Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Beatriz Ruiz IonicvsCovalentBondingLabInvestigation-2-3
Hochgeladen von
LeslieOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Beatriz Ruiz IonicvsCovalentBondingLabInvestigation-2-3
Hochgeladen von
LeslieCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Beatriz Ruiz Nov 5,2012 Period.2 Ionic vs.
Covalent Bonding Lad Investigation Introduction: Most Atoms are never found by themselves; instead they are bonded to another atoms in a ionic or covalent bond. This is because it has to share valence e-, so it can bond together and create a full octet. Hypothesis: Table1; The extending results of testing five different chemical
Compounds to be Tested
Chemical Formula
Hypothesis 1: Ionic or Covalent
Hypothesis 2: High or low Melting Point Low
Hypothesis 3: conduct electricity
Distilled (pure) Water Sodium Chloride
H20
Covalent
No
C12H22O11
Ionic
High
Yes
Sucrode (sugar) Dextrose Sodium Sulfate
C12H22O11 C66H12O6 NaSO4
Covalent Ionic Ionic
Low High High
Yes Yes No
Procedure: PART I: Melting Point and Strength of Bonds 1. Fold aluminum foil into a square that will neatly fit on the ring-stand. Place a small sample of each of the 4 different compounds (water is already melted) on
Beatriz Ruiz Nov 5,2012 Period.2 Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lad Investigation Introduction: your square of aluminum foil (all 4 at the same time). Be careful not to mix them up & keep track of them! 2. Carefully place the tray on the ring stand and heat with the Bunsen burner (no longer than 1-2 min). 3. Immediately begin recording your detailed observation, keeping track of the order in which the sample melt (or dont melt if that case)-which ones have strong bonds & which have weak? 4. Allow the square of foil to cool and the wash it off into the sink Part II: 1. Weigh and approximately 0.1 gram sample of each compound in different wells late (make sure to ZERO the well plate on the balance) 2. Test the dry compound foe conductivity with he tester. Record your observation (Yes or No). 3. Add enough drop of distilled water to the well to dissolve the compound as best you can. 4. Test the solution for conductivity with the tester. Record your observation (Yes or No) Make sure to wash the conductivity tester with distilled water after every use! 5. Repeat for all of the samples.
Beatriz Ruiz Nov 5,2012 Period.2 Ionic vs. Covalent Bonding Lad Investigation Introduction:
Results: Name/Chemical Formula: 1. Distilled (pure)water 2. Sodium Chloride / 3.Sucrose (sugar)/ C12H22O11 4.Dextrose / C6H12O6 5. Sodium sulfate / NaSO4
Part I: Melting Point (1-5; High, Med. or ow?) 1 4 2 1 3
PART II: Conducted Electricity? (Yes/NO) Dry Dissolved No Yes No NO No No Yes No No Yes
FINAL CONCLUION Ionic or Covalent Bonds? Covalent Ionic Covalent Covalent Ionic
Conclusion: After this laboratory, it was concluded that sodium chloride and sodium sulfate were ionic compound, while sucrose dextrose were covalent compound. All of the initial hypotheses were correct except dextrose. Because dextrose is a covalent and it does conduct electricity. From the results ionic compounds were those that conducted electricity in water and had a high melting point meaning a stronger bond, however, the covalent compound have a low melting point because it does not conduct electricity, Ionic bond are formed from metal cation which is positive and non-metal anion which is negative, so when they dissolve in water, electricity the moving charge can flow through the solution, Additionally ionic bond are very strong since they are the one that actually conduct electricity with water even though it was harder for this to melt faster.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- EC Plant List June 2020Dokument1 SeiteEC Plant List June 2020LeslieNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Poetry Essay": Palma, Christopher Period, 1 October, 10 2012Dokument3 SeitenPoetry Essay": Palma, Christopher Period, 1 October, 10 2012LeslieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Apple Tasting Results: All ClassesDokument3 SeitenApple Tasting Results: All ClassesLeslieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Noel Orozco Sept.12 2012 Period 2 Ms - LiptonDokument3 SeitenNoel Orozco Sept.12 2012 Period 2 Ms - LiptonLeslieNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Ismael Jimenez Per. 5Dokument3 SeitenIsmael Jimenez Per. 5LeslieNoch keine Bewertungen
- HarlemDokument3 SeitenHarlemLeslie0% (1)
- Statement of Teaching Interests-Example 3Dokument2 SeitenStatement of Teaching Interests-Example 3NedelcuGeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- EMBO 2013 HandoutDeuterationDokument54 SeitenEMBO 2013 HandoutDeuterationRigel_TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- (C. Grosche F. Steiner) Handbook of Feynman Path I (B-Ok - Xyz)Dokument459 Seiten(C. Grosche F. Steiner) Handbook of Feynman Path I (B-Ok - Xyz)gog100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Critical Review On The Shear Lag Effect of Steel Channel Sections Subject To Tensile LoadingDokument9 SeitenA Critical Review On The Shear Lag Effect of Steel Channel Sections Subject To Tensile LoadingGRENZE Scientific Society100% (2)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hkdse Chemistry - A Modern View (Chemistry) : Coursebook 3 Suggested AnswersDokument60 SeitenHkdse Chemistry - A Modern View (Chemistry) : Coursebook 3 Suggested AnswersAlexis Wong100% (3)
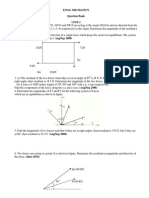
- Engg Mechanics Question Bank UNIT-1Dokument10 SeitenEngg Mechanics Question Bank UNIT-1Thiyagarajan GurusamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Flow Properties Testing and Powder Flowability - Powder & Bulk Solids Solutions PDFDokument3 SeitenFlow Properties Testing and Powder Flowability - Powder & Bulk Solids Solutions PDFSukaran SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 B264 D 01Dokument18 Seiten0 B264 D 01didikkrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- PHSC2112 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Remedial Exam WEWO!Dokument10 SeitenPHSC2112 PHYSICAL SCIENCE Remedial Exam WEWO!Christian PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- States of Matter-I Gas: Course OutlineDokument9 SeitenStates of Matter-I Gas: Course OutlineMansoor SarwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Metals and Chemical ChangeDokument285 SeitenMetals and Chemical ChangeGustavo Adolfo Piñero BorgesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Year 10 Physics Holiday PackDokument10 SeitenYear 10 Physics Holiday Packivan micoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Design of Coping Beam (Portal) : A. Basic DataDokument7 SeitenDesign of Coping Beam (Portal) : A. Basic DataUzziel Abib GabiolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Thermite Reactions - Their Utilization in The Synthesis and Processing of MaterialsDokument16 SeitenThermite Reactions - Their Utilization in The Synthesis and Processing of Materialssoapmaker72100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Thesis My 76Dokument69 SeitenThesis My 76Jyotsana RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- AISC Properties MMDokument31 SeitenAISC Properties MMManuel JuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard Coils and Proportional Valve CoilsDokument8 SeitenStandard Coils and Proportional Valve CoilsElias Oliveira DomingosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Mechanics of Buried PipesDokument11 SeitenStructural Mechanics of Buried PipesSheikh Mizanur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proceedings of Spie: Design and Simulation Analysis of A Magnetic Shielding Box For Ring Laser GyroscopeDokument9 SeitenProceedings of Spie: Design and Simulation Analysis of A Magnetic Shielding Box For Ring Laser GyroscopeTanzil ZaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin Plate Beam-To-column-flange Connection (GB)Dokument16 SeitenFin Plate Beam-To-column-flange Connection (GB)Vlad MosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session I - DC Circuit AnalysisDokument126 SeitenSession I - DC Circuit Analysismohan kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Form Three Q&a1Dokument110 SeitenChemistry Form Three Q&a1MajaningumbaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11CD108 Plasticity and Metal Forming - First Series Test PART-A (9 X 2 18 Marks) Answer ALL QuestionsDokument1 Seite11CD108 Plasticity and Metal Forming - First Series Test PART-A (9 X 2 18 Marks) Answer ALL Questionsselva_raj215414Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Jayanthan's Friction ClutchesDokument4 SeitenJayanthan's Friction Clutchess_nimalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green's Functions For Analysis of Dynamic Response of Wheel/rail To Vertical ExcitationDokument28 SeitenGreen's Functions For Analysis of Dynamic Response of Wheel/rail To Vertical ExcitationCalina OpreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRB Chapter 3Dokument26 SeitenPRB Chapter 3jesús Iván Santamaria najarNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE-pH 2013 HandoutsDokument31 SeitenPE-pH 2013 HandoutsAna Luisa Garnica SalgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 신소재과학 시험문제모음Dokument9 Seiten신소재과학 시험문제모음Hanjin SeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numc PDFDokument18 SeitenNumc PDFMadhur MayankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)