Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hemolytic Anemia
Hochgeladen von
Teus FatamorganaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hemolytic Anemia
Hochgeladen von
Teus FatamorganaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CSC Jun-02
Hemolytic Anemia
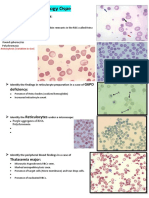
Key Points: Think of hemolytic anemia as intracorpuscular vs. extracorpuscular Coombs positivity = immune-mediated hemolysis; the pattern of the Coombs (IgG vs. C3) can be useful I. Etiology: Many different ways of classifying (intra- v. extravascular, acquired v. hereditary) this is probably the most common/intuitive A. Intracorpuscular: Enzyme defects (pyruvate kinase, G6PD, etc) Hemoglombinopathies (sickle cell, thalassemia) Hereditary spherocytosis, elliptocytosis Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (acquired mutation causing membrane protein destabilization; causes hemolytic anemia, venous thrombosis, deficient hematopoiesis; dx by flow cytometry) Spur cell anemia (seen in advanced cirrhosis) B. Extracorpuscular: Hypersplenism Antibody-mediated immune hemolysis (warm, cold or drug-induced) Microangiopathic hemolysis (TTP, DIC) Infections (bartonella, malaria, babesiosis) Toxins (venom, copper) Trauma (marching, shearing with prosthetic valves) II. Approach to diagnosis: Once youve figured out that hemolysis is going on, how do you determine the cause? Most useful tools to begin with: the peripheral smear and the Coombs test. Finding on smear Spherocytes Schistocytes Spur cells/acanthocytes Target cells Agglutinated cells Heinz bodies Seen in Hereditary spherocytosis, AIHA MAHA, prosthetic valves, mechanical Liver disease (spur cell anemia) Primary hemoglobinopathy, liver disease Cold agglutinin Unstable Hgb, oxidant stress
Coombs test: positive only in antibody-mediated (i.e. autoimmune) hemolysis a. Direct = patients RBCs plus antisera against IgG and C3 -- will be positive in almost all cases of warm autoimmune hemolysis and most cases of cold agglutinin disease (if test done properly) -- pattern of anti-IgG vs. anti-C3 can help determine etiology (see below) b. Indirect = patients serum plus normal RBCs -- mainly used to detect Rh alloimmunization in pregnant women III. Types of Immune-mediated Hemolytic (i.e. Coombs positive) Anemia: 1. Warm (IgG): Idiopathic Lymphoma, CLL SLE (IgG and C3), other CVD Drugs Aldomet-type (IgG) Postviral Penicillin -type (IgG) Other malignancies (rare) Quinidine-type 2. Cold (IgM):* Acute Mycoplasma EBV/infectious mono Chronic Idiopathic Lymphoma, paraneoplastic 3. Cold (IgG):* this is Paroxysmal Cold Hemoglobinuria unusual; called Donath-Landsteiner antibody causes: tertiary syphilis, viral, or autoimmune
* Cold antibodies usually react with anti-C3 but not anti-IgG in direct Coombs test
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fast Facts: Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Prompt action saves livesVon EverandFast Facts: Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Prompt action saves livesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular Diseases and LiverDokument20 SeitenCardiovascular Diseases and LiverKrishna KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- HPLC PPT - KarishmaDokument76 SeitenHPLC PPT - KarishmaDivya GauravNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Systemic Pathology S4T1 - RBC and Bleeding Disorders PDFDokument27 Seiten2021 Systemic Pathology S4T1 - RBC and Bleeding Disorders PDFAlexis Bondad100% (1)
- Abnormal CBC - PresentationDokument23 SeitenAbnormal CBC - PresentationMateen ShukriNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistDokument68 SeitenDR Nilukshi Perera Consultant HaematologistThaveeshaLindsayWhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- CML, CLLDokument118 SeitenCML, CLLMunesh SherawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renal PathologyDokument49 SeitenRenal PathologyQusaiBadrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphoid NeoplasmsDokument52 SeitenLymphoid NeoplasmsAmalia Riska GNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Medicine HematologyDokument78 Seiten2 Medicine HematologyAmitNoch keine Bewertungen
- S0850alug 1670953860959-SEU HDokument56 SeitenS0850alug 1670953860959-SEU HAziz KhwajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Red Blood Cell Disorders Anemia: Anemia Is A Laboratory DiagnosisDokument3 SeitenRed Blood Cell Disorders Anemia: Anemia Is A Laboratory DiagnosisAnonymous 8hJAATBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasma Cell NeoplasmsDokument36 SeitenPlasma Cell Neoplasmsdrafq2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- CBCDokument12 SeitenCBCDaNa Al-jomah100% (1)
- WBC Usmle QuestionsDokument17 SeitenWBC Usmle Questionssplinter594100% (1)
- 3 Bone Marrow ExaminationDokument105 Seiten3 Bone Marrow ExaminationShourav SarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faquin Milian System and Molecular Advances in Diagnosis Salivary Gland TumorsDokument87 SeitenFaquin Milian System and Molecular Advances in Diagnosis Salivary Gland TumorsJoanna Marie100% (1)
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia-BookDokument15 SeitenAcute Myeloid Leukemia-BookRhoda Lom-ocNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fast Facts: Measurable Residual Disease: A clearer picture for treatment decisionsVon EverandFast Facts: Measurable Residual Disease: A clearer picture for treatment decisionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- (MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyDokument6 Seiten(MICROA - 2.1) Myeloid Tissue HistologyHenryboi CañasNoch keine Bewertungen
- RBC MorphologyDokument9 SeitenRBC MorphologybiancsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Autoimmune Hemolytic AnemiaDokument55 SeitenAutoimmune Hemolytic AnemiaNicky SebastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bone Marrow TransplantationDokument21 SeitenBone Marrow TransplantationMorrison George100% (1)
- Cell Inclusions: John SantangeloDokument45 SeitenCell Inclusions: John Santangelosaint5470Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphoid NeoplasmsDokument7 SeitenLymphoid NeoplasmsMaribel SchullNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Components Where Do They Come From?: Introduction To HaematologyDokument11 SeitenBlood Components Where Do They Come From?: Introduction To Haematologydorsa koraeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leukocyte DisordersDokument55 SeitenLeukocyte DisordersSherlyn Yee100% (1)
- CNS PathologyDokument126 SeitenCNS PathologyMichael-John FayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anemia and Its Classification by DR Bashir Ahmed Dar A Sopore Kashmir 1228039135310976 9Dokument30 SeitenAnemia and Its Classification by DR Bashir Ahmed Dar A Sopore Kashmir 1228039135310976 9hercolaniumNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBC Reviewer Anaphy LabDokument9 SeitenCBC Reviewer Anaphy LabARVINE JUSTINE CORPUZNoch keine Bewertungen
- HaematinicsDokument2 SeitenHaematinicsGerardLum100% (2)
- Hematology Ospe A1Dokument5 SeitenHematology Ospe A1Zain Ul AbidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 10 AnemiasDokument25 SeitenTop 10 AnemiasJames StaffordNoch keine Bewertungen
- HAEMOPOIESISDokument6 SeitenHAEMOPOIESISDiyana ZahariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oncology Revision: Paul BaillieDokument299 SeitenOncology Revision: Paul BaillieMourian AmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Flow Cytometry in Diagnosis of ALLDokument30 Seiten06 Flow Cytometry in Diagnosis of ALLcandiddreamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron Deficiency AnaemiaDokument6 SeitenIron Deficiency AnaemiaBhavya agarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Red Cell and White Cell Counting, BloodDokument89 SeitenRed Cell and White Cell Counting, BloodJovel GangcuangcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratorial Diagnostics Keypoints RevisionDokument6 SeitenLaboratorial Diagnostics Keypoints RevisionFathimathNoch keine Bewertungen
- White Blood Cell Disorders: Neoplastic Diseases of The BloodDokument81 SeitenWhite Blood Cell Disorders: Neoplastic Diseases of The BloodMiguel Cuevas Dolot100% (1)
- Systemic Pathology Study NotesDokument33 SeitenSystemic Pathology Study NotesLaura BourqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Granulomatous Inflammation ThyroidDokument55 SeitenGranulomatous Inflammation ThyroidKamlesh PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDokument15 SeitenAnemia Type Pathogenesis Clinical Manifestations Diagnosis Peripheral Blood Lab FindingsDanielle FosterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bone Marrow ExaminationDokument31 SeitenBone Marrow ExaminationMonique BorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of The Thalassemias - UpToDateDokument52 SeitenClinical Manifestations and Diagnosis of The Thalassemias - UpToDatesushi37Noch keine Bewertungen
- Haematology - Blood Films.Dokument6 SeitenHaematology - Blood Films.kkkssbb100% (1)
- Morphology OF Red Blood CellsDokument36 SeitenMorphology OF Red Blood CellsFrancis ValdezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leukemias & Lymphomas - HY USMLEDokument87 SeitenLeukemias & Lymphomas - HY USMLEMatt McGlothlinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Grouping ReagentsDokument7 SeitenBlood Grouping ReagentsDominic EmerencianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hematologic Pathology p48-64Dokument17 SeitenHematologic Pathology p48-64zeroun24100% (1)
- Bethesda System of Reporting Thyroid CytologyDokument131 SeitenBethesda System of Reporting Thyroid CytologyMandavi HindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia QuestionsDokument22 SeitenAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Questionsđoàn lươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateDokument3 SeitenClinical Medicine - Lecture: - Topic: - DateqselmmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Megaloblastic Anemia Testing AlgorithmDokument1 SeiteMegaloblastic Anemia Testing AlgorithmkatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug HaemolysisDokument3 SeitenDrug HaemolysisGerardLumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsDokument16 SeitenChapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsOmar100% (1)
- Hematology NotesDokument4 SeitenHematology NotesHannah Grace CorveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gizi BumilllDokument93 SeitenGizi BumilllTeus FatamorganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1201 3568 1 PBDokument9 Seiten1201 3568 1 PBTeus FatamorganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gizi Pada Ibu Hamil PDFDokument5 SeitenGizi Pada Ibu Hamil PDFArfiana_FaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdominal TraumaDokument47 SeitenAbdominal TraumaWidya Rahayu100% (1)
- Pharmacology of Drugs For AnemiaDokument49 SeitenPharmacology of Drugs For AnemiaTeus Fatamorgana100% (2)
- Copd 7 271Dokument12 SeitenCopd 7 271Teus FatamorganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lymphopoietic System PaDokument47 SeitenLymphopoietic System PaKathrine SiahaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFK: Dept - Farmakologi & Therapeutik Fak - Kedokteran UhnDokument39 SeitenDR - Datten Bangun MSC, SPFK: Dept - Farmakologi & Therapeutik Fak - Kedokteran UhnTeus FatamorganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 7 Tape ScriptDokument5 SeitenUnit 7 Tape ScriptTeus FatamorganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Study of Nigella Sativa and Triple Therapy in Eradication of Helicobacter Pylori in Patients With NonDokument12 SeitenComparative Study of Nigella Sativa and Triple Therapy in Eradication of Helicobacter Pylori in Patients With NonTeus FatamorganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chronic Inflamation: Bagian Patologi Anatomi FK - UmiDokument35 SeitenChronic Inflamation: Bagian Patologi Anatomi FK - UmiTeus FatamorganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dear GodDokument3 SeitenDear GodDedeVortexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Study of Nigella Sativa and Triple Therapy in Eradication of Helicobacter Pylori in Patients With NonDokument12 SeitenComparative Study of Nigella Sativa and Triple Therapy in Eradication of Helicobacter Pylori in Patients With NonTeus FatamorganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDokument5 SeitenSystemic Lupus ErythematosusThayk FerolsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nilai Normal Laboratorium Pada AnakDokument6 SeitenNilai Normal Laboratorium Pada AnakMaharani Primastuti ArganistNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hubungan Hiperplasia Endometrium Dengan Mioma Uteri Studi Kasus Pada Pasien Ginekologi Rsud Prof. Dr. Margono Soekardjo PurwokertoDokument8 SeitenHubungan Hiperplasia Endometrium Dengan Mioma Uteri Studi Kasus Pada Pasien Ginekologi Rsud Prof. Dr. Margono Soekardjo PurwokertorinieeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDokument9 SeitenSystemic Lupus ErythematosusTeus FatamorganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Study of Nigella Sativa and Triple Therapy in Eradication of Helicobacter Pylori in Patients With NonDokument12 SeitenComparative Study of Nigella Sativa and Triple Therapy in Eradication of Helicobacter Pylori in Patients With NonTeus FatamorganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corpal Nindya Duri IkanDokument10 SeitenCorpal Nindya Duri IkanRadianNasutionNoch keine Bewertungen
- CarcinogenesisDokument40 SeitenCarcinogenesisNatasha AmaldaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesser Metatarsal Osteotomy Complications: Lowell S. Weil and Erin E. KleinDokument9 SeitenLesser Metatarsal Osteotomy Complications: Lowell S. Weil and Erin E. KleinAntonio FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parenteral NutritionDokument8 SeitenParenteral NutritionivanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Counseling Parents About Cochlear ImplantsDokument6 SeitenCounseling Parents About Cochlear ImplantsJordan HansonNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Zealand Data Sheet: ActionsDokument17 SeitenNew Zealand Data Sheet: Actionsheri siswanto nur sidikNoch keine Bewertungen
- JCIA Handbook 2020Dokument61 SeitenJCIA Handbook 2020WAQASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pebc Evaluating Exam Sample QuestionDokument50 SeitenPebc Evaluating Exam Sample QuestionZain zanzoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lactose Intolerance in InfantsDokument10 SeitenLactose Intolerance in InfantsflorenceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7: Emotional and Behavioural Problems: DR Jessie EarleDokument28 SeitenChapter 7: Emotional and Behavioural Problems: DR Jessie EarlejajmajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of Normal ECG: Prepared By: Ben Ryan Jucay SauceDokument25 SeitenBasic Principles of Normal ECG: Prepared By: Ben Ryan Jucay SauceSoySauceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Source: Bioethics Topics: Exam Questions & Answers Legal Medicine & Medical EthicsDokument67 SeitenSource: Bioethics Topics: Exam Questions & Answers Legal Medicine & Medical Ethicsjamestery0% (1)
- Chapter 1 Essay NegligenceDokument3 SeitenChapter 1 Essay NegligenceVladimir Hechavarria100% (1)
- Stages of Labor and DeliveryDokument4 SeitenStages of Labor and DeliveryvienreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reiki 1Dokument19 SeitenReiki 1api-246890707Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2016 S 0042 108641 PDFDokument29 Seiten2016 S 0042 108641 PDFMadalina StoicescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vertigo MeniereDokument5 SeitenVertigo MeniereHamba AllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Case 6 MBUDokument12 Seiten2015 Case 6 MBUDinesh TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- CD4 Count CutDokument51 SeitenCD4 Count Cutibrahim 12Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ais YesDokument15 SeitenAis YesLauriz Dillumas MachonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Hip Replacement SurgeryDokument13 Seiten10 Hip Replacement SurgeryDIA PHONG THANGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connecticut Health PlanDokument2 SeitenConnecticut Health PlanHelen BennettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brockton Police Log Updated 10/01/2013Dokument19 SeitenBrockton Police Log Updated 10/01/2013BB0% (1)
- Hospitals in KochiDokument6 SeitenHospitals in Kochianandrv86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Principle of Laser Application in Medicine & LASER SAFETY5Dokument62 SeitenPrinciple of Laser Application in Medicine & LASER SAFETY5melisandrianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCI Chart BookletDokument66 SeitenIMCI Chart Bookletnorwin_033875Noch keine Bewertungen
- Procalcitonin Testing To Guide Antibiotic Therapy in Acute Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDokument2 SeitenProcalcitonin Testing To Guide Antibiotic Therapy in Acute Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsMr. LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lactated Ringer'sDokument7 SeitenLactated Ringer'sPPLaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Sector EHSMS Requirements-June 2012Dokument31 SeitenHealth Sector EHSMS Requirements-June 2012Aya MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- FCBDokument26 SeitenFCBsprapurNoch keine Bewertungen