Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Assignment 2nd - 566 - Computer Application
Hochgeladen von
M Hammad ManzoorOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Assignment 2nd - 566 - Computer Application
Hochgeladen von
M Hammad ManzoorCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Department of Business Administration
Block No. 13, Sector H-8, Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad.
Computer Application (566)
Assignment No. 02
Submitted to:
Mrs. Sana Akbar Khan
Block No. 13, Department of MBA AIOU, ISLAMABAD (051-905 7141)
Submitted by:
Muhammad Hammad Manzoor MBA (HRM) 2nd Semester
Roll No. 508195394 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC) Block 08, Clifton, KARACHI (0321-584 2326, 0322-555 5901)
Computer Application (566)
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
All praises to Almighty Allah, the creator of the Universe who blessed me with the knowledge and enabled me to complete this research. I feel great pleasure and honor to express my sincere gratitude and heartfelt thanks to my worthy subject faculty member Mrs. throughout the period of M.B.A (Semester II). SANA AKBAR, for her guidance, encouragement and friendly attitude during the present study and
I pay my thanks to all the Faculty of the Department & AIOU Karachi Campus Staff for their kind support, constructive criticisms and real encouragement. I wish to thank Ms. Madiha Ahmed Khan for valuable discussions and knowledge sharing during the completion of this project. I further wish to record my thanks to all my students, class fellows, well wishers and especially Nadra Management, Saima Mangi (Assistant Manager), Mr. Usman Javed , Mr. Khizar Iftikhar, Khurram Shahzad, Rehan Hassan, Sohail, Waleem, Javed for their help, valuable suggestions, whole hearted cooperation and prayers.
Finally, I owe all my academic success and progress in life to my loving parents and sisters, whose affection, endless prayers, good wishes and inspiration remained with me for higher ideals of life.
M. Hammad Manzoor
2
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
ABSTRACT
The study had been carried out by keeping in mind about the selection criteria for and use of appropriate inventory system in the Nadra (Pakistan). Nadra (Pakistan) has been selected for the sake of the data analysis and working on its merits and demerits, the methodology includes the utilization of ICT; techniq8es had been worked out from Nadra which lead the study for further SWOT analysis. SWOT analysis had been carried out and conclusion followed by recommendations had been made in this regards.
3
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
Sr. No.
1
Contents Description
Introduction
What is ICT Introduction? ICT in Pakistan Key Organizations & departments dealing with ICT
Page No.
5-8
Review of Literature
ICT Related Industries in Pakistan Legal & Regulatory Environment for ICT in Pakistan ICT related Education and Capacity Building Programs ICT and ICTD Research and Development Company Profile Data Collection
6-13
3 4
National Registration and Database Authority (NADRA)
14-33 34
Data Analysis
Demerits and Deficiencies Merits & Strengths
Recommendations
35
References
36
4
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566) Introduction Information and communications technology (ICT)
ICT Stands for "Information and Communication Technologies." ICT refers to
technologies that provide access to information through telecommunications. It is similar to Information Technology (IT), but focuses primarily on communication technologies. This includes the Internet, wireless networks, cell phones, and other communication mediums.
In the past few decades, information and communication technologies have provided society with a vast array of new communication capabilities. For example, people can communicate in real-time with others in different countries using technologies such as instant messaging, voice over IP (VoIP), and video-conferencing. Social networking websites like Facebook allow users from all over the world to remain in contact and communicate on a regular basis. Modern information and communication technologies have created a "global village," in which people can communicate with others across the world as if they were living next door. For this reason, ICT is often studied in the context of how modern communication technologies affect society. ICT is an acronym that stands for Information Communications Technology However, apart from explaining an acronym, there is not a universally accepted definition of ICT? Why? Because the concepts, methods and applications involved in ICT are constantly evolving on an almost daily basis. Its difficult to keep up with the changes - they happen so fast. Lets focus on the three words behind ICT: - INFORMATION - COMMUNICATIONS - TECHNOLOGY A good way to think about ICT is to consider all the uses of digital technology that already exist to help individuals, businesses and organizations use information. ICT covers any product that will store, retrieve, manipulate, transmit or receive information electronically in a digital form. For example, personal computers, digital television, email, robots. So ICT is concerned with the storage, retrieval, manipulation, transmission or receipt of digital data. Importantly, it is also concerned with the way these different uses can work with each other.
5
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
In business, ICT is often categorized into two broad types of product: (1) The traditional computer-based technologies (things you can typically do on a personal computer or using computers at home or at work); and (2) The more recent, and fast-growing range of digital communication technologies (which allow people and organisations to communicate and share information digitally) Let's take a brief look at these two categories to demonstrate the kinds of products and ideas that are covered by ICT: Traditional Computer Based Technologies These types of ICT include:
Application Use Standard Office Applications - Main Examples Word processing E.g. Microsoft Word: Write letters, reports etc Spreadsheets E.g. Microsoft Excel; Analyse financial information; calculations; create forecasting models etc Database software E.g. Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, Access; Managing data in many forms, from basic lists (e.g. customer contacts through to complex material (e.g. catalogue) Presentation E.g. Microsoft PowerPoint; make presentations, either directly using a computer software screen or data projector. Publish in digital format via email or over the Internet Desktop publishing E.g. Adobe Indesign, Quark Express, Microsoft Publisher; produce newsletters, magazines and other complex documents. Graphics software E.g Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator; Macromedia Freehand and Fireworks; create and edit images such as logos, drawings or pictures for use in DTP, web sites or other publications Specialist Applications - Examples (there are many!) Accounting E.g. Sage, Oracle; Manage an organisation's accounts including revenues/sales, package purchases, bank accounts etc. A wide range of systems is available ranging from basic packages suitable for small businesses through to sophisticated ones aimed at multinational companies. Computer Aided Computer Aided Design (CAD) is the use of computers to assist the design process. Design Specialised CAD programs exist for many types of design: architectural, engineering, electronics, roadways Customer Relations Software that allows businesses to better understand their customers by Management (CRM) collecting and analysing data on them such as their product preferences, buying habits etc. Often linked to software applications that run call centres and loyalty cards for example.
Traditional Computer Based Technologies
6
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
The C part of ICT refers to the communication of data by electronic means, usually over some distance. This is often achieved via networks of sending and receiving equipment, wires and satellite links. The technologies involved in communication tend to be complex. You certainly don't need to understand them for your ICT course. However, there are aspects of digital communications that you needs to be aware of. These relate primarily to the types of network and the ways of connecting to the Internet. Let's look at these two briefly (further revision notes provide much more detail to support your study). Internal networks Usually referred to as a local area network (LAN), this involves linking a number of hardware items (input and output devices plus computer processing) together within an office or building. The aim of a LAN is to be able to share hardware facilities such as printers or scanners, software applications and data. This type of network is invaluable in the office environment where colleagues need to have access to common data or programmes. External networks Often you need to communicate with someone outside your internal network, in this case you will need to be part of a Wide Area Network (WAN). The Internet is the ultimate WAN - it is a vast network of networks. ICT in a Broader Context Your ICT course will almost certainly cover the above examples of ICT in action, perhaps focusing on the use of key applications such as spreadsheets, databases, presentation, graphics and web design software. It will also consider the following important topics that deal with the way ICT is used and managed in an organization: - The nature of information (the "I" in ICT); this covers topics such as the meaning and value of information; how information is controlled; the limitations of ICT; legal considerations - Management of information - this covers how data is captured, verified and stored for effective use; the manipulation, processing and distribution of information; keeping information secure; designing networks to share information
7
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
- Information systems strategy - this considers how ICT can be used within a business or organization as part of achieving goals and objectives As you can see, ICT is a broad and fast-changing subject. We hope our free study materials (revision notes, quizzes, presentations etc) will help you master IT!
ICT in Pakistan:
The year 2007 was historic for Pakistan. Alternatively listed as an A+ investment country and then as the most dangerous place on earth, Pakistan see-sawed between optimistic economic reports, violence, political instability, and uncertainty. However, despite the odds, the country experienced a strong foreign investment influx, with over USD 9 billion invested in the telecom sector alone (Rising Pakistan 2007). Exponential growth in the telecom sector, which constitutes 2 percent of Pakistans Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and is expected to account for 3 percent in the next three to four years, has resulted in the creation of 80,000 jobs directly and 500,000 jobs indirectly.1 Currently, Pakistan has about 95.7 million phones: 89 million cellular, 4.5 million fixed lines, and 2.2 million Wireless Local Loop WLL (PTA 2008). Teledensity in 2008 stood at 59.8 percent from a mere 4 percent in 2003. With a score of 3.7 out of 10, Pakistan ranks 63rd in 67 countries in the e-readiness ratings (Economist Intelligence Unit 2007). The information technology (IT) and IT-enabled services (ITES) sectors also boast an impressive 61.18 percent growth in exports, making Pakistan a country to watch very closely. Information and communications technologies (ICTs) have been responsible for progress in social development areas as well, with various ICT-supported initiatives aiming to contribute to Pakistans on track status in connection with the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) of gender equality; maternal and child health; combating HIV/AIDs, malaria and other diseases; and ensuring environmental sustainability. However, work toward the goals for education and poverty alleviation is off track and, in the case of poverty, it is regressing. ICT planning by the government of Pakistan (GoP) has not been able to sufficiently address this critical issue. There is failure to recognize that overall growth in telecom and ICT will be in vain if poverty and lack of education continue to destabilize the country.
Key Organization & Department dealing with ICT in Pakistan:
ICT development in Pakistan has gone beyond the purview of a few key entities and promotion of ICT use has been taken up by different organizations and user groups. However, on an institutionalized basis the following organizations are responsible for ICT development: The Ministry of Information Technology and Telecommunications (MoITT) is responsible for policy in IT and telecommunications. The PTA is the telecom regulatory body.
8
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
The Universal Service Fund Guarantee Ltd (USF) is responsible for telecom development in the under-developed areas via subsidies from a contributed Fund. The Pakistan Software Export Board (PSEB) oversees IT growth and export. There are several trade bodies, some of which are powerful although informal in nature. They include: Pakistan All Software Houses Association (PASHA) Internet Service Providers Association of Pakistan (ISPAK) Computer Society of Pakistan Federation of Pakistan Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FPCCI)
ICT Related Industries in Pakistan:
With a growth rate of 61.18 percent, Pakistani ICT and ITES companies have shown remarkable growth in 2007, and local companies have been recognized at various international events. The total industry size is USD 2.8 billion. IT and ITES exports were valued at USD 1.4 billion in 2007. The export target for 20062007 was USD 108 million (PSEB 2008). At the end of 2007, 1,082 IT companies were registered with PSEB. Most of these are based in Karachi (384), Lahore (353), and Islamabad (276). There are 60 foreign IT and telecoms companies in Pakistan. There are 11 IT Parks covering an area of 750,000 square feet. Aggressive efforts by P@sha (Pakistan Software Houses Association) and the PSEB have made quality a major thrust of the industry, and international quality certifi cations such the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) have been actively promoted by both the private sector and government. One company is at CMM Level 5, another at CMMI Level 5, three at CMMI Level 3, and nine at CMMI Level 2. While the majority of companies are small, several have attracted sizeable foreign direct investments, and it is anticipated that within the next year or two, if Pakistan remains politically stable, the industry will see the formation of some large and more mature companies. In 2005 there were 110,000 IT professionals employed in Pakistans IT sector, of which more than 15,000 were engaged in export-oriented activities (e.g. software development, callcentres). Total IT spending in 20052006 amounted to USD 1.4 billion.
LEGAL AND REGULATORY ENVIRONMENT FOR ICT DEVELOPMENT
The Electronic Transaction Ordinance (ETO) was issued in 2002. It covers public key infrastructure (PKI) and certification authorities (CA), electronic transactions, digital signatures, and related elements that constitute the basis for secure electronic transactions over the Internet.
9
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
Recently a bill on cybercrime was promulgated amid protests from the industry against the draconian penalties and the lack of clarity with regard to building the capacity of the implementers (police, investigation agencies, lawyers, courts). The bill will undergo necessary changes after review by the new government. New laws relating to Internet Protocol (IP) protection, data security, and consumer protection are also being drafted. The telecoms sector has a comprehensive set of laws that are supplemented by the requisite rules and regulations. The licensing process and sector regulation have proceeded successfully and a policy review is scheduled this year. Issues related to spectrum (e.g. WiMAX) and broadband are being tackled on a real time basis (as the issues evolve) and resolved. Considerable spectrum clearance has taken place and it is expected that more bands will be cleared for licence-free transmission, 2 in addition to the current 2.5 GHz and 5.8 GHz Wireless Fidelity (WiFi) bands.
ONLINE SERVICES e-Banking
There has been a steady increase in the number of e-banking products and services. According to the State Bank of Pakistans quarterly report, the volume and value of e-banking transactions in the fi rst quarter of 20072008 (JulySeptember) reached 30.1 million and PKR 3.4 trillion, respectively, indicating a growth of 7.5 percent and 9.6 percent, respectively. The total number of active cards (ATM, credit, and debit) grew by 11.9 percent to reach 6.5 million. The total number of ATM machines as of the first quarter of 2007 2008 reached 2,470, representing an increase of 7.7 percent over the previous quarter. Real Time Online Branches (RTOB) reached 4,444 and now constitute 57 percent of the total branch network in the country. The number of Point of Sale (POS) terminals available to customers was 50,004 as of the first quarter of 20072008, reflecting a growth of 7.9 percent over the total for the previous quarter.
e-Commerce
One of the more innovative of recent e-commerce initiatives in Pakistan is Thread Net Hunza (www.threadnethunza.com.pk), an e-commerce site spearheaded by the Karakoram Handicraft Development Programme (KHDP), a community-based enterprise system. The project promotes culture-sensitive and environmentally sustainable micro-enterprises, thereby creating village-based income and employment opportunities for artisans, small producers, women, disabled members of the community, and other disadvantaged groups. At present, around 3,000 women
10
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
artisans are working from their homes under the Thread Net Hunza project. Another 60 women work at seven workshops daily and produce finished products that are marketed under the brand name of Thread Net Hunza by local and national retailers. Tourists are the prime market, and local and national exhibitions are held to romote the products. The site has generated over PKR 3.5 million in sales.
e-Government
The government of Pakistan through its e-Government Directorate (EGD) as well as other ministries has undertaken several important projects with a potential large scale impact specifically in terms of transparency and accountability. But although some of these projects were implemented several years ago, implementation hurdles, lack of integration with appropriate agencies, poor coordination, and a lack of project scaling/replication have prevented many projects from achieving the potential levels of impact. Independent of the EGDs initiatives, work in different autonomous government departments has been proceeding at an excellent pace. This underlines the basic fallacy of trying to drive e-government via central control instead of decentralized implementations. Some of the latter are described as follows:
CBR Automation.
The GoP through the National Trade Corridor (NTC) aims to provide a single electronic window operation for trade and commerce. To achieve this objective, the Pakistan Customs Computerized System (PaCCS) was developed as a pilot project and launched on 23 March 2005. It is currently operational in all three container terminals located at Karachi Port and Port Qasim. For the second phase of the project, CBR (Central Board of Revenue, now renamed Federal Board of Revenue or FBR) plans on building on the existing system by implementing the new Pakistan Automated Commercial Community System (PACCS) throughout the country.
NADRA Database.
The National Database and Registration Authority (www.nadra.gov.pk) has created the largest citizens database in Pakistan, covering data for over 80 million people. The database is being used for activities ranging from issuance of identity (ID) cards and machine readable passports to creating electoral rolls. The applications, software, and systems were developed in-house and are now being used to develop similar systems in other countries.
Land and Revenue Records Automation.
The automation of land records service delivery has been a landmark project, contributing to long-lasting tenure security and more efficient functioning of land markets. The project has been recommended for implementation across the country.
11
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
The implementation has been started in several pilot areas and since this is a provincial jurisdiction, the speed and pattern of implementation is variable across Pakistan. However, at this time each province has pilots (e.g. Lahore) and full blown public-private partnership (PPP) based programs (e.g. Karachi) are now operating.
Wetland Project by UNDP and WWF Pakistan.
The Protection and Management of Pakistan Wetlands Project is a project funded by the United Nations Development Programme/Global Environment Facility (UNDP/GEF) being implemented by World Wildlife Fund (WWF) Pakistan. The project has produced a detailed geographic information system (GIS) with cartographic maps, satellite images, and Global Positioning System (GPS)-based field observations for better management of Pakistans natural resources.
ICT-RELATED EDUCATION AND CAPACITY-BUILDING PROGRAMS
National Education Database Program (NEDP) Pakistan
The NEDP is a collaborative and innovative PPP program launched by a consortium of expert private sector enterprises and supported by Intel, Microsoft, Oracle, TeleCard, and the MOE. The project utilizes a Web-based school management software available in the local regional languages, to facilitate the collection of data at the grassroots level, thus modelling the creation of a constantly updated National Education Database. The pilot project, which was initiated in October 2005, had the additional objective of identifying key problem areas in actual implementation, to be used in planning nationwide implementation. The project successfully implemented the locally developed EMIS system in 100 government schools. However, the project is experiencing problems due to lack of understanding of implementation issues (business processes, content, development of software and applications, backend systems, and consistent delivery and follow-up) by the MoE.
ICT in Higher Education
Pakistans Higher Education Commission (HEC) is implementing an agenda for reform that includes: (i) faculty development; (ii) improving access; (iii) excellence in learning and research; and (iv) relevance to national priorities. Over 500 scholars (teachers and students of graduate and postgraduate programs) are sent abroad annually to universities in Australia, Austria, France, Germany, New Zealand, Sweden, the Netherlands, the UK, and the US, and there are plans to increase the number to 1,000 scholars per year. The HEC has also launched a mirror site of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Open Courseware on the Pakistan Education and Research Network (PERN) (see
12
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
The Pakistan Education and Research Network [PERN]) that enables open sharing of syllabi, lecture notes, and related materials of 914 courses. Higher education institutions that are leading the way in ICT supported education in Pakistan are the Virtual University (VU) and the Allama Iqbal Open University (AIOU). VU (www.vu.edu.pk) is Pakistans first university relying completely on modern ICTs. It was established by the government as a public sector, not-for-profi t institution to provide affordable world-class education to aspiring students all over the country. Using free-to-air satellite television broadcasts and the Internet, VU allows students to follow its rigorous programmes regardless of their physical location. The AIOU (www.aiou.edu.pk), which was established in 1974, is the first open and distance learning university in Pakistan and Asia. Its main campus is in Islamabad and it has a large network of regional centers spread all over Pakistan and the Middle East. Together with the Virtual University, AIOU serves over 750,000 students (growing at 14 percent annually), three times the combined student populations of all other universities in Pakistan.
ICT AND ICTD RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT
While ICT has penetrated into the far reaches of the country, ongoing R&D on localization tools and rural connectivity and access will be the key to whether the potential of ICT is harnessed by ordinary citizens. The release of Urdu language tools by the Centre for Research in Urdu Language Processing (CRULP) has already proven to be instrumental in the extension of e-services to the masses. The CRULP has already successfully developed the Urdu lexicon, speech recognition system and fonts, and it is now also coordinating the PAN Localization project (http://www. panl10n.net/) for seven Asian languages. The Government of Pakistan also continues to support ICT research with the R&D Fund, which is no longer being administered by the PTCL. The new independent fund is managed by a 17-person committee and annually receives 1 percent of the gross revenue of all telecommunication service providers. Funded projects include: Automatic Control Programming of Robots through Imitation, GIS-based Optical Fibre Network Monitoring and Management System, Low Cost Ultrasound Training Simulator, and Artificial Immune System-based General Purpose Intrusion Detection System.
13
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
Practical Study of National Database & Registration Authority (NADRA)
History & Introduction
History
National Database Organization (NDO) was established under Ministry of Interior as an attached department to undertake the function of handling the data being collected through National Data Forms during the Population Census 1998, which was conducted from 2nd March 1998 to 18th March 1998. National Data Forms (NDFs) were designed by a committee of experts encompassing maximum social and fiscal indicators as implements for future planning, documentation of economy and for creation of a comprehensive Citizens' Database. To cater for a cohesive and unified approach in both Registration and Social fields NADRA was created on 10 March 2000 by merging the National Database Organization (NDO) and Directorate General of Registration. NADRA is an independent corporate body with requisite autonomy to remain free of political pressure and interventions for all times to come.
Preamble
NADRA has been established with the objective of introducing a new, improved and modernized registration system for the entire population and things of Pakistan (Refer to NADRA Ordinance 2000 for details). Culminating among other things is the issuance of state-of-the-art National Identity Cards (NICs) to all adult citizens of Pakistan. These NICs shall be duly backed by the computerized database and data warehouse respectively called the Citizens' Database and National Data Warehouse (NDW).
14
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
The concept was developed to help government in implementing a fact based system of good governance in the country by encountering evils of undocumented population growth and registration of items belonging to citizens and organizations. NADRA had completed the creation of a comprehensive Citizens' Database by the new millennium based on National Data Forms. An upgraded version of citizen's database is being collected now-a-days with the help of National Form Application for issuance of new computerized NICs.
NADRA Headquarters
NADRA is located in the State Bank Building, which constitutes history of being the National Assembly building in the old days where in the historical Parliament Hall, the 1973 Constitution was discussed and approved by the Parliament. NADRA is working with speed and efficiency to establish a countrywide data communication network for linking central data warehouse with 5 Provincial Islamabad, Karachi, Lahore, Peshawar, Quetta and 3 Regional Head Quarters located at Sukkur, Multan and Sargodha. The quality of data will be regularly updated at Provincial and District Offices for use by the authorized users and monitored through the direct inputs from the user and feeder agencies. The data will be most comprehensive including statistical details of resource and complete biographic details of every citizen.
15
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
Hierarchy NADRA
Chairman
D.G All NSRC
D.G Peshawar
D.G Quetta
D.G Lahore
D.G Karachi
D.D.G
Dir Admin
Dir CBRC
Dir O pperation
Dir HR
D.D Admin
D.D CBRC
D.D Opperation
D.D Tchnical
Area Manager
Assistant Projec t Manager
Sys tem Engineer
Supervisor
Offic e Assistant
DEO
16
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
Network Information Infrastructure
The NADRA Frame-Relay network infrastructure is made up of eight regional sites and over a 100 smaller Swift Registration Centers (SRCs) which have dial-up connectivity to their local Provincial headquarters. The main backbone uses 256 Kbps DXX between all the sites in the design depicted in Fig. 1. Each of the links is terminated on site at the Passport 6440 Frame-Relay Cloud Generator. The Passport 6440 is a network consolidation switch which delivers a powerful range of standards-based interfaces and services, high performance multiprotocol routing and simultaneously supports voice, data, video and image traffic. These devices provide Packet Switching at Layer2. The advantage of packet switching lies in the ability of the technology for intelligent path determination based on factors like link congestion, utilization, bandwidth and cost. End result is that data packets may follow multiple paths to a single destination or in case of link failures an alternate path.
As well as using Frame-Relay as the basic frame work for a robust network, all of NADRAs PHQs incorporate Satellite technology for redundancy and back up links. So all of NADRAs main sites are connected via terrestrial as well as Satellite links for a
17
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
complete and un-beatable data communication solution. Fig 2 represents the data trunks all over Pakistan.
Organizational Structure
The Nadra network department will go Commercial as 15th September 2002. The entire department has been restructured to create a flexible, productive, commercially viable and independent business entity. The aim of this realignment is to gain a return on the original investment through commercial ventures which in turn will facilitate and finance NADRAs plans for expansions to over a 144 data and communication sites that span the country as the largest network of its type. The network department falls directly under the Chairman NADRA and is responsible for its own finances and business decisions. The network team is made up of a number of technology specialists and engineers that are presently manning all the various sites.
18
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
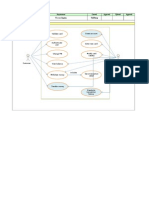
Applicant Signs a Receipt at the Reception
The Data Entry Process
CNIC Photograph
Thumb Impression/Signature
Checkout & Delivery of Form
Verification Process
Information Transfer
Checks & Balances
Delivery
Departments at NADRA
19
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
Computerized National Identity Card
Application Processing Procedures The First Step Applicants require a token number for processing their application. The applicants can either wait for their turn in a queue to receive the token at the token window or call ahead for an appointment. Acquiring the token allows the person to proceed to the next step i.e. data collection by SRC Data Entry Operator. Applicant Signs a Receipt at the Reception On receiving the token, the applicant is provided a slip on which the applicant signs his/her name. The signature is scanned at the station and is stored in association with the applicants token number. The Data Entry Process When the token number is called, the applicant proceeds to the Data Entry Station where he/she provides the station operator with his/her particulars. This information is entered into the database by the operator and saved for further processing. CNIC Photograph Once the photo station is available, the next token number is called. The photo station pulls the applicants token number and attaches the digital photograph with the rest of the form. Then the applicant is guided towards the thumb station for scanning of thumb impression. Thumb Impression/Signature The customer then proceeds to the thumb impression station where both thumb impressions are read through a digitizer. In case the signature scanner hardware is not available to the station, a signature capture device will be present at the station.
20
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
Here the applicant signs the signature pad that is than saved with his other information. Checkout & Delivery of Form The applicant proceeds to a checkout or printout station where he/she receives a copy of the filled out form, ready for attestation. The form is required to be attested by authorized personnel and than re-submitted to the SRC station. Verification Process Once the form has been attested, the applicant submits the form to SRC. From here the form is sent for verification through internal procedures. Information Transfer At the end of day, the SRC compiles the number of application received after verification and these records are transmitted electronically to the NADRA Head quarters. Checks & Balances At the NADRA HQ, the data received from the SRC's nationwide are subjected to checks enforced to verify authenticity of the records. Delivery The ID Cards are printed and packaged in boxes for delivery. The urgent cards are dispatched to the present address of the applicant through TCS and normal cards through Urgent mail Service. Documentation Requirements for Applicants
Documentation For re- issuance of Card
o o
Old National Identification Card NIC Number of Head of Family
Documentation For FRESH Applications 21
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
o o o
BAY Form Matriculation Mark Sheet (if available) Birth Certificate (in case matriculation mark sheet and BAY form is not available) NIC # of head of the family
For FRESH Applications For Registration With Spouse (for women only)
Nikkah Namma Fathers NIC Husband NIC BAY Form Matriculation Mark Sheet (if available) Birth Certificate (in case matriculation mark sheet and BAY form is not available) NIC # of head of the family
For Re-Issuance of Card For Registration With Spouse (for women only)
Nikkah Namma Fathers NIC Husband NIC Old National Identification Card NIC Number of Head of Family
Lost Card Change of Date of Birth
Matriculation mark sheet BAY Form Birth Certificate (in case matriculation mark sheet and BAY form is not available) NIC # of head of the family Copy of the First Investigation Report (FIR) or Affidavit from a Notary Public Other supporting documents e.g. Birth certificate, Passport, Matriculation sheet etc. Old National Identification Card NIC Number of Head of Family
Change of Date of Birth
Matriculation mark sheet BAY Form Old National Identification Card NIC Number of Head of Family
Change of Address
Registry copy Allotment letter Matriculation mark sheet BAY Form Birth Certificate (in case matriculation mark sheet
Change of Address
Registry copy Allotment letter Old National Identification Card
22
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
and BAY form is not available)
NIC # of head of the family
NIC Number of Head of Family
Change of Name
Affidavit signed by notary public Advertisement in the newspaper stating the same Name change in Matriculation mark sheet
Change of Name
Affidavit signed by notary public Advertisement in the newspaper stating the same Name change in Matriculation mark sheet
In Case the applicant has no documentary proof then Police verification report of applicant from local police Station is required. Attester cannot attest his/her own form. For attestation please check for attester's name, Attester's Signature, Attester's Stamp, Attester's NIC and Attester's Designation. Nazim, Naib Nazims and counselor can only attest form for the applicant of their concerned area. Pakistani Citizen Living abroad is not eligible to process from the center
Card Processing Fee:
Urgent Cards: Rs.180/Normal Cards: Rs.60/Card Processing Time:
Urgent cards: process will be completed in Normal cards: Process will be completed in 30 working days.
10
working
days.
23
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
ICT Uses by NADRA:
Computerized National Identity Card (CNIC)
NADRA is issuing new Computerized National Identity Cards (CNICs) to all Pakistani citizens. The CNIC is a comprehensive identification document that authenticates an individuals identity as a Pakistani citizen. The CNIC may serve as a proof of identity and enables validated transactions being availed by various social or commercial services across Pakistan. The CNIC is integrated with the National Data Warehouse, enabling instant, online electronic verification of an individuals identity through the swipe-able VeriSys system. The composite CNIC-Verisys system thus provides a new and an innovative dimension to national security services. Computerized National Identity cards are being issued to all adult citizens of Pakistan, whereas, existing manual records of National Identity Cards (NICs) has been switched over to the computerized database.
Security Features
The Computerized National Identity Cards (CNIC) include a sophisticated array of security features to safeguard any probable forgery. The CNIC contains machinereadable information, although certain characters may be visible to the naked eye, others must be verified through the use of optical aids. The special characteristics of the CNIC will protect and ensure integrity, authenticity, and sophistication.
24
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
NATIONAL IDENTITY CARD FOR OVERSEAS PAKISTANI (NICOP)
Among other cards, NADRA Ordinance envisages issuance of cards to Pakistani workers/emigrants and citizens /resident abroad and Pakistanis holding dual nationality who have got themselves registered under the NADRA Ordinance. This card is known as the National Identity Card for Overseas Pakistanis (NICOP). On account of its utility, it is an identification document usable in place of NIC whenever required. However NICOP is more than just an identification document. The NICOP have the same design and color as the CNIC card issued in Urdu, but with minor differences, bear a MRZ (Machine Readable Zone) code at the back of the card, which is readable by a machine. National Identity Card for Overseas Pakistanis (NICOP) carry a printed statement in English to the effect that applicant is entitled to Visa free entry in to Pakistan.
25
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
BENEFITS TO NICOP CARD HOLDERS
(1) Without prejudice to any other rights, benefits, privileges or capacities enjoyed by or available to a non-resident citizen who simultaneously holds the nationality or citizenship of any other country or state together with his Pakistani citizenship, such non-resident citizen shall, upon issuance of the card to him and during the period of validity of his said card, have the right to enter into Pakistan without a visa from such port or place, by such route and in accordance with such conditions, if any, as are prescribed pursuant to the Passport Act, 1974 (XX of 1974). (2) A card validly issued to a non-resident citizen shall be the conclusive proof of his being a citizen of Pakistan for the purposes of availing protection of the Government of Pakistan in any foreign country or state as a Pakistani citizen. The Federal Government shall recognize, afford and ensure full protection as citizens of Pakistan available under the law to all cardholders abroad.
Fee of NICOP
The Fee of National Identity Card for Overseas Pakistanis (NICOP) is US $ 15 and its validity for 10 years
26
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566) PAKISTAN ORIGIN CARD (POC)
A person shall be an eligible foreigner of Pakistan origin or eligible for Pakistan Origin Card if he is a foreigner; and he had been a citizen of Pakistan at any time during his life. Among other cards, NADRA Ordinance envisages issuance of cards to foreigners of Pakistani origin who have got themselves registered under the NADRA Ordinance. This card is called the Pakistan Origin Card. On account of its utility, it is an identification document usable in place of NIC whenever required. However POC is more than just an identification document.
The POC have the same design as the NICOP, but bears blue color. It has an MRZ (Machine Readable Zone) code at the back of the card, which is machine readable. A POC holder is entitled to Visa free entry in Pakistan. The POC number (printed on the face of the card) has a similar format as the CNIC number, but is of a different series. It is not the same as the CNIC number printed on the NICOP card.
27
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566) Children Registration Certificate
Child registration is the fundamental right that every country should provide to the children of its citizens. The right of name and nationality is ensured in Article 7 of the United Nation Convention on the Rights of the Child, where Pakistan was a signatory. It states that: The child shall be registered immediately after birth and shall have the right to acquire a nationality, and as far as possible, the right to know and be cared for by his or her parents Children registration is essential not only for their identity but also for governments for their social services planning. It ensures the availability of health and educational facilities to the children. Registration is a proof that is needed for a number of services and it recognizes the child as a citizen of a country with rights to be cared for. Despite of all the policies and legislations for birth registration, Pakistan has not been able to achieve the targets and many children in Pakistan are still deprived of this fundamental right. NADRA is planning to take on the initiative of issuing Children Registration Certificate for every Pakistani child less than 18 years of age. The certificate includes the information about minors name & registration number, parents name and CNIC (Computerized National Identity Card) numbers, date of birth, place of birth and gender. Children will be allotted same registration number when he/she applies for CNIC on attaining 18 years of age. It is the responsibility of every Childs parents/guardian to register their children who are less than 18 years of age. Application for CRC will be received from NADRA Swift Registration Centers
28
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
29
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566) Driving License
The prevailing turmoil and security concerns in the world demand hi-tech identification and verification systems that would allow authorities to be constantly vigilant, thus preventing crimes. NADRA recognizes its responsibility in doing whatever is possible to ensure safety through the use of secure documents, to enhance public safety, hence contributing to national security. To cater to the need, both for homeland security and constant vigilance, NADRA has developed an RFID-based driver license that bears the license holders personal information and stores data regarding traffic violations, tickets issued, and outstanding penalties. The data is stored in two halves in the chip. One half is brunt electronically, so it cannot be changed or modified. This half contains the personal information of the license holder. The second half is the re-writable part, where the history of violations is recorded. The policemen/law enforcement agencies then transfer the data from their PDA to the Central Server through a special key for data security. This installation of RFID chips, makes it harder to counterfeit or steal driving licenses. These RFID tags thus foil identity theft and prevent criminals from using false documents. The license cards are designed so that driving rights are revoked electronically in case of any offence or traffic violation. The system tracks all movement of users of RFID drivers' licenses, while a comprehensive data of violations is stored electronically at the same time. Any outstanding penalties are payable at electronic payment kiosks, while comprehensive data of past violations and outstanding penalties is available to the authorities.
30
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
Online Bill Payment
Building on the existing technologies of Biometric Identification and Online Verification, NADRA has developed automated kiosks for various day-to-day transactions involving the banking as well as the service sector. The Online Payment Kiosk is designed to enable utility bills payments as well as perform electronic banking after proper authentication from biometric and online verification systems using the computerized national identity cards. This Kiosk offers a convenient, low-cost alternative to bill payments and other financial transactions without compromising customer convenience. These kiosks can be installed at public places and are connected to NADRA's National Data Warehouse through secure internet connections. High level encryption ensures protection of an individual's data being transmitted to the warehouse for verification. Additional Benefits
Offers online banking and other services reducing teller lines and labor costs. User-friendly touch-screen increases throughput and speeds-up transaction time. Kiosks installed at offsite/remote locations offer convenience and more timely payments. Selection of English and Urdu options empowers a wide-range of customers to use the kiosk easily. Security algorithms ensure safety in each online transaction.
Return on Investment
Electronic input reduces mistakes and errors. These Kiosks reduce the overall costs by lowering employee headcount. Additional incremental revenue through e-services.
31
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
Vehicle Identification and Tracking System (VITS)
National Database and Registration Authority (NADRA) has developed a state-of-the-art Vehicle Identification and Tracking System (VITS) based on leading RFID technology.
VITS is being introduced as a sophisticated and high-tech system to help control vehicle related crimes including car thefts, through centrally controlled tracker chip, fixed on each vehicle, known as Vehicle Identification Number (VIN). A unique Vehicle Identification Number is assigned to all vehicles in Pakistan and issued the same on a secure document to the applicant. The VIN tag contains vehicle information and attributes (colour, engine no., chassis no. etc), and endorsement, to be accessible to law and order agencies through online access. This access can be provided through existing communication networks in mobile and field environments. Data on the vehicle owner registration document will be stored using a robust encryption algorithm to prevent tampering.
VITS gates shall be strategically located and vehicle crossing these designated points shall be recorded (vehicle data as well as photograph). The VITS gates are equipped with cameras and with the day and night capability to photograph vehicles with or without VIN Tags installed. Security personnel would be in a better position to use handheld mobile units to retrieve all information for on-the-spot review of vehicle records.
This system would serve as an effective security/deterrence tool against car snatching and other related criminal activities. The VIN would link NADRAs existing network and data warehouse infrastructure, which provides connectivity and information access to all the provinces through one common database. It would thus be mandatory for every vehicle to get VIN.
Every police checkpoint in the country, all major bridges and entry/exit point of cities/towns would be equipped with scanners and antennas to read the details of every car/vehicle.
32
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
The vehicles allotted VIN would be automatically identified, photographed, and checked while those without VIN be monitored at the same time. VITS project is being piloted in Islamabad. It will be then rolled out to other parts of the country.
33
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
Merits, Demerits, Strengths and Deficiencies: Merits & Strengths:
SMS Service to verify voter registration Up to date and real world technology Polio initiative Data are saved in many places other than just one location Cost effectiveness Creation of new jobs Accuracy in Census and Surveys Ease in data accessibility Vehicle Identification and Tracking System (VITS), Automated Border Control System (ABC) to screen and validate all incoming and outgoing passengers holding either National Identity Card FACIAL recognition systems are being designed
Demerits and Deficiencies:
Lack of job security Lack of HR Policies Financial Constraints Slow rate of technological change
Opportunities:
International Market
Threats:
Employee Turnover Govt. Policies Changes
34
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566) Recommendations:
Paper less working environment should be adopted by using Ultimus Online System already in use. Avoid Discrimination Government should provide financial assistance to the organization Proper set up of R&D department Job security for the sake of consistent progress
35
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Computer Application (566)
Mrs. SANA AKBAR KHAN Block No. 13, MBA Dept AIOU, Sector H-8 ISLAMABAD. (0519057141)
M. Hammad Manzoor 508195394 # 508, 5th Floor, CTC Continental Trade Centre, Block-08 08, KARACHI. (0321Clifton 584 2326) Computer Application 02 566
36
By: M. Hammad Manzoor, MBA HRM-II, 508, 5th Floor, Continental Trade Centre (CTC), Clifton 08, Karachi. (Roll No. 508195394)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Rubrik CDM Version 7.0 User Guide (Rev. A3)Dokument853 SeitenRubrik CDM Version 7.0 User Guide (Rev. A3)R100% (1)
- ISBP745 International Standard Banking PracticeDokument74 SeitenISBP745 International Standard Banking PracticeMahendar Weezyholic Bist100% (1)
- MIS Chapter 2 - IT Infrastructure PDFDokument6 SeitenMIS Chapter 2 - IT Infrastructure PDFp-jorn100% (3)
- Information Technology History in MalaysiaDokument7 SeitenInformation Technology History in MalaysiaRaam D' Satanz100% (1)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDokument15 Seiten6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- UntitledDokument11 SeitenUntitledGegeNoch keine Bewertungen
- FedRAMP Control Quick Guide V12Dokument2 SeitenFedRAMP Control Quick Guide V12Chris Hohman100% (1)
- Aurora Chain White Paper enDokument36 SeitenAurora Chain White Paper enwahyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ga d600 V2afterDokument2 SeitenGa d600 V2afterjessa vandykNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sppu-Mis-Ch3-4-Open LearnDokument53 SeitenSppu-Mis-Ch3-4-Open LearnAjinkya NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bachelor of Science in Information Technology: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument9 SeitenBachelor of Science in Information Technology: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaClaire Ann SantillanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Management & IT Services - ProjectDokument62 SeitenTechnical Management & IT Services - ProjectPrashant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Ict: I. Ii. Iii. Iv. v. VIDokument16 SeitenFundamentals of Ict: I. Ii. Iii. Iv. v. VIArnold NdukuyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week3-4 - Current IT Trends of ICTDokument109 SeitenWeek3-4 - Current IT Trends of ICTZꪖʀᥴʜTɀꪗ.Noch keine Bewertungen
- ICT Application To Technical Report Writing, RecordDokument14 SeitenICT Application To Technical Report Writing, Recordanon_230653802Noch keine Bewertungen
- Need NotesDokument2 SeitenNeed NotessumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIT-506 Infomation Technology Innovation in BusinessDokument10 SeitenCIT-506 Infomation Technology Innovation in BusinessUmar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- BS Information Technology: Course DescriptionDokument2 SeitenBS Information Technology: Course DescriptionVendy JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Infrastructure Time Frame and Evolutions 9 OctDokument3 SeitenIT Infrastructure Time Frame and Evolutions 9 Octtania elNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is ICTDokument3 SeitenWhat Is ICTCatherine BaliteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information TechnologyDokument6 SeitenInformation TechnologyWenice CampbellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile CommerceDokument10 SeitenMobile CommerceAbel JacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Irjet V4i6216 PDFDokument10 SeitenIrjet V4i6216 PDFArthee PandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC 101 SG1Dokument16 SeitenCC 101 SG1Aaron CarolinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Ict, Computer and WindowsDokument49 SeitenIntroduction To Ict, Computer and WindowshoxyberryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Example of Term Paper About Information TechnologyDokument6 SeitenExample of Term Paper About Information TechnologyafdtwbhykNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minder Chen: A Methodology For Building Mobile Computing ApplicationsDokument25 SeitenMinder Chen: A Methodology For Building Mobile Computing Applicationsjhosep_darioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Broadway Cafe ProjectDokument5 SeitenBroadway Cafe ProjectKimuel TenerifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Report: Industrial Training (1 JULY, 2011-28 JULY, 2011) AT Indian Telephone Industries LTD, BangaloreDokument31 SeitenA Report: Industrial Training (1 JULY, 2011-28 JULY, 2011) AT Indian Telephone Industries LTD, BangalorePrashant KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 2 - IT6205A-2013TDokument2 SeitenLesson 2 - IT6205A-2013TLara UyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIS Chapter 2 - IT InfrastructureDokument7 SeitenMIS Chapter 2 - IT InfrastructureKenneth Kibet NgenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 Intro To ICTDokument36 SeitenModule 1 Intro To ICTZariyah IslaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Information TechnologyDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To Information TechnologyMuthoharoh MuthoharohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Implementation of The Customer ExperienDokument26 SeitenDesign and Implementation of The Customer ExperiengriseldahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: An Introduction To Professionalism: ObjectivesDokument12 SeitenChapter 1: An Introduction To Professionalism: ObjectivesMark FirmanesNoch keine Bewertungen
- OF Sap Erp Solutions in Ahmedabad": "Study of Market PotentialDokument71 SeitenOF Sap Erp Solutions in Ahmedabad": "Study of Market PotentialPancholi ChiragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To IntranetDokument18 SeitenIntroduction To IntranetmwakondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report On It Industry: Submitted By: Group 11 Ashwin Sarah Surendra Ankit PallaviDokument49 SeitenReport On It Industry: Submitted By: Group 11 Ashwin Sarah Surendra Ankit PallaviSurendra Kumar KandruNoch keine Bewertungen
- EAPPDokument5 SeitenEAPPbernardzNoch keine Bewertungen
- The IT Landscape 2018Dokument45 SeitenThe IT Landscape 2018Debaditya MaitiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of IT Report 123Dokument6 SeitenRole of IT Report 123Soni SubediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fm-Aa-CIA-15 CC 101 Study Guide 1 FinalDokument13 SeitenFm-Aa-CIA-15 CC 101 Study Guide 1 Finalkamina ayatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pros and Cons of ICTDokument5 SeitenPros and Cons of ICTPriyankar SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Science and Technology ChittagongDokument5 SeitenUniversity of Science and Technology ChittagongMd. AkibNoch keine Bewertungen
- MISDokument4 SeitenMISJayaJayashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Technology (IT) Is The Acquisition, Processing, Storage and Dissemination of Vocal, Pictorial, Textual andDokument1 SeiteInformation Technology (IT) Is The Acquisition, Processing, Storage and Dissemination of Vocal, Pictorial, Textual andMukesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week3 4 - Current IT Trends of ICT 1Dokument109 SeitenWeek3 4 - Current IT Trends of ICT 1Hannah DuyagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On:-Information Technology Management For Post Graduation Diploma in Management (NBA, NAAC and IAO (USA) Accredited)Dokument24 SeitenProject Report On:-Information Technology Management For Post Graduation Diploma in Management (NBA, NAAC and IAO (USA) Accredited)sandeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge Management Infrastructure: Knowledge Technology Knowledge TechnologyDokument43 SeitenKnowledge Management Infrastructure: Knowledge Technology Knowledge TechnologyeFretNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technology and Operations ManagementDokument8 SeitenTechnology and Operations ManagementBeboy TorregosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 30-Ict Applications in BusinessDokument7 Seiten30-Ict Applications in BusinessAnnonymous963258Noch keine Bewertungen
- PCA20S01L - IT Infrastructure ManagementDokument25 SeitenPCA20S01L - IT Infrastructure ManagementMOHAMED FIRNAS (RA1931005020191)Noch keine Bewertungen
- ReportDokument24 SeitenReportAizaz Khan Zäziíìì0% (1)
- Submitted By: Rabia Shafiq - : Dvanced ICT Issues IN UsinessDokument15 SeitenSubmitted By: Rabia Shafiq - : Dvanced ICT Issues IN UsinessRa Biya ShafiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Assignment Submitted On-RaghvendraDokument22 SeitenAn Assignment Submitted On-Raghvendradeepu0787Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management: Management Information System MISDokument3 SeitenManagement: Management Information System MIScolle178Noch keine Bewertungen
- RMK 03 - RMK 3-Sti: IT Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies - Information SystemsDokument4 SeitenRMK 03 - RMK 3-Sti: IT Infrastructure and Emerging Technologies - Information SystemsEhsanul FahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bp624 Curriculum NotesDokument11 SeitenBp624 Curriculum NotesKreshna MudhooNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.) What Is ICTDokument7 Seiten1.) What Is ICTbernardzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimizing Your Network On A Budget: Expert Reference Series of White PapersDokument16 SeitenOptimizing Your Network On A Budget: Expert Reference Series of White PapersgynxNoch keine Bewertungen
- MB0047 Set 2Dokument20 SeitenMB0047 Set 2Ahmed BarkaatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Computing and Networks. - FinalDokument29 SeitenFundamentals of Computing and Networks. - FinalSchneizeL CruszewskYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cloud Computing Send S-1Dokument15 SeitenCloud Computing Send S-1RafiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Three Era ModelDokument34 SeitenThe Three Era ModelVihara AbeysingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- C V CVVV V VVVVV V V: V V VV V º VV R V VDokument3 SeitenC V CVVV V VVVVV V V: V V VV V º VV R V VAkshay PatialNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Perspectives Conference: The Future of Information TechnologyVon EverandIT Perspectives Conference: The Future of Information TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Science Self Management: Fundamentals and ApplicationsVon EverandComputer Science Self Management: Fundamentals and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass-Transport Complexes of Trinidad and VenezulaDokument30 SeitenMass-Transport Complexes of Trinidad and VenezulaM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- April 2014 BillDokument1 SeiteApril 2014 BillM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic Attributes in Your FaciesDokument6 SeitenSeismic Attributes in Your FaciesM Hammad Manzoor100% (2)
- Seismic Inversion - The Best Tool For Reservoir CharacterizationDokument7 SeitenSeismic Inversion - The Best Tool For Reservoir CharacterizationM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Transport Deposits in Offshore Morocco, Safi Haute Mer AreaDokument31 SeitenMass Transport Deposits in Offshore Morocco, Safi Haute Mer AreaM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Superimposed Geologic Features in Seismic InterpretationDokument12 SeitenSuperimposed Geologic Features in Seismic InterpretationM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1st - 522 - EconomicsDokument31 SeitenAssignment 1st - 522 - EconomicsM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seismic Attributes - A Promising Aid For Geologic PredictionDokument12 SeitenSeismic Attributes - A Promising Aid For Geologic PredictionM Hammad Manzoor100% (1)
- Economic Analysis Presentation by HammadDokument27 SeitenEconomic Analysis Presentation by HammadM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1st - 523 - Business Mathematics and StatisticsDokument16 SeitenAssignment 1st - 523 - Business Mathematics and StatisticsM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Accounting Presentation by Hammad.Dokument40 SeitenFinancial Accounting Presentation by Hammad.M Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2nd - 522 - EconomicsDokument35 SeitenAssignment 2nd - 522 - EconomicsM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1st - 524 - Business ReserachDokument28 SeitenAssignment 1st - 524 - Business ReserachM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Managment HRM Presentation by HammadDokument32 SeitenCost Managment HRM Presentation by HammadM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Application Presentation by HammadDokument37 SeitenComputer Application Presentation by HammadM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Research Methods Presentation by HammadDokument47 SeitenBusiness Research Methods Presentation by HammadM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1st - 566 - Computer ApplicationDokument39 SeitenAssignment 1st - 566 - Computer ApplicationM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Mathmatics & Statistics Presentation by HammadDokument36 SeitenBusiness Mathmatics & Statistics Presentation by HammadM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2nd - 523 - Business Mathematics and StatisticsDokument47 SeitenAssignment 2nd - 523 - Business Mathematics and StatisticsM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Managment HRM Presentation by HammadDokument32 SeitenCost Managment HRM Presentation by HammadM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Managment HRM Presentation by HammadDokument32 SeitenCost Managment HRM Presentation by HammadM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Resource Managment HRM Presentation by HammadDokument30 SeitenHuman Resource Managment HRM Presentation by HammadM Hammad ManzoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cyber Security: Dr. Robert StaticaDokument55 SeitenCyber Security: Dr. Robert StaticaBisimungu100% (1)
- Ms Preli Private CircularDokument3 SeitenMs Preli Private CircularBD TitansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java RingDokument31 SeitenJava Ringyogesh100% (1)
- QGCIO Sample SoA Annd Essential 8 For WorkshopDokument29 SeitenQGCIO Sample SoA Annd Essential 8 For WorkshopMark VerdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Previous ID Card No (2020-21) : Student Bus Pass Application Upto SSCDokument1 SeitePrevious ID Card No (2020-21) : Student Bus Pass Application Upto SSCGaming with RajeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-30106C2P LP51021 CRYPT2Pay CRYPT2Protect Security Policy V2.2-1554489077.52112-DN PDFDokument87 Seiten4-30106C2P LP51021 CRYPT2Pay CRYPT2Protect Security Policy V2.2-1554489077.52112-DN PDFRifat Hasif PutrafebrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution Manual For Guide To Firewalls and Vpns 3rd EditionDokument36 SeitenSolution Manual For Guide To Firewalls and Vpns 3rd Editiontriunitycorypheexhxq100% (31)
- Advantages of Electronic EvidenceDokument18 SeitenAdvantages of Electronic EvidenceKenneth James Carlo Hizon100% (1)
- Tech Note 892 - Configure SQL and Alarm DB Logger Manager PDFDokument11 SeitenTech Note 892 - Configure SQL and Alarm DB Logger Manager PDFtabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAQ D v3 MerchantDokument79 SeitenSAQ D v3 MerchantMeraqui SingerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules On Electronic Evidence 2019 PDFDokument20 SeitenRules On Electronic Evidence 2019 PDFDevilleres Eliza DenNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSharp Platinum SDK To One Touch For Windows SDK 1.6.1Dokument19 SeitenCSharp Platinum SDK To One Touch For Windows SDK 1.6.1faucondufeuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Report On BluetoothDokument21 SeitenTechnical Report On BluetoothManisha Gupta50% (4)
- Dimensions of E-Commerce Security - IntegrityDokument17 SeitenDimensions of E-Commerce Security - IntegrityGaurav SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biometric Authentication Technique Using Smartphone Sensor: Asadullah Laghari, Waheed-ur-Rehman, Dr. Zulfiqar Ali MemonDokument4 SeitenBiometric Authentication Technique Using Smartphone Sensor: Asadullah Laghari, Waheed-ur-Rehman, Dr. Zulfiqar Ali MemonAnkush MalodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protecting Your Data and PrivacyDokument13 SeitenProtecting Your Data and PrivacySalman ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speaker AuthenticationDokument22 SeitenSpeaker AuthenticationsudeendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tpam Suite Quickstart OfferingDokument3 SeitenTpam Suite Quickstart Offeringujang.pantryNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATM System - Use CaseDokument7 SeitenATM System - Use CaseMinh NguyễnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jasmine Research Sem FinalDokument46 SeitenJasmine Research Sem Finaljupiter stationeryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless LAN SecurityDokument15 SeitenWireless LAN SecuritySanjeet KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biometric Service Provider (BSP) : John "Jack" Callahan VeridiumDokument20 SeitenBiometric Service Provider (BSP) : John "Jack" Callahan VeridiumSamir BennaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital - SignatureDokument28 SeitenDigital - SignatureRishabh GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Privacy Impact Assessment CBP One™ Mobile Application: For TheDokument22 SeitenPrivacy Impact Assessment CBP One™ Mobile Application: For The0 HourNoch keine Bewertungen