Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
DSP Matlab Exercise
Hochgeladen von
surbhisharma2210Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DSP Matlab Exercise
Hochgeladen von
surbhisharma2210Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
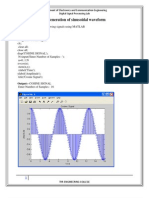
%% GENERATION OF DISCRETE TIME SEQUENCES USING MATLAB % PROGRAM 1: MATLAB code to generate basic discrete-time signals n = 0:9; %unit
impulse sequence dn = [1,zeros(1,9)]; subplot(3,1,1); stem(n,dn,'r','filled'); title('UNIT IMPULSE SEQUENCE'); xlabel('0<=n<=9'); ylabel('d[n]'); grid on; %unit step sequence un = ones(1,10); subplot(3,1,2); stem(n,un,'r','filled'); title('UNIT STEP SEQUENCE'); xlabel('0<=n<=9'); ylabel('u[n]'); grid on; %ramp sequence rn = n; subplot(3,1,3); stem(n,rn,'r','filled'); title('UNIT RAMP SEQUENCE'); xlabel('0<=n<=9'); ylabel('r[n]'); grid on; % PROGRAM 2: MATLAB code to generate a sinusoidal sequence where and L = input('Desired length = '); A = input('Amplitude = '); omega = input('Angular frequency = '); phi = input('Phase = '); n = 0:L-1; x = A*cos(omega*n + phi); stem(n,x); xlabel('Time index');ylabel('Amplitude'); title(['\omega_{o} = ',num2str(omega)]); % PROGRAM 3: MATLAB code to generate causal discrete-time real exponential sequence n = 0:9; % -1<a<0 a = -0.75; en1=(a*ones(1,10)).^n; subplot(3,1,1); stem(n,en1,'r','filled'); title('discrete-time exponential (-0.75)^n');
xlabel('0<=n<=9'); ylabel('e1[n]'); grid on; % 0<a<1 a = 0.75; en2=(a*ones(1,10)).^n; subplot(3,1,2); stem(n,en2,'r','filled'); title('discrete-time exponential (0.75)^n'); xlabel('0<=n<=9'); ylabel('e2[n]'); grid on; % a>1 a = 1.25; en3=(a*ones(1,10)).^n; subplot(3,1,3); stem(n,en3,'r','filled'); title('discrete-time exponential (1.25)^n'); xlabel('0<=n<=9'); ylabel('e3[n]'); grid on; %% FILTER DESIGN PROGRAM 4: Plot the magnitude and phase responses of the causal IIR digital transfer function . What type of filter does this transfer function represent? Determine 3dB cutoff frequency from the plot. B = conv([1 -2 1],[1 -2 1]); A = conv([1 -1.499 0.8482],[1 -1.5548 0.6493]); freqz(B,A); PROGRAM 5: Design a 5th order elliptic IIR lowpass filter with the following specifications: Passband edge = 0.4 Passband ripple = 0.5 dB Min. stopband attenuation = 40 dB N = input('type in the order = '); Rp = input('type in the passband ripple = '); Rs = input('type in the min. stopband attenuation = '); Wn = input('type in the passband edge frequency = '); [b,a] = ellip(N,Rp,Rs,Wn); fvtool(b,a) PROGRAM 6: Plot highpass filter Passband edge = Passband ripple the magnitude response of a 4th order Chebyshev Type-1 IIR with the following specifications: 0.7 = 1 dB
N = input('type in the order = '); Rp = input('type in the passband ripple = ');
Wn = input('type in the passband edge frequency = '); [b,a] = cheby1(N,Rp,Wn,'high'); fvtool(b,a) PROGRAM 7: Determine the minimum order of the transfer function of a type 2 Chebyshev digital highpass filter operating at a sampling rate of 4 kHz with the following specifications: Passband edge = 1000 Hz Stopband edge = 600 Hz Passband ripple = 1 dB Minimum stopband attenuation = 40 dB FT = input('type in the sampling frequency = '); Fp = input('type in the passband edge frequency = '); Fs = input('type in the stopband edge frequency = '); Rp = input('type in the passband ripple = '); Rs = input('type in the minimum stopband attenuation = '); Wp = Fp/(FT/2); Ws = Fs/(FT/2); [N,Wn]= cheb2ord(Wp,Ws,Rp,Rs); fprintf('order of the filter is %f \n',N);
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Apu White SmokeDokument3 SeitenApu White SmokeGoutam SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 Book IrrigationAndDrainageEngineeriDokument747 Seiten2016 Book IrrigationAndDrainageEngineeriJesús Garre Ruiz100% (2)
- Niche PartitioningDokument3 SeitenNiche PartitioningKhang LqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Signal Processing Matlab ProgramsDokument34 SeitenDigital Signal Processing Matlab ProgramsAnuja BhakuniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insulation Resistance TestDokument7 SeitenInsulation Resistance Testcarlos vidalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Signal Processing Lab ExperimentsDokument33 SeitenDigital Signal Processing Lab ExperimentsAnonymous Ndsvh2soNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementing Product ManagementDokument156 SeitenImplementing Product ManagementJyoti MohantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB Lab Project - Mtech IIsemDokument61 SeitenMATLAB Lab Project - Mtech IIsemSatya NarayanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solucion A Algunos Ejercicios Capitulo 7Dokument14 SeitenSolucion A Algunos Ejercicios Capitulo 7Giancarlo Blandino AbreuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combinatorial Algorithms: For Computers and CalculatorsVon EverandCombinatorial Algorithms: For Computers and CalculatorsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)
- MATLAB Signals and ConvolutionDokument82 SeitenMATLAB Signals and ConvolutionSETNHILNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write A Mat Lab Program To Perform Linear and Circular Convolution of The Discrete Time Sequences XDokument26 SeitenWrite A Mat Lab Program To Perform Linear and Circular Convolution of The Discrete Time Sequences XD Geetha Durai50% (2)
- Digital Filter Design ExperimentsDokument30 SeitenDigital Filter Design ExperimentsSundram InvinsibleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bharathidasan Engineering College: Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringDokument71 SeitenBharathidasan Engineering College: Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringnarasimhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Implementation and Design of Digital and Analog FiltersDokument20 SeitenImplementation and Design of Digital and Analog FiltersksbalajiautNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP Lab Manual For VTU (Mechatronics)Dokument15 SeitenDSP Lab Manual For VTU (Mechatronics)souravmohanty2005100% (1)
- Digital Signal ProcessingDokument23 SeitenDigital Signal ProcessingSanjay PalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Programs ManualDokument18 SeitenMatlab Programs Manualsudharsan100% (1)
- MatLab ProgramsDokument11 SeitenMatLab ProgramsAniketNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fir Filter Using Rectangular/Boxcar WindowDokument11 SeitenFir Filter Using Rectangular/Boxcar WindowvijeeshalleppeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP Practical FileDokument18 SeitenDSP Practical FileDivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP Record EndDokument91 SeitenDSP Record Endpapa pepaamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matlab Code For Basic DSP Signals MATLAB PROGRAM TO DISPLAY THE PROPERTIES OF DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM (DFT)Dokument16 SeitenMatlab Code For Basic DSP Signals MATLAB PROGRAM TO DISPLAY THE PROPERTIES OF DISCRETE FOURIER TRANSFORM (DFT)Sabithkk2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Dgital Signal Processing Lab - ManualDokument16 SeitenDgital Signal Processing Lab - Manualsultan erboNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP Lab Programs Word-2Dokument39 SeitenDSP Lab Programs Word-2Sai Jaswanth SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Index: S.No Program Page No. Signatur E 1. 2Dokument22 SeitenIndex: S.No Program Page No. Signatur E 1. 2Shiv AhujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dspmanual MatlabDokument26 SeitenDspmanual MatlabgsnaveenkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiments Using MatlabDokument8 SeitenExperiments Using MatlabAnanyaNairNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXPERIMENT 12: Butterworth Digital LPF: If ElseDokument4 SeitenEXPERIMENT 12: Butterworth Digital LPF: If ElseappuamreddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP ManualDokument84 SeitenDSP ManualBala913100% (1)
- MUET SZAB Signals & Systems Lab 02 Discrete Time SignalsDokument6 SeitenMUET SZAB Signals & Systems Lab 02 Discrete Time SignalsAaqibRNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSP_lab2[1]Dokument17 SeitenSSP_lab2[1]Syamantak SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB Programming File for DSP ConceptsDokument31 SeitenMATLAB Programming File for DSP ConceptsJasvinder kourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Signal Processing Lab ManualDokument37 SeitenDigital Signal Processing Lab ManualVishurockNoch keine Bewertungen
- FIR Filter Design MatlabDokument9 SeitenFIR Filter Design Matlabrajendra4343Noch keine Bewertungen
- DSP Lab Programs 2013Dokument38 SeitenDSP Lab Programs 2013shankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Signal Processing: Practical FileDokument13 SeitenDigital Signal Processing: Practical FilePawan SehgalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part-A Experiments Using Matlab: DSP Lab ManualDokument40 SeitenPart-A Experiments Using Matlab: DSP Lab ManualSharth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC1306 Digital Signal Processing Laboratory (REC)Dokument50 SeitenEC1306 Digital Signal Processing Laboratory (REC)jeyaganesh100% (1)
- DSP Experiments: Experiment 1Dokument20 SeitenDSP Experiments: Experiment 1Sàçhïñ KúshwàháNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Butterworth Filters Using Bilinear Transformation & Impulse InvarianceDokument2 SeitenDesign Butterworth Filters Using Bilinear Transformation & Impulse Invarianceudaya57Noch keine Bewertungen
- MatlabDokument66 SeitenMatlabappurono100% (1)
- Ece107l B1 17 Exp5Dokument19 SeitenEce107l B1 17 Exp5Nico LomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Labsheet-1: Question No.1:Basic Signal Generation and PlottingDokument15 SeitenLabsheet-1: Question No.1:Basic Signal Generation and PlottingmanasNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP Lab01 HandoutDokument9 SeitenDSP Lab01 HandoutHina ImtiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Butterworth Filter Design"The title "TITLE Butterworth Filter DesignDokument4 SeitenButterworth Filter Design"The title "TITLE Butterworth Filter DesignSomesh royNoch keine Bewertungen
- G N I S S e C o R P L A N G I S L A T I G I DDokument36 SeitenG N I S S e C o R P L A N G I S L A T I G I DjijoviNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB Fair Record (Model)Dokument71 SeitenMATLAB Fair Record (Model)Nandagopal SivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find The Impulse Response of A Discrete Time System Whose Function Is Given AsDokument5 SeitenFind The Impulse Response of A Discrete Time System Whose Function Is Given AsRishav DattaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open Ended Exp DSPDokument55 SeitenOpen Ended Exp DSPTilak shastriNoch keine Bewertungen
- WindowsDokument39 SeitenWindowsSaurabhMoharirNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS PracticalDokument20 SeitenSS PracticalMayur ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSP Lab ReportDokument26 SeitenDSP Lab ReportPramod SnkrNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATLAB DSP EXPERIMENTSDokument7 SeitenMATLAB DSP EXPERIMENTSSanjay ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Signal Processing Lab ExperimentsDokument29 SeitenDigital Signal Processing Lab ExperimentsSumanth SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Experiment-1 (A) Conversion of A Matrix Into Its Row Echelon FormDokument29 SeitenLab Experiment-1 (A) Conversion of A Matrix Into Its Row Echelon FormVineeth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADSP Lab ManualDokument33 SeitenADSP Lab ManualsunithrNoch keine Bewertungen
- All All: %two Channel Quadrature Mirror Filter Bank %perfect Reconstruction of InputDokument17 SeitenAll All: %two Channel Quadrature Mirror Filter Bank %perfect Reconstruction of InputSachin George ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas 1 Zani AkbariDokument7 SeitenTugas 1 Zani AkbariIsa MahfudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bartlett Window Using MatlabDokument5 SeitenBartlett Window Using MatlabAnushree ShahdeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS Practical (18) .Dokument21 SeitenSS Practical (18) .Mayur ChavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programs For Matlab1Dokument7 SeitenPrograms For Matlab1Harshavardan AkellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Signal Processing Matlab ProgramDokument5 SeitenDigital Signal Processing Matlab ProgramgoitomyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fir High Pass Flter: ProgramDokument3 SeitenFir High Pass Flter: ProgramVineeth KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsVon EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Negotiation SkillsDokument26 SeitenNegotiation SkillsRush ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clipping 2DDokument52 SeitenClipping 2Dsurbhisharma2210100% (1)
- Fill Algorithms: Soon Tee Teoh CS 116BDokument11 SeitenFill Algorithms: Soon Tee Teoh CS 116Bsurbhisharma2210Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fill Algorithms: Soon Tee Teoh CS 116BDokument11 SeitenFill Algorithms: Soon Tee Teoh CS 116Bsurbhisharma2210Noch keine Bewertungen
- MAG Infinite S 10SC-017XIBDokument3 SeitenMAG Infinite S 10SC-017XIBPedro Garcia DiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Despiece Des40330 Fagor Sr-23Dokument45 SeitenDespiece Des40330 Fagor Sr-23Nữa Đi EmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mouse Molecular Genetics Student Activity 2Dokument7 SeitenMouse Molecular Genetics Student Activity 2Jonathan ZhouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Đề Thi Thử Sở Bình PhướcDokument7 SeitenĐề Thi Thử Sở Bình Phướcbinh caoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advisory Note 11 ASFP Cell Beam RationaleDokument2 SeitenAdvisory Note 11 ASFP Cell Beam RationalePavaloaie Marian ConstantinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cilindros Parker 3H & 3HD, Parts Identification, Maintenance & Seal KitsDokument6 SeitenCilindros Parker 3H & 3HD, Parts Identification, Maintenance & Seal KitsFernandoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manifest Merger Debug ReportDokument14 SeitenManifest Merger Debug ReportRam PankhaniyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Axle, Front Drive - Housing, Swivel PDFDokument2 SeitenAxle, Front Drive - Housing, Swivel PDFLeo VegaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLT - Ate 2022Dokument28 SeitenDLT - Ate 2022chellep.uniNoch keine Bewertungen
- ED 107 162 Author Morphology. Pub Date Aug 69 Note Austin Edrs Price MF-$O.76 DescriptorsDokument75 SeitenED 107 162 Author Morphology. Pub Date Aug 69 Note Austin Edrs Price MF-$O.76 DescriptorsTalha KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 330 Computer Reset AddendumDokument75 Seiten330 Computer Reset AddendumA WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNR Status. - Train Details: Number Name Class QuotaDokument1 SeitePNR Status. - Train Details: Number Name Class QuotaPranshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Particulate Contamination in Aviation Fuels by Laboratory FiltrationDokument11 SeitenParticulate Contamination in Aviation Fuels by Laboratory FiltrationMuhammad KhairuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Jambeli Culture of South Coastal Ecuador Estrada Meggers y EvansDokument93 SeitenThe Jambeli Culture of South Coastal Ecuador Estrada Meggers y EvansMarco VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overhead Line Splices Automatic Copper: Splices For Metric ConductorDokument27 SeitenOverhead Line Splices Automatic Copper: Splices For Metric ConductorAzad RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systems ClassDokument53 SeitenSystems ClassBhetariya PareshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System Reaction PaperDokument3 SeitenNervous System Reaction PaperJohn Ruel Sanchez IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemera Creality CR10s Pro Upgrade Guide (Edition 1)Dokument24 SeitenHemera Creality CR10s Pro Upgrade Guide (Edition 1)gumushNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accountability Report Ba CharityDokument24 SeitenAccountability Report Ba CharityBintang sonda sitorus PaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jakob's Ten Usability Heuristics: Nielsen Norman GroupDokument11 SeitenJakob's Ten Usability Heuristics: Nielsen Norman GroupPiyush ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Accumulator - Test and Charge: Cerrar SIS Pantalla AnteriorDokument9 SeitenHydraulic Accumulator - Test and Charge: Cerrar SIS Pantalla AnteriorHomer Yoel Nieto Mendoza100% (1)
- INCaDokument47 SeitenINCaMehdi SoltaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 9712 2012 PDFDokument19 SeitenIso 9712 2012 PDFBala KrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Children's Film in The Digital Age - Essays On Audience, Adaptation and Consumer Culture (PDFDrive)Dokument211 SeitenChildren's Film in The Digital Age - Essays On Audience, Adaptation and Consumer Culture (PDFDrive)Basia KowalskaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Monkey's PawThe Lady of The Barge and Others, Part 2. by Jacobs, W. W., 1863-1943Dokument20 SeitenThe Monkey's PawThe Lady of The Barge and Others, Part 2. by Jacobs, W. W., 1863-1943Gutenberg.orgNoch keine Bewertungen































![SSP_lab2[1]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/721895426/149x198/8944563ec9/1712783501?v=1)