Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Future Perfect Tense
Hochgeladen von
Vilma Taneo VillaranOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Future Perfect Tense
Hochgeladen von
Vilma Taneo VillaranCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
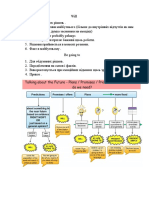
The Future Perfect Tense (#1)
The English future perfect tense can be understood as a combination of future time and the present perfect tense: it shows an action or event that started in the past, is starting or will start in the future and that will also be completed at some future time. The form of the future perfect tense has these parts: will + have + the past participle (third form of the verb) Examples: will have finished something will have lived here will have known each other will have left will have owned something will have been The future perfect tense is used as was outlined above: the action or event started before now, is starting now, or will start after now, but it will not be completed until some point in the future. Examples: In December, 2001 Dave's ESL Cafe will have been online for six years. (It hasn't yet been online for six years.) I hope that I will have finished this Hint by 9:30 PM. (It isn't finished yet). At 2:30 tomorrow afternoon, I will have finished my third class. (My classes won't
begin until tomorrow morning and they won't finish until tomorrow at 2:30 PM.) In about five minutes, I will have thought of at least five example sentences. (I'm thinking of example sentences now, but I still don't have five of them.) In June, 2001, my niece will have been married for two years. (She got married in June, 1999. Her two-year anniversary won't be until June, 2001.) It's 8:45 PM now. By 9:30 PM, I hope that I will have sent this Hint to Dave Sperling. (I haven't sent it yet.) ________________________________________________ Special Notes: 1. The form of the future perfect combines the forms of the future with will and the present perfect: will (or any modal verb) + simple form have / has + past participle will + simple form ( = have) + past participle
Because the first part of a future perfect verb is a one-word modal auxiliary, the second part is the simple (base) form of have: S-forms, past forms, and -ing forms cannot be used. Because the last two parts are like the present perfect in form, the third part is always the past participle. 2. The main verb (the past participle) shows the end point of the action or event. In the first
example sentence above, "be online for six years" will finish in December, 2001. In the last example sentence above, I hope that "send this Hint" will be finished at 9:30 PM.
_____________________________
Next: another use of the future perfect tense
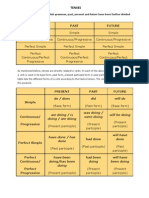
The PRESENT TENSE uses the verb's base form (write, work), or, for third-person singular subjects, the base form plus an -s ending (he writes, she works).
The PRESENT TENSE indicates that an action is present, now, relative to the speaker or writer. Generally, it is used to describe actions that are factual or habitual -- things that occur in the present but that are not necessarily happening right now: "It rains a lot in Portland" is a kind of timeless statement. Compare that to the present progressive -- "It is raining in Portland" -- which means that something is, in fact, going on right now. "I use my bike to get around town." is in the present, but I'm not actually on my bike right now. An instantaneous sense of the present can be conveyed with either the simple present or the progressive: "Watch him now: he holds [is holding] down the control key at the same time that he presses [is pressing] the letter d." The present tense is used to describe events that are scheduled (by nature or by people): "High tide is at 3:15 p.m. The Super Bowl starts at 6:15 p.m." The present tense can be used to suggest the past with what is sometimes called the fictional (or historic) present: "We were watching the back door when, all of a sudden, in walks Dierdre." With verbs of communicating, the present tense can also suggest a past action: "Dierdre tells me that she took her brother to the dentist." Most oddly, the present tense can convey a sense of the future, especially with verbs such as arrive, come, and leave that suggest a kind of plan or schedule: "The train from Boston arrives this afternoon at two o'clock." The present tense is used to describe events that are scheduled (by nature or by people): "High tide is at 3:15 p.m. The Super Bowl starts at 6:15 p.m." The present tense can be used to suggest the past with what is sometimes called the fictional (or historic) present: "We were watching the back door when, all of a sudden, in walks Dierdre." With verbs of communicating, the present tense can also suggest a past action: "Dierdre tells me that she took her brother to the dentist." Most oddly, the present tense can convey a sense of the future, especially with verbs such as arrive, come, and leave that suggest a kind of plan or schedule: "The train from Boston arrives this afternoon at two o'clock." Examples.. I walk to work every day. The Chicago Bulls sometimes practice in this gymnasium. Dr. Espinoza operates according to her own schedule. Coach Calhoun recruits from countries outside the U.S.A.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- English Tenses: Present TenseDokument17 SeitenEnglish Tenses: Present Tensedare_numero5Noch keine Bewertungen
- English Grammar Microsoft WordDokument18 SeitenEnglish Grammar Microsoft WordMarysia AndrunyszynNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspects and Tenses ExplainedDokument6 SeitenAspects and Tenses ExplainedflaviniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Simple Tense QuizDokument16 SeitenPresent Simple Tense QuizMay Ann DioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future Tenses: Predictions/statements of Fact Intentions Arrangements Scheduled EventsDokument27 SeitenFuture Tenses: Predictions/statements of Fact Intentions Arrangements Scheduled Eventsroxxi89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses Bridge CourseDokument6 SeitenTenses Bridge CourseJacintha RohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple PresentDokument27 SeitenSimple PresenthootanNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensesDokument7 SeitenTensesdharoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- TensesDokument9 SeitenTensesShanmuga VadivuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Means of Expressing FuturityDokument10 SeitenMeans of Expressing FuturityPereteanu ElenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is The Present TenseDokument11 SeitenWhat Is The Present TenseWindi SetianyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future Perfect Tense: What Will The Future Bring and When?Dokument6 SeitenFuture Perfect Tense: What Will The Future Bring and When?Jose Jacob Ortiz MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- TENSES AND VERB FORMSDokument7 SeitenTENSES AND VERB FORMSMohammed ShahabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present Tense GuideDokument10 SeitenPresent Tense GuideDarcy DeeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of The Present Perfect TenseDokument20 SeitenDefinition of The Present Perfect TenseSelebriti Rafiq ChikidotNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Grammar Compendium: Present SimpleDokument4 SeitenEnglish Grammar Compendium: Present SimpleDavide BressiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfect Tenses and AspectDokument5 SeitenPerfect Tenses and Aspectaquiles borgonovoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Perfect Tenses: It's A Latin Word Per Factus' Completely DoneDokument16 SeitenThe Perfect Tenses: It's A Latin Word Per Factus' Completely DoneWayan AndreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future in English PDFDokument3 SeitenFuture in English PDFLachin NamazNoch keine Bewertungen
- B2 ExamDokument4 SeitenB2 ExamKathy IsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding the 12 Verb TensesDokument10 SeitenUnderstanding the 12 Verb TensesMohamad Fakhri Al-BanjariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Grammar TensesDokument9 SeitenSimple Grammar TensesMega TrianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- XauqueDokument25 SeitenXauqueLindsey StokesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspects of TensesDokument4 SeitenAspects of TenseszoroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Means of Expressing FuturityDokument9 SeitenMeans of Expressing FuturityEma Ghita50% (2)
- PDF CzasyangielskieDokument7 SeitenPDF CzasyangielskieAndrzej StańczakNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Expression of Future in Contemporary English: João Bittencourt de Oliveira (UERJ/UNESA)Dokument19 SeitenThe Expression of Future in Contemporary English: João Bittencourt de Oliveira (UERJ/UNESA)degr8sidNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Future Perfect TenseDokument6 SeitenThe Future Perfect TenseTia RahmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Verb TensesDokument5 SeitenUsing Verb TensesklipordNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Tenses: Tenses in English Present Tense Simple Present TenseDokument7 SeitenTypes of Tenses: Tenses in English Present Tense Simple Present TenseBaqirNoch keine Bewertungen
- English GrammarDokument8 SeitenEnglish Grammargeddam06108825Noch keine Bewertungen
- Leaf StudyDokument5 SeitenLeaf StudyNatália DiasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 10VerbsIVDokument18 SeitenLecture 10VerbsIVIsabela BmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar RulesDokument8 SeitenGrammar RulesMed JabrNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is TenseDokument9 SeitenWhat Is Tensesobonoj644Noch keine Bewertungen
- Uses of The Perfect InfinitiveDokument24 SeitenUses of The Perfect InfinitivemiraeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Narrative Tenses ExplainedDokument5 SeitenNarrative Tenses ExplainedElena LópezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb Tenses: The Present Simpleor Simple Present. It's Mainly Used in The Following WaysDokument9 SeitenVerb Tenses: The Present Simpleor Simple Present. It's Mainly Used in The Following WaysFOANoch keine Bewertungen
- Future Tenses ExplainedDokument6 SeitenFuture Tenses ExplainedЧарли ЖутиNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb as the central part of speechDokument12 SeitenVerb as the central part of speechАлина ГолубенкоNoch keine Bewertungen
- FutureDokument30 SeitenFutureStefanDribler998Noch keine Bewertungen
- PSY131 Final 2Dokument4 SeitenPSY131 Final 2Study SmartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses UietDokument27 SeitenTenses UietMohitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Future Tense Forms ExplainedDokument10 SeitenFuture Tense Forms ExplainedEvi SulastriNoch keine Bewertungen
- JWJWJWDokument26 SeitenJWJWJWShankSoham MohantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Grammar Tenses and Speech GuideDokument16 SeitenEnglish Grammar Tenses and Speech GuideSandeep Goud KalalNoch keine Bewertungen
- English TensesDokument7 SeitenEnglish TensesAtif Azhar100% (1)
- Present Perfect ArticleDokument5 SeitenPresent Perfect ArticleEdward Tamayo DuqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repaso de Gramática InglésDokument18 SeitenRepaso de Gramática InglésDaniel Márquez GómezNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are Verb TensesDokument10 SeitenWhat Are Verb TensesNoah LunetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verb TensesDokument35 SeitenVerb TensesTiê FelixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn Past Tenses in 40 CharactersDokument5 SeitenLearn Past Tenses in 40 CharactersCayo Eder FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Simple Vs Present PerfectDokument3 SeitenPast Simple Vs Present PerfectnoriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenses NotesDokument7 SeitenTenses NotesFatima AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- HND Year 2 Common Texts NewDokument64 SeitenHND Year 2 Common Texts Newbsonleader5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Present Continuous TenseDokument4 SeitenPresent Continuous TensesanmohdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grammar Guide: Verb Tenses ExplainedDokument108 SeitenGrammar Guide: Verb Tenses ExplainedCaren SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Present PerfectDokument10 SeitenPresent PerfectMeli PasikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Los Verbos Reflexivos-RubricDokument4 SeitenLos Verbos Reflexivos-Rubricamn628Noch keine Bewertungen
- Part of Speech Powerpoint Presentation: English I HonorsDokument14 SeitenPart of Speech Powerpoint Presentation: English I HonorsRetnoWulandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drainage Patterns and Their CharacteristicsDokument26 SeitenDrainage Patterns and Their Characteristicsfilza zakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- K-12 BOW Quarter 1 Budget of Work in English 4 WeekDokument5 SeitenK-12 BOW Quarter 1 Budget of Work in English 4 WeekKimttrix WeizsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 3Dokument11 SeitenLesson 3hasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- English File 3rd - Pre-Inter TB 106Dokument1 SeiteEnglish File 3rd - Pre-Inter TB 106Liliana LardoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Latihan B. Inggris SMP 7Dokument19 SeitenSoal Latihan B. Inggris SMP 7herbal produkNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Irregular Verbs Gym PDFDokument2 SeitenThe Irregular Verbs Gym PDFValeria ManginiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01.1.29 Ism - Comprehensive Review PDFDokument4 Seiten01.1.29 Ism - Comprehensive Review PDFamtulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting English Speaking SkillsDokument8 SeitenFactors Affecting English Speaking SkillsCharles Kevin Cañete ArabeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Second Quarterly Test in English 4Dokument4 SeitenSecond Quarterly Test in English 4Val AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity SheetsDokument10 SeitenActivity SheetsMary Grace SerofiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Morphology: The Words of Language Part 1: 1. Morpheme Is A Short Segment of Language That Meets Three CriteriaDokument8 SeitenUnit 1 Morphology: The Words of Language Part 1: 1. Morpheme Is A Short Segment of Language That Meets Three CriteriaLaarnie BbbbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jadual Spesifikasi Ujian (Jsu) Bahasa Inggeris Pemahaman 013 Mock Test 1 2017Dokument2 SeitenJadual Spesifikasi Ujian (Jsu) Bahasa Inggeris Pemahaman 013 Mock Test 1 2017Blur LagikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social Case Malayalam 05Dokument2 SeitenSocial Case Malayalam 05Vinesh PvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conditional Sentence Type 1: Example: If I Find Her Address, I'll Send Her An InvitationDokument9 SeitenConditional Sentence Type 1: Example: If I Find Her Address, I'll Send Her An InvitationIvyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Numeral and The PronounDokument5 SeitenThe Numeral and The PronountemurlankuziboevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linguistic Topic # 9: The Noun Phrase and The VerbDokument8 SeitenLinguistic Topic # 9: The Noun Phrase and The Verbpbars100% (1)
- Use of Passive Voice ExplainedDokument6 SeitenUse of Passive Voice ExplainedMilena Aguacia Moreno100% (1)
- Pronouns and Verb To BeDokument6 SeitenPronouns and Verb To BeAna Felix GodoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Space 1 Adaptable Unit Test 8Dokument4 SeitenYour Space 1 Adaptable Unit Test 8leandro lozano100% (1)
- Exercicios Gramatica InglesDokument158 SeitenExercicios Gramatica Inglesleticiamlucas100% (1)
- Speakout Writing Extra Starter Unit 10 PDFDokument1 SeiteSpeakout Writing Extra Starter Unit 10 PDFadolfoursoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules of Affirmative To NegativeDokument2 SeitenRules of Affirmative To Negativeanup20janNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Are You - Wie Geht's GermanDokument4 SeitenHow Are You - Wie Geht's Germandegraded 4resterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lexical Morphology 1Dokument20 SeitenLexical Morphology 1fajar sukmana100% (1)
- Indefinite Articles: in English Indefinite Articles A An. A AnDokument2 SeitenIndefinite Articles: in English Indefinite Articles A An. A AnvidaloothsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical JargonDokument7 SeitenTechnical JargonZain UlabideenNoch keine Bewertungen
- There Is A Practice: NAME: Lizeth Apeña Ramirez Grade: 4to Sabado MañanaDokument3 SeitenThere Is A Practice: NAME: Lizeth Apeña Ramirez Grade: 4to Sabado MañanaArpasi A. CesarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Academic WritingDokument34 SeitenBasic Academic WritingWARIH MIFTAKHUL J JNoch keine Bewertungen