Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Marker Placement Guide
Hochgeladen von
Sam StuartOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Marker Placement Guide
Hochgeladen von
Sam StuartCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
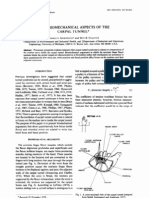
MARKER PLACEMENT GUIDE
The marker placement in this document is only one of many possible combinations. T his guide will only show the standard marker placement thats being used in the motion capture laboratory. The marker placement in this guide resembles the one that is shown and explained in the Vicon 512 manual. As such, the Vicon 512 M anual can offer additional information. The difference with the marker set in this document from the Vicon 512 M anual is the addition of 4 m arkers, namely RARM , L ARM , RLEG, a nd LLEG. Before starting, below are some general rules of thumb one should follow: Have the person whos going to be motion captured wear tight fitt ing clot hes strap down any areas of the clothing that is loose. The marker balls posit ion s hould move as lit tle as poss ible and should be properly seen. Place the marker balls as close to the bone as pos sible. T his follow s t he rule of having the marker balls stay stationary during movement.
To help the motion capture sys tem distinguish the marker balls the left side and the right side of t he body, place marker balls asymmetrically when appropriate. For example, the RTHI and LTH I, as shown in t he picture above, are placed
asymmetrically from each ot her. If a marker ball is placed improperly and one decides t o reposition it before the motion capture begins , replace the tape of the s aid marker ball with a fresh tape t o make sure the marker ball will stay put . If a marker ball falls off during t he motion capture, one has to recalibrate the subject and redo the motion capture in order to get accurate results .
Head an d Wrist There are head bands and wris t bands with marker balls att ached provided. H subject wear them with the sign facing forw ard. ave the
S houlders Place the marker ball on the s houlder bone of the subject . T o find the shoulder bone, have the subject move his or her arm up and down and find the area of the s houlder that doesnt move when the arm is moved up and down. Do the s ame for bot h sides.
Clavicl e The marker ball for the clavicle should be placed in between the two collar bones and below the base of the neck.
Elbow
Find the area where the upper arm and forearm connect. Place the marker ball above the area of the upper arms bone that connects to the forearms bone. The marker ball should be place along the line connecting the upper arms bone from one side to the other. Make sure the marker ball doesnt move when the arm is bent up and down. the same Do for both sides.
Left Hand Put the marker ball on the base of the ring finger.
Right Hand Put the marker ball on the base of the index finger
Upper Arm Place the marker ball for the upper arm somewhere along the line that connects the marker ball on the shoulder and the marker ball on the elbow. Place the marker ball asymmetrically on the other arm.
Forearm Place the marker ball for the forearm on the outer edge of the forearm, preferably near the edge of the outer bone of the forearm. Put the marker ball on the other forearm asymmetrically.
S ternum
Put the marker ball on the base of the middle of the ribcage. For women, the marker ball is placed below the breas t s o it is advisable to t ape down that area in order to keep the marker ball unobstructed.
C7 Have the subject bend his or head down. The C7 bone is located along t he spinal column right where the back of the neck ends. A small bone jutting out will indicate that. Put the marker ball right on the bone.
T10 The T10 is also located along the spinal column. Count 10 vert ebrae down from C7 and place the marker ball on the 10 th vertebrae.
To better see and feel the spinal column, have the subject bend down and push his or her shoulders inward.
Pelvis Put the marker balls on the area of the pelvis bone that juts out the most. The figure on the left shows where this is located.
Back Waist At the back of the pelvis bone, there are two more areas that jut out a little. P lace the marker balls on t hese areas. T his is located at the base of ones back and right before the buttocks start.
Foot
For each foot, put a marker ball on t he bone right before t he toe s tarts. P ut another marker ball on the outer edge of the foot on the bone right before the pinky toe starts.
Ankle
The same with the elbow, put the marker ball along the line that connects the opposite sides of the ankle bone.
Heel The marker ball for the heel should be placed on the heel bone and it should be placed such that the line connecting t he toe marker ball and heel marker ball is parallel to the ground.
Knee Have the subject swing his or her lower leg back and forth. F ind t he low es t area of the upper leg that doesnt move when the lower leg is swung back and forth. This corresponds to the bone right above the ball joint of the knee. Place the marker ball about above the break between the upper and lower leg. The marker ball should also be placed along the line that connect s t he opposite sides of the upper legs bone. Make sure th e marker ball doesn t move when the lower leg is swung back and forth. For women, the marker balls must be place more to the front than usual. M ore masculine subjects should have marker balls put a little more to the back since the muscle of the legs may move the marker balls during movement.
Thigh
Find the area of the femur that juts out the most to the side of the body. Tis should be h located somewhere below the pelvis. The marker ball s hould be placed along the line t hat connects the said area of the bone and the knee marker ball. Place the marker ball asymmetrically on the other thigh.
Leg
Visualize a triangle that connects the knee marker ball, t he ankle marker ball and t he opposite side of the ankle bone. The marker ball should be placed along the line that connects the knee marker ball and the ankle marker ball. To help the person putting the marker ball visualize the line connecting the ankle marker ball and the opposite side of the ankle bone, put a paper under the subjects feet such that the edge of the paper lines up with the line connecting the ankle marker ball and the opposite side of the ankle bone. The person might want to as k help from t he s ubject because the best vantage view for visualizing the three lines is directly above the subjects leg.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Stickfighting - A Practical Guide For Self-Protection.Dokument272 SeitenStickfighting - A Practical Guide For Self-Protection.Roberto Díaz Hernández100% (2)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Human Anatomy. The Human Muscles.Dokument70 SeitenHuman Anatomy. The Human Muscles.Stefania Ungureanu100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Golf Fitness 101: How Golf-Specific Training Can Improve Your GameDokument9 SeitenGolf Fitness 101: How Golf-Specific Training Can Improve Your GameJean-Christophe Lendormy100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Jaeger J Band Cuff ExcercisesDokument16 SeitenJaeger J Band Cuff Excercisesapi-358920268Noch keine Bewertungen
- Observational Gait Analysis ChecklistDokument2 SeitenObservational Gait Analysis ChecklistSam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sports Injuries Their Prevention and Treatment PDFDokument567 SeitenSports Injuries Their Prevention and Treatment PDFAngeliki Kostaki92% (25)
- Upper Limb AnatomyDokument20 SeitenUpper Limb AnatomyGabriel Botezatu100% (1)
- Dermoneuromodulation Treatment Manual: Self-Published June 2007 by Diane Jacobs, PTDokument57 SeitenDermoneuromodulation Treatment Manual: Self-Published June 2007 by Diane Jacobs, PTXavier De Haro MiretNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marksmanship Theory & CoachingDokument91 SeitenMarksmanship Theory & Coachingadamhome100% (1)
- Derived PositionsDokument18 SeitenDerived PositionsChetan Rathi50% (2)
- Silk Reeling Energy BookDokument156 SeitenSilk Reeling Energy BookAssaf Feldman0% (1)
- Niosh - RulaDokument18 SeitenNiosh - RulaDomingo Carrasco Guzmán100% (1)
- OMM Review SheetDokument9 SeitenOMM Review SheetSolomon Seth Sallfors100% (2)
- Brachial Plexus InjuryDokument14 SeitenBrachial Plexus InjuryYugaraj ThangaveluNoch keine Bewertungen
- RULA Employee Assessment Worksheet: A. Arm and Wrist Analysis B. Neck, Trunk and Leg Analysis ScoresDokument1 SeiteRULA Employee Assessment Worksheet: A. Arm and Wrist Analysis B. Neck, Trunk and Leg Analysis ScoresAlvinWijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 WHO Standard Acupuncture Point Locations in The Western Part 3Dokument30 Seiten3 WHO Standard Acupuncture Point Locations in The Western Part 3Virgil AnmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSP Whiplash GuidelineDokument199 SeitenCSP Whiplash GuidelineyaasarloneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Pone 0019079 PDFDokument8 SeitenJournal Pone 0019079 PDFSam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recpresentation 281111Dokument42 SeitenRecpresentation 281111Sam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fearnley Lees BRAIN 1991Dokument19 SeitenFearnley Lees BRAIN 1991Sam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- 007529Dokument13 Seiten007529Sam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pioneers of Eye Movement ResearchDokument36 SeitenPioneers of Eye Movement ResearchSam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fearnley Lees BRAIN 1991Dokument19 SeitenFearnley Lees BRAIN 1991Sam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- 007529Dokument13 Seiten007529Sam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 2Dokument13 SeitenScience 2Sam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 2Dokument13 SeitenScience 2Sam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 1Dokument18 SeitenScience 1Sam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ageing effects on attention demands of walking and foot targeting taskDokument12 SeitenAgeing effects on attention demands of walking and foot targeting taskSam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- 512 Vic On SW ManualDokument289 Seiten512 Vic On SW ManualSam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- 111 FullDokument10 Seiten111 FullSam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Functional Anatomy of Attention To Visual Motion: A Functional MRI StudyDokument14 SeitenThe Functional Anatomy of Attention To Visual Motion: A Functional MRI StudySam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- 512 Vic On SW ManualDokument289 Seiten512 Vic On SW ManualSam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vic On TutorialDokument3 SeitenVic On TutorialSam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vicon Manual v1 2Dokument15 SeitenVicon Manual v1 2Sam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1979 - Bio Mechanics of Carpal TunnelDokument4 Seiten1979 - Bio Mechanics of Carpal TunnelSam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welcome To Vicon2Dokument19 SeitenWelcome To Vicon2Sam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carpal FracturesDokument4 SeitenCarpal FracturesSam StuartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Range PDFDokument16 SeitenProduct Range PDFKevin MichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plexopathy and MononeuropathyDokument38 SeitenPlexopathy and MononeuropathySOUMYADEEP BHUINYANoch keine Bewertungen
- 2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsDokument16 Seiten2ND Grading Laboratory SheetsAllecia Leona Arceta SoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4HB0 01 Que 20120307Dokument28 Seiten4HB0 01 Que 20120307muhajireenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meynardo M. Farol and Feliciano Gomez For Appellants. Acting Solicitor-General Peña For AppelleeDokument60 SeitenMeynardo M. Farol and Feliciano Gomez For Appellants. Acting Solicitor-General Peña For AppelleeKristabelleCapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied AnatomyDokument76 SeitenApplied Anatomysantosh bhandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advice For Patients With A Fractured Wrist in A Plaster CastDokument4 SeitenAdvice For Patients With A Fractured Wrist in A Plaster Castmohit bansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- People Vs ValerianoDokument11 SeitenPeople Vs ValerianoKhristine Ericke De MesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spine Lumbar Low Back Core ExercisesDokument2 SeitenSpine Lumbar Low Back Core Exercisessmnabeel100% (1)
- Management of Limb Injuries in Adults and Children Over 2 YearsDokument17 SeitenManagement of Limb Injuries in Adults and Children Over 2 YearsjustforuroNoch keine Bewertungen
- HF GUIDELINES 1st Year by ARC RevisedDokument39 SeitenHF GUIDELINES 1st Year by ARC RevisedKamran ShabbirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disability Evaluation: Radhika ChintamaniDokument58 SeitenDisability Evaluation: Radhika ChintamaniBhavya Amin0% (1)
- Statics ProblemsDokument14 SeitenStatics ProblemsHamza ShabbirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Axillary ArteryDokument28 SeitenAxillary Arteryshrishti shadangiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument34 SeitenChapter 7SaudNoch keine Bewertungen
- FractureDokument71 SeitenFractureRegime San Juan AtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen