Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Unit 4
Hochgeladen von
Sri Ram KCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Unit 4
Hochgeladen von
Sri Ram KCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EE 2351
IFET COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF EEE POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS YEAR/SEM: III/VI UNIT-4 FAULT ANALYSIS - UNBALANCED FAULTS (16) (16)
1. Derive an expression for a Single Line-to-Ground fault on an unloaded generator. 2. Derive an expression for a Line-to-Line fault on an unloaded generator.
3. Derive an expression for a Double-Line-to-Ground fault of an unloaded generator. (16) 1. 2. 3. 4. Write the initial conditions for the D-L-G fault. Write the symmetrical component of voltage in matrix form. Write the equation to determine the positive sequence current for D- L-G fault. Write the equation to find the fault current for L-L fault.
4. Draw the Zero sequence equivalent circuits for the various possible transformer connections. (16) a. b. c. d. e. star/star connected transformer with neutral of either winding is solidly grounded. Y-Y transformer with both neutrals grounded. Y- transformer with earthed neutral point. Y- transformer with unearthed neutral point. - connected transformer.
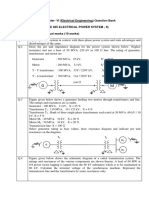
5. Fig shows a single line diagram of a simple power system by omitting the resistance and shunt admittances. Draw the positive, negative and zero sequence for the system shown in fig. (16)
6. Fig shows single line diagram of a simple power system by omitting resistance and shunt admittances draw positive, negative and zero sequence network. (16)
IFETCE/EEE/III YEAR/VI SEM/EE 2351/PSA/VER 1.0
7. Draw positive, negative and zero sequence reactance diagram for the fig shown below.
(16)
8. Determine the positive, negative and zero sequence networks for the system shown in fig. Assume zero sequence reactances for the generators and synchronous motors as 0.06 p.u. current limiting reactors of 2.5 are connected in the neutral of the generator and motor 2.The zero sequence reactance of the transmission line is j300 . (16) IFETCE/EEE/III YEAR/VI SEM/EE 2351/PSA/VER 1.0
9. Determine the positive, negative and zero sequence networks for the system shown in fig. Assume zero sequence reactances for the generator and synchronous motors as 0.08 p.u. Current limiting reactors of 3 are connected on the neutral of the generator and motor 2. The zero sequence of the transmission line is j400. (16)
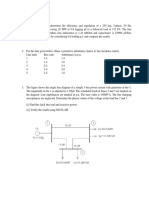
10. Two 11KV, 20 MVA, three phase, star connected generators operate in parallel as shown in fig. The positive, negative and zero sequence reactances of each being respectively, j0.18, j 0.15, j0.10 p.u. The star point of one of the generator is isolated and that of the other is earthed through a 2.0 resistor. A single line-to-ground fault occurs at the terminals of one of the generators. Estimate (i) fault current (ii) current in grounded resistor and (iii) voltage across grounding resistor. (Nag)
11. A salient-pole generator without dampers is rated 20 MVA, 13.8 KV and has a direct axis subtransient reactance of 0.25 per unit. The negative and zero sequence reactances are 0.35 and 0.10 per unit respectively. The neutral of the generator is solidly grounded. Determine the sub-transient current in the generator and the line-to-line voltages for subtransients conditions when a single lineto-ground fault occurs at the generator terminals with generator operating unloaded at rated voltage. Neglect resistance. (16) 12. Two synchronous machines are connected through three phase transformers to the transmission line as given in fig. The ratings and reactances of the machines and transformers are: Machines 1 and 2: 100 MVA; 20 KV; Xd=X1=X2=20 %; Xo=4 %; Xn = 5%. IFETCE/EEE/III YEAR/VI SEM/EE 2351/PSA/VER 1.0
Transformers T1 and T2: 100 MVA; 20 Y/345 Y KV; X=8%. Both transformers are solidly grounded on two sides on a chosen base of 100 MVA, 345 KV in the transmission line circuit. The line reactances are X1=X2=15% and Xo =50 %. The system is operating at nominal voltage without prefault currents when a bolted (Zf=0) single line-to-ground fault occurs on phase a at bus 3. Determine the subtransient current to ground at the fault. (16)
13. A salient-pole generator without dampers is rated 20 MVA, 13.8 KV and has a direct axis subtransient reactance of 0.25 per unit. The negative and zero sequence reactances are 0.35 and 0.10 per unit respectively. The neutral of the generator is solidly grounded. Find the subtransient currents and line-to-line voltages at the fault under subtransient conditions when a line-to-line fault between phase b and phase c occurs at the terminals of the generator. Assume that the generator is unloaded and operating at rated terminal voltage when the fault occurs. Neglect resistance. (16) 14. A salient-pole generator without dampers is rated 20 MVA, 13.8 KV and has a direct axis subtransient reactance of 0.25 per unit. The negative and zero sequence reactances are 0.35 and 0.10 per unit respectively. The neutral of the generator is solidly grounded. Find the subtransient currents and the line-to-line voltage at the fault under subtransient conditions when a double line-to-ground fault involving phase b and occurs at the terminals of the generator. Assume that the generator is unloaded and operating at rated voltage when the fault occurs. Neglect resistance. (16) 15. A generator of negligible resistance having 1 p.u. voltage behind transient reactance is subjected to different types of faults. Type of fault Resulting fault current in p.u 3-Phase 3.33 L-L 2.23 L-G 3.01 Calculate the per unit value of 3 sequence reactances. (16) 16. A double line to ground fault occurs at bus 3 through a fault impedance Zf= j0.1 of the network shown in fig. Determine (a) The fault current at bus 3. (4) (b) Post fault line to ground voltages at bus 3. (4) (c) line to line voltages at bus 3. (4) (d) Actual value of fault current at respective phases. (4)
IFETCE/EEE/III YEAR/VI SEM/EE 2351/PSA/VER 1.0
17. A double line fault occurs at bus 3 between b and c phases through a fault impedance Zf= j 0.15 of the network as shown in fig. (a) The fault current at bus 3. (6) (b) Actual value of fault current at respective values. (6) (c) Line to line voltages at bus 3. (4)
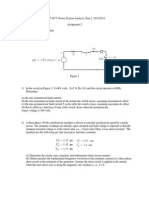
18. A generator is feeding power to a synchronous motor through two transformers and a transmission line. The data for the equipment are as under Synchronous generator: 15 MVA, 11 KV with X1=X2=20% , X0=10%. 3 phase transformer:1.5 MVA, 11KV/66 KV, X2=10%. Transmission line: 1.5 MVA/66 KV, X1=X2=40 %, X0=60% on a base of 1.5 MVA, 66KV. Synchronous motor: 1.5 MVA, 11KV X1=X2=20% X0=10%. Neutral grounding reactors: 10 % on the KVA and voltage base of the machine. The transmission line is connected between two transformers and two buses. A single line to ground fault (on phase a) occurs on the bus 1 of the system through a fault impedance of j0.15 . Find current during the fault. (use Zbus method). (16) 19. Draw the flow chart for the unsymmetrical fault analysis. 20. Evaluate the step by step procedure to find fault using Zbus matrix. (16) (16)
IFETCE/EEE/III YEAR/VI SEM/EE 2351/PSA/VER 1.0
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsVon EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit4questions 100415042439 Phpapp01Dokument4 SeitenUnit4questions 100415042439 Phpapp01Mohamad HishamNoch keine Bewertungen
- QueBank - Unit 3 - Unsymmetrical Fault AnalysisDokument3 SeitenQueBank - Unit 3 - Unsymmetrical Fault AnalysisBelayneh TadesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE61 Power System AnalysisDokument3 SeitenEE61 Power System AnalysisMartin De Boras PragashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment IDokument5 SeitenAssignment IPrasenjit DeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psa Unit 4Dokument21 SeitenPsa Unit 4Aish KrishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee6501 Psa Eee VST Au Units IVDokument24 SeitenEe6501 Psa Eee VST Au Units IVManeesh K ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-IDokument8 SeitenPower Systems-II Question Bank: Unit-ISoniya GJNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 6501 - Fault Analysis Unbalanced Faults Sequence ComponentsDokument2 SeitenEE 6501 - Fault Analysis Unbalanced Faults Sequence ComponentsVbalaji VaithiyanathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper CodeDokument6 SeitenQuestion Paper Codeprasad powerNoch keine Bewertungen
- A1Dokument4 SeitenA1hsvskumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power SystemDokument4 SeitenPower Systemj settyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System AnalysisDokument23 SeitenPower System AnalysisSaeed Al BlooshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Analysis and Simulation Question PaperDokument2 SeitenPower System Analysis and Simulation Question PaperKeyur PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE-311 Tutorial Sheet Fault CurrentsDokument5 SeitenEE-311 Tutorial Sheet Fault CurrentsRishabh Kalia100% (1)
- Power System Analysis-BE (PT) NEWDokument13 SeitenPower System Analysis-BE (PT) NEWMATHANKUMAR.SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure For Question No. 1Dokument4 SeitenFigure For Question No. 1noybit mondalNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE700 Assignment 2 QuestionsDokument2 SeitenEE700 Assignment 2 QuestionsAnil GugulothNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSADokument25 SeitenPSAramyadspNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEHRAN UNIVERSITY BE EXAM 2009 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSISDokument2 SeitenMEHRAN UNIVERSITY BE EXAM 2009 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSISkeerthanavijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment No. 2 Due Date: 15/10/2014 For All StudentsDokument3 SeitenAssignment No. 2 Due Date: 15/10/2014 For All StudentsZARGHAM KHANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module IV Fault Analysis & Short Circuit CalculationsDokument14 SeitenModule IV Fault Analysis & Short Circuit Calculationsbobby4u143Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work Sheet On Per UnitDokument3 SeitenWork Sheet On Per UnitteddydemerewNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT-I INTRODUCTIONDokument11 SeitenEE2351 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS UNIT-I INTRODUCTIONdrmsrmurty9473Noch keine Bewertungen
- Find subtransient fault current for BC fault at bus 3Dokument3 SeitenFind subtransient fault current for BC fault at bus 3Naman SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unsymmetrical FaultsDokument16 SeitenUnsymmetrical Faultslerato_lechelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BE Semester-VI (Electrical Engineering) Question Bank (E 605 Electrical Power System - Ii) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Dokument5 SeitenBE Semester-VI (Electrical Engineering) Question Bank (E 605 Electrical Power System - Ii) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Adesh Bhortakke100% (1)
- 14-05 Power System Analysis (EL)Dokument2 Seiten14-05 Power System Analysis (EL)Javed samejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignments - 2 July - December 2021Dokument5 SeitenAssignments - 2 July - December 2021Ayush AgrwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFDokument6 SeitenTutorial Faults - Update - 020413 - SV PDFnanangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kuppam Engineering College, KuppamDokument1 SeiteKuppam Engineering College, KuppamManohar_3020Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pse Problems Group AssignmentDokument14 SeitenPse Problems Group AssignmentSajid KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fault Calculation ExamplesDokument28 SeitenFault Calculation Examplestaufiqishak09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Analysis and Stability Subject Question BankDokument7 SeitenPower System Analysis and Stability Subject Question BankNaveen RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee2351 Psa Im 2013Dokument11 SeitenEe2351 Psa Im 2013ZARGHAM KHAN100% (1)
- Unit PsaDokument14 SeitenUnit Psasulthan_81100% (1)
- Power System Analysis (Jan-2014)Dokument10 SeitenPower System Analysis (Jan-2014)Likhitha YerraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument15 Seiten1Saravanaraja KumaresanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSE 6TH SEM UNIT 1 & 2 PER UNIT IMPEDANCE DIAGRAMSDokument33 SeitenPSE 6TH SEM UNIT 1 & 2 PER UNIT IMPEDANCE DIAGRAMSMahesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument4 SeitenAssignment 1Preetham ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab QPDokument8 SeitenLab QPpmahesh268Noch keine Bewertungen
- DC GeneratorDokument6 SeitenDC GeneratorUditya K100% (1)
- Unit - 2 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Dokument6 SeitenUnit - 2 Short Questions (2 & 3 Marks)Sujit KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet 1Dokument5 SeitenSheet 1meeedooo.abo.elenenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System AnalysisDokument10 SeitenPower System AnalysisAlluri Appa RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEN345 Tutorial Sheet 2 Short Circuit AnalysisDokument3 SeitenEEN345 Tutorial Sheet 2 Short Circuit AnalysisMohammed ShifulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank Samples For Power System II EE602Dokument4 SeitenQuestion Bank Samples For Power System II EE602AvijitNoch keine Bewertungen
- BEKP 3673 - Assignment 2Dokument4 SeitenBEKP 3673 - Assignment 2Shaiful Ashwat ShukorNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE4533Tutorial Questions - 2021Dokument5 SeitenEE4533Tutorial Questions - 2021Daniel ChaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSAs : Questions from Ch-1 Current and Voltage Relations on a Transmission LineDokument14 SeitenPSAs : Questions from Ch-1 Current and Voltage Relations on a Transmission Linemsthacker0% (1)
- Elx303 ExamDokument5 SeitenElx303 ExamNadeesha BandaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 2ksajjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Methodist College of Engineering & Technology, abids. Three phase to two phase conversionDokument5 SeitenMethodist College of Engineering & Technology, abids. Three phase to two phase conversionDasari BaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shivaji University Question Bank For Power System-II SubjectDokument7 SeitenShivaji University Question Bank For Power System-II SubjectAditya PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Analysis Assignment Fault CurrentsDokument2 SeitenPower System Analysis Assignment Fault CurrentsdeepanshuNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE6501-Question BankDokument16 SeitenEE6501-Question BankBelayneh TadesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Analysis Question Papers (2021-)Dokument29 SeitenPower System Analysis Question Papers (2021-)Jishnuraj KubandrarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- End Sem 3Dokument2 SeitenEnd Sem 3Nikhil Kumar JaiswalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Von EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Bewertung: 2.5 von 5 Sternen2.5/5 (3)
- Process ValidationDokument116 SeitenProcess ValidationsamirneseemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duty Entitlement Pass BookDokument3 SeitenDuty Entitlement Pass BookSunail HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Non Technical Part: Sample Interview Questions For Network EngineersDokument5 SeitenThe Non Technical Part: Sample Interview Questions For Network EngineersblablaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leapfroggers, People Who Start A Company, Manage Its Growth Until They Get Bored, and Then SellDokument3 SeitenLeapfroggers, People Who Start A Company, Manage Its Growth Until They Get Bored, and Then Sellayesha noorNoch keine Bewertungen
- VB 2Dokument11 SeitenVB 2Sudhir IkkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Harry Styles: The Rise of a Pop StarDokument9 SeitenHarry Styles: The Rise of a Pop StarBilqis LaudyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Borneo United Sawmills SDN BHD V Mui Continental Insurance Berhad (2006) 1 LNS 372Dokument6 SeitenBorneo United Sawmills SDN BHD V Mui Continental Insurance Berhad (2006) 1 LNS 372Cheng LeongNoch keine Bewertungen
- PaySlip ProjectDokument2 SeitenPaySlip Projectharishgogula100% (1)
- A Dream Takes FlightDokument3 SeitenA Dream Takes FlightHafiq AmsyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- InvoiceDokument1 SeiteInvoiceAnurag SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Ology ManualDokument2 SeitenRisk Ology ManualGregoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- DEFCON ManualDokument13 SeitenDEFCON Manualbuyvalve100% (1)
- City Gas Distribution ReportDokument22 SeitenCity Gas Distribution Reportdimple1101100% (9)
- WEEK 8 HW WS - B - Graphs & ChartsDokument6 SeitenWEEK 8 HW WS - B - Graphs & Chartsangela trioNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 Prospectus 2Dokument69 Seiten2023 Prospectus 2miclau1123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Evan Gray ResumeDokument2 SeitenEvan Gray Resumeapi-298878624Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Management NotesDokument115 SeitenMarketing Management NotesKajwangs DanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Solvents For Chemistry - William M NelsonDokument401 SeitenGreen Solvents For Chemistry - William M NelsonPhuong Tran100% (4)
- Keynes Presentation - FINALDokument62 SeitenKeynes Presentation - FINALFaith LuberasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Daftar PustakaDokument2 Seiten13 Daftar PustakaDjauhari NoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Successful Organizational Change FactorsDokument13 SeitenSuccessful Organizational Change FactorsKenneth WhitfieldNoch keine Bewertungen
- RoboticsDokument2 SeitenRoboticsCharice AlfaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ДСТУ EN ISO 2400-2016 - Калибровочный блок V1Dokument11 SeitenДСТУ EN ISO 2400-2016 - Калибровочный блок V1Игорь ВадешкинNoch keine Bewertungen
- Request For AffidavitDokument2 SeitenRequest For AffidavitGhee MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance: ASU-600 SeriesDokument54 SeitenMaintenance: ASU-600 SeriesMichael Maluenda Castillo100% (2)
- Final Project Report: Uop, LLCDokument165 SeitenFinal Project Report: Uop, LLCSiddharth KishanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Road Safety GOs & CircularsDokument39 SeitenRoad Safety GOs & CircularsVizag Roads100% (1)
- AssDokument9 SeitenAssJane SalvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study Infrastructure ProjectsDokument1 SeiteCase Study Infrastructure ProjectsAnton_Young_1962Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 Yoshimura Book of SpeedDokument83 Seiten2010 Yoshimura Book of Speedacornwoods_brentNoch keine Bewertungen