Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pneumatics
Hochgeladen von
SRIREKHAOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pneumatics
Hochgeladen von
SRIREKHACopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
MODULE: ELECTRO PNEUMATICS
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
INTRODUCTION
Pneuma means Compressed air. Pneumatic systems use compressed air to transmit and control power. Pneumatic cylinders convert pneumatic energy into mechanical energy. Advantages o o o o Air is available everywhere in unlimited quantities. Air can be easily transported in pipelines over large distances. Compressed air can be stored in a reservoir and removed as required. Compressed air is insensitive to temperature fluctuations. Compressed air offers minimal risk of explosion or fire. The operating components are of simple construction and therefore relatively inexpensive. Higher working speeds can be achieved.
Disadvantages Compressed air requires good preparation. It is not always possible to achieve uniform and constant piston speed with compressed air. Noisy operation. This system is economical up to a certain force requirement.
Applications 1. Material handling o o o o o o o o o o o o o o Clamping Shifting Positioning Orienting
2. Machining and working operations Drilling Turning Milling Sawing Finishing Forming Quality control
3. General applications Packaging Feeding Metering
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
CIRCUIT STRUCTURE & ISO SYMBOLS AND STANDARDS
Pneumatic circuit structure The structure of the circuit diagram should correspond to the control chain, whereby the signal flow is represented from the bottom to the top. Simplified or detailed symbols may be used for the representation of the circuit diagram. Signal flow The various levels form a control path for signal flow from the signal (input) side to the work (output) side.
System structure The primary levels in a pneumatic system are:
Energy supply Input elements Processing elements Actuating devices
ISO symbols The development of pneumatic systems is assisted by a uniform approach to the representation of the elements and the circuits. The symbols used for the individual elements must display the following characteristics:
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
o o o o o o Function Actuation and return actuation methods Number of connections Number of switching positions General operating principle Simplified representation of the flow path
The symbols used in pneumatics are standardized by the code DIN ISO 1219.
Symbols used in energy conversion and preparation Supply Compressor with fixed capacity
Air receiver and T junction
Service equipment Filter separation and filtration of particles
Water separator
partial water removal
Lubricator
metered quantities of oil passed to the air stream relieving type vent hole for excess upstream pressure adjustable
Pressure regulator
Combined symbols Air service unit Filter, Regulator, Gauge, Lubricator.
Simplified air service unit
Pressure source
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Directional control valves: ports and positions (ways)
2/2 way directional valve
3/2 way directional valve Normally closed
3/2 - way directional valve Normally open
4/2 way directional valve
5/2 way directional valve
5/3 way directional valve Mid position closed
Method of actuation Mechanical General manual operation
Push button
Lever operated
Detent lever operated
Foot pedal
Roller operated
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Plunger operated
Spring return
Spring centered
Idle return, roller
Pneumatic Direct pneumatic actuation
Indirect pneumatic actuation (piloted)
Electrical Single solenoid operation
Double solenoid operation Combined Double solenoid and pilot operation With manual override
Non-return valves and derivatives
Check valve
Spring loaded check valve
Shuttle valve OR function Two pressure valve AND function
Quick exhaust valve
Flow control valves
Flow control valve adjustable
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
One way flow control valve
Pressure valves
Adjustable pressure regulating valve, Non relieving type
Adjustable pressure regulating valve, Relieving type (overloads are vented)
Sequence valve combination
Linear actuators
Single acting cylinder
Double acting cylinder
Double acting cylinder with double ended piston rod
Double acting cylinder with non-adjustable cushioning in one direction
Double acting cylinder with single adjustable cushioning
Double acting cylinder with adjustable cushioning at both ends
Linear drive with magnetic coupling
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Rotary actuators
Air motor, rotation in one direction fixed capacity
Air motor, rotation in one direction variable capacity
Air motor, rotation in both directions variable capacity
Rotary actuator limited travel in both directions
Auxiliary symbols
Exhaust port
Exhaust port with threaded connection
Silencer
Line connection (fixed)
Crossing lines (not connected)
Pressure gauge
Visual indicator
Signal flow (electrical)
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Electropneumatic symbols
Switches and relay contacts
Manual actuation
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Relay and actuator coil symbols
Relay coil and contact symbols
10
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Mechanical and electrical actuation
COMPRESSED AIR GENERATION & DISTRIBUTION
Compressed air generation and supply Air preparation For the continuing performance of control systems and working elements it is necessary to guarantee that the air supply is: clean dry and at the required pressure
If these conditions are not fulfilled, then short to medium term degeneration of the system will be accelerated. The effect is downtime on the machinery in addition to increased costs for repair or replacement of parts. The equipment to be considered in the generation and preparation of air include: Inlet filter Air compressor Air reservoir Air dryer Air filter with water separator Pressure regulator Air lubricator as required Drainage points
11
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Pneumatic components are designed for a maximum operating pressure of 800 to 1000 kPa (8 10 bar). Practical experience has shown that approximately 600 kPa (6 bar) should be used for economic operation. The compressors system should provide at least 650 to 700 kPa (6.5 to 7 bar) for a desired operating pressure level of 600 kPa (6 bar). Air compressors The various types of compressor are:
Selection of compressors The selection of compressor is based on: Quantity of air Pressure Quality and cleanliness of the air required.
The optimum ranges of pressures for reciprocating compressors are approximately : Up to 400 kPa Up to 1500 kPa Over 1500 kPa (4 bar) single stage
(15 bar) double stage (> 15 bar) treble or multi stage
Diaphragm compressor is used where oil is to be excluded from the air supply, for example in the food, pharmaceutical and chemical industries. Here there is no need for lubrication in the compression area. Rotary piston compressors use rotating members to compress and increase the pressure of the air. They are smooth in operation but the compression is not as high as with multistage reciprocating compressors. Flow compressors produce large volumes of air at small increase in stage pressure. The air is accelerated by the blades of the compressor but there is only a small increase in pressure of about 1.2 times the inlet pressure per stage.
12
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Reservoirs A reservoir compensates the pressure fluctuations when the compressed air is taken from the system. If the pressure in the reservoir drops below a certain value, the compressor will compensate until the set higher value is reached again. This has the advantage that the compressor does not need to operate continuously.
The large surface area of the reservoir cools the air. Thus, a portion of the moisture in the air is separated directly from the reservoir as water, which has to be regularly drained via a drain cock.
The size of a compressed air reservoir depends on the : Delivery volume of the compressor Air consumption for the applications Type of compressor cycle regulation Permissible pressure drop in the supply network. AIR DRYERS Air dryers reduce the moisture content to a level, which suits the application, and the elements used. Water produces a hardening of seals, corrosion and the washing-out of the original lubrication of cylinders. Oil and water may cause seals and diaphragms to swell. In paint-spraying plants, water and dust cause contamination, poor paint adhesion and the formation of blisters. In the food, pharmaceutical and chemical industries, oil, dirt, bacteria and germs destroy the storage properties of products. There are three methods of reducing the moisture content in air: Low temperature drying Adsorption drying Absorption drying
13
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Air service equipment It is a combination of : Compressed air filter Compressed air regulator and gauge Compressed air lubricator
Air service equipment is also termed as FRL unit. Filter Filter removes the dust particles. The compressed air passes through the filter from left to right and is fed through a baffle plate in the filter bowl. The effect of the baffle plate is that the air is caused to rotate, and the heavier dust particles and water droplets are spun by centrifugal force against the inner wall of the filter bowl. The air, which has pre-cleaned in this way, then passes through the filter element, which filters out the smaller dirt particles. The filte The degree of separation depends on the pore size of the filter element used. Guide line for maintenance: Filter cartridge should be changed or cleaned with kerosene or trichloroethylene or other cleaning mediums. But no chemicals like CTC, acetone are to be used for cleaning plastic parts. The condensate level must be checked regularly, as the height specified on the sight glass must not be exceeded.
Drain off the accumulated water and other foreign particles from the filter bowl.
14
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Regulator Regulators ensure a constant supply pressure and also regulate the pressure of the air.
Basically there are two types: o o Relieving type Non relieving type
Relieving type:
Non relieving type:
15
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Setting and adjusting: The pressure regulator can be adjusted between the limits of zero and the supply pressure of the compressor network. The adjustment to a higher pressure is achieved by increasing spring compression. When reducing pressure settings, it is necessary to relieve the pressure well below the limit required to relieve the air from the vent and then increase the pressure up to the lower limit required.
Guide line for maintenance: Check if the supply of the pressure air is steady or not. Pressure limits should be tested. Look for an external damage to the regulator.
Lubricator: Lubricators are used to lubricate the air. For power components it may be necessary to lubricate the air. But as a rule the compressed air should be free of oil. Fig. shows an air lubricator:
The compressed air passing through the lubricator causes a pressure drop between the oil reservoir and the upper part of the lubricator. The pressure difference is sufficient to force the oil upwards through a via duct where it then drips into a nozzle which can be seen through an inspection glass. Here the oil is atomized and taken up by the air stream to a greater or lesser extent.
16
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Problems that occur with excessive lubrication: o o o o Malfunctioning of the components Oil mist pollution of the environment Gumming-up of parts occurs Difficulties in adjusting the lubricator correctly
Guide line for maintenance: Check the oil level in the oil sight glass and top up, if necessary, to the level indicated. Lubricator bowl must not be cleaned with trichloroethylene. Only mineral oils can be used for the lubricator. Inspect the colour of the oil in the bowl and if the colour turns grayish, replace the oil.
DIRECTIONAL CONTROL VALVES
These valves influence the path taken by an air stream. These valves: o Allows the passage of air directing it to particular airlines Canceling the air signals as required by blocking the passage Relieve the air through the exhaust port
Based on their design the valves are classified as: Poppet valves o Ball seat valves Disc seat valves
Slide valves Longitudinal slide valve Longitudinal flat slide valve Plate slide valve
Poppet valve uses balls, discs, plates or cones for opening or closing the connections. Slide valve uses spool slides, spool flat slides or sliding disc valves for linking the connections together or closed. Also based on the number of ports, switching positions and method of actuation the valves are classified. 3/2-way valve: ball seat Fig. shows a stem or plunger actuated 3/2 way valve. Unactuated position
17
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Actuated position
The 3/2-way valve has three ports and two positions. The addition of the exhaust port 3(R) enables the signal generated via the passage through the 3/2-way valve to be cancelled. The valve connects the output signal 2(A) to exhaust 3(R) and atmosphere in the initial position.
3/2-way valve hand slide valve: Fig. shows a 3/2 way valve hand slide valve.
The 3/2-way valve hand slide valve is used to supply air to a leg of the supply network upstream of the consuming devices. The construction of the valve is simple and it is used as a shut-off valve.
Servo controlled 3/2-way roller lever valve: Fig. shows a Servo controlled 3/2-way roller lever valve.
18
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
To avoid a high actuating force, mechanically controlled directional valves can be equipped with an internal pilot valve and servo piston to assist opening. The valve actuating force is often the determining factor in applications and the servo assistance allows for larger bore valves to be operated with small actuating forces. This increases the sensitivity of the system.
5/2-way valve: longitudinal slide principle Fig. shows a 5/2-way valve.
The 5/2-way valve has five ports and two positions. The 5/2-way valve is used primarily as a final control element for the control of cylinders. The longitudinal slide valve uses a pilot spool as a control component. This connects or separates the corresponding lines by means of longitudinal movements. All forms of actuation can be used with longitudinal slide valves, i.e. manual, mechanical, electrical or pneumatic.
Solenoid controlled valves: In electro pneumatics, valves are actuated by solenoids. Solenoid operating principle: If a conductor (a length of copper wire) is formed into the shape of one turn of a coil and a current is passed through the conductor, an electromotive force (EMF) is generated.
19
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
The circular form concentrates the lines of force around the conductor. This circular form concentrates the EMF in one direction, whereas the straight conductors EMF is spread along its length. By adding turn to the conductor, the magnetic field is strengthened and the EMF is increased. For solenoid applications, an electromagnet consisting of simple coils of wire do not generate sufficient EMF to drive the stems of most valves. 3/2-way single solenoid valve normally closed: Fig. shows a single solenoid operated 3/2-way valve.
This NC valve is directly actuated by a solenoid and is returned to the idle position by spring return. 5/2-way single solenoid valve: Fig. shows a single solenoid operated 5/2-way valve.
20
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
The 5/2 way valve performs a similar function as the 4/2 way valve. The main difference is that this valve has two exhaust ports, whereas the 4/2 way valve has one exhaust port. Energizing the solenoid moves the armature and opens the pilot air passage. The pilot air applies pressure to the right side of the valve piston, in turn forcing the suspended dics against the opposite sealing seat, resulting in: Air exhausts from 2 to 3 Exhaust port 5 is blocked Air flows from 1 to 4
In the neutral state, the spring return forces the large diameter seal at the spring end against its seat, blocking airflow from 1 to 3. The spring force also loads the suspended disc against port 4 blocking the passage of air from 1 to 4. The suspended disc opens the air flow from 1 to 2. 5/2-way double solenoid valve: Fig. shows a double solenoid operated 5/2-way valve.
In case of a double solenoid valve, the spring return has been replaced by a second solenoid. Assuming that the last signal applied was at solenoid Y1, air flows from 1 to 2 and 4 is exhausted via 5. When the signal is removed from Y1 the suspended disc remains stationary and no change occurs in the switched state of the valve.
21
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
A signal applied at solenoid Y2 reverses the valve and air flows from 1 to 4 and 2 is exhausted via 3. Non return valves Check valves: Check valves can stop the flow completely in one direction. In the opposite direction the flow is free with a minimal pressure drop due to the resistance of the valve. Blocking of the one direction can be effected by cones, balls, plates or diaphragms.
Two pressure valve: AND function The two pressure valve has two inlets and one outlet. Compressed air flows through the valve only if signals are applied to both inlets.
One input signal blocks the flow. If signals are applied to both X and Y, the signal which is last applied passes to the outlet. This valve is used mainly for interlocking controls, safety controls, check functions and logic operations.
22
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Shuttle valve: OR function This non-return valve element has two inlets and one outlet.
If compressed air is applied to the first inlet, the valve seat seals the opposing inlet. A signal is generated at the outlet. When the airflow is reversed, i.e. a cylinder or valve is exhausted, the seat remains in its previously assumed position because of the pressure conditions. This valve is also called an OR component. Flow control valves These valves influence the volumetric flow of the compressed air in both directions.
One-way flow control valve These valves are used for speed regulation of actuators. In this valve, the airflow is throttled in one direction only. A check valve blocks the flow of air in the bypass leg and the air can flow only through the regulated cross-section.
23
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
In the opposite direction, the air can flow freely through the opened check valve. These valves are mounted directly on the cylinder. There are two types of throttling circuits: o o Supply air throttling Exhaust air throttling
Pneumatic timer (Time delay valve NC) These valves delay the signals. Fig. shows a NC type time delay valve.
The time delay valve is a combined 3/2-way valve, one way flow control valve and air reservoir. The delay time is generally 0 30 seconds.
24
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
ELECTROPNEUMATIC COMPONENTS Relays Relays are electromagnetically operated devices very suitable for automatic control. They are relatively small and sensitive magnetic contacts capable of controlling large and remote loads, with high efficiency and matching accuracy.
Relays are used in switching circuits to amplify or multiply signals, to provide memory and to invert or convert signals. PE converter This device combines a pneumatically actuated stem and an electric switch. Fig. shows a PE converter.
25
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
When a pneumatic signal of sufficient pressure to overcome the opposing spring force is applied to the diaphragm, the resultant force operates. The force required to operate the stem is controlled by the adjusting screw. Movement of the stem actuates a micro switch via a switching lever.
Contacts Switches are primarily distinguished by their contact configuration: Normally open (path 3 to 4) Normally closed (path 1 to 2) Change over contacts (path 1 to 2 or 1 to 4)
On actuation, a normally open (NO) contact enables energy flow and a normally closed contact (NC) disables energy flow. The changeover contacts (CO) can be used as either normally open or normally closed contacts. Reed switches Reed switches are also known as magnetically actuated proximity switches. Fig. shows the reed switch.
In Electropneumatic control circuits, reed switches are commonly used to sense the positions of pneumatic cylinder piston rods and the angle of rotation of shaft in rotary actuators.
26
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Electronic sensors Certain applications require the use of electronic sensors employing: Electrical induction Capacitance Infra red light
These are represented by the following illustrated symbols.
PNEUMATIC CYLINDERS (ACTUATORS)
Actuators Pneumatic cylinders convert pneumatic energy into mechanical energy. It has the following general characteristics: Diameters Stroke lengths Available forces Piston speed 2.5 to 320mm 1 to 2000mm 2 to 45000 N at 6 bar 0.1 to 1.5 m/s
There are two types of actuators: Linear actuator o o o o o Single acting cylinders Double acting cylinders
Rotary actuator Air motor Rotary cylinders Rotary actuator
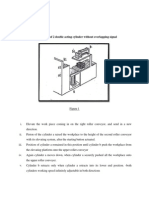
Single acting cylinders In single-acting cylinders compressed air can be applied on only one side of the piston face. Fig. shows a single-acting cylinder.
The cylinder can produce work in only one direction. The return movement of the piston is effected by a built-in spring or by the application of an external force.
27
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
The single-acting cylinder has a single piston seal which is fitted on the air supply side. Sealing is by a flexible material that is embedded in a metal or plastic piston. During motion, the sealing edges slide over the cylinder bearing surface. There are varying designs of single-acting cylinders including: o o Diaphragm cylinder Rolling diaphragm cylinder
Double - acting cylinders Fig. shows a double acting cylinder.
There are two ports namely supply and exhaust ports. This cylinder has the capability to carry out work in both directions of motion.
28
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Fig. shows a double acting cylinder with end position cushioning.
If large masses are moved by a cylinder, cushioning is used in the end positions to prevent sudden damaging impacts. The various types of double acting cylinders are: Tandem double acting cylinder Cylinders with through piston rod Multi position cylinders
Cylinders with through piston rod This cylinder has a piston rod on both sides, which is a through piston rod. There are two bearing points to guide the piston rod.
The force is identical in both directions.
Rotary cylinders With this design of double acting cylinder, the piston rod has a gear tooth profile. The piston rod drives a gear wheel, and a rotary movement results from a linear movement. The range of rotation varies from 45 , 90 , 180 , 270 to 360 . The torque is dependent on pressure, piston surface and gear ratio. Rotary actuator With a rotary actuator, force is transmitted direct to the drive shaft via a vane.
0 0 0 0 0
Angular displacement is infinitely adjustable from 0 to approx. 180 . Torque should not exceed 10 Nm.
29
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Guidelines for Maintenance: The cylinder should be perfectly aligned for efficient and trouble free operation. Piston rods dismantled during servicing, should be properly supported to retain it in line. Tie rods connecting the end covers, should be tightened with equal tension as possible to avoid strain on the rods. No reworking on cylinders should be taken on cylinders. While servicing cylinders all seals are to be replaced. Cylinders should be properly lubricated.
30
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
MAINTENANCE & TROUBLE-SHOOTING OF PNEUMATIC SYSTEMS
Maintenance need of Pneumatic systems While designing a pneumatic system, specific care should be taken to make the system simpler and easy to handle. Guidelines on pneumatic system It should be easy to operate, reliable, light in weight, simple and easily serviceable. For each system, the circuit diagram and functional diagram should be available. The control system should be as small as possible. The impulsive valves should be guarded against dirt, cooling water and mechanical shocks. Before assembly of the unit, care must be taken so that the unit is free of dirt. Do not open the ports of the elements before the line connection. All elements must be given proper identification numbering from the circuit diagram. The service unit should be visible, serviceable and be placed at a higher level than the rest of the equipment. Valves should be assembled near to the drive units. When dismantling and assembling valves and cylinders, take care of the sealing materials. Silencers should be used as they decrease the noise of air. Lines should be short, tension-free and bend-free. Cut the plastic hoses straight. Connections of plastic hoses to the elements must be screwed properly. Maintenance schedule of pneumatic system A. Air mains, lines and fittings Name of work 1. Detection and arrest of leakage of air 2. Thorough inspection of the complete line system 3. Inspection of unions, bends, tees, couplings, etc. 4. Pressure rating at strategic points 5. Condensate traps 6. Automatic draining of condensate 7. Airlines, shocks, cuts in lines and holes Periodicity Monthly Once in a year Once in 3 months Once in 3 months Daily Once in 3 months Weekly
31
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
B. FRL unit 1. Detection and arrest of leakage of air 2. Drain condensate from filter 3. Cleaning of filter cartridge 4. Pressure rating of pressure regulator 5. Calibrate pressure gauge 6. Cleaning filter bowl and oiler bowl 7. Top up oil level 8. Clean up oil jet passage 9. Arrest oil leakage 10. Adjust oil jet 11. Change of oil after thorough cleaning of bowl Daily Daily Half yearly Monthly Half yearly Yearly Weekly Half yearly Once in 3 months As needed Yearly or Half yearly
C. Pneumatic control valves 1. Possible air leakage and its arrest 2. Check for possible seal failure 3. Inspect actuating elements 4. Check valve adjustment 5. Check solenoid and its electrical parameter 6. Mechanical damage to valves and their parts Monthly Half yearly Half yearly Half yearly Monthly Yearly or earlier
D. Air cylinders and Air motors 1. Check for leakage and its arrest 2. Check the tie-rod tensions 3. Inspect the cylinder for force and speed accuracy 4. Check alignment of piston, piston rod & cylinder body 5. Mechanical damage to piston rod 6. Replace cup seal 7. Check rpm of motor 8. Check torque of motor 9. Check vibration produced by motor Monthly Half yearly Weekly Yearly or as needed Weekly Half yearly or as needed Weekly Weekly Weekly
32
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
TROUBLE, POSSIBLE CAUSES AND REMEDIES
The following is a list of common pneumatic system operating problems and the corresponding possible causes and remedy for each trouble.
A. Compressor
Trouble
Possible causes
Remedies
Dirt in suction filter
Clean filtering plate and filter disc. Do not use gasoline for danger of explosion.
Defective sealing of cylinder head Valve interference through dislocated valve seat and valve guide Worn out pistons and piston rings as well as worn out cylinder Inadeuquate performance Piston rings broken or not sealed
Mount fresh packing of the cylinder head. Exchange valve insert plate.
Exchange piston with rings and also the cylinder if necessary
Repalce piston rings as per manufacturers instructions.
End gap not staggered in grooves
Stagger the end gaps, make the rings free in the grooves.
Rough, scratched or excessive end gaps
Replace
Cylinders or piston scratched, worn or scored
Replace or repair
33
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Trouble
Possible causes Leaking cylinder valve
Remedies Adjust and stop leakage
Loose belt in compressor wheel, motor pulley
Adjust the belt as recommended
Motor with excessive end play in shaft
Adjust the end paly
Carbon on top of the piston
De-carbonise
Leaking, broken or wornout constant speed unloader parts Valve seats worn
Adjust or replace
Recondition valve seat
Unusual noise Worn or scored connecting rod, piston pin or crank pin bearings. Defective ball bearings on crank shaft or on motor shaft Recondition the conneting rod, replace or condition gudgeon pin and crank pin bearings. Replace bearings
Loose motor fan
Tighten the motor fan
Cylinders or pistons scratched, worn or scored.
Rebore cylinders and replace pistons.
34
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Trouble
Possible causes Binding in machine leakage
Remedies Check linkage to ensure that excessive friction loads are not present.
Pressure too low.
Check the pressure at the cylinder to make certain that it is in accordance with circuit requirements.
Cylinder fails to move the load when valve is actuated
Cylinder undersized for loads
Re-calculate force needs and install appropriate sized cylinders to carry the load
Piston rod broken at piston end
Disassemble and replace piston rod.
Valve sticking or binding
a) Check for dirt or gummy deposits b) Check for worn parts
Cyinder sticking or binding
a) Check for overtightened packing on rod seal or piston. b) Check for mis-
Erratic cylinder action
alignment or worn parts. Loose tie rods Tighten the tie rods according to manufacturers recommendations Excessive pressure Reduce the pressure to the rated limits.
Pinched or extruded seal Cylinder body seal leak
Replace the cylinder body seal
Seal deterioration
Check the compatibility of seal material with the lubricant used
35
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Rod gland seal leak
Torn or worn seal
Examine the piston rod for dents and nicks. Replace the piston rod if the surface is rough
Excessive or rapid piston seal wear
Seal installed incorrectly
Check installation instruction and make necessary corrections
Valves
Trouble
Possible causes
Remedies
Inlet poppet not seating properly.
a) poppet is damaged, it must be replaced b) Dirt in poppet seals, clean it c) Poppet seat damaged, Replace the entire valve body assembly
Nicked, torn or swelling seals
Replace it
Cylinder leaks
Leakage in the packing of the air cylinder connected to the valve. Replace the packings
Valve blows to exhaust
Damage spools
Replace it
Cylinder leaks Leakage in the packing of the air cylinder connected to the valve. Replace the packings Damage spools Replace it.
Air supply pressure too low and causes the valve to actuate partially
Inspect the system for undersized supply lines, sharp bends, fittings and clogged
36
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
filter elements or a defective pressure regulator and adjust. Water or oil contamination Ensure that the air is dry and that the air filter is drained frequently Low pilot or signal pressure Check the valve specification for minimum pilot or signal pressure required Swollen seals Replace it
Varnish deposits in spool Poppet chatters valve
Remove varnish using a water soluble detergent or solvent such as kerosene
Air supply pressure low
Inspect the system
Low pilot or signal pressure
Check the valve specification for minimum pilot or signal pressure requirements.
Poor or no lubrication
Check the system lubricator to see that it is working as it should
Faulty silencer/ muffler
a) Remove the silencer to see if valve performance has improved b) Clean the silencer to see if
Spool valve action is sluggish
valve performance has improved c) Verify if the silencer is of adequate size Water or oil contamination Ensure the supply air is dry.
37
TVS TRAINING & SERVICES LTD Vanagaram, Chennai 600 095
Air flow is normal only in actuated position
Broken return spring
Replace the return spring
Low voltage at solenoid Solenoid buzzes
Voltage should be checked at the solenoid coil and repaired
High transient voltage Solenoid burns out
Isolate solenoid circuits from main power circuits
Faulty piston seal
Replace it.
Excessive lubrication
Check the system lubrication
Sequence valve gives erratic timing Fluctuating air pressure Install a pressure regulator set at the systems lowest expected pressure. Accumulated water Re-route the pilot supply lines to eliminate low points
Excessive lubrication
Check the system lubrication
Flow control valve does not respond to adjustment
Incorrect installation
Install properly
Dirt in valve
Clean the valve
38
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Cranes & Davits Heavy Duty Winches & Capstan Pilot Ladder & Fire Wire Reels Air Motors Air /electric Winches A Driven & Hand PumpDokument14 SeitenCranes & Davits Heavy Duty Winches & Capstan Pilot Ladder & Fire Wire Reels Air Motors Air /electric Winches A Driven & Hand PumpChieuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 Rotary Percussive DrillingDokument28 Seiten02 Rotary Percussive DrillingDivanshu0% (1)
- Handout Basic Electrical and Electronics AllisonDokument6 SeitenHandout Basic Electrical and Electronics AllisonSRIREKHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian EpicsDokument8 SeitenIndian EpicsSRIREKHANoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is MatterDokument131 SeitenWhat Is MatterSRIREKHANoch keine Bewertungen
- 7qc Tools TestDokument154 Seiten7qc Tools TestKAMAL BEHL71% (7)
- A Gas Compressor Is A Mechanical Device That Increases The Pressure of A Gas by Reducing Its VolumeDokument8 SeitenA Gas Compressor Is A Mechanical Device That Increases The Pressure of A Gas by Reducing Its VolumeSRIREKHA100% (1)
- Neumatic Echanic Ertification: Including Study Guide, Solutions, & Pre-TestsDokument82 SeitenNeumatic Echanic Ertification: Including Study Guide, Solutions, & Pre-TestsMohan Shanmugam100% (1)
- Dynamic Analysis of Compressed Air Energy Storage in The CarDokument14 SeitenDynamic Analysis of Compressed Air Energy Storage in The Carlokesh_045Noch keine Bewertungen
- Air Operated Oil Pumps: PL192 PL191Dokument6 SeitenAir Operated Oil Pumps: PL192 PL191HANIF AKBARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engine - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument12 SeitenEngine - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaShumway GordonNoch keine Bewertungen
- IR LM100A Crawlair Drill PDFDokument8 SeitenIR LM100A Crawlair Drill PDFAnonymous 8yIptglHhNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOUTECDokument34 SeitenDOUTECDoutecPowerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globe Brochure - Air MotorDokument2 SeitenGlobe Brochure - Air MotorHarshal shahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ARO Industrial Chain HoistsDokument20 SeitenARO Industrial Chain HoistsAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 HYDRAULIC MOTORS (Module-IV)Dokument19 Seiten04 HYDRAULIC MOTORS (Module-IV)Pyae Phyoe AungNoch keine Bewertungen
- TM-80 Heat Exchanger Cleaner 5224XLDokument6 SeitenTM-80 Heat Exchanger Cleaner 5224XLgshdavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bhriy T: Tube ToolsDokument25 SeitenBhriy T: Tube ToolsCesarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modec Case StudiesDokument15 SeitenModec Case Studiessamah eskanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- APHDokument1 SeiteAPHsai987650Noch keine Bewertungen
- P1V M Technical Catalogue UKDokument28 SeitenP1V M Technical Catalogue UKLiliana RosalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Repair Pump GracoDokument50 SeitenRepair Pump GracoariwibowoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winches For Industrial Appliance: Product Leafl Ets Technical DataDokument44 SeitenWinches For Industrial Appliance: Product Leafl Ets Technical DataJosé RoqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- The WorksDokument64 SeitenThe WorksJames KhooNoch keine Bewertungen
- MuconIDV Brochure F 1Dokument24 SeitenMuconIDV Brochure F 1abs0001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Arel Guna PneumaticDokument8 SeitenArel Guna PneumaticKhairul SyahreelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Year Mechanical Projects in Bangalore (HTTP://WWW - Modainnovations.com)Dokument7 SeitenFinal Year Mechanical Projects in Bangalore (HTTP://WWW - Modainnovations.com)modainnovationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- WachsDokument64 SeitenWachsJorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bethlahem Institute of Engineering Karungal - 629 157: Internal Assessment Test - IDokument4 SeitenBethlahem Institute of Engineering Karungal - 629 157: Internal Assessment Test - ICOMMANDER ALANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brosur SPX FlowDokument8 SeitenBrosur SPX FlowAltino Mangiwa100% (1)
- Aesculap Power Systems: Elan 4 and Acculan 4Dokument72 SeitenAesculap Power Systems: Elan 4 and Acculan 4yolany quinteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- F-E-25 AFX 5 Gallon 50-1 Industrial Grease Pump and PackagesDokument2 SeitenF-E-25 AFX 5 Gallon 50-1 Industrial Grease Pump and PackageskenriNoch keine Bewertungen
- OIE 751 ROBOTICS Unit 2 Class 1 (26-8-2020)Dokument10 SeitenOIE 751 ROBOTICS Unit 2 Class 1 (26-8-2020)MICHEL RAJ0% (1)
- E Catalogue Airhoists eDokument8 SeitenE Catalogue Airhoists eAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hawk Pneumatic DpsDokument39 SeitenHawk Pneumatic DpsWilliamNoch keine Bewertungen