Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Manual Del Regulador Electrónico de Velocidad DGC-2007
Hochgeladen von
pevareOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Manual Del Regulador Electrónico de Velocidad DGC-2007
Hochgeladen von
pevareCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
- 1 -
April 2007 Ver. 1.00
Fig.1 Wiring Diagram and Outline
Description
DGC-2007 Governor controller unit is an electronic device designed to control Engine speed with fast and precise
response to transient load changes which is based on PID algorithm. The device is composed of a Main Controller with
the function of single operation (Isochronous mode) and parallel operation (Droop mode), and with an Auxiliary Controller
enabling the emergency operation in case of malfunction of the main controller.
Mounting & Warning
Mount the controller unit vertically to the surface of a control cabinet, protected from the weather and high
humidity, and do not expose the controller unit to the source of radiant heat.
Do not rely exclusively on the governor system electric actuator to prevent overspeed. A secondary shutoff device,
such as a fuel solenoid must be used.
EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility)
To satisfy EMC requirements, the controller unit should be mounted on the grounded metal side, and it is required to
use shielded wires for all signal lines and ground all the shields to one of the bolts used to mount the controller.
Functions
<< Auxiliary (Emergency) Control mode>>
Em. Speed : Engine Speed adjustment pot in case of "Auxiliary Controller mode".
Em. Test : Test push button for "Auxiliary Controller mode".
Jumper Wire : To be cut off in case of "Auxiliary Controller mode".
Em. SW : Selector switch between "Main controller mode" and "Auxiliary Controller mode".
OFF : Main controller mode ON : Auxiliary Controller mode
Em. Test
Speed
M
Over. Test
Idle
Pick-Up
C B A
Actuator
E F D
Battery
J H G
Speed Trim
L K
Droop
Em. Run
Pick up
Control
Fuel
Starting
Ramping
N
AUX
Stability Gain
Droop
4
5
6 TB1
Speed adjustment V.R
7
8
9
10 Adjustment SW
Monitoring lamp 11
13 TB3
TB2 12
Frame GND bolt
EM. Jumper cable
Push button SW
Push button SW
EM. Speed adj V.R
Stability adjustment V.R
Gain adjustment V.R
Run lamp adjustment V.R
Speed Ramping adjustment V.R
Starting fuel adjustment V.R
Droop adjustment V.R
Idle speed adjustment V.R
Overspeed adjustment V.R
2 1 3 6 4 5
10V
P
Idle
Em. Speed
Over Speed
Over Speed
Run
Run
Speed
CB2
CB1
OFF ON
Em.SW
EM. Selector SW
Over Speed 1
2
3
O N
1 2
- 2 -
<< Main Control mode >>
Over. Test : Test Push button to detect the overspeed signal while overspeed setting or thereafter.
Potentiometer Speed : Adjusting the Engine speed.
Stability : Adjusting the stability (governing response).
Gain : Adjusting the gain (governing sensitivity).
Potentiometer Starting Fuel : Adjusting the fuel amount at Engine start up.
Speed Ramping : Adjusting the time to reach the rated speed.
Run lamp : Adjusting the point when run lamp is on and the relevant relay is activated.
Potentiometer Droop : Adjusting the percentage of Droop.
Idle : Adjusting the idle speed.
Overspeed lamp : Adjusting the point when overspeed lamp is on and
the relevant relay is activated.
Selector Switch : selecting the differential function (Refer to chapter "Instability" - Page.6~7).
TB1 : Terminal block for input & output.
TB2 : Relay terminal for running mode (capacity - 0.5A/125VAC).
TB3 : Relay terminal for overspeed mode(capacity - 0.5A/125VAC).
Adjustments
For potentiometer adjustment, use a small sized (-) screw driver. (be cautious of potentiometers being damaged)
Check that all electrical connections are correctly made and terminal screws tightened.
Engine Start up
1. Move [Em.SW] to OFF position to choose "Main controller mode".
2. Connect terminals G & M (with Idle switch ON).
3. Turn Starting Fuel clockwise at 5 Oclock. (Full CW).
* The more Starting Fuel approaches to Full CW, the easier the engine can start up.
4. Turn Speed Ramping between 9 ~ 12 Oclock.
* The time to reach the rated speed (run speed) prolongs as turning
Speed Ramping clockwise (max. over 10 sec)
* With Speed Ramping biased to counterclockwise direction, a symptom of overshoot
or hunting can occur.
5. Start cranking the Engine.
Rated speed & Idle speed
6. Rated speed adjustment.
* After Engine start up, remove the connection between terminals G & M
(with Idle switch OFF)
* Under no load condition, adjust Speed.
Clockwise ( ) RPM increase / counterclockwise ( ): RPM decrease
7. Idle speed adjustment.
* With Idle switch ON again, set the Engine speed at 800rpm by
idle potentiometer (between 12 ~ 3 Oclock)
Clockwise ( ) RPM increase / counterclockwise ( ): RPM decrease
Idle speed is the important factor to determine the characteristics of Engine Start-up.
therefore, its necessary to adjust the Idle speed after Rated speed adjustment regardless of
use of idle mode.
Governor performance adjustment
8. Remove the connection between terminals G & M (with idle switch OFF), so that and
the Engine will be at operating speed and at no Load.
9. Gain adjustment.
* Rotate Gain clockwise( ) until instability develops at no load.
* Gradually move Gain counterclockwise( ) until stability returns.
* Move Gain counterclockwise( ) further by around 20 minutes (10) to insure
stable performance.
10. Stability adjustment.
* Rotate Stability clockwise( ) until instability develops at no load.
* Gradually move Stability counterclockwise( ) until stability returns.
Gain Stability Speed
Fuel
Starting
Ramping
Speed
Run
Em. selection SW
OFF ON
Em.SW
2 1
N O
Droop
Over
Speed
D1 D2
Idle
Idle
G M
OFF ON
IDLE S/W
Idle
Starting
Fuel
Speed
Ramping
Gain
Stability
- 3 -
* Move Stability counterclockwise( ) further by around 20 minutes (10) to
insure stable performance.
Accessory adjustment
11. Run Lamp ON.
* At the rated speed, rotate Run counterclockwise( ) until the lamp is on.
* Move Run counterclockwise( ) further by 1/4 turn to avoid the lamp flickering.
12. Overspeed lamp ON.
* At the rated speed, as pressing the button Over.Test, gradually turn Over Speed
counterclockwise( ) until Overspeed lamp is on and the Engine is shut off
simultaneously.
* With the adjustment above, the overspeed function is triggered at around 115%
of the rated speed.
On completion of all the adjustments, start up the Engine again to insure the stable operation at Engine start up,
at no load and at load operation respectively.
Starting Fuel adjustment (to minimize the Engine s exhaust smoke)
* Place the Engine in idle by connecting terminals M & G.
* Set the idle at 800 rpm.
* Rotate Starting Fuel counterclockwise until the Engine speed begins to fall.
* Move Starting Fuel clockwise slightly so that the idle speed is returned to the desired level.
it is recommended to place Starting Fuel between 3 ~ 5 Oclock as long as the Engines exhaust smoke is
within tolerance. If Starting Fuel is set too low, it may be hard to start the engine and cause the speed overshoot
on engine start up, even resulting in exceeding the preset overspeed value.
When the engine won t start,
* If wrong wiring is not found, Return all adjustments to "factory set values" (Refer to table 2. - Page.5)
Start up the engine again.
* if the attempts above is unsuccessful : The controller may be at fault, and replace the controller with new one.
Fig.2 Wiring Diagram
Monitoring lamp
Over Speed
Control
Pick up
Em. Run
Run
Em. Speed
Over. Test
Em. Test
Actuator
shield cable (cover with insulation tube)
fuse(10A) Power switch
3
2
1
Idling switch
Droop swtich
ON OFF
Load sharing
Auto
<Auxiliary unit >
0.75 2C shield
1.3 2C
1.3 2C
5
Frame GND
Jumper
OFF ON
synchronizer
unit
1
0
V
24V
BATTERY
+
Magnetic
pick-up
-
D
r
o
o
p
A
U
X
I
d
l
e
G
a
i
n
S
t
a
b
i
l
i
t
y
S
p
e
e
d
B
a
t
t
e
r
y
S
p
e
e
d
T
r
i
m
P
i
c
k
-
U
p
A
c
t
u
a
t
o
r
- 4 -
External Wiring
Wiring to the speed control unit should be as shown in Fig. 2. .
All the cables should be 0.75 or larger and it is recommended to use shielded cables for all external
connections.
Other shielded cables not described in Fig. 2 should be grounded to the frame.
It is recommended to use thick and twisted cables for actuator connections.
The normal reading of resistance between terminals A & B is 3.5 ~4.5 .
Magnetic speed sensor connections to terminals C and D must be shielded for their entire length.
The speed sensor cable shield should only be connected to terminal D.
The shield should be insulated to insure no other part of the shield comes in contact with engine ground.
otherwise stray speed signals may be introduced to the speed control unit resulting in instability, etc.
Be cautious that the Batterys polarity to terminal E & F should not be interchanged, and a 10 amp fuse
must be Installed between Battery (+) and terminal F. after the wiring work, check the voltage
between terminals which should be 24VDC (4VDC). and ground the terminal E to the frame. (wiring )
As illustrated in Fig.2. , connecting the optional 5 resistance enables fine adjustment of engine speed
within the range of preset speed 210Hz range.
In case of 12V system, or of actuator with current consumption over 5 amp or above, connect terminals
between G & H.
Selector switch, switching over "IDLE mode" and "RUN mode".
ON(CLOSE) : idle mode OFF(OPEN) : run rated mode
"DROOP" mode selector switch.
ON(CLOSE) : DROOP mode OFF(OPEN) : Isochronous mode
The signal from Auxiliary device for parallel Operation System should be connected to terminal N.
It is necessary to use the shielded cable for the signal.
The +10[V] & 20[mA] of current supply, Terminal P, Can be untilled to provide power to governor
system accessory.
<CAUTION> Wrong or erroneous wiring & Battery Voltage can cause the fatal damage to the controller.
Magnetic speed sensor connections
With the Engine stopped, adjust the gap between the magnetic speed sensor and the ring gear teeth.
The gap should not be any smaller than 0.45mm. usually, backing out the speed sensor by 3/4 turn after
touching the ring gear teeth will achieve a satisfactory air gap.
The signal from the speed sensor can be measured between Terminals C & D in engine operation.
Controller can control the engine with signal as low as VAC 1.5 or around, but its more reliable to get the signal
VAC 3 or above.
Remote speed adjustment
As illustrated in Fig.3. , a remote speed adjustment potentiometer can be used to adjust the engine speed
over specific speed range. Select the desired speed range and the corresponding potentiometer value
(Refer to table 1.)
When the minimum speed setting is used in remote adjustment mode, the speed drop phenomenon may occur
due to instability and load in the system. to maintain engine stability at the minimum speed setting above,
a small amount of droop can be added by turn Droop counterclockwise.
on the other hand, at the maximum speed setting, the governor performance will be near Isochronous regardless
of the droop adjustment setting.
Fig.3. TABLE 1. Variable speed range potentiometer
cw
G J K L
* a characteristic maintaining
the desired engine speed,
independent of load.
speed range Potentiometer value
900 Hz 1K
2,400 Hz 5K
3,000 Hz 10K
3,500 Hz 25K
3,700 Hz 50K
Fn|| Locd IctcdSjccd
(NoLocd Sjccd-Fn|| Locd IctcdSjccd) * 100
- 5 -
Table 2. Factory Set Values
* CW : clockwise CCW : counterclockwise
DROOP Parallel Operation mode (Manual paralleling)
Definition: Engine speed on the decrease against Engine load on the increase.
DROOP(%) =
Description : Droop is typically used for the load sharing and paralleling of engine driven generators.
without the Droop mode in Paralleling system, generators can be overloaded or motorized.
Application : For DROOP Operation,
1. Close DROOP selector switch between K-L terminals.
2. When in droop operation, the Engine speed will decrease as Engine load increase.
The percentage of droop governing can be varied with Droop Potentiometer.
The higher level of droop is achieved as turning Droop clockwise.
Droop level requirements above 10% are unusual. and the minimum droop level to keep the stability of
speed droop governor is 2.5% or above. After the droop level has been adjusted, the rated engine speed setting
may need to be reset. Check the engine speed and adjust the speed setting accordingly.
Accessory Input (automatic paralleling)
The Auxiliary terminal N accepts input signals from load sharing units, auto synchronizers, and other governor system
accessories. It is recommended that this connection from accessories be shielded as it is a sensitive input terminal.
When an accessory is connected to Terminal N, the speed will decrease and the speed adjustment must be reset.
When operating in the upper end of the control unit frequency range, a jumper wire or frequency trim control may be
required between Terminals G and J. This increases the frequency range of the speed control to over 7000Hz.
Auxiliary Controller Operation(Emergency Operation) & TEST
When the Main Controller is malfunctioning, or auxiliary Controller is in the test and speed
setting mode, Placing the Switch [Em.SW] to ON position makes the lamp [Em.Run] on and
enters into Auxiliary Operation mode (Refer to Fig.1.).
< Setting : 1500rpm > < Setting : 1800rpm >
E.M SW : "OFF" (Main Controller Operation mode) E.M SW : "OFF" (Main Controller Operation mode)
Overspeed : 1725rpm (No. of teeth = 160) Overspeed : 2070rpm (No. of teeth = 160)
Run lamp : Maximum CW Run lamp : Maximum CW
Gain : Mid-range(12 Oclock) Gain : Mid-range(12 Oclock)
Stability : Mid-range(12 Oclock) Stability : Mid-range(12 Oclock)
Starting Fuel : Full CW(Maximum Fuel) Starting Fuel : Full CW (Maximum Fuel)
Speed Ramping : 9 Oclock Speed Ramping : 9 Oclock
Droop : Full CCW (minimum) Droop : Full CCW (minimum)
E.M Speed
Adjustment
: about 1000 rpm
(No. of teeth = 160)
E.M Speed
Adjustment
: about 1000 rpm
(No. of teeth = 160)
Speed Adjustment : 4000Hz (15 turns clockwise) Speed Adjustment : 4800Hz (18 turns clockwise)
: No. of teeth = 160 1500 rpm : No. of teeth 160 1800 rpm
: No. of teeth = 152 1579 rpm : No. of teeth 152 1894 rpm
: No. of teeth = 146 1644 rpm : No. of teeth 146 1972 rpm
Idle Adjustment : 2137 Hz (between 1 ~ 3 Oclock) Idle Adjustment : 2137 Hz (between 1 ~ 3 Oclock)
: No. of teeth 160 800 rpm : No. of teeth 160 800 rpm
: No. of teeth 152 842 rpm : No. of teeth 152 842 rpm
: No. of teeth 146 877 rpm : No. of teeth 146 877 rpm
OFF ON
Em.SW
- 6 -
Test of Auxiliary Controller & speed setting
1. Move [Em.SW] to ON position.
2. As pressing the button [ Em.Test], Start up the engine.
3. Keep pressing the button [ Em.Test] after Engine start up, and turn [ EM.Speed]
Potentiometer for the desired engine speed which is increased by turning the potentiometer
clockwise.
4. Release the button [ Em.Test], and the engine will be stopped.
5. Move [Em.SW] to OFF position to go back to Main controller mode.
Auxiliary Controller mode
1. Cut off jumper wires of CB1 & CB2 respectively.
2. Move [Em.SW] to ON position.
3. Start up the Engine.
4. Check the engine speed and reset it if necessary.
Auxiliary Controller mode characteristics & cautions
1. In Auxiliary Control mode, the Engine speed will decrease as Engine load increase and it is necessary to keep the
percentage of load within 30 ~50 of the rated load (it depends on engine output).
2. It is recommend to use auxiliary control mode only in case there is no replacement controller available.
3. After cutting off jumper wires of CB1 and CB2, it is not possible to use the controller in "Main controller mode"
Therefore, it is recommended to keep the button [ Em.Test] pressed for test purpose only.
4. When the engine will not start in Auxiliary Controller mode, turn [ EM.Speed] fully counterclockwise(full CCW)
and reverse it clockwise by 15~16 turns, which restores the controller to the factory set condition and make any of
engine model start up.
5. In case PCB patterns connected to the Terminal array are seized due to over current in main controller mode, be
aware that the operation in auxiliary controller mode is not possible either.
Controller LAMP display (diagnosis)
Over Speed : When the Engine reaches the preset overspeed, the lamp is on and relevant
relay is activated and the power to the actuator is shut off.
Run Speed : When the Engine reaches the preset rated speed, the lamp is on and
relevant relay is activated.
Pick Up : When the voltage between terminals C & D is VAC 1.5 or above, the lamp is on.
Control : When the battery power is connected and inner control power (DC 10V) is
achieved, the lamp is on and Main controller is ready to function ([Em.SW] OFF).
Em.Run : When moving [Em.SW] to ON position, the lamp is on and the auxiliary Controller
is ready to function.
System Troubleshooting
Instability
Fast instability
1. Usage of switch D1 & D2 (Refer to Fig.1. )
When the position of switch D1 is ON, the differential function is activated.
It provides fast transient response against Engine speed changes.
however, it may generate fast instability being sensitive to external high frequency noise.
In this case, place the switch D1 to OFF position and readjust Gain & Stability.
If instability should be still present, placing D2 to OFF position may help stabilize
the Engine. Again, readjust Gain & Stability for optimum control.
Em. Speed
Em. Test
2 1
N O
Droop
Over
Speed
D1 D2
Idle
Monitoring lamp
Over Speed
Control
Pick up
Em. Run
Run
- 7 -
Slow instability
Slow instability can have many causes, most of which are due to improper setting against the Engine
characteristics. Adjustment of Gain & Stability usually cures most situations.
(refer to chapter Adjustments - Page.2)
If the troubleshooting above is not successful,
- Due to the controller at fault -> Replace the controller with new one.
- Due to the external devices at fault (Actuator, fuel injection device, turbine, etc) rectify the mechanical devices.
System inoperative
If the Engine governing system does not function, the fault may be determined by performing the voltage tests
described in Steps 1, 2, and 3. (+) and (-) refer to meter polarity. If normal values should be indicated as a result
of following the trouble shooting steps, the fault may be with the actuator or the wiring to the actuator. therefore,
check the Actuator.
STEP TERMINALS NORMAL READING PROBABLE CAUSE OF ABNORMAL READING
1 F(+) & E(-)
Battery supply voltage
(24 VDC)
1. DC battery power not connected, Low Battery voltage, blown fuse.
2. Wiring error.
2 C & D
1.5 VAC RMS min.,
while cranking
1. Gap between speed sensor and gear teeth too great. Check gap.
2. Improper or defective wiring to the speed sensor. Resistance
between terminals C and D should be 30 to 1,200 ohms.
3. Defective speed sensor.
3 F(+) & A(-)
9 ~ 15 VDC
1.0~2.0 VDC
while cranking
on rated speed
1. SPEED adjustment set too low. the(measurement) voltage
is increased than normal value.
2. Short/open in actuator wiring. short : the(measurement) voltage
and battery voltage is not different.
3. Short/open in actuator wiring. open : the(measurement) voltage
is increased than normal value.
4. Defective speed controller.
5. Defective actuator.
6. The speed sensor open/defective the measurement voltage
is less than 1[V].
SYMPTOM TEST PROBABLE FAULT
Engine overspeeds
Do not crank.
Apply DC power to the
governor system
1. Actuator goes to full fuel. Then, disconnect speed sensor
at Terminals C & D.
If actuator still at full fuel speed control unit defective.
If actuator at minimum fuel position erroneous speed
signal. Check speed sensor data.
Manually hold the Engine at
the desired running speed.
Measure the DC voltage
between Terminals A(-) &
F(+) on the speed control
unit.
(Normal : 9~15VDC)
1. If the voltage reading is normal.
a) SPEED adjustment set above desired speed.
b) Defective speed control unit.
2 If the voltage reading is above normal,
a) Actuator or linkage binding.
3. If the voltage reading is below normal,
a) Defective speed control unit.
4. Gain set too low.
Actuator does
not energize fully.
Measure the voltage at
the battery while cranking.
1. If the voltage is less than 15V, replace the battery.
Momentarily connect
Terminals A and F The
actuator should move to
the full fuel position.
1. Actuator or battery wiring in error.
2. Actuator or linkage binding.
3. Fuse opens.
Check for short in actuator or actuator wiring harness.
4. Defective Actuator, check the lubrication of rod bearing
joining actuator and pump.
Engine remains
below desired
governed speed.
Measure the actuator
output. Terminals A & B,
while running under
governor control.
If voltage measurement volts of the battery supply voltage,
then fuel control restricted from reaching full fuel position.
Possibly due to interference from the mechanical governor,
carburetor spring or linkage alignment.
Speed setting too low.
Check if the present operation mode is IDLE.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Square D Wiring Diagram BookDokument109 SeitenSquare D Wiring Diagram BookVieruth Pascua Paet100% (10)
- ADEC™ - Electronics Documentation For Electronic Engine Control Unit ECU-7 - 2007 - MTU® PDFDokument246 SeitenADEC™ - Electronics Documentation For Electronic Engine Control Unit ECU-7 - 2007 - MTU® PDFpevare90% (30)
- Service: Industrial Generator SetsDokument147 SeitenService: Industrial Generator SetsmohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- EKIP Connect - User S Manual - 1SDH000891R0002 - ABB PDFDokument51 SeitenEKIP Connect - User S Manual - 1SDH000891R0002 - ABB PDFpevare100% (1)
- EKIP Connect - User S Manual - 1SDH000891R0002 - ABB PDFDokument51 SeitenEKIP Connect - User S Manual - 1SDH000891R0002 - ABB PDFpevare100% (1)
- GEP62SP-3 (Single Phase)Dokument5 SeitenGEP62SP-3 (Single Phase)Jose PirulliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Servicio Motor Cummins X2.5G4Dokument69 SeitenManual de Servicio Motor Cummins X2.5G4Almy Rose100% (2)
- KM376Dokument2 SeitenKM376Burik8Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2806C E16tag2Dokument2 Seiten2806C E16tag2IKNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADEC™ - Advanced Diesel Engine Controller For Genset Application - 2007 - MTU® PDFDokument11 SeitenADEC™ - Advanced Diesel Engine Controller For Genset Application - 2007 - MTU® PDFpevare100% (5)
- ADEC Advanced Diesel Engine ControllerDokument49 SeitenADEC Advanced Diesel Engine Controllerpevare100% (12)
- Fault Finding Manual For Stamford AC Generators - July 2009 - CUMMINS Generator Technologies PDFDokument29 SeitenFault Finding Manual For Stamford AC Generators - July 2009 - CUMMINS Generator Technologies PDFpevare78% (9)
- Engine Troubleshooting Guide: Shortcuts To Costly Engine DiagnosticsDokument24 SeitenEngine Troubleshooting Guide: Shortcuts To Costly Engine DiagnosticssubruaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accsesory 11BG For ASCO® Series 300 - Kit Installation - 381339-252 E - ASCO™ PDFDokument4 SeitenAccsesory 11BG For ASCO® Series 300 - Kit Installation - 381339-252 E - ASCO™ PDFpevareNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATC-300+ - Standard Schematic - Breaker Based Transfer Switch - CE231377 - January 2015 - EATON® PDFDokument2 SeitenATC-300+ - Standard Schematic - Breaker Based Transfer Switch - CE231377 - January 2015 - EATON® PDFpevareNoch keine Bewertungen
- WEG Regulador de Tensao Grt7 Th4 10040217 Manual Portugues BRDokument50 SeitenWEG Regulador de Tensao Grt7 Th4 10040217 Manual Portugues BRJuan I. Meza Lozano100% (1)
- 2506A E15TAG3 (TPD1581e2)Dokument14 Seiten2506A E15TAG3 (TPD1581e2)Rurouni Martínez100% (1)
- WEG Regulador de Tensao Automatico Ea05a WG Manual Portugues BR DCDokument16 SeitenWEG Regulador de Tensao Automatico Ea05a WG Manual Portugues BR DCAsdrubal AraujoNoch keine Bewertungen
- QSZ13-G7: EU Stage IIIA / U.S. EPA Tier 3Dokument3 SeitenQSZ13-G7: EU Stage IIIA / U.S. EPA Tier 3Franyusmid Gomez Bolivar100% (1)
- EMCPIIDokument12 SeitenEMCPIIJosé María Rodríguez Rivera100% (1)
- QSG12-G2: Specification SheetDokument3 SeitenQSG12-G2: Specification SheetAlejandro Dominado100% (1)
- Parts Catalog - Option Detail: Option Group Graphic Film Card DateDokument3 SeitenParts Catalog - Option Detail: Option Group Graphic Film Card DateagvassNoch keine Bewertungen
- SS15A3P ManualDokument6 SeitenSS15A3P ManualBurce MherjheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ricardo 6105AZLD PDFDokument2 SeitenRicardo 6105AZLD PDFLogistician MALCOMSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Catalogue Cummins 6LTAA8.9 G3Dokument5 SeitenCatalogue Cummins 6LTAA8.9 G3José Diaz100% (2)
- TWD1643GE: Volvo Penta Genset EngineDokument2 SeitenTWD1643GE: Volvo Penta Genset Enginemohsen_cumminsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Partes Sección Motor e Implementos Ggo-01Dokument96 SeitenManual de Partes Sección Motor e Implementos Ggo-01Eduardo SainzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Optimized: Specification SheetDokument3 SeitenFuel Optimized: Specification SheetArslan AnnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Customer) Doosan Diesel Operation Manual - P158LE, P180LE, P222LE, PU158TI, PU180TI, PU222TIDokument170 Seiten(Customer) Doosan Diesel Operation Manual - P158LE, P180LE, P222LE, PU158TI, PU180TI, PU222TIAngelo RuedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulador de Voltaje GAVR8AhDokument2 SeitenRegulador de Voltaje GAVR8AhcrecosiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engines Model NotesDokument6 SeitenEngines Model NotesAungphone Maeoo100% (1)
- Wiring Diagram ConfigurationDokument2 SeitenWiring Diagram Configurationwoulkan50% (2)
- AGC-3 Operators Manual 4189340525 ESDokument40 SeitenAGC-3 Operators Manual 4189340525 ESWilliam AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor N67Dokument5 SeitenMotor N67Anonymous CMS3dL1TNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gu301 ADokument3 SeitenGu301 AJosé Da Silva MataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specifications of Avr - Uvr7Dokument4 SeitenSpecifications of Avr - Uvr7Александр ЩеблыкинNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ge3000 Sofware ManualDokument15 SeitenGe3000 Sofware ManualJose RiobuenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Partes Cummins C170Dokument64 SeitenManual de Partes Cummins C170Carlos Alberto Ramirez Parra100% (1)
- PI221227 (S.parts For M6D30 Series)Dokument3 SeitenPI221227 (S.parts For M6D30 Series)jesusbritomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linz - New Product - AlumenDokument4 SeitenLinz - New Product - AlumenTTIBCCANoch keine Bewertungen
- 3306 164-200KW PRDokument4 Seiten3306 164-200KW PRvanaselvan vpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine N45 TM2A 96 kW (1500 rpm) - 107 kW (1800 rpmDokument3 SeitenEngine N45 TM2A 96 kW (1500 rpm) - 107 kW (1800 rpmDave Wallace100% (2)
- WEG Automatic Voltage Regulator Grt7 Th4 r2 10001284109 Manual EnglishDokument78 SeitenWEG Automatic Voltage Regulator Grt7 Th4 r2 10001284109 Manual Englisht8823pcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Instalacion de GeneracDokument142 SeitenManual de Instalacion de Generacsolounsiervo100% (2)
- GPMR 72 P (72X72) Operation: (12 and 24vcc)Dokument3 SeitenGPMR 72 P (72X72) Operation: (12 and 24vcc)carlosmarciosfreitas50% (2)
- Manual Parts - Ir - Compresor - XP375 Wcu T2 PMDokument94 SeitenManual Parts - Ir - Compresor - XP375 Wcu T2 PMAhbdi Torres100% (1)
- Altronic Ignition Coil 501 061 Data Sheet V 2Dokument1 SeiteAltronic Ignition Coil 501 061 Data Sheet V 2TariqMaqsoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- AGC 200 Manual de Instalação PDFDokument67 SeitenAGC 200 Manual de Instalação PDFMarco Olivetto100% (1)
- 6BTA5.9G2 - Engine Data SheetDokument5 Seiten6BTA5.9G2 - Engine Data SheethormatomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three-Phase Synchronous Generator AVR WT-2: VOLT - Potentiometer For Adjusting The OutputDokument3 SeitenThree-Phase Synchronous Generator AVR WT-2: VOLT - Potentiometer For Adjusting The OutputBradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Silent Type 30kw Diesel Generator 480v 60hz - Buy 30kw Diesel Generator 480v 60hz, Chinese Engine Generators, Engine Generator Product On PDFDokument6 SeitenSilent Type 30kw Diesel Generator 480v 60hz - Buy 30kw Diesel Generator 480v 60hz, Chinese Engine Generators, Engine Generator Product On PDFM-Aulan Niam AunimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cummins China 4BTA3.9 G2Dokument5 SeitenCummins China 4BTA3.9 G2joshua surbaktiNoch keine Bewertungen
- KohlerDokument5 SeitenKohlerRajesh S BhattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perkins 1103A-33T - 50 kVA - 17653 - Generators - Roban TrucksDokument8 SeitenPerkins 1103A-33T - 50 kVA - 17653 - Generators - Roban TrucksAbdulrahman Al Huriby100% (1)
- MANUAL DE TALLER PLANTA Ext12d HONDADokument63 SeitenMANUAL DE TALLER PLANTA Ext12d HONDAEMILIO GONZALEZ50% (2)
- SED MAN GC2599 002 Manual For GC2599 ControllerDokument78 SeitenSED MAN GC2599 002 Manual For GC2599 ControllerkrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inteligen NTCDokument141 SeitenInteligen NTCMohamed AbdelmalekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generator Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation Manual: Tel: - Fax: - @Dokument8 SeitenGenerator Automatic Voltage Regulator Operation Manual: Tel: - Fax: - @Syed Mohammad Naveed100% (1)
- EG3000 ManualDokument7 SeitenEG3000 ManualJose Armando Perez AcostaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DYN1-10693-001-0-12 or DYN1-10693-001-0-24 PDFDokument8 SeitenDYN1-10693-001-0-12 or DYN1-10693-001-0-24 PDFSyed Mohammad Naveed100% (1)
- Eg1069x Manual en PDFDokument24 SeitenEg1069x Manual en PDFtecnigenelecNoch keine Bewertungen
- BPM24RT100BL Specspecifications UpdateDokument8 SeitenBPM24RT100BL Specspecifications UpdatemalleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Warning: ESD5500E Series Speed Control UnitDokument6 SeitenWarning: ESD5500E Series Speed Control UnitLuis Alberto LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eg2000 Manual de Gobernador ElectronicoDokument7 SeitenEg2000 Manual de Gobernador ElectronicolibertyplusNoch keine Bewertungen
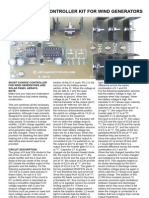
- ISO 9001 CERTIFIED SPEED CONTROL UNIT DOCUMENTDokument2 SeitenISO 9001 CERTIFIED SPEED CONTROL UNIT DOCUMENTajcapetillog100% (2)
- EG-3000 Governor Controller Operation ManualDokument7 SeitenEG-3000 Governor Controller Operation ManualrepelindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Combustion (Ic) Engine Used in Generation of ElectricityDokument46 SeitenInternal Combustion (Ic) Engine Used in Generation of ElectricitynatarajansiyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ESD5100 Series Speed Control UnitDokument2 SeitenESD5100 Series Speed Control UnitJaimeCoelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eg 2000 PDFDokument7 SeitenEg 2000 PDFAaron VillareteNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument94 SeitenPDFTrần Quang TuyênNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adjustable Speed Drives TutorialDokument13 SeitenAdjustable Speed Drives Tutorialapi-3765150100% (2)
- ADEC™ - Error List - 2006 - MTU® PDFDokument33 SeitenADEC™ - Error List - 2006 - MTU® PDFpevare100% (4)
- Transfer Switches (Manual & Automatic) - SENR2164 - June 1981 - CATERPILLAR®Dokument50 SeitenTransfer Switches (Manual & Automatic) - SENR2164 - June 1981 - CATERPILLAR®pevareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Easygen-3100 and 3200 - P1-P2 - Software Version 1.2102 or Higher - 37532E - WOODWARD® PDFDokument754 SeitenEasygen-3100 and 3200 - P1-P2 - Software Version 1.2102 or Higher - 37532E - WOODWARD® PDFpevare100% (3)
- UltrasoundDokument175 SeitenUltrasoundsky rain100% (15)
- ATS Contactor Type - 9Y-7900 - Operation & Maintenance Manual - SEBU6324-02 - January 1996 - CATERPILLAR®Dokument123 SeitenATS Contactor Type - 9Y-7900 - Operation & Maintenance Manual - SEBU6324-02 - January 1996 - CATERPILLAR®pevareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transfer Switches (Manual & Automatic) - SENR2164 - June 1981 - CATERPILLAR®Dokument50 SeitenTransfer Switches (Manual & Automatic) - SENR2164 - June 1981 - CATERPILLAR®pevareNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM 55 1930 209 14 and P 9 4Dokument848 SeitenTM 55 1930 209 14 and P 9 4moussaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCDGV4 Protección de GeneradorDokument1.070 SeitenMCDGV4 Protección de GeneradorIngJGM100% (1)
- Electric Motor NEMA Frame Sizes Table PDFDokument6 SeitenElectric Motor NEMA Frame Sizes Table PDFpevareNoch keine Bewertungen
- TE809-ATS - Instructions Manual - Project v1.1.3 - TECNOELETTRA® PDFDokument36 SeitenTE809-ATS - Instructions Manual - Project v1.1.3 - TECNOELETTRA® PDFpevare50% (2)
- Spanish Latin America Master Glossary - 2011 - CATERPILLAR® PDFDokument135 SeitenSpanish Latin America Master Glossary - 2011 - CATERPILLAR® PDFpevare100% (1)
- Catalogo Sensors - For - Instrumentation 2010 VDODokument176 SeitenCatalogo Sensors - For - Instrumentation 2010 VDOMilton Pazmiño BritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- P158LE - P180LE - P122LE Doosan PDFDokument162 SeitenP158LE - P180LE - P122LE Doosan PDFroyert80100% (2)
- RTS Automatic Transfer Switch - Technical Manual - GENERAC PDFDokument28 SeitenRTS Automatic Transfer Switch - Technical Manual - GENERAC PDFpevare100% (2)
- Digitrip™ 520 Trip Unit For Use Only in Magnum and Magnum DS Circuit Breaker - IL70C1037H05 - Oct 2009 - EATON® PDFDokument40 SeitenDigitrip™ 520 Trip Unit For Use Only in Magnum and Magnum DS Circuit Breaker - IL70C1037H05 - Oct 2009 - EATON® PDFpevareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operation and Maintenance Manual Automatic Transfer Switch ZTSH Series 30 - 4000 AMPSDokument37 SeitenOperation and Maintenance Manual Automatic Transfer Switch ZTSH Series 30 - 4000 AMPSYassin AlkadyNoch keine Bewertungen
- ATC-600 Automatic Transfer Switch Controller - Instructional Booklet - IB ATS-1005 - EATON® PDFDokument36 SeitenATC-600 Automatic Transfer Switch Controller - Instructional Booklet - IB ATS-1005 - EATON® PDFpevareNoch keine Bewertungen
- O & M Manual For The Fixed and Drawout Magum Transfer Switches - Instruction Booklet - IB01602011E - EATON® PDFDokument44 SeitenO & M Manual For The Fixed and Drawout Magum Transfer Switches - Instruction Booklet - IB01602011E - EATON® PDFpevareNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEA 2342 Basic of Electronic Engineering: Lab Sheet 4Dokument6 SeitenDEA 2342 Basic of Electronic Engineering: Lab Sheet 4Afieza TumijanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7sk80 Pa En-2Dokument1 Seite7sk80 Pa En-2api-241473079Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assesment With AnswersDokument4 SeitenAssesment With Answersdedik83Noch keine Bewertungen
- High Input Voltage Buck-Boost Converter With 2A Switch CurrentDokument31 SeitenHigh Input Voltage Buck-Boost Converter With 2A Switch Currentbarmircea10Noch keine Bewertungen
- FC4 - : Name Data Type Address CommentDokument7 SeitenFC4 - : Name Data Type Address Commentpk cfctkNoch keine Bewertungen
- JFETsDokument78 SeitenJFETsLai Yon Peng100% (2)
- A1512 Panasonic SemiconductorDokument2 SeitenA1512 Panasonic SemiconductorbrneiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terminaiton Kit SpecificaitonDokument5 SeitenTerminaiton Kit SpecificaitonVaibhav ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-I Vlsi QBDokument6 SeitenUnit-I Vlsi QBMohamed MusthafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- lm3420 PDFDokument27 Seitenlm3420 PDFLUis PEpeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Interrupt or Ter Mom Agn É Tico SquaredDokument272 SeitenInterrupt or Ter Mom Agn É Tico SquaredDaniel MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datasheet Trilogy Systems With Smartpack2Dokument4 SeitenDatasheet Trilogy Systems With Smartpack2JoseGarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- K241 AwebnotesDokument3 SeitenK241 Awebnotespetre_blackNoch keine Bewertungen
- HT TransformerDokument6 SeitenHT TransformerMaintenance CircleNoch keine Bewertungen
- VARROCDokument9 SeitenVARROCmaniamson87% (15)
- Potential transformers and other switchboard devices protectionDokument4 SeitenPotential transformers and other switchboard devices protectionJoel JusayNoch keine Bewertungen
- PD InterviewDokument5 SeitenPD Interviewjayanthi_kondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ds1233 5V Econoreset: Features Pin AssignmentDokument5 SeitenDs1233 5V Econoreset: Features Pin AssignmentMezghiche Salah EddineNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSR Wiring DiagramsDokument43 SeitenGSR Wiring DiagramsJamie WinklehoffenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Single Phase Half Wave Uncontrolled RectifierDokument10 SeitenSingle Phase Half Wave Uncontrolled RectifierHa Hamza Al-rubasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toshiba TV T1450TBDokument3 SeitenToshiba TV T1450TBHelder MartinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- RC Snubber Circuit Design For Thyristor Using Turn-Off Model in PspiceDokument5 SeitenRC Snubber Circuit Design For Thyristor Using Turn-Off Model in PspiceIjsrnet EditorialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gic SM 301Dokument3 SeitenGic SM 301srinivasgateNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSS - 05-Week 5 - Module 5 - Networking CablingDokument7 SeitenCSS - 05-Week 5 - Module 5 - Networking CablingMorelei FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- LTC 1267 FDokument1 SeiteLTC 1267 FEdson HenriqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Half Wave Rectifier with Resistive Load ExplainedDokument10 SeitenHalf Wave Rectifier with Resistive Load ExplainedYounas AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEYA ELECTRICAL CO.,LTD Instruction Manual for Single-function Time Relay GRT8-A&BDokument2 SeitenGEYA ELECTRICAL CO.,LTD Instruction Manual for Single-function Time Relay GRT8-A&BSanny HamdaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photodiode PDFDokument13 SeitenPhotodiode PDFRizkyAnandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Parts of Color TVDokument9 SeitenMajor Parts of Color TVmark david sabellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM2930 3-Terminal Positive Regulator: General Description FeaturesDokument8 SeitenLM2930 3-Terminal Positive Regulator: General Description FeaturesAnkitNoch keine Bewertungen