Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Meng 342 - Lab Report 6
Hochgeladen von
Hany Raafat SamaanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Meng 342 - Lab Report 6
Hochgeladen von
Hany Raafat SamaanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
School of Sciences and Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department MENG 342-81 Lab Report 6 Control Charts (P, nP and
MR charts)
Prof. Hatem Elayat T.A: Moukhtar Kamel
By:
Submission date: October 22nd, 2011
|Page1
Table of contents: Introduction Control Charts Experimental Data and Calculations Discussion and Conclusion References page 3 page 4 page 5 page 6 page 7
|Page2
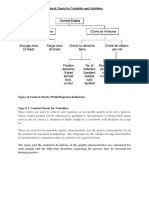
Introduction: Attributes Control Charts: is a statistical tool used to distinguish variations in a process by classifying each inspected item as either conforming or nonconforming to the specifications of that quality characteristic. Types of Control charts: 1- Control chart for fraction nonconforming ( p chart ) 2- Control chart for nonconformities (c chart ) 3- Control chart for nonconformities per unit (u chart )
Attributes charts are generally not as informative as variables charts because there is typically more information in a numerical measurement than in merely classifying a unit as conforming or nonconforming. However, attributes charts do have important applications. They are particularly useful in service industries and in nonmanufacturing quality improvement efforts because so many of the quality characteristics found in these environments are not easily measured on a numerical scale.
|Page3
The control chart for fraction nonconforming (p chart): The fraction nonconforming is the ration of the number of nonconforming items in a population to the total number of items in that population. The statistic estimates the unknown fraction nonconforming p. The
centerline and control limits of the control chart for fraction nonconforming are computed as follows: UCL=
Center Line=
LCL= Where and Di in the number of non conforming units in a sample. The control chart for number nonconforming (np chart): Its also possible to base a control chart on the number of nonconforming rather than the fraction nonconforming. This is called an number nonconforming (np) control chart. The parameters of this chart are: UCL= Center Line= LCL=
|Page4
Individual X and Moving Range charts: They are a set of control charts for variables data (data that is both quantitative and continuous in measurement). The individual-X chart monitors the process location over time, based on the current subgroup, containing a single observation. The moving range chart monitors the variation between consecutive subgroups over time. Constructing X charts: 1- Small sample are collected in equal spaces intervals of time
2- The mean is calculated for each sample 3- For each sample, the range is calculated: Range = Xlargest-Xsmallest 4- Upper and lower limits for X chart is calculated using the following equations:
Constructing the Moving Range chart: UCL= D4
CL=
LCL= D3
Experimental Data and Calculations: are attached in MS Excel Sheets
|Page5
Discussion & Conclusion:
1- Points falling out of control: a) P chart: Sample 14 was below LCL b) nP chart didnt show any out of control observations c) X chart: Sample 13 was below LCL d) MR chart: Sample 8,9 were above UCL 2- Points which has a pattern: There is no patterns 3- Alarming points: a) MR chart: Sample 4 is just on the LCL
|Page6
References: 1- Montgomery, Douglas C., Statistical Quality Control A Modern Introduction, Six Edition, 2009, John Wiley & sons, 2- Basic tools for process improvement, Control Chart, http://www.doh.state.fl.us/hpi/pdf/ControlChart2.pdf
|Page7
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- SQCDokument36 SeitenSQCMandeep SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPM Data Sync With FDMEE 11.1.2.4Dokument11 SeitenEPM Data Sync With FDMEE 11.1.2.4Aravind AllamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Improvement and Statistical Process ControlDokument64 SeitenQuality Improvement and Statistical Process ControlSakthi Tharan SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 Qualtiy ControlDokument83 SeitenChapter 7 Qualtiy ControlEngineerMqNoch keine Bewertungen
- All Control ChartsDokument23 SeitenAll Control Chartssrinusutram1116100% (2)
- A Guide To Control ChartsDokument12 SeitenA Guide To Control ChartsAnonymous utfuIcnNoch keine Bewertungen
- RF DC Bias TeeDokument15 SeitenRF DC Bias TeechrisjennNoch keine Bewertungen
- PPT4-Statistical Process Control and Capability AnalysisDokument120 SeitenPPT4-Statistical Process Control and Capability AnalysisDini MaharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Chart: Basic Tools For Process ImprovementDokument70 SeitenControl Chart: Basic Tools For Process ImprovementGen Sue100% (2)
- Short Run Statistical Process ControlDokument21 SeitenShort Run Statistical Process ControlEdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Description and Operation: Component Maintenance ManualDokument8 SeitenDescription and Operation: Component Maintenance ManualLou Parker100% (1)
- Which Control Charts To Use WhereDokument115 SeitenWhich Control Charts To Use Whereanbarasuar1964Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rocess Ontrol Tatistical: C C I P P S E EDokument71 SeitenRocess Ontrol Tatistical: C C I P P S E EalwaleedrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Notes On SQCDokument12 SeitenFinal Notes On SQCShashank Srivastava100% (1)
- Ch.4 - Control Charts For AttributesDokument34 SeitenCh.4 - Control Charts For AttributesAbdullah Hazeem100% (3)
- Mod10 Control ChartDokument70 SeitenMod10 Control ChartArnela Hodzic100% (1)
- Control Charts GuideDokument36 SeitenControl Charts GuideGulshan KandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Chart For Attributes-AizrulDokument44 SeitenControl Chart For Attributes-AizrulAizrul ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six Sigma Green Belt, Round 2: Making Your Next Project Better than the Last OneVon EverandSix Sigma Green Belt, Round 2: Making Your Next Project Better than the Last OneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ChartsDokument7 SeitenControl ChartsAkansha SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit IiiDokument101 SeitenUnit IiiMECH HODNoch keine Bewertungen
- Six Sigma BooK Part2Dokument83 SeitenSix Sigma BooK Part2foofoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONTROL CHARTS GUIDEDokument26 SeitenCONTROL CHARTS GUIDEAnurag KushwahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On - The Statistical Principles Underlying The Control Chart For Fraction Nonconforming Are Based On The Binomial DistributionDokument6 SeitenOn - The Statistical Principles Underlying The Control Chart For Fraction Nonconforming Are Based On The Binomial DistributionSiegfred LaborteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seven Basic Quality Control ToolDokument7 SeitenSeven Basic Quality Control ToolAhmed M. HashimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Production & Operations Control ChartsDokument37 SeitenProduction & Operations Control ChartsNeelima AjayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPCDokument62 SeitenSPCRajesh DwivediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Chart and TypesDokument4 SeitenControl Chart and TypesrajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality Control, Basic Control ChartsDokument20 SeitenQuality Control, Basic Control Chartsmalyduzy0% (1)
- Control ChartsDokument2 SeitenControl ChartsYeoh KhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ChartsDokument36 SeitenControl ChartsArpit AgarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control ChartsDokument36 SeitenControl ChartsEr Vaibhav NyatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Four Control Charts For Variables-I: Implementing SPC in A Quality Improvement ProgramDokument10 SeitenChapter Four Control Charts For Variables-I: Implementing SPC in A Quality Improvement ProgramComputer Maintainance Hardware and softwareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Chart: Looking For More Quality Tools?Dokument3 SeitenControl Chart: Looking For More Quality Tools?Cloud Redfield100% (1)
- Sta S Cal Process Control (SPC)Dokument3 SeitenSta S Cal Process Control (SPC)Naresh KhanderayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Process Control ToolsDokument25 SeitenStatistical Process Control ToolsVickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Statistical Quality ControlDokument24 SeitenOverview of Statistical Quality ControlJayalal WettasingheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Chart BasicsDokument36 SeitenControl Chart Basicstikar69314Noch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Cmt651Dokument5 SeitenAssignment Cmt651Khairun NiesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3Dokument9 SeitenAssignment 3api-265324689Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quality ControlDokument41 SeitenQuality ControlPrashantNoch keine Bewertungen
- 22 - Control ChartshghgyugyuDokument5 Seiten22 - Control ChartshghgyugyuBishnu Ram GhimireNoch keine Bewertungen
- LT-44&45 U5-7QC Tools and Its AdvancementsDokument10 SeitenLT-44&45 U5-7QC Tools and Its Advancementsakanksha pandey100% (1)
- Using Cumulative Count of Conforming CCC-Chart To Study The Expansion of The CementDokument10 SeitenUsing Cumulative Count of Conforming CCC-Chart To Study The Expansion of The CementIOSRJEN : hard copy, certificates, Call for Papers 2013, publishing of journalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CONTROL CHARTS FOR ATTRIBUTESDokument26 SeitenCONTROL CHARTS FOR ATTRIBUTESmuhammad_mmd50% (2)
- NTPC's Reliability Improvement through Pareto AnalysisDokument4 SeitenNTPC's Reliability Improvement through Pareto AnalysisVanshika Srivastava 17IFT017Noch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement Technologies Calibration GuideDokument49 SeitenMeasurement Technologies Calibration Guideغيث منعمNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 2: Statistical Process Control in IndustryDokument103 SeitenUnit - 2: Statistical Process Control in IndustrySUJITHA NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Chart: Basic Tools For Process ImprovementDokument70 SeitenControl Chart: Basic Tools For Process ImprovementSudipto BanerjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7-QC Tools: 1) Run ChartDokument10 Seiten7-QC Tools: 1) Run Chartkevin21790Noch keine Bewertungen
- TQM 7 SPC ToolDokument7 SeitenTQM 7 SPC ToolPratik TambeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Quality ControlDokument15 SeitenStatistical Quality ControlMoniruzzaman MoNirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shewhart Individuals Control ChartDokument2 SeitenShewhart Individuals Control ChartBalram JiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control Charts For Variables and AttributesDokument4 SeitenControl Charts For Variables and AttributesshobhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Control Charts ExplainedDokument27 SeitenStatistical Control Charts ExplainedEileen LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- TQM Unit 3Dokument106 SeitenTQM Unit 3Shibamay MitraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Satistical Quality ControlDokument21 SeitenSatistical Quality Controladitya v s sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical and Computer Modelling Cost OptimizationDokument7 SeitenMathematical and Computer Modelling Cost OptimizationDr Abhijeet GangulyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistical Quality ControlDokument36 SeitenStatistical Quality ControlHarshit SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compressed SensingDokument14 SeitenCompressed Sensingnigel989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gaussian Filtering FpgaDokument7 SeitenGaussian Filtering Fpgaakkala vikasNoch keine Bewertungen
- AQA Physics A-Level Electricity Questions (Pack 3)Dokument90 SeitenAQA Physics A-Level Electricity Questions (Pack 3)BDNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOAC Virtual Lab ExercisesDokument3 SeitenMOAC Virtual Lab ExercisesJyoti PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review of Online Registration SystemDokument8 SeitenLiterature Review of Online Registration Systemzepewib1k0w3100% (1)
- GS401-6100 - B (GeoSwath 4 Deck Unit Operation Manual)Dokument57 SeitenGS401-6100 - B (GeoSwath 4 Deck Unit Operation Manual)Rhenryan Panes100% (1)
- TranslatorsDokument3 SeitenTranslatorsijas100% (1)
- Soltek SL 65meDokument88 SeitenSoltek SL 65meBernardo AntunesNoch keine Bewertungen
- EWFC 1000: "Quick-Chill and Hold" Cold ControlDokument5 SeitenEWFC 1000: "Quick-Chill and Hold" Cold ControlGede KusumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DataStage Tip For Beginners - Developer Short CutsDokument6 SeitenDataStage Tip For Beginners - Developer Short CutsCary WhiteNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSS Format DescriptionDokument5 SeitenSSS Format Descriptionmartinos22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sandip University: End Semester Examinations-June 2021Dokument1 SeiteSandip University: End Semester Examinations-June 2021Industrial Training Institute ITI,SilvassaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weather Report Project AbstractDokument1 SeiteWeather Report Project AbstractSomething To Know0% (2)
- Unit 1 - IMEDDokument37 SeitenUnit 1 - IMEDAlishka RawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Deep Learning: Technical Seminar by Md. Abul Fazl (14261A05A0) CSE DeptDokument21 SeitenIntroduction To Deep Learning: Technical Seminar by Md. Abul Fazl (14261A05A0) CSE DeptpavansfdsfNoch keine Bewertungen
- BioSystems A-15 Analyzer - Maintenance Manual PDFDokument23 SeitenBioSystems A-15 Analyzer - Maintenance Manual PDFGarcía XavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of Information Systems in BusinessDokument28 SeitenFoundations of Information Systems in BusinessRaheel PunjwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bio Data Cum Declaration Form of Scribe/WriterDokument1 SeiteBio Data Cum Declaration Form of Scribe/WriterGajendrashih ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altivar Process ATV600 - ATV6A0C40Q4Dokument4 SeitenAltivar Process ATV600 - ATV6A0C40Q4pikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP Model Company For FinanceDokument1 SeiteSAP Model Company For FinanceAmar UbheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Una Buena Configuracion de CmiDokument72 SeitenUna Buena Configuracion de Cmivicente rojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- LM M530Dokument58 SeitenLM M530Victor VilcapomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper 1 - Summary Revision Notes - OL CSDokument53 SeitenPaper 1 - Summary Revision Notes - OL CSjanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Developer Profile Bayu Cucan HerdianDokument1 SeiteSoftware Developer Profile Bayu Cucan HerdianAlsolious BayuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1Dokument13 SeitenWeek 1hadiqhusnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gravity WorkoutDokument4 SeitenGravity WorkoutMIIBNoch keine Bewertungen