations, direct customer-facing operations and IT departments. There will be a collective ownership of the project with tasks that are spread among these stakeholders. The project will follow the standard project management team organization which calls for a division of labour within the team. Figure 2 illustrates the organization structure with members from the organization and representatives from an IT consultant or vendor who can work with the
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
24
team to guide it in both technical and functional areas. In addition, there is a need to activate or create an oversight body such as steering committee that can provide high management support for the project in terms of project funding, strategic change management approvals, and status monitoring to ensure that the project is completed as expected.
Figure 2: Project team organization chart
Project Steering Committee (Heads of Operations, Finance, IT and other invited corporate decision makers and stakeholders)
Leadership Project Manager (1) Support
System Documentation Specialist (2)
IT Consultant / Vendor Representatives (1)
IT Department Representative (1)
Direct
Public Relations Lead (1) Blogging Development Lead (1) Media Content Lead (1)
Staff (3)
Staff (3)
Staff (3)
4.4
Work Breakdown Structure and deliverables per milestone Table 6 summarizes the projects milestones and their respective deliverables.
Table 6: Project WBS milestones and deliverables
WBS Task Name
Deliverables
1 2 3 4
Approve Project Create project team Acquire Tablets (ipad2 or equivalent) Develop and activate Google +
Approved project budget and signed contract with consultant Complete project team Trouble free iPad2 Tablets Activated BAC Google+ site
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
25
5 6 7 8
Create and activate commissions-based revenue sharing in BAC website Create and activate YouTube Account Activate Blogging presence Turnover project to operations
Enhanced website for commission-based revenue streams At least 12 15 YouTube video content
Activated BlogSpot site
Project Completion with user sign-off
4.4.1
Activity duration
Table 7 shows a high level activity Gantt chart for the milestone tasks calculated from MS Project and summarized using MS Excel worksheet for this paper. The project WBS details are in Annex B. This proposal aims to start the project after the Christmas holiday rush and the second week of January 2013 is the target start. The project is expected to last until the first week of December 10`3, just before the holiday season, with a cumulative contingency of plus or minus 20 days to accommodate delays in any of the milestone tasks.
Table 7: Project milestone task duration high level Gantt chart
Months 1 2
WBS Task Name Duration Start Finish
10
11
12
1 Approve Project 2 Create project team 3 Acquire Tablets (ipad2 or equivalent)
11 days? 76 days 92 days 57 days
Mon 1/7/13 Tue 1/22/13 Tue 1/22/13 Wed 5/8/13 Thu 5/30/13 Thu 5/30/13 Thu 5/30/13 Thu 9/12/13
Mon 1/21/13 Tue 5/7/13 Wed 5/29/13 Thu 7/25/13 Wed 9/11/13 Wed 9/4/13 Fri 9/6/13 Fri 12/6/13
4 Develop and activate Google + 5 6
Create and activate commissions75 days based revenue sharing in BAC Create and activate YouTube Account 70 days 72 days
7 Activate Blogging presence
8 Turnover project to operations 62 days Total
Approximately 12 months
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
26
4.5
General Project performance metrics The proposed Web 2.0 business improvement project will have performance metrics
that quantitatively assess the performance of the team, individually and collectively by the Project Manager or in tandem with existing work performance measures implemented by the company HR department. But the basic measures will include meeting budgets, deadlines, and the planned or anticipated quality and quantity of deliverables. These metrics include the following:
Table 8: Project performance metrics
Areas Team Performance
Metrics Attendance not more than 10% lost time within a week due to aggregate tardiness or absences in any project activity that includes presentations, staff meetings, and engagements with 3rd party suppliers and corporate departments. This translates to no more than 2 days unplanned absence in a month. Any tardiness is recorded and compensated for by leaving late for home. This is expected to maximize the members utilization in the project. 100% compliance with computing security standards. This requires the use of automatic screen blanking or screensaver, computer lockout, and auto log out from the company network as well as the use of secure VPN (Virtual Private Network) when telecommuting. This ensures security of user data, significantly reducing the risk of anyone eavesdropping into member PC when not around. Quality of 100% compliance with the objectives set for each planned deliverables deliverable. No more than10% error rate in data accuracy, syntax, spelling and diction in generating reports for internal and external use. Time Management Deadlines of project deliverable to be met 90% of the time. The Performance 5% instance when deadlines are not met should not exceed more than 20% of the allocated time for the task to be completed. This means that a two-day delay can be tolerable in a 20-day task duration, provided that the down line task that depends on the delayed task will not be severely penalized by the delay. Towards this end, the tasks have built-in slacks as contingency for unplanned events that could cause a delay. Every effort must be done to ensure that down line tasks can absorb delays in a
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
27
Cost Performance
Ethical Conduct
previous tasks to which they depend. Not more than 10% cumulative budget overrun for the entire project budget as initially approved. This ensures a tight reign over project expenses to ensure the project will not go overboard unless absolutely demanded to complete a project deliverable. Nevertheless, any unplanned upward cost adjustments will require approval by the steering committee. 100% compliance with workplace ethics as defined by HR. Zero complaints from external stakeholders (higher management, consultants and suppliers) on ethical conduct or behaviour of team members, shortfalls in expected commitments and deliverables, on time start of meetings, etc. Zero incidence of misdemeanors resulting in local police or court action. Zero complaints from fellow team members about violent, intimidating, abusive or generally offensive behaviour.
4.5.1
Project Milestone Metrics
Each milestone will be marked with a status progress report to be provided to the project sponsor or the project steering committee. The metrics of each milestone differ based on the expected deliverables as indicated in Table 9. Some of the metrics, such a signed contract are essentially the main deliverables expected in a milestone and their availability on the expected date will comprise a positive metric result for the team.
Table 9: Milestone Metrics
WBS Task Name
Metrics
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Approve Project Create project team Acquire Tablets (ipad2 or equivalent)
Develop and activate Google + Create and activate commissions-based On-Time completion of task revenue sharing in BAC website Create and activate YouTube Account On-Time completion of task Create and activate blogging presence On-Time completion of task Complete user confidence through a sign-off on Project turnover to users committed date
Project budget as planned and signed contract with consultant on the committed date Complete project team members iPad2 tablets with 0% returns or warranty calls within 12 months. On-Time completion of task
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
28
4.5
Communication Plan The project will generate regular project status reports as well as generate
summaries for fulfilment reports from 3rd party vendors and consultants, both of which will be presented to project stakeholders consisting of project sponsors, management and team members with the objective of ensuring a smooth flow of information that is needed by them for appropriate action or fore purely informational purposes. Towards this end, communications channels shall be supported by both tradition channels such as No project can be implemented with any success unless the results and anticipated problems in the project are communicated clearly within the group and to its external stakeholders such as project sponsors in higher management (Charvat, 2002).
Table 10: Communications Project Plan
Information Project status and deliverables report
Author Project Manager
Frequency Weekly and Monthly
Key Audience Steering Committee, Team members
Action (I,C,A) I,C
Communication Channel Presentation in regular meeting via PowerPoint, emailed document or through shared document access in Google Docs. Emailed document or through shared document access in Google Docs. Emailed document or through shared document access in Google Docs
Vendor delivery report Issue and problem log and resolution
Vendor
As Needed
Project Manager
I,C
Project Manager, ERP Vendors
Monthly or as required
Steering Committee, Departments Heads depending on the nature of issues to be resolve Project Sponsor, V{ Finance, HR Director, IT Director and Team members HR Head and to each team member Project Manager
I,C
Contingency and Risk Mitigation Plan
Project Manager
Start of project and with new risks identified Weekly and Monthly Weekly, Monthly,
C,A
Emailed document or through shared document access in Google Docs
Project team performance assessment Actual vs. Budget expense report
Project Manager Accounting Head
I,C
Weekly staff meeting
I,C
Weekly staff meeting
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
29
Information Internal policy and standards change recommendations Request for additional budget
Author Project Manager Program Manager
Frequency As required
Key Audience Steering Committee Project Sponsor
Action (I,C,A) A
Communication Channel Reposited in Google Docs for online access Special presentation to Steering Committee with advanced emailed documentation
As required
Key: I: Information only; C: For review and comments; A: For review and approval
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
30
References
Abady, T. (2012). Social Networks at the Brisbane Airport and a way forward Retrieved from http://thadreina.wordpress.com/2012/10/08/social-networks-at-the-brisbaneairport-and-a-way-forward/. Blue Coat. (2011). Technology primer: Web 2.0. Sunnyvale, CA.: Blue Coat Systems, Inc. Retrieved from http://www.bluecoat.com/sites/default/files/documents/files/bcs_tp_Web20_v3b.pdf BNE (2012a). Visitor markets to BNE see significant growth in August, Media Centre, Brisbane Airport. Retrieved from http://www.bne.com.au/news/visitor-markets-bnesee-significant-growth-august. BNE (2012b). BNE first Aussie airport to join pinning craze. Media Centre, Brisbane Airport. Retrieved from http://www.bne.com.au/news/bne-first-aussie-airport-joinpinning-craze BNE (2012c). Awards. Media Centre, Brisbane Airport. Retrieved from http://www.bne.com.au/corporate/about-us/our-company/awards Charvat, J.P. (2002), Project communications: A plan for getting your message across. Tech Republic. Retrieved from http://www.techrepublic.com/article/projectcommunications-a-plan-for-getting-your-message-across/1061894, CISCO (2012). Brisbane Airport Corporation Selects Cisco, EMC and VMware to Virtualize the Data Center for Increased Business Agility and Streamlined Operation. Retrieved from http://newsroom.cisco.com/press-releasecontent?type=webcontent&articleId=980427. Damodaran, A. (2012). Cost of capital be sector, Updated January 2012. Retrieved from http://people.stern.nyu.edu/adamodar/New_Home_Page/datafile/wacc.htm Dreiling, A. (2012). Airports Where next? Brisbane Airport Corporation and Queensland University of Technology. Gonzalez, R., Cuevas, R., Rejale, R., & Cuevas, A. (2012). Google+ or Google-?: Examining the Popularity of the new OSN. Retrieved from http://arxiv.org/pdf/1205.5662v2.pdf Hogan, M. (2008). Cloud Computing & Databases: How databases can meet the demands of cloud computing ScaleDB, Inc. Retrieved from http://www.scaledb.com/pdfs/CloudComputingDaaS.pdf Index Mundi (2012), Australia economy profile 2012. Retrieved from http://www.indexmundi.com/australia/economy_profile.html Ingelvaldson, P. (2010). Why an IT Steering Committee should be Mandatory. Center for CIO leadership, Dec 3, 2010. Retrieved from
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
31
http://www.cioleadershipcenter.com/community/center_blogs/blog/2010/12/03/whyan-it-steering-committee-should-be-mandatory Ingram, R, (2010). Legal issues in Web 2.0 and cloud computing. JISC. Retrieved from http://rspproject.wordpress.com/2010/12/01/legal-issues-in-web-2-0-and-cloudcomputing/. JISC (2012). Tools & techniques: Pestle and SWOT analyses, for JISC InfoNet, Northumbria University. Retrieved from http://www.jiscinfonet.ac.uk/tools/pestleswot. Leskovec, J, Adamic, L.A., & Huberman, B.A. (2006), The dynamics of viral marketing EC, pages 228237. Mayfield, A. (2008). What is social media? iCrossing eBooks,, Retrieved from http://www.icrossing.co.uk/fileadmin/uploads/eBooks/What_is_Social_Media_iCr ossing_ebook.pdf. McAfee. (2010). A complex balancing act: The first global study on Web 2.09 usage, risks and best practices. Retrieved from http://www.mcafee.com/us/resources/reports/rpfirst-global-study-web-2.0-usage.pdf. Musser, J., & OReilly, T. (2008). Web 2.0 Principles and Best Practices, Fall 2006, OReilly Radar. Retrieved from http://oreilly.com/catalog/web2report/chapter/web20_report_excerpt.pdf Skwire, D.D., & Teppema, S.C. (2012). Being social Its a game changer, Paper presented at the Health Meeting 13-15 June 2012 of the Society of Actuaries. Stokes, R. (2012). Ch.13: Video search engine optimization, in Marketing: The essential guide to digital marketing (4th Ed). Troy, MI: Quirk Publishing, Swabey, P. (2008). Web 2.0 in business. Information Age. Retrieved from http://www.information-age.com/channels/informationmanagement/features/650221/web-20-in-business.thtml Thomas, G, Gawn, J, & Vaughan, D 2007, Marketing report: New business venture in Slovenia, viewed 28 July 2012, http://projects.daibach.co.uk/uni/uploads/EBMM10MarketingReport.pdf. Thomas, JW 2007, Market Segmentation, Arlington, Decision Analyst. http://www.decisionanalyst.com/Downloads/MarketSegm.pdf Thomson, H. (2008). Wikis, Blogs & Web 2.0 technology. Copyright & Information Policy, University of Melbourne Information Services. Retrieved from http://www.unimelb.edu.au/copyright/information/guides/wikisblogsweb2blue.pdf
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
32
Olander, D. (2012). On Google+ growth, Google says were pleased. The Next Web (TNW), July 2012. Retrieved from http://thenextweb.com/google/2012/07/19/ongoogle-growth-google-says-were-pleased/ Weihrich, H. (1982), The TOWS matrix: a tool for situational analysis. Long Range Planning, 15(2), 54-66.
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
33
Appendices
Annex A: Statement on Collaborative Efforts in the Developing the Proposal The project called for developing a suitable Web 2.0 proposal for the Brisbane Airport and required input in the following areas: (1) a background on Web 2.0, (2) brief about Brisbane Airport and its current situation, (3) the proposed solution, and (4) the project management. The three members of the team were assigned specific areas without exclusivity and all of them collaborated to improve any area or all areas in the paper. Toward this end, the team used Google Docs which allowed them to share information in the form of PDF, JPG images and MS Office files for sources, but more importantly, provided a collaborative editing platform where members can download, edit and reupload the paper in progress. The website provided ready accessibility through the latest versions of Internet Explore and Firefox as the teams preferred browsers for desktop PCs and laptops. In addition, one team member used an Android smartphone to check and view the latest revised documents while another used an iPad (with Safari browser) to view the documents and PDF files used for references. All the team members have Gmail addresses which already gave them access to Google Docs. The free use of Google Docs had a limit of 5 GB for uploaded files which was more than was needed considering that the proposal document only ate less than 1 MB, while the sources and drafts in the directory occupied less than 1 GB in total. In addition 10 concurrent users were allowed which was just fine since the team only had three members. The initial proposal draft served as the master draft that was uploaded in Google Docs using the team leaders account for private use with the team members authorized to access the document for offline concurrent editing. File version numbers were the most
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
34
important aspect in the current work in Google Docs or any collaborative editing tool so that any other members will immediately recognize the status of the document he or she was working on and who made the last changes. Google Gears which alerted the document owner for changes was not used. Instead, team members updated the document offline and re-uploaded them using a file naming convention representing the latest updates to the master draft as follows: File naming convention BAC_1.0 Description BAC: The main filename for the Brisbane Airport Corporation proposal master draft. 1.0: Main file version number as drafted by the team head and uploaded in Google Docs to be worked on by the team members. 1.1: File version number incremented as a second level after a partial revision done by a team member and upload back to Google Docs Drew: Name of the team member who made changes or revisions to the file 1.1.2: If the revision made in 1.1 was further edited or changed by another team member, in this case by Elise, then a third level version number is appended. In the example, there were already two revisions made on the 1.1 version to become 1.1.2. 2,0: Incrementing the main file number means that the team head has edited the latest draft containing the various updates made by the team members and reuploaded to Google Docs for another round of review or, if no changes are made, are accepted as the final version of the document
BAC_1.1_Drew
BAC_1.1.2_Elise
BAC_2.0
A team member was free to proofread and edit any part of the paper and uploaded the edited paper according to the described file naming convention described. While each member has a responsibility for certain parts of the paper, this was not exclusive and any member could edit or improve on any part of the paper. Google Docs significantly facilitated and hastened the completion of the proposal and while there were initial minor problems, it was just a matter of referring to the help guides to get it right and using offline
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
35
editing so as not to complicate the learning process when using the sites realtime online editing features. A member simply texted the other members over the cellphone when an update was uploaded.
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
36
Annex B: Work Breakdown Structure elements Using MS Project Management, the Work Breakdown Structure was developed to arrive at a realistic task duration and timeline that can be used to generate a Gantt chart and a Critical Path in the application. The MS Project file can is attached here.
WBS Task Name
Duration
Start
Finish
1 1.1 1.3 1.2 2 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 3 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 4 4.1 4.2 4.7 4.3
Approve Project Present project plan to steering committee and secure working approval (budget and team) Sign contract with consultant Create project accounting elements for expense accounting Create project team Finalize shortlisted team candidates Select and process team members Present team to management Conduct bonding sessions among team members Brief team members re project details, expectations and responsibilities Train team members on Web 2.0 technologies Acquire Tablets (ipad2 or equivalent) Define and finalize technical specifications for purchase order Disseminate requests for tenders or negotiate terms with accredited suppliers Identify users to be assigned a tablet for social media engagement outside of office hour. Process supplier payment Receive and distribute iPads to authorized users Conduct tests on Social media access from Tablets Develop and activate Google + Define media content requirements in Google+ Create account and develop site Develop media content or re-use existing content from Facebook Identify persons authorized to access and administer the site
11 days? Mon 1/7/13 10 days 1 day 1 day 76 days 15 days 5 days 1 day 10 days 5 days 40 days 92 days 10 days 30 days 10 days 10 days 15 days 11 days 57 days 10 days 30 days 15 days 5 days Mon 1/7/13 Mon 1/21/13 Mon 1/21/13 Tue 1/22/13 Tue 1/22/13 Tue 2/12/13 Tue 2/19/13 Wed 2/20/13 Wed 3/6/13 Wed 3/13/13 Tue 1/22/13 Tue 1/22/13 Tue 2/5/13 Wed 4/10/13 Tue 2/5/13 Tue 2/19/13 Wed 5/15/13 Wed 5/8/13 Thu 5/30/13 Wed 5/8/13 Wed 6/19/13 Wed 7/10/13
Mon 1/21/13 Fri 1/18/13 Mon 1/21/13 Mon 1/21/13 Tue 5/7/13 Mon 2/11/13 Mon 2/18/13 Tue 2/19/13 Tue 3/5/13 Tue 3/12/13 Tue 5/7/13 Wed 5/29/13 Mon 2/4/13 Mon 3/18/13 Tue 4/23/13 Mon 2/18/13 Mon 3/11/13 Wed 5/29/13 Thu 7/25/13 Wed 6/12/13 Tue 6/18/13 Tue 7/9/13 Tue 7/16/13
Web 2.0 Business Improvement Proposal
37
4.8 5 5.1 5.4 5.2 5.3 5.5 6 6.3 6.2 6.4 7 7.1 7.2 7.3 8 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4
Initiate and conduct tests of site Create and activate commissions-based revenue sharing in BAC website Identify business concessions for sales commissions as referred by BAC site Negotiate commission rates as applicable Create and develop website for sales referrals Activate online automatic payment systems Test commission revenue online system Create and activate YouTube Account Identify authorized users to update YouTube Develop video content based on ad materials and archive Test video functionalities Activate Blogging presence Create and develop blogging account in Blogspot Develop unique text and media content Create initial blogging content and engagement with market feedbacks Turnover project to operations Conduct omnibus system test Conduct user training for each social media channel as necessary Present final project accomplishment report User acceptance
7 days 75 days 15 days 30 days 10 days 5 days 15 days 70 days 5 days 60 days 5 days 72 days 12 days 30 days 30 days 62 days 15 days 45 days 1 day 1 day
Wed 7/17/13 Thu 5/30/13 Thu 5/30/13 Thu 6/20/13 Thu 8/1/13 Thu 8/15/13 Thu 8/22/13 Thu 5/30/13 Thu 5/30/13 Thu 6/6/13 Thu 8/29/13 Thu 5/30/13 Thu 5/30/13 Mon 6/17/13 Mon 7/29/13 Thu 9/12/13 Thu 9/12/13 Thu 10/3/13 Thu 12/5/13 Fri 12/6/13
Thu 7/25/13 Wed 9/11/13 Wed 6/19/13 Wed 7/31/13 Wed 8/14/13 Wed 8/21/13 Wed 9/11/13 Wed 9/4/13 Wed 6/5/13 Wed 8/28/13 Wed 9/4/13 Fri 9/6/13 Fri 6/14/13 Fri 7/26/13 Fri 9/6/13 Fri 12/6/13 Wed 10/2/13 Wed 12/4/13 Thu 12/5/13 Fri 12/6/13
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Evolution of Cloud Computing: How to plan for changeVon EverandThe Evolution of Cloud Computing: How to plan for changeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Al-Maktoum Airport ProjectDokument18 SeitenAl-Maktoum Airport ProjectFajr MirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web 2.0 Is The Business Revolution in The Computer Industry Caused by The Move To TheDokument8 SeitenWeb 2.0 Is The Business Revolution in The Computer Industry Caused by The Move To TheAnurag kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentación Florida UniversitariaDokument34 SeitenPresentación Florida UniversitariaJose Luis SolerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aviation APADokument27 SeitenAviation APAMuhammad UsmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19b080 'Seminar Doc'Dokument29 Seiten19b080 'Seminar Doc'Piyusha Purohit080Noch keine Bewertungen
- 20111215_DIGITALEUROPE Cloud Computing Paper_final_210e80ba-345e-482a-be7e-c94d15eca9d2Dokument24 Seiten20111215_DIGITALEUROPE Cloud Computing Paper_final_210e80ba-345e-482a-be7e-c94d15eca9d2Vishal kumar MauryaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Accounting A New Business Model in A Challenging ContextDokument7 SeitenCloud Accounting A New Business Model in A Challenging ContextmohammedelamenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web Services Infrastructure: October 2002Dokument20 SeitenWeb Services Infrastructure: October 2002Jeetu PawraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Paradigm Shift, Technology Stack and Business Value: Web 2.0 Re-ExaminedDokument12 SeitenThe Paradigm Shift, Technology Stack and Business Value: Web 2.0 Re-Examinedjamesyu100% (1)
- British AirwaysDokument19 SeitenBritish AirwaysMishal RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emirates Airline Innovation ApproachDokument7 SeitenEmirates Airline Innovation ApproachOreo FestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Services in Europe Trends in Ecosystem Development and Services IntegrationDokument14 SeitenCloud Services in Europe Trends in Ecosystem Development and Services IntegrationAshish KhandekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web 2.0 Seminar ReportDokument17 SeitenWeb 2.0 Seminar ReportjessilcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Future of The Internet of Services For Industry: The Serviceweb 3.0 RoadmapDokument9 SeitenThe Future of The Internet of Services For Industry: The Serviceweb 3.0 Roadmapbarfoo123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Partnered With Gulf Learning To Announce The Smart MEP SummitDokument3 SeitenPartnered With Gulf Learning To Announce The Smart MEP SummitPR.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction Notes - DetailedDokument29 SeitenIntroduction Notes - DetailedSunil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- B2B Commerce Implications on Buyer-Supplier RelationshipsDokument19 SeitenB2B Commerce Implications on Buyer-Supplier RelationshipssarathkkkkNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Implement Marketing 2.0 SuccessfullyDokument8 SeitenHow To Implement Marketing 2.0 SuccessfullyN ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing For Education and LearningDokument6 SeitenCloud Computing For Education and LearningkberezkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - Finding The Human in TechnologyDokument8 SeitenCase Study - Finding The Human in TechnologySONUNoch keine Bewertungen
- DWC AviationDistrict PlanningRegulations&DevelopmentGuidelines 022010Dokument49 SeitenDWC AviationDistrict PlanningRegulations&DevelopmentGuidelines 022010Ihab SubohNoch keine Bewertungen
- PWC and Web2.0Dokument10 SeitenPWC and Web2.0sindhu_78Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Return of The City Centre Airport: Philip Butterworth-Hayes Editorial Director, PMI Media LTDDokument17 SeitenThe Return of The City Centre Airport: Philip Butterworth-Hayes Editorial Director, PMI Media LTDLTE002Noch keine Bewertungen
- 05 NFM 05 de 12Dokument23 Seiten05 NFM 05 de 12Oz GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web 2.0: Taking The Noise Out of The Information, Part 1: Executive SummaryDokument16 SeitenWeb 2.0: Taking The Noise Out of The Information, Part 1: Executive SummaryEDAG_USPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Advertising: Oecd Digital Economy PapersDokument43 SeitenOnline Advertising: Oecd Digital Economy PapersValentin MotocNoch keine Bewertungen
- EU SME Centre Invitation To Tender Web Design Web Development 2022Dokument15 SeitenEU SME Centre Invitation To Tender Web Design Web Development 2022EVA liebe (kemo)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Online Social Lending Platform Enables Borrower Content SharingDokument9 SeitenOnline Social Lending Platform Enables Borrower Content SharingRocco TriccadantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dubai Airports Brochure - Front FINALDokument19 SeitenDubai Airports Brochure - Front FINALSalamaAlAmryNoch keine Bewertungen
- GOSI Monthly Movement Web Service GuideDokument22 SeitenGOSI Monthly Movement Web Service GuideshifaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modelo Resumen EjecutivoDokument1 SeiteModelo Resumen EjecutivoPedro Nel Gualteros PradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Taxi Mini Project 2Dokument15 SeitenAir Taxi Mini Project 2Aatif AatifNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Guide to Understanding Different Types of Web PortalsDokument27 SeitenA Guide to Understanding Different Types of Web Portalsamitwin1983Noch keine Bewertungen
- MIT - CISR Research PaperDokument24 SeitenMIT - CISR Research PaperMrDorakonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tourism 2.0: Definition and Key ConceptsDokument12 SeitenTourism 2.0: Definition and Key ConceptsMikhailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Empowerment Technology: NamesDokument2 SeitenIntroduction To Empowerment Technology: NamesXyrille FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important NotesDokument4 SeitenImportant NotesRish SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Google Apps Business PlanDokument23 SeitenGoogle Apps Business PlanWaqar Qureshi100% (1)
- Avionics Magazine - September 2016Dokument38 SeitenAvionics Magazine - September 2016publi2030Noch keine Bewertungen
- Application For Final Project ThesisDokument4 SeitenApplication For Final Project ThesisanevelkoskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Report PDFDokument20 SeitenFinal Report PDFkaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Improvement Proposal - FINDokument18 SeitenBusiness Improvement Proposal - FINAlex LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- It3225 U1a1Dokument5 SeitenIt3225 U1a1Aaron VWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seminar Report On:-: Gandhinagar Institute of Technology Moti Bhoyan, Kalol, Gujarat, IndiaDokument28 SeitenSeminar Report On:-: Gandhinagar Institute of Technology Moti Bhoyan, Kalol, Gujarat, IndiaSaloni BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ELECTRIC AVIATION AND URBAN AIR MOBILITY BUSINESS PLANDokument34 SeitenELECTRIC AVIATION AND URBAN AIR MOBILITY BUSINESS PLANLeandroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airport World, Issue 5, 2014Dokument25 SeitenAirport World, Issue 5, 2014Airport World MagazineNoch keine Bewertungen
- NDC Strategy PaperDokument44 SeitenNDC Strategy PaperMariano Pizarro100% (1)
- Final Industry ReportDokument9 SeitenFinal Industry ReportbrookruleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airport-Digital-Transformation DIGITAL SpreadsDokument17 SeitenAirport-Digital-Transformation DIGITAL SpreadsGoentoro Bukan Guntoro100% (1)
- AIAL Final Master Plan 2013 PDFDokument31 SeitenAIAL Final Master Plan 2013 PDFAnousack KittilathNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Report On ICT at Dubai AirportDokument8 SeitenA Report On ICT at Dubai Airportmanikandan039715Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carrier Digital Communications Agility and Innovation Will Maximize Service Provider Opportunities.Dokument20 SeitenCarrier Digital Communications Agility and Innovation Will Maximize Service Provider Opportunities.Ashish KhandekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProQuestDocuments 2023 09 09Dokument3 SeitenProQuestDocuments 2023 09 09Ashutosh FalegaonkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategic AlliancesDokument15 SeitenStrategic AlliancesAli AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On Web 2.0Dokument29 SeitenProject Report On Web 2.0ojaskaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Creating Successful Airport CityDokument8 SeitenCreating Successful Airport CityAshutosh Prateek100% (2)
- 5jlwnklt820x-En NEW FORMS OF WORK IN DEDokument44 Seiten5jlwnklt820x-En NEW FORMS OF WORK IN DECeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turban - Ec2012Dokument36 SeitenTurban - Ec2012Boro HammanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Improvement Proposal - FINDokument18 SeitenBusiness Improvement Proposal - FINAlex LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Would Communication Affect Multicultural ProjectsDokument71 SeitenHow Would Communication Affect Multicultural ProjectsAlex LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Negative Stigma On Seeking Mental Heath Counseling (October 2012)Dokument21 SeitenNegative Stigma On Seeking Mental Heath Counseling (October 2012)Alex LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airport PDA ProjectDokument22 SeitenAirport PDA ProjectAlex LimNoch keine Bewertungen
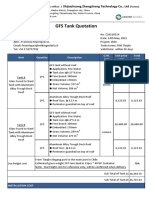
- GFS Tank Quotation C20210514Dokument4 SeitenGFS Tank Quotation C20210514Francisco ManriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Damcos Mas2600 Installation UsermanualDokument26 SeitenDamcos Mas2600 Installation Usermanualair1111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Combined Set12Dokument159 SeitenCombined Set12Nguyễn Sơn LâmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mounting InstructionDokument1 SeiteMounting InstructionAkshay GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mrs. Universe PH - Empowering Women, Inspiring ChildrenDokument2 SeitenMrs. Universe PH - Empowering Women, Inspiring ChildrenKate PestanasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 JHS INSET Template For Modular/Online Learning: Curriculum MapDokument15 Seiten2021 JHS INSET Template For Modular/Online Learning: Curriculum MapDremie WorksNoch keine Bewertungen
- N4 Electrotechnics August 2021 MemorandumDokument8 SeitenN4 Electrotechnics August 2021 MemorandumPetro Susan BarnardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Standard: Pla Ing and Design of Drainage IN Irrigation Projects - GuidelinesDokument7 SeitenIndian Standard: Pla Ing and Design of Drainage IN Irrigation Projects - GuidelinesGolak PattanaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective Mech II - IES 2009 Question PaperDokument28 SeitenObjective Mech II - IES 2009 Question Paperaditya_kumar_meNoch keine Bewertungen
- TJUSAMO 2013-2014 Modular ArithmeticDokument4 SeitenTJUSAMO 2013-2014 Modular ArithmeticChanthana ChongchareonNoch keine Bewertungen
- LEARNING ACTIVITY Sheet Math 7 q3 M 1Dokument4 SeitenLEARNING ACTIVITY Sheet Math 7 q3 M 1Mariel PastoleroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vector 4114NS Sis TDSDokument2 SeitenVector 4114NS Sis TDSCaio OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Composite Structures: A. Grimaldi, A. Sollo, M. Guida, F. MaruloDokument15 SeitenComposite Structures: A. Grimaldi, A. Sollo, M. Guida, F. MaruloSharan KharthikNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Aleksandar VladimirovDokument6 Seiten7 Aleksandar VladimirovDante FilhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFO TagsDokument95 SeitenCFO Tagssatyagodfather0% (1)
- Bula Defense M14 Operator's ManualDokument32 SeitenBula Defense M14 Operator's ManualmeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pfr140 User ManualDokument4 SeitenPfr140 User ManualOanh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grading System The Inconvenient Use of The Computing Grades in PortalDokument5 SeitenGrading System The Inconvenient Use of The Computing Grades in PortalJm WhoooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Done - NSTP 2 SyllabusDokument9 SeitenDone - NSTP 2 SyllabusJoseph MazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dance Appreciation and CompositionDokument1 SeiteDance Appreciation and CompositionFretz Ael100% (1)
- Qad Quick StartDokument534 SeitenQad Quick StartMahadev Subramani100% (1)
- Committee History 50yearsDokument156 SeitenCommittee History 50yearsd_maassNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3d Control Sphere Edge and Face StudyDokument4 Seiten3d Control Sphere Edge and Face Studydjbroussard100% (2)
- Ball Valves Pentair Valves and ControlsDokument16 SeitenBall Valves Pentair Valves and ControlsABDUL KADHARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dell Compellent Sc4020 Deploy GuideDokument184 SeitenDell Compellent Sc4020 Deploy Guidetar_py100% (1)
- Crystallizers: Chapter 16 Cost Accounting and Capital Cost EstimationDokument1 SeiteCrystallizers: Chapter 16 Cost Accounting and Capital Cost EstimationDeiver Enrique SampayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arta Kelmendi's resume highlighting education and work experienceDokument2 SeitenArta Kelmendi's resume highlighting education and work experienceArta KelmendiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embryology-Nervous System DevelopmentDokument157 SeitenEmbryology-Nervous System DevelopmentGheavita Chandra DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexible Regression and Smoothing - Using GAMLSS in RDokument572 SeitenFlexible Regression and Smoothing - Using GAMLSS in RDavid50% (2)
- Defensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityVon EverandDefensive Cyber Mastery: Expert Strategies for Unbeatable Personal and Business SecurityBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Python for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldVon EverandPython for Beginners: The 1 Day Crash Course For Python Programming In The Real WorldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultimate Guide to LinkedIn for Business: Access more than 500 million people in 10 minutesVon EverandUltimate Guide to LinkedIn for Business: Access more than 500 million people in 10 minutesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- CISM Certified Information Security Manager Study GuideVon EverandCISM Certified Information Security Manager Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- So You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community that Will ListenVon EverandSo You Want to Start a Podcast: Finding Your Voice, Telling Your Story, and Building a Community that Will ListenBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (35)
- The Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellVon EverandThe Digital Marketing Handbook: A Step-By-Step Guide to Creating Websites That SellBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (6)
- How to Be Fine: What We Learned by Living by the Rules of 50 Self-Help BooksVon EverandHow to Be Fine: What We Learned by Living by the Rules of 50 Self-Help BooksBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (48)
- How to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyVon EverandHow to Do Nothing: Resisting the Attention EconomyBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (421)
- Content Rules: How to Create Killer Blogs, Podcasts, Videos, Ebooks, Webinars (and More) That Engage Customers and Ignite Your BusinessVon EverandContent Rules: How to Create Killer Blogs, Podcasts, Videos, Ebooks, Webinars (and More) That Engage Customers and Ignite Your BusinessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- The Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerVon EverandThe Wires of War: Technology and the Global Struggle for PowerBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (34)
- Nine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersVon EverandNine Algorithms That Changed the Future: The Ingenious Ideas That Drive Today's ComputersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (7)
- Ultimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessVon EverandUltimate Guide to YouTube for BusinessBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- IAPP CIPM Certified Information Privacy Manager Study GuideVon EverandIAPP CIPM Certified Information Privacy Manager Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEO: The Ultimate Guide to Optimize Your Website. Learn Effective Techniques to Reach the First Page and Finally Improve Your Organic Traffic.Von EverandSEO: The Ultimate Guide to Optimize Your Website. Learn Effective Techniques to Reach the First Page and Finally Improve Your Organic Traffic.Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Facing Cyber Threats Head On: Protecting Yourself and Your BusinessVon EverandFacing Cyber Threats Head On: Protecting Yourself and Your BusinessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (27)
- A Great Online Dating Profile: 30 Tips to Get Noticed and Get More ResponsesVon EverandA Great Online Dating Profile: 30 Tips to Get Noticed and Get More ResponsesBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- The Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationVon EverandThe Internet Con: How to Seize the Means of ComputationBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (6)
- Monitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataVon EverandMonitored: Business and Surveillance in a Time of Big DataBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The Social Media Bible: Tactics, Tools, and Strategies for Business SuccessVon EverandThe Social Media Bible: Tactics, Tools, and Strategies for Business SuccessBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (19)
- Tiny Python Projects: Learn coding and testing with puzzles and gamesVon EverandTiny Python Projects: Learn coding and testing with puzzles and gamesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Coding for Beginners and Kids Using Python: Python Basics for Beginners, High School Students and Teens Using Project Based LearningVon EverandCoding for Beginners and Kids Using Python: Python Basics for Beginners, High School Students and Teens Using Project Based LearningBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- CEH Certified Ethical Hacker Practice Exams, Third EditionVon EverandCEH Certified Ethical Hacker Practice Exams, Third EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachineVon EverandThe Ultimate LinkedIn Sales Guide: How to Use Digital and Social Selling to Turn LinkedIn into a Lead, Sales and Revenue Generating MachineNoch keine Bewertungen