Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Jenninngs Disaster Nursing Management Model Annotated Bibliography
Hochgeladen von
EmergencyPlanning101Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Jenninngs Disaster Nursing Management Model Annotated Bibliography
Hochgeladen von
EmergencyPlanning101Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
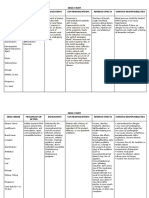
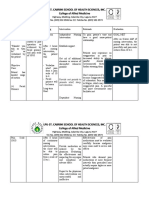
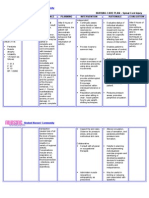
Jennings-Saunders, A. (2004). Teaching disaster nursing by utilizing the Jennings disaster nursing management model.
Nursing Education in Practice, 4, 69-76. This article outlines the Jenning Disaster Nursing Management Model and how it can benefit Nursing students in a Community Health Nursing Course. The Jennings Disaster Model is divided into 4 phases. Phase one is the Pre-disaster phase in which the nurse performs an initial assessment of the community, looking at resources and risks. Nurses utilize interprofessional collaboration to work with established shelters, community agencies, and other professions to help identify and assess current resources and emergency plans. Once an initial assessment has been made, the nurse can move into the planning segment of phase one. In the planning segment, the nurse works with other professions to allocate resources; make collaborative agreements with the town council, police, firefighters, physicians, nurses, administrators of local schools, etc.; Define specific roles to all of those in the community; develop and activate disaster management tools that help plan for a disaster, assess damage, and assess individual health status; develop disaster management education program so that the community is aware of what to do during a disaster; develop volunteer opportunities so the community can get actively involved; and finally implement all of the aspects mentioned and practice the disaster plan on a regular basis. Phase two of the Jennings Nursin Management Model is when the disaster actually occurs and the nurse takes the role of a caregiver, educator or case manager. As a caregiver the nurse will focus on all aspects of care of an individual; including physical, emotional, psychosocial, and cultural. As an educator the nurse will teach clients about treatment of health problem, so the nurse would teach a client about how to care for a broken limb if the client fractured a limb during a disaster. Finally, as a case manager, the nurse will give the client resources from the community agency, such as providing food vouchers for people in need. Phase three of the model is the Post-disaster phase where the nurse performs
an assessment of the plan in place and re-evaluates it, plans on how to strengthen the weaknesses in the disaster plan and implements the new plan to the community. Finally, phase four of the model looks at the population outcomes and looks at statistics such as decreased mortality rates, improved health care status, and increased disaster knowledge and so on to see if the plan was effective. The article applied this model to a case study and the model was found to be an effective and interactive way for students to learn about disaster management.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Sally Mann Hold Still - A Memoir With Photographs (PDFDrive)Dokument470 SeitenSally Mann Hold Still - A Memoir With Photographs (PDFDrive)danitawea100% (1)
- 05 The Scriptures. New Testament. Hebrew-Greek-English Color Coded Interlinear: ActsDokument382 Seiten05 The Scriptures. New Testament. Hebrew-Greek-English Color Coded Interlinear: ActsMichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Check ProcessingDokument1 SeiteElectronic Check Processingaaes2Noch keine Bewertungen
- TLG 82201Dokument7 SeitenTLG 82201beatmymeat100% (2)
- Unit 5 - Simulation of HVDC SystemDokument24 SeitenUnit 5 - Simulation of HVDC Systemkarthik60% (10)
- NCP Alzheimers DiseaseDokument2 SeitenNCP Alzheimers DiseaseShawn TejanoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SD OverviewDokument85 SeitenSD OverviewSamatha GantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Role, Preparedness and Management of Nurses During Disasters 1325648617Dokument26 SeitenThe Role, Preparedness and Management of Nurses During Disasters 1325648617Pepper Mint0% (1)
- MAHILOM NCP Risk For FallDokument2 SeitenMAHILOM NCP Risk For Fallkasandra dawn BerisoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 13 Ethics Through Thick and ThinDokument7 SeitenMODULE 13 Ethics Through Thick and ThinCristobal M. CantorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Battle Against Covid-19 Filipino American Healthcare Workers on the Frontlines of the Pandemic ResponseVon EverandThe Battle Against Covid-19 Filipino American Healthcare Workers on the Frontlines of the Pandemic ResponseNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHN Notes PrelimDokument30 SeitenCHN Notes PrelimCHINGCHONG SLAYERNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP PainDokument2 SeitenNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deficient Knowledge: Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Care Plans (NCP)Dokument3 SeitenDeficient Knowledge: Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Care Plans (NCP)Vincent Paul SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug-Study NCPDokument5 SeitenDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Accreditation of The Healthcare SystemDokument3 SeitenAccreditation of The Healthcare SystemGracea Mae AranetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDokument2 SeitenScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cefipime HCL (AXERA)Dokument2 SeitenCefipime HCL (AXERA)Kristine YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 107 Activity 4-TabioloDokument5 SeitenNCM 107 Activity 4-TabioloAce TabioloNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Dokument20 SeitenSLCN Gazette Magazine, Volume 1, Issue 1, 2019Mayzelle RizNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 114 Ethical Aspects of Care PromotionDokument2 SeitenNCM 114 Ethical Aspects of Care PromotionJane DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Pedia SleepapneaDokument2 SeitenNCP Pedia SleepapneaDavid Brillo100% (1)
- Thoracentesis Reflective EssayDokument2 SeitenThoracentesis Reflective EssayAnjae GariandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cues Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument2 SeitenCues Diagnosis Background Knowledge Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationhaniehaehaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan Borderline PD (Client A) NCP #1: Pia Mae D. Buaya N-31Dokument9 SeitenNursing Care Plan Borderline PD (Client A) NCP #1: Pia Mae D. Buaya N-31Pia Mae BuayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan For Low SelfDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan For Low SelfMarissa AsimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermDokument4 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objective Interventions Rationale Expected Outcome Short Term: Short TermGensen Cu RoxasNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Community Health Nursing 2Dokument1 SeiteWhat Is Community Health Nursing 2Soleil MaxwellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomsDokument2 SeitenCase Report On Bipolar Affective Disorder: Mania With Psychotic SymptomskslhfwoiebvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity#1 - Development of CCRNDokument4 SeitenActivity#1 - Development of CCRNJennah JozelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manuel - Reflection Paper - Cmca2Dokument1 SeiteManuel - Reflection Paper - Cmca2Shawn ManuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCPDokument4 SeitenNCPyasayayasay yasayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epoetin AlfaDokument3 SeitenEpoetin Alfaapi-3797941Noch keine Bewertungen
- Involving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialDokument10 SeitenInvolving Family, Domestic Relations, Women and Children. (2015) - Philippine JudicialAngel MayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan D-CDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan D-CGian MonillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Huntingtons Disease NCPDokument4 SeitenHuntingtons Disease NCPJerich Mark SalasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 THE PARTNERSHIP APPROACH TO COMMUNITY HEALTH PRACTICE Mam ThaiDokument14 Seiten4 THE PARTNERSHIP APPROACH TO COMMUNITY HEALTH PRACTICE Mam ThaiKasandra Dawn Moquia BerisoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP Total Hip ReplacementDokument11 SeitenNCP Total Hip ReplacementDoneva Lyn MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Nursing Informatics in AsiaDokument2 SeitenSummary of Nursing Informatics in AsiaJake Yvan Dizon0% (1)
- NCP FeuDokument2 SeitenNCP FeuFejlean Angelica AntineoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buddy WorksDokument3 SeitenBuddy WorksJamaica Leslie NovenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan: Provide Rest Periods To Promote Relief, Sleep, and RelaxationDokument2 SeitenNursing Care Plan: Provide Rest Periods To Promote Relief, Sleep, and RelaxationGrace MellaineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task 7,8&9Dokument11 SeitenTask 7,8&9joyrena ochondraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plans ...Dokument16 SeitenNursing Care Plans ...Santos Kyla Patricia T.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Working With Groups Towards Community DevelopmentDokument49 SeitenWorking With Groups Towards Community DevelopmentUndine TapangNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIABETES Nursing ManagementDokument11 SeitenDIABETES Nursing ManagementKaloy KamaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discharge Plan Post SeizureDokument2 SeitenDischarge Plan Post SeizureVecky TolentinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Task - Traction BARTOLOME, JANIZE KHATEDokument2 SeitenCourse Task - Traction BARTOLOME, JANIZE KHATEKhate BartolomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing TheoristDokument22 SeitenNursing TheoristG a i l R i c h w e l lNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokument10 SeitenAnatomy and PhysiologyChris CHris ChRis100% (1)
- Role - Responsibilities of Psychiatry Health NurseDokument3 SeitenRole - Responsibilities of Psychiatry Health NurseDhAiRyA ArOrANoch keine Bewertungen
- Baiae NCPDokument1 SeiteBaiae NCPreignyfayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Care Delivery System & COPARDokument52 SeitenHealth Care Delivery System & COPARDharylle Cariño100% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument3 SeitenAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationMikhaelEarlSantosTacordaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDokument2 SeitenNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4 Worksheet 3Dokument1 SeiteModule 4 Worksheet 3pot poootNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursingcribcom Nursing Care Plan Spinal Cord InjuryDokument2 SeitenNursingcribcom Nursing Care Plan Spinal Cord InjuryJanine Erika Julom Brillantes100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokument11 SeitenAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDeo OlarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map - Colon CancerDokument2 SeitenConcept Map - Colon Cancerbea pegadNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Study Resource Was: HypomagnesemiaDokument1 SeiteThis Study Resource Was: HypomagnesemiaMaica LectanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleDokument8 SeitenNursing Care Plan 1: Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions RationaleTrysna Ayu SukardiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument13 SeitenNursing Care Planyumiko0% (1)
- Department of Health - Soil Transmitted Helminth Control Program - 2011-10-19Dokument5 SeitenDepartment of Health - Soil Transmitted Helminth Control Program - 2011-10-19daryl ann dep-asNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ppe4 Reflection AssignmentDokument11 SeitenPpe4 Reflection Assignmentapi-318846856100% (1)
- Therapeutic Communication: Department of Health, PhilippinesDokument35 SeitenTherapeutic Communication: Department of Health, PhilippinesKeith Clarence BunaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- C CEF Roles, Character, Team PlainDokument10 SeitenC CEF Roles, Character, Team PlainConrad C. CatimbangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mil CompiledDokument62 SeitenMil CompiledDan VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modern Prometheus Editing The HumanDokument399 SeitenModern Prometheus Editing The HumanHARTK 70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Art 3-6BDokument146 SeitenArt 3-6BCJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of The Performance of HRCT in The Diagnostic and Management of Covid-19Dokument7 SeitenEvaluation of The Performance of HRCT in The Diagnostic and Management of Covid-19IJAR JOURNALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boxnhl MBS (Design-D) Check SheetDokument13 SeitenBoxnhl MBS (Design-D) Check SheetKumari SanayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- F07 hw07Dokument2 SeitenF07 hw07rahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Young Entrepreneurs of IndiaDokument13 SeitenYoung Entrepreneurs of Indiamohit_jain_90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unilateral Lower Limb SwellingDokument1 SeiteUnilateral Lower Limb SwellingLilius TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7A Detailed Lesson Plan in Health 7 I. Content Standard: Teacher's Activity Students' ActivityDokument10 Seiten7A Detailed Lesson Plan in Health 7 I. Content Standard: Teacher's Activity Students' ActivityLeizel C. LeonidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Normalization Techniques For Multi-Criteria Decision Making: Analytical Hierarchy Process Case StudyDokument11 SeitenNormalization Techniques For Multi-Criteria Decision Making: Analytical Hierarchy Process Case StudyJohn GreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom Management PaperDokument7 SeitenClassroom Management PaperdessyutamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roman Catholic of Aklan Vs Mun of Aklan FULL TEXTDokument33 SeitenRoman Catholic of Aklan Vs Mun of Aklan FULL TEXTDessa Ruth ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Individual Assignment: Prepared By: Tigist WoldesenbetDokument12 SeitenIndividual Assignment: Prepared By: Tigist WoldesenbetRobel YacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pplied Hysics-Ii: Vayu Education of IndiaDokument16 SeitenPplied Hysics-Ii: Vayu Education of Indiagharib mahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operations Management and Operations PerformanceDokument59 SeitenOperations Management and Operations PerformancePauline LagtoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscar Characterization TemplateDokument3 SeitenOscar Characterization Templatemqs786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Course-Outline EL 102 GenderAndSocietyDokument4 SeitenCourse-Outline EL 102 GenderAndSocietyDaneilo Dela Cruz Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- EmanDokument3 SeitenEmanCh NawazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Far 1 - Activity 1 - Sept. 09, 2020 - Answer SheetDokument4 SeitenFar 1 - Activity 1 - Sept. 09, 2020 - Answer SheetAnonn100% (1)
- G12 PR1 AsDokument34 SeitenG12 PR1 Asjaina rose yambao-panerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mark Scheme Big Cat FactsDokument3 SeitenMark Scheme Big Cat FactsHuyền MyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pitch PDFDokument12 SeitenPitch PDFJessa Mae AnonuevoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Week in My CountryDokument2 SeitenA Week in My CountryAQhuewulland Youngprincess HokageNarutoNoch keine Bewertungen