Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
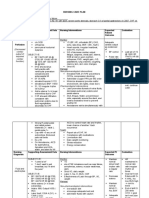
Anti HTN
Hochgeladen von
AvrilOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Anti HTN
Hochgeladen von
AvrilCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hypertension- sustained elevation of either systolic >120 or diastolic >90 IDEAL BP = 110/70 Betablocker = cardioprotective but not for
Diabetes mellitus
SYMPHATOPLEGICS: Blockers of: A. CNS = Methyldopa (Aldomet) works Brain in relay area of solitary nucleus, acts as A2 receptor agonist >reduce symphatetic tone to ur peripheral structures blood vessel thus: decreased PVR, HR, plasma renin P.O. well absorbed , IV 1) HTN heptaic metab C450excretion: parent and metabolites via urine 2) CHF 1) mild edema from increased plasma volume 2) first few weeks= sedation CAUTION: elderly, first floor ; dizziness; headache (diminishes in time as tolerance develops 3) mild bradycardia 4) flu like symptoms 5) may cause lupus-like syndrome 6) (+) Coomb's test drug induced
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES
MOA
Pharmakokinetics
Clinical Use
Side Effects
Clonidine (replaced Nifedipine) =
same as of methyldopa
PO, transdermal patch (for 1) HTN = small doses only noncompliant pts; provides initially or else manifest side aesthetic plasam; fewer effects side effects
1)high dose= causes interaction with A1 receptors => vasconstriction, incr BP 2) drowsiness, diz ziness, HA 3) mild edema 4) mild bradycardia 5) xerostomia 6) constipation
live excretion: urine (unchanged, majority) Guanabenz = not internationally marketed because SITE OF ACTIOn is unknown and extreme side effects; same as solitary nucleus ***usually combined with HTCZ(hydrochlorothiazide) diuretic B. GANGLIA PERIPHERALLY ACTING DRUGS Mecamylanine(Inversine) Which of the ff. sympthatoplegic is also recognized as as ganglionic blocker: will competitively nondepolarizing ganglionic blocker?? Mecamyline inhibit AcH at the nicotinic receptors at postganglionic autonomic neurons => vasodilatation of peripheral blood vessels, decr BP excretion: urine
2) CHF transdermal: itchiness, skin irritation and redness of the area 1) confusion, headache, nausea 2) mental depression 3) array of antimuscarinic s/e even at normal doses (when given alone)
PO excretion= 90% unchanged 1) HTN ***not commonly in urine used d/t numerous s/e
, 1) at normal dose => convulsio 2) mental changes 3) tremors 4) confusion 5) hypotension
C. NERVE TERMINAL note: differentiate Gunabenz vs Guanadrel Reserpine
*** adrenergic neuronal blocker (blocks reuptake of NE & DA in vesicles) by inhibiting an enzyme magnesium Atpase => depletion of NE and DA => decr activity of NE, DA in blood vessels & heart partial hepatic (parent and metabolites) excretion: urine, feces combined with other drugs d/t CNS side effects: diuretics, beta blockers 1) suicide 2) severe depression 3) sedation 4) bradycardia
Guanethidine and Guanadrel = differ only in formulation ***superior to Reserpine
replaces NE bound to ATP inside the vesicles => decr NE release during nerve stimulation => reduced arteriolar vasoconstriction
PO hepatic metab excretion: urine (parent and metabolites)
1) moderate & severe HTN
1) angina pectoris 2)peripheral edema 3) pulmonary edema 32% 4) fatigue 5) severe diarrhea = warrant dr to d/c treatmnt 1) severe diarrhea 2) orthostatic hypotension 3) GIT disturbances = n/v 4) body malaise severe allergic rxn, EPS, severe diarrhea
Metyrosine
*** very unique because it inhibits an enzyme PO tyrosine hydroxylase => reduced synthesis of NE => decr BP
urine = unchanged
1) secondary HTN 2) prophylaxis and treatment HTN associated with pheochromocytomectomy 3) chronic treatment for malignant pheochromocytoma
D. ALPHA/BETA BLOCKERS 1. A1-ADRENERGIC Phentolamine =
nonselective alpha adrenergic blocker => decr sytemic vascular resistance => decr BP
IV & IM ONLY not well defined metab not well defined excretion, some in urine
1) dx of pheochromo 2) prophylaxis and treatment HTN associated with pheochromocytomectomy
1) reflex tachycardia 2) ortho. Hypotension 3) GIT disturbances 4) body malaise
Phenoxybenzamine =
nonselective alpha adrenergic blocker => decr sytemic vascular resistance => decr BP
PO hepatic C450 excretion= metabolites in urine, feces
1) prophylaxis and treatment similar to phentolamine s/e HTN associated with pheochromocytomectomy
2) UNIQUE USE: for BPH
2. SELECTIVE ALPHA BLOCKERS Prazosin
for all: PO 1) HTN hepatic active metabolites BPH excretion= parent & metabolites in BILE, feces
for all: 2) ***main advantage vs nonselective= causes lesser reflex tachycardia
***first dose effect= orthostatic hypotension => syncope CAUTION: careful dosing, take before bedtime 1) drowsiness, dizziness, HA 2) peripheral edema, palpitation Terazosin PO hepatic active metabolites excretion = parent & metabolites in URINE , feces Doxazosin (cardura) PO hepatic active metabolites excretion= parent & metabolites in BILE, feces
2. BETA BLOCKERS = recommended as 1st linetherapy 1) decreases primarily by decresing cardiac i.e. when concomitant dse is present e.g. CHF+ HTN output ***very efficacious but also with Contraindications Generalizations: 1)more effective in CAUCASIANS 2)more effective in young HTN Generalizations that will discourage use: 1)very severe COPD 2) Chronic CHF 2) very severe symptomatic occlusive peripheral vascular disease USE WITH CAUTION: DM, elderly, HTN with other dse, with SVTach, HTN with post M.I., HTN with angina, chronic CHF, migraine HA ) 2) decreases SANS outflow from CNS
1) Acute CHF
WARNING 1 : Taper the dose 2-3 weeks when withdrawing because ABRUPT CESSATION induces angina and M.I. WARNING 2 : alters serum lipid metabolism = decreases HDL ; increases plasma TG most causes bradycardia and CNS (fatigue,lethargy, insomina, severe CNS hallucination and hypotension, impotence) all betablockers decreases compliance d/t 1) bronchonstriction 2) hypotension 3) sexual dysfunction
2) PVD
3) inhibit RENIN from kidneys =>decr angiotensin II and aldosterone
Propanolol= prototype
full effect = after SEVERAL weeks
PO = extensive 1st pass; IV excretion = metabolites urine
1) HTN 2) angina
***Absolutely Contraindicated for asthmatics because blocks B1 receptors in heart => increasing its nonselective, blocks B2 bronchodilatation (lungs) SANS activity => decreased BP as well blocks beta receptors in JG cells => decr renin release
3) cardiac arrythmias 4) migraine 5) acute MI 6 )essential tremors (hyperthyroid Contraindication: asthma, COPD, DM, PVD
Metoprolol = selective; most commonly used
same as Propanolol
PO
1) for HTN over propanolol bec; nonselective and lesser side effecs angina CHF Acute MI
1) lesser bronchoconstriction
Atenolol= selective; most commonly used
urine
E. A/B BLOCKERS Carvedilol
beta blockade: 1) decreases heart rate
PO, VERY EXTENSIVE 1stpass 1) HTN CF450 2) CHF
bradycardia, dizziness, hypotension
2) decr plasma rennin activity excretio=; FECES only 3) incr plasma volume alpha blockade: 1) decr PVR = good for cold fingers and toes 1) decr PVR = good for cold fingers and toes Labetalol selective A1 blocking but predominantly nonselective beta blocking : beta blockade: decreases heart rate plasma rennin activity volume 1) 2) decr 3) incr plasma PO, IV
mainly for HTN
PO form = postural hypotension
hepatic metab ecxretion= parent and metabolites in urine, feces
dizziness, hypotension, n/v
fatigue
alpha blockade: 1) decr PVR = good for cold fingers and toes
VASODILATORS A. ARTERIAL VASODILATORS Hydralazine
arterial smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation by cAMP and Calcium
PO, IM, 1) HTN PO = very extensive 1st pass hepatic acetylation
CHF
toxicity in slow acetylators like tachycardia, dizziness, nausea, flushing, redness in the face, sweating, nasal congestion, lupus-like syndromes memorize: LUPUS_LIKE inducers
***hepatic acetylation is genetically predetermined ===>
caucasians = slow acetyylators asians = fast acetylators => excertion= urine PO, topical hepatic 1)HTN metab excretion= metabolites in urine
Minoxidil
inhibits phosphodiesterase => incr. levels of cAMP => arterial smooth muscle relaxation thru Calcium modulation
2) alopecia
tachycardia, massive fluid retention hypertrichosis ECG changes pericarditis REFLEX TACHYCARDIA
Diazoxide
decreases PVR via direct vasodilatory effects IV only on the smooth muscles of the peripheral partial hepatic metab arterioles excretion: parent and metabolites in urine
1) AHE (acute hypertensive emergencies)
2) hypoglycemia in pts who have hyperinsulinemia how??? inhibits insuline release
B. ARTERIAL & VENOUS VASODILATORS Na Nitroprusside *** Cyanide is a byproduct of it =>hepatic enzyme rhodanase metabolizes it to thiocyanate ( more soluble and urine excretable) Candidates for Cyanide pOisoning: 1) alcoholics (ROH poisons rhodanase) 2)
acting directly
IV 1) AHE (acute hypertensive local metabolism by tissues emergencies) and RBCs excretions= metabolites in feces, urine, and LUNGS (exhale) ***covered with foil= easily broken down by UV light 2) CHF
Nitroglycerin advantage: 1)not light sensitive 2) does not cause cyanide toxicity 3) readily available than Na nitroprosside = cost effective
SL, PO, IV , ointment, skin patch hepatic active metabolites excretion= converted to nitric oxide intracellularly => activates guanylate cyclase => cGMP cascade => dephosphorylation of myosin light chains => relaxation of vascular smooth mushcles => vasodilatation
HA repeated admin => loss of effect (from systemic compensation ****large degree of cross tolerance b/n other organic nitrates
readily available than Na nitroprosside = cost effective
CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS Verapamil (Isoptin)
for all: 1) blocks voltage-sensitive Ca channels in heart, vascular smooth muscles => decr in Intracellular calcium
PO extensive 1st pass , IV,
1) HTN Angina anti-arryhtmics
2) 3)
for all ALL = potential for peripheral ede ALL = potential for hypotension palpitation due to reflex tachycardia i.e. NIFEDIPINE lesser with verapamil and diltiazem dizziness, HA, ALL = constipation but PRONOUNCED in VERAPAMIL
2) blocks cyclcic nucleotide PDE => incr hepatic C450 ACTIVE cGMP => decr Calcium influx => dilatation of metabolites peripheral arterioles and venules urine, feces Diltiazem PO IV hepatic C450 LESS active metabolites urine, feces Nifedipine = prototype of Ca-channel Blockers PO extensive 1st pass hepatic C450 INACTIVE metabolites urine, feces DRUGS INTERFERING WITH ANGIOTENSIN Captopril = drug prototype 1) decr BP by inhibiting enzyme for AngII (ACE) ALL PO, Enalapril has IV form 1) HTN HTN and Angina only
1) common complain = nonproductive cough (d/t bradykinin's effect of cough and skin rash) 2) TERATOGENIC
Prodrug= enalaprila
2) prevents breakdown of bradykinin
Prodrug => hepaticactive metabolite urine
2) CHF
3) hyperkalemia 4) neutropenia 5) hypotension 6) ARF same above but NO COUGH
SYMPHATETIC ANTAGONISTS Angiotensin Recept Antagonsis Losartan
Angio Receptor blockade prevents vasconstriction of AngI PO hepatic C450 urine, feces 1) HTN 2) CHF
RENIN INHIBITORS
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Antifungal AgentsDokument13 SeitenAntifungal AgentsAvrilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathology+Lab - 2Dokument7 SeitenPathology+Lab - 2AvrilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Techno UserDokument29 SeitenTechno UserAvrilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 3Dokument27 SeitenExperiment 3Avril50% (4)
- Medical AbbreviationsDokument4 SeitenMedical AbbreviationsNelly PaniaguaNoch keine Bewertungen
- InFocus X6 X7 Datasheet enDokument2 SeitenInFocus X6 X7 Datasheet enAvrilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenda User GuideDokument76 SeitenTenda User GuideAvrilNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Updatesincardiacarrest Resuscitation: Vivian Lam,, Cindy H. HsuDokument15 SeitenUpdatesincardiacarrest Resuscitation: Vivian Lam,, Cindy H. HsuFia Bella KusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAILMediclaim Scheme Guidline 2011Dokument4 SeitenSAILMediclaim Scheme Guidline 2011Bibhu Ranjan PatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angiography - Clinical Science Questions and AnswersDokument2 SeitenAngiography - Clinical Science Questions and AnswersSaqibKhan100% (1)
- Rigel Uni Sim Lite DatasheetDokument5 SeitenRigel Uni Sim Lite Datasheetmailalexmd.vrn.ruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arshi Zeb Nursing Care PlanDokument4 SeitenArshi Zeb Nursing Care Planarshi khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Focus:: Canossa CollegeDokument23 SeitenFocus:: Canossa CollegeZyrene RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio Lab MedsDokument11 SeitenCardio Lab MedsDianne Erika MeguinesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arterial LineDokument2 SeitenArterial LineRaghav Goyal100% (1)
- N220 W9 Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenN220 W9 Nursing Care PlanVivian PhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- CardiovascularDokument5 SeitenCardiovascularVipinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 5910 2018Dokument15 SeitenIso 5910 2018Vũ QuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Failure Clinical Records DatasetDokument14 SeitenHeart Failure Clinical Records Datasetpanca saputraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Makalah Vital SignDokument23 SeitenMakalah Vital SignDefina 17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intraoperative Management of Shock in Adults - UpToDateDokument36 SeitenIntraoperative Management of Shock in Adults - UpToDateYessica RivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pat Physical Readiness QuestionareDokument1 SeitePat Physical Readiness Questionarejohn jaycoh veranoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardio Pulmonary AssessmentDokument8 SeitenCardio Pulmonary AssessmentSHAIK SHABEENANoch keine Bewertungen
- On CPRDokument32 SeitenOn CPRPiyush Dutta100% (1)
- Acvc Handbook HMDokument336 SeitenAcvc Handbook HMakina1100% (1)
- AccuDx CQ BrochureDokument4 SeitenAccuDx CQ Brochurehttps://www.slideshare.net/MrAsadAhmed/accurex-product-guidepdfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventricular Isovolumetric Contractions: Tiara Calvo Leon, M.DDokument1 SeiteVentricular Isovolumetric Contractions: Tiara Calvo Leon, M.DSarah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prosedur Pemeriksaan MSCT Angiografi Kepala Dengan Klinis StrokeDokument5 SeitenProsedur Pemeriksaan MSCT Angiografi Kepala Dengan Klinis StrokeImroatul hafidzahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 - Ms1 Course Task - Cu 2Dokument3 SeitenWeek 2 - Ms1 Course Task - Cu 2jaira magbanuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Vascular System - EditedDokument5 SeitenThe Vascular System - Editedgilbert michaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Core Concepts in Health Canadian 2nd Edition Insel Test BankDokument34 SeitenCore Concepts in Health Canadian 2nd Edition Insel Test Bankalanholt09011983rta100% (29)
- Case PresentationDokument16 SeitenCase PresentationAnuja NairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predictive Value of The Negative Inspiratory ForceDokument8 SeitenPredictive Value of The Negative Inspiratory ForceTam HmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ebstein Anomaly: By:-Vaibhav SwarupDokument22 SeitenEbstein Anomaly: By:-Vaibhav SwarupOlga GoryachevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anticoagulation Therapy Following Embolic or Hemorrhagic Stroke in The Patient With A Mechanical Heart Valve 2155 6148.1000160Dokument3 SeitenAnticoagulation Therapy Following Embolic or Hemorrhagic Stroke in The Patient With A Mechanical Heart Valve 2155 6148.1000160Nguyen Huu TinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atlas of ECGDokument162 SeitenAtlas of ECGMiuschaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protective Effect of Hydroxytyrosol Against Cardiac Remodeling After Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction in RatDokument12 SeitenProtective Effect of Hydroxytyrosol Against Cardiac Remodeling After Isoproterenol-Induced Myocardial Infarction in RatMba DghisNoch keine Bewertungen