Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
L. The Set-Up Is Shown in The Following Figure.: Glass
Hochgeladen von
Hanis ZafriOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
L. The Set-Up Is Shown in The Following Figure.: Glass
Hochgeladen von
Hanis ZafriCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1.
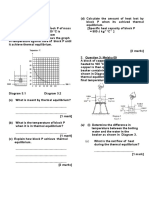
Eileen is going to cook some vegetable. She is choosing between frying vegetable or cooking it with water. If Eileen fries vegetable, she will use 20-g olive oil, heat the oil to about 200 C from 27 C, fry vegetable and add a pinch of salt. If she cooks vegetable with water, she will boil 1-kg water and then add 10-g olive oil and a pinch of salt. The output power of her stove is 2000 W. (Given: Specific heat capacity of olive oil = 1970 J kg1 C1 Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg1 C1) (a) Eileen decides to fry vegetable. (i) Find the energy required to heat up the oil. (2 marks) (ii) If 6000 J is required to cook the vegetable, how long will it take for the whole cooking process? (2 marks) (iii) In practice, will Eileen use a longer or a shorter time to cook? Why? (2 marks) (iv) Eileen adds salt after frying the vegetable and finds that salt does not melt. Why? Explain your answer briefly. (2 marks) (b) If Eileen cooks vegetable with water, how much energy is required to heat up water from 27 C to 100 C? Which cooking method consumes more energy? (3 marks) Kate is going to calibrate a mercury-in-glass thermometer and to use it in an experiment. (a) Describe how she calibrates the thermometer with Celsius scale. (4 marks) (b) In (a), Kate finds the lengths of the mercury thread at the upper and the lower fixed points are 24.0 cm and 4.0 cm respectively. When she puts the thermometer in a beaker of liquid L at room temperature, the length of the mercury thread is 8.4 cm. Find the room temperature. (2 marks) (c) The thermometer is then used to measure the specific heat capacity of a beaker of liquid L. The set-up is shown in the following figure.
2.
glass
The following are the readings taken in the experiment: Power of the heater = 50 W Mass of liquid L in the beaker = 500 g Initial length of the mercury thread = 8.4 cm Final length of the mercury thread = 15.5 cm Time taken to heat up liquid L = 5 min (i) (ii) Liquid L does not boil during the experiment. Calculate the specific heat capacity of liquid L. (3 marks) It is found that the result obtained in (i) is different from the actual value of the specific heat capacity of liquid L. Why? Suggest two methods to improve the experiment. (3 marks)
3.
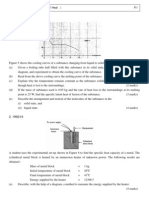
A 200-W immersion heater is immersed in 0.2 kg of water in a polystyrene cup. The heater is switched on and the temperature of water is taken every 30 s. The following data are obtained: Time t / s 0 30 60 90 120 150 180 210 240 20 27 34 41 48 55 61 67 70 Temperature / oC (a) Using a scale of 1 cm to 10 C and 1 cm to 30 s, plot a graph of against t on graph paper.
(b)
(i) (ii) (iii)
Find the energy supplied by the heater from t 0 to t 240 s. Find the energy absorbed by the water from t 0 to t 240 s. (Given: Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg1 C1)
(4 marks) (2 marks)
(c)
(2 marks) State TWO reasons to explain the difference between your answers in (i) and (ii). (2 marks) How will the difference between your answer in (b)(i) and (ii) change if the polystyrene cup is replaced by a beaker? Give reasons to support your answer. (3 marks)
4.
Jimmy uses the apparatus as shown in the following figure to find the specific heat capacity of water.
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(e) (f) (g) 5.
Draw a diagram to show how the apparatus should be arranged for the experiment. (3 marks) What is the function of the joulemeter in this experiment? (1 mark) Explain why the water should be stirred throughout the experiment. (1 mark) Jimmy obtains the following results: Mass of water = 0.2 kg Initial temperature of water = 25 C Final temperature of water = 42 C Initial joulemeter reading = 64 350 J Final joulemeter reading = 79 470 J Calculate the specific heat capacity of water. (2 marks) The value obtained in (d) is found to be higher than the actual value. Suggest TWO reasons for this and explain your answer briefly. (3 marks) If Jimmy adds a lid to cover the cup and repeats the experiment, would you expect the specific heat capacity of water obtained to be higher or lower than that obtained in (d)? Explain briefly. (2 marks) Suggest two reasons for using a polystyrene cup in the experiment. (2 marks)
A student uses the apparatus shown in the following figure to find the specific heat capacity of a metal.
*(a) How can the energy supplied by the heater be measured? Explain your answer with the aid of a diagram. (6 marks) (b) Explain why a few drops of oil should be added in the hole for the thermometer. (1 mark)
(c) (d)
(e) (f)
Explain why the heater should not be switched on unless it is in contact with the metal block. (1 mark) The following data are obtained: Mass of metal block = 1 kg Initial temperature = 25 C Final temperature = 32 C Energy supplied by the heater = 6750 J Calculate the specific heat capacity of the metal. (3 marks) The value obtained in (d) is found to be higher than the accepted value of the specific heat capacity of the metal. Suggest a reason for this and explain your answer briefly. (2 marks) Suggest TWO methods to improve the accuracy of the experiment. (2 marks)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Specific Heat Capacity StrucDokument4 SeitenSpecific Heat Capacity Strucyokecheng20003826Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Bonds ExplainedDokument8 SeitenChemical Bonds ExplainedSARAVANAN A/L MANIAM MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energetics Revision Exam QuestionsDokument13 SeitenEnergetics Revision Exam QuestionsDulshan JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Mark Schemes 2021Dokument17 SeitenChemistry Mark Schemes 2021keshane Johnson100% (1)
- Edexcel IAS Bonding 1Dokument14 SeitenEdexcel IAS Bonding 1mostafa barakatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculating Moles and Mass in Chemical ReactionsDokument3 SeitenCalculating Moles and Mass in Chemical ReactionsFatema KhatunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions and Equations FinalDokument29 SeitenChemical Reactions and Equations FinalRenemartin RebambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csec Chemistry Notes 7Dokument2 SeitenCsec Chemistry Notes 7debestieNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 10 Salts & Its PreparationDokument25 SeitenCH 10 Salts & Its Preparationapi-3774259100% (7)
- Energy changes in reactionsDokument2 SeitenEnergy changes in reactionsSamandarbek Numonov100% (1)
- Energetics (Thermochemistry) : Page 1 of 12Dokument12 SeitenEnergetics (Thermochemistry) : Page 1 of 12MBOTAKE Lawson100% (1)
- Reaction Kinetics NotesDokument40 SeitenReaction Kinetics Notesapi-234602673Noch keine Bewertungen
- METALS and NON-METALSDokument24 SeitenMETALS and NON-METALSTushti Ramlogan100% (1)
- CSEC Rates of Reaction 2014Dokument90 SeitenCSEC Rates of Reaction 2014Carl Agape Davis100% (2)
- Basic Principles of Chemistry PracticalsDokument41 SeitenBasic Principles of Chemistry PracticalsGodfrey MuchaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- StructureDokument22 SeitenStructureFatema KhatunNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrochemistryDokument152 SeitenElectrochemistrypapaioasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science - Learn CBSEDokument21 SeitenChemical Reactions and Equations Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 Science - Learn CBSESohail Ahmed0% (1)
- The Particulate Nature of Matter 1 MSDokument7 SeitenThe Particulate Nature of Matter 1 MSKHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Young'SmodulusDokument7 SeitenYoung'SmodulusBrandon SookdeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersDokument12 SeitenH2 Jun Holiday Assignment 2013 AnswersKaitlyn HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet #3 - Mole ConceptDokument6 SeitenWorksheet #3 - Mole Conceptjfkdmfmdf100% (1)
- IB Chemistry Topic 1 Quantitative Chemistry TestDokument9 SeitenIB Chemistry Topic 1 Quantitative Chemistry TestPak Hei Marcus CHOWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sDokument10 SeitenPractice estimating to find the best answer.: Δt 5 x rate = -Δ (B) 5 x 0.0243 M/s = - Δ (B) -0.12125~ - 0.122 M/sjeffrey XiaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC Grade 11 Chemistry Energetics CWDokument3 SeitenCC Grade 11 Chemistry Energetics CWMaliq MorrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2019 Lesson 12 Empirical and Molecular FormulasDokument42 Seiten2019 Lesson 12 Empirical and Molecular FormulasMinenhle Mnikathi100% (1)
- Practical MYP 4 Speed of SoundDokument6 SeitenPractical MYP 4 Speed of SoundPrasanna PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Grade 8Dokument5 SeitenWorksheet Grade 8willadahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat of Solution & Preparation of Copper Sulfate ExperimentDokument4 SeitenHeat of Solution & Preparation of Copper Sulfate ExperimentQudianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redox Review - IB-Short QuestionsDokument8 SeitenRedox Review - IB-Short QuestionsStephanie LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Energy changes in chemical and physical processesDokument8 SeitenEnergy changes in chemical and physical processesCitron AkhalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mole-Concept Final PDFDokument57 SeitenMole-Concept Final PDFSatyanshu JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics Independent Study Booklet Part DDokument13 SeitenMechanics Independent Study Booklet Part DnavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction MechanismDokument41 SeitenReaction MechanismJyöt SîlvērNoch keine Bewertungen
- Salt PreparationDokument26 SeitenSalt PreparationMenaga A/P IlangkovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- G. Cape Chem Sample Mult-ChoiceDokument9 SeitenG. Cape Chem Sample Mult-ChoiceGervent GayleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry WorksheetsDokument16 SeitenChemistry Worksheetsapi-262668586100% (2)
- Group IV ElementsDokument11 SeitenGroup IV ElementsVince MarsNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9th Icse Pressure - Test LabzDokument48 Seiten9th Icse Pressure - Test Labzmanojboa100% (1)
- Rutherford's Alpha-Particle Scattering ExperimentDokument10 SeitenRutherford's Alpha-Particle Scattering ExperimentAhmad HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charles Law PDFDokument3 SeitenCharles Law PDFIvan BayonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- St. Joseph’s Anglo-Chinese School HKDSE Physics Notes: Chapter 1 Temperature and ThermometersDokument111 SeitenSt. Joseph’s Anglo-Chinese School HKDSE Physics Notes: Chapter 1 Temperature and Thermometersjared liNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Worksheet - ElectrochemistryDokument4 SeitenCBSE Class 12 Chemistry Worksheet - ElectrochemistryArya VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry MYP 3 Section 3Dokument15 SeitenChemistry MYP 3 Section 3Hadeel IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- O Level Chemistry NotesDokument195 SeitenO Level Chemistry NotesZarah Tahir60% (5)
- Csec Chemistry Notes 5Dokument2 SeitenCsec Chemistry Notes 5debestieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrochemistry Strong and Weak ElectrolytesDokument4 SeitenElectrochemistry Strong and Weak ElectrolytesChris McLeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Salt (Preparation of Insoluble SaltDokument10 SeitenChemistry Salt (Preparation of Insoluble Saltcheers96Noch keine Bewertungen
- Measuring Enthalpy ChangeDokument20 SeitenMeasuring Enthalpy ChangedhruviniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of Atom QuestionsDokument5 SeitenStructure of Atom QuestionssingamroopaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BT2 Revision Package 2013 - AnsDokument70 SeitenBT2 Revision Package 2013 - AnsSean Ng Jun JieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic Equations WorksheetDokument1 SeiteIonic Equations Worksheetgimarreyes23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anglican High School Sec 2 Science Worksheet: Mass, Weight, DensityDokument4 SeitenAnglican High School Sec 2 Science Worksheet: Mass, Weight, DensityFrancis Ho HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mole Mole ProblemsDokument3 SeitenMole Mole ProblemsfeliciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 08 Simple PendulumDokument8 SeitenExperiment 08 Simple PendulumAnonymous rswF6CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional Figures with AnswersVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional Figures with AnswersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phy S1 Heat (Fixed Version)Dokument12 SeitenPhy S1 Heat (Fixed Version)Holdon ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ikpeka Et Al-2018-Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production TechnologyDokument24 SeitenIkpeka Et Al-2018-Journal of Petroleum Exploration and Production TechnologyNwakile ChukwuebukaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogen and Nitrogen Control in Ladle and Casting OperationsDokument62 SeitenHydrogen and Nitrogen Control in Ladle and Casting OperationsJasmin HalilovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process CalculationsDokument225 SeitenProcess CalculationsIsabel Justiniano Olivera86% (22)
- Ssasas DSDSDDokument9 SeitenSsasas DSDSDZia RathoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - Ceramic MaterialsDokument31 SeitenChapter 3 - Ceramic Materialsming hueNoch keine Bewertungen
- RMS Speed of Electrons in the Sun's AtmosphereDokument10 SeitenRMS Speed of Electrons in the Sun's AtmosphereMD Al Fahad NirobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of Molecular Compositions in China's Giant Natural Gas FieldsDokument22 SeitenCharacteristics of Molecular Compositions in China's Giant Natural Gas FieldsMonel LenomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endothermic Gas Production Overview: Tmosphere Ngineering OmpanyDokument6 SeitenEndothermic Gas Production Overview: Tmosphere Ngineering OmpanyJhon ChitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Jan2012 Unit-1 QPDokument24 SeitenChemistry Jan2012 Unit-1 QPAkila RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07 SurfaceTension 2022 2023 v1Dokument28 Seiten07 SurfaceTension 2022 2023 v1Sema KurdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Peracetic Acid by Potentiometric Titration: Sample Preparation and ProceduresDokument6 SeitenDetermination of Peracetic Acid by Potentiometric Titration: Sample Preparation and ProceduresHasan Zeki BayrakNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1412 3632Dokument8 Seiten1412 3632HomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chelate Table of Stability ConstantsDokument2 SeitenChelate Table of Stability ConstantsNathaniel AnchoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Wet Scrubbing: A. Arrowsmith and N. F. AshtonDokument2 Seiten13 Wet Scrubbing: A. Arrowsmith and N. F. AshtonDHAVALESH AMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tasker-Milward School 1Dokument19 SeitenTasker-Milward School 1Younes AlahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: Paper 9701/12 Multiple ChoiceDokument14 SeitenChemistry: Paper 9701/12 Multiple ChoiceAbubakar shaban omarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Mesoporous Carbon MaterialsDokument7 SeitenSynthesis of Mesoporous Carbon MaterialsMaria IgnatNoch keine Bewertungen
- L3 Equilibrium ConversionDokument17 SeitenL3 Equilibrium ConversionChristopher RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Reaction Technology 2nd EditionDokument643 SeitenChemical Reaction Technology 2nd EditionRicardo Gómez LoaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IPC-TM-650 Test Methods Manual: Association Connecting Electronics IndustriesDokument2 SeitenIPC-TM-650 Test Methods Manual: Association Connecting Electronics IndustriesYork LiaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glass Is AnDokument26 SeitenGlass Is AnMahfuzur Rahman SiddikyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 Metallic Glass: Aggregated Diamond or Hyper DiamondDokument3 Seiten22 Metallic Glass: Aggregated Diamond or Hyper DiamondMariam AbdulkariamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rate and Extent of Chemical ChangeDokument11 SeitenThe Rate and Extent of Chemical ChangeKirsten AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desalination: Yawen Wang, Aimin Li, Hu YangDokument10 SeitenDesalination: Yawen Wang, Aimin Li, Hu YangDrFatema HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultraviolet Spectroscopy and Uv Lasers - Compress PDFDokument566 SeitenUltraviolet Spectroscopy and Uv Lasers - Compress PDFmagsNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Overview of Aluminum Foam Production MethodsDokument8 SeitenAn Overview of Aluminum Foam Production Methodsgouhua yuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report Stirling Engine CompleteDokument28 SeitenReport Stirling Engine CompleteNurul Nadia33% (3)
- How Oxygen and Acids in Uence The Aging of TransformersDokument12 SeitenHow Oxygen and Acids in Uence The Aging of TransformersRajesh MadapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textile Chemical Brochure 8.6.22 - 031Dokument1 SeiteTextile Chemical Brochure 8.6.22 - 031NIKESH PRAKASHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Langmuir Probes Experiment GuideDokument11 SeitenLangmuir Probes Experiment GuideAli SafdariNoch keine Bewertungen