Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Global Warming
Hochgeladen von
manirathinaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Global Warming
Hochgeladen von
manirathinaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
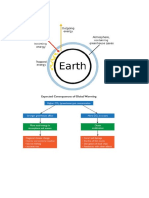
What is global warming? Global warming is when the earth heats up (the temperature rises).
It happens when greenhouse gases (carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrous oxide, and methane) trap heat and light from the sun in the earths atmosphere, which increases the temperature. This hurts many people, animals, and plants. Many cannot take the change, so they die.
What are the reasons for global warming?
Global Warming is caused by many things. The causes are split up into two groups, man-made or anthropogenic causes, and natural causes. Natural Causes
How can I help? About Us References
Natural causes are causes created by nature. One natural cause is a release of methane gas from arctic tundra and wetlands. Methane is a greenhouse gas. A greenhouse gas is a gas that traps heat in the earth's atmosphere. Another natural cause is that the earth goes through a cycle of climate change. This climate change usually lasts about 40,000 years. Man-made Causes Man-made causes probably do the most damage. There are many man-made causes. Pollution is one of the biggest man-made problems. Pollution comes in many shapes and sizes. Burning fossil fuels is one thing that causes pollution. Fossil fuels are fuels made of organic matter such as coal, or oil. When fossil fuels are burned they give off a green house gas called CO2. Also mining coal and oil allows methane to escape. How does it escape? Methane is naturally in the ground. When coal or oil is mined you have to dig up the earth a little. When you dig up the fossil fuels you dig up the methane as well. Another major man-made cause of Global Warming is
population. More people means more food, and more methods of transportation, right? That means more methane because there will be more burning of fossil fuels, and more agriculture. Now your probably thinking, "Wait a minute, you said agriculture is going to be damaged by Global Warming, but now you're saying agriculture is going to help cause Global Warming?" Well, have you ever been in a barn filled with animals and you smell something terrible? You're smelling methane. Another source of methane is manure. Because more food is needed we have to raise food. Animals like cows are a source of food which means more manure and methane. Another problem with the increasing population is transportation. More people means more cars, and more cars means more pollution. Also, many people have more than one car. Since CO2 contributes to global warming, the increase in population makes the problem worse because we breathe out CO2. Also, the trees that convert our CO2 to oxygen are being demolished because we're using the land that we cut the trees down from as property for our homes and buildings. We are not replacing the trees (an important part of our eco system), so we are constantly taking advantage of our natural resources and giving nothing back in return.
What Causes the Greenhouse Effect? Life on earth depends on energy from the sun. About 30 percent of the sunlight that beams toward Earth is deflected by the outer atmosphere and scattered back into space. The rest reaches the planet's surface and is reflected upward again as a type of slow-moving energy called infrared radiation. The heat caused by infrared radiation is absorbed by "greenhouse gases" such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, ozone and methane, which slows its escape from the atmosphere. Although greenhouse gases make up only about 1 percent of the Earth's atmosphere, they regulate our climate by trapping heat and holding it in a kind of warm-air blanket that surrounds the planet. This phenomenon is what scientists call the "greenhouse effect." Without it, scientists estimate that the average temperature on Earth would be colder by approximately 30 degrees Celsius (54 degrees Fahrenheit), far too cold to sustain our current ecosystem.
How Do Humans Contribute to the Greenhouse Effect? While the greenhouse effect is an essential environmental prerequisite for life on Earth, there really can be too much of a good thing. The problems begin when human activities distort and accelerate the natural process by creating more greenhouse gases in the atmosphere than are necessary to warm the planet to an ideal temperature.
Burning natural gas, coal and oil -including gasoline for automobile engines-raises the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Some farming practices and land-use changes increase the levels of methane and nitrous oxide. Many factories produce long-lasting industrial gases that do not occur naturally, yet contribute significantly to the enhanced greenhouse effect and "global warming" that is currently under way. Deforestation also contributes to global warming. Trees use carbon dioxide and give off oxygen in its place, which helps to create the optimal balance of gases in the atmosphere. As more forests are logged for timber or cut down to make way for farming, however, there are fewer trees to perform this critical function. Population growth is another factor in global warming, because as more people use fossil fuels for heat, transportation and manufacturing the level of greenhouse gases continues to increase. As more farming occurs to feed millions of new people, more greenhouse gases enter the atmosphere.
Ultimately, more greenhouse gases means more infrared radiation trapped and held, which gradually increases the temperature of the Earth's surface and the air in the lower atmosphere.
Greenhouse effects in Earth's atmosphere
Main article: Greenhouse effect
Modern global anthropogenic Carbon emissions.
In order, the most abundant greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere are:
water vapor carbon dioxide methane nitrous oxide ozone
chlorofluorocarbons
The contribution to the greenhouse effect by a gas is affected by both the characteristics of the gas and its abundance. For example, on a molecule-for-molecule basis methane is about eighty times stronger greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide ,[8] but it is present in much smaller concentrations so that its total contribution is smaller. When these gases are ranked by their contribution to the greenhouse effect, the most important are:[9]
Gas Formula Contribution (%) H2O CO2 CH4 O3 36 72 % 9 26 % 49% 37%
Water Vapor Carbon Dioxide Methane Ozone
It is not possible to state that a certain gas causes an exact percentage of the greenhouse effect. This is because some of the gases absorb and emit radiation at the same frequencies as others, so that the total greenhouse effect is not simply the sum of the influence of each gas. The higher ends of the ranges quoted are for each gas alone; the lower ends account for overlaps with the other gases.[9][10] The major non-gas contributor to the Earth's greenhouse effect, clouds, also absorb and emit infrared radiation and thus have an effect on radiative properties of the greenhouse gases.[9][10] In addition to the main greenhouse gases listed above, other greenhouse gases include sulfur hexafluoride, hydrofluorocarbons and perfluorocarbons (see IPCC list of greenhouse gases). Some greenhouse gases are not often listed. For example, nitrogen trifluoride has a high global warming potential (GWP) but is only present in very small quantities.[11]
Atmospheric absorption and scattering at different electromagnetic wavelengths. The largest absorption band of carbon dioxide is in the infrared.
Scientists who have elaborated on Arrhenius' theory of global warming are concerned that increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are causing an unprecedented rise in global temperatures, with potentially harmful consequences for the environment and human health.[12] Although contributing to many other physical and chemical reactions, the major atmospheric constituents, nitrogen (N2), oxygen (O2), and argon (Ar), are not greenhouse gases. This is because molecules containing two atoms of the same element such as N2 and O2 and monatomic molecules such as Ar have no net change in their dipole moment when they vibrate and hence are almost totally unaffected by infrared light. Although molecules containing two atoms of different elements such as carbon monoxide (CO) or hydrogen chloride (HCl) absorb IR, these molecules are short-lived in the atmosphere owing to their reactivity and solubility. As a consequence they do not contribute significantly to the greenhouse effect and are not often included when discussing greenhouse gases. Late 19th century scientists experimentally discovered that N2 and O2 do not absorb infrared radiation (called, at that time, "dark radiation") while, at the contrary, water, as true vapour or condensed in the form of microscopic droplets suspended in clouds, CO2 and other poly-atomic gaseous molecules do absorb infrared radiation. It was recognized in the early 20th century that the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere caused the Earth's overall temperature to be higher than it would be without them.
Can you answer these global warming issues questions?
When do warm days usually begin What would happen to the earth if there was global warming Why do some scientists think that global warming is not a serious thing How does hydroelectricity affect the environment
Related answers: What are the good points about global warming? 1. Heating costs for places like Canada and Russia will decrease severely. 2. Iceland could become an economic superpower. 3. The democrats and environmentalists of the world will finally leave this... Can global warming be good? Yes. It will result in fewer human deaths due to cold weather. Cold weather kills more people than hot weather, even though you hear a lot more about deaths due to heat waves. Moreover, global...
Is there anything good about global warming? yes Is global warming good for the econimy? no Is global warming good or bad? Global warming may have bad consequences for man and his society, and other species of Earth life. At the same time, it could promote or benefit certain living things. The basis for global warming is...
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Presentation 10 (1)Dokument15 SeitenPresentation 10 (1)xoranek474Noch keine Bewertungen
- Greenhouse Effect and GasesDokument4 SeitenGreenhouse Effect and Gasespradeep aggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 10Dokument20 SeitenPresentation 10xoranek474Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2007 Editorial Oct Nov 2007 THE EFFECTS OF GLOBAL WARMING AND HOMOEOPATHYDokument9 Seiten2007 Editorial Oct Nov 2007 THE EFFECTS OF GLOBAL WARMING AND HOMOEOPATHYAram BamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Greenhouse EffectDokument4 SeitenThe Greenhouse EffectimienazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green House EffectDokument11 SeitenGreen House EffectChandan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Change Manmade or NaturalDokument5 SeitenGlobal Change Manmade or NaturalVamsi KrishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NG One of The Biggest Threats To HumanityDokument2 SeitenNG One of The Biggest Threats To HumanityRhea CabillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Greenhouse Effect and Thinning of The Ozone Layer On The EcosystemDokument21 SeitenThe Greenhouse Effect and Thinning of The Ozone Layer On The EcosystemShahirah NsnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Warming: Tania Milagros Delgado ChoqqueDokument15 SeitenGlobal Warming: Tania Milagros Delgado ChoqqueTANIA MILAGROS DELGADO CHOQQUENoch keine Bewertungen
- PP 31 the Atmosphere and Climate ChangeDokument97 SeitenPP 31 the Atmosphere and Climate ChangeOlerato NtsimaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green House EffectDokument6 SeitenGreen House EffectVir PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Climate Change and Its EffectsDokument7 SeitenClimate Change and Its EffectsHassan ImamNoch keine Bewertungen
- TUGAS Global WarmingDokument4 SeitenTUGAS Global WarmingPolsek Siantar SelatanNoch keine Bewertungen
- List of ContentsDokument9 SeitenList of ContentsMaria JBieber BrandonizerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globle WarmingDokument87 SeitenGloble WarmingVijay Maurya100% (1)
- Commented (U1) : BURNING FOSSIL FUELDokument2 SeitenCommented (U1) : BURNING FOSSIL FUELBusiness OnlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Warming Assignment (Final)Dokument8 SeitenGlobal Warming Assignment (Final)Howard How100% (4)
- The "Greenhouse Effect" Often Gets A Bad Rap Because ofDokument8 SeitenThe "Greenhouse Effect" Often Gets A Bad Rap Because ofaratipatil1990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Global WarmingDokument12 SeitenGlobal Warmingshoeb100% (1)
- Greenhouse Effect ExplainedDokument19 SeitenGreenhouse Effect ExplainedsayyadsajidaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Skills Development-1: Global WarmingDokument13 SeitenPersonal Skills Development-1: Global WarmingFiza MajidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global WarDokument4 SeitenGlobal WarARUNGREESMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Adobe Scan Jun 14, 2023Dokument10 SeitenAdobe Scan Jun 14, 2023xoranek474Noch keine Bewertungen
- Global WarmingDokument8 SeitenGlobal WarmingsamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Iv Climate ChangeDokument35 SeitenChapter Iv Climate ChangeAminus SholihinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project WorkDokument10 SeitenProject WorkKazi Anwarul Azim SohelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green House EffectDokument6 SeitenGreen House EffectMuhammad ArslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green House EffectDokument28 SeitenGreen House EffectVyshnavi P VNoch keine Bewertungen
- STS Notes On Climate ChangeDokument2 SeitenSTS Notes On Climate Changetabeb chanNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Global WarmingDokument4 SeitenWhat Is Global WarmingLê Tú QuyênNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greenhouse GassDokument4 SeitenGreenhouse GassBella Yunita100% (1)
- Green House EffectsDokument8 SeitenGreen House Effectssme chemistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green House EffectDokument12 SeitenGreen House EffectRaja BhattacharjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greenhouse Gases Cause Global WarmingDokument5 SeitenGreenhouse Gases Cause Global WarmingAnanya SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Warming & Ozone LayerDokument12 SeitenGlobal Warming & Ozone LayerWayne JohannesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global WarmingDokument11 SeitenGlobal Warmingghataksampa816Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effects of Green House Gases (Chemistry Project Class-11)Dokument15 SeitenEffects of Green House Gases (Chemistry Project Class-11)Anujeet Saha86% (7)
- Cma433 Topics 2Dokument55 SeitenCma433 Topics 2Muhammad AizatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green House EffectDokument13 SeitenGreen House Effectaruba anwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meaning To Global WarmingDokument17 SeitenMeaning To Global Warmingneeraj sahaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- NowadaysDokument2 SeitenNowadaysalexnder_rjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geography: Global WarmingDokument11 SeitenGeography: Global WarmingzeropointwithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green House EffectDokument4 SeitenGreen House EffectHuria MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green House Effect ExplainedDokument4 SeitenGreen House Effect ExplainedAhilan KannanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birtkan English AssigmentDokument5 SeitenBirtkan English AssigmentDenaw AgimasNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Global WarmingDokument12 SeitenWhat Is Global Warmingsachinkc25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Global WarmingDokument22 SeitenGlobal WarmingKetan AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fossil Fuel's: Consequences of Using Fossil FuelsDokument4 SeitenFossil Fuel's: Consequences of Using Fossil FuelsDaniel FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- HeyDokument7 SeitenHeyHASHIM TRUNKWALANoch keine Bewertungen
- Project in EthicspicDokument19 SeitenProject in EthicspicOdellien SajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Enhanced Greenhouse EffectDokument4 SeitenThe Enhanced Greenhouse EffectIreoluwa AjayiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greenhouse Gases: Climate Change Is Real - Causes and Impacts of Climate ChangeDokument15 SeitenGreenhouse Gases: Climate Change Is Real - Causes and Impacts of Climate ChangeAhmad Hassan ChathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project On Global WarmingDokument22 SeitenProject On Global WarmingHilda DsouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RA L9 Global Warming 9Dokument29 SeitenRA L9 Global Warming 9md.daud.ul.islamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecology and EnviromentDokument20 SeitenEcology and Enviromentpallavi maheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Green House EffectDokument30 SeitenThe Green House EffectxzerlaxyrellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global WarmingDokument7 SeitenGlobal WarmingHardik TankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Warming Has Become Perhaps The Most Complicated Issue Facing World NowadaysDokument47 SeitenGlobal Warming Has Become Perhaps The Most Complicated Issue Facing World Nowadaysrishad mufasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cinderella PDFDokument124 SeitenCinderella PDFmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NmsagidelinesDokument74 SeitenNmsagidelinesmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advantages of Ayurvedic Cow Urine TherapyDokument2 SeitenAdvantages of Ayurvedic Cow Urine TherapymanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cinderella PDFDokument124 SeitenCinderella PDFmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dimethyl Amine SL Salts of 2,4-DDokument1 SeiteDimethyl Amine SL Salts of 2,4-DmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Path 171Dokument118 SeitenPath 171manirathina100% (1)
- Gas Liquid ChromatographyDokument18 SeitenGas Liquid ChromatographymanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sterlite Industries From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokument7 SeitenSterlite Industries From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediamanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- House Fly - Appearance, Behaviour, Diet and Facts: Physical Appearance of A HouseflyDokument26 SeitenHouse Fly - Appearance, Behaviour, Diet and Facts: Physical Appearance of A HouseflymanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Std10 Tamil 1Dokument93 SeitenStd10 Tamil 1ஹரிஷ் கமுகக்குடி மாரிமுத்துNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nib - ,Y Cs SJ XW Iwf FZ, Y Iy. New WPF FZ . NGDH FPHPLK Fow WKDokument33 SeitenNib - ,Y Cs SJ XW Iwf FZ, Y Iy. New WPF FZ . NGDH FPHPLK Fow WKmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tamil Nadu pay scale rulesDokument3 SeitenTamil Nadu pay scale rulesphysicspalanichamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banned Chemicals ListDokument5 SeitenBanned Chemicals ListmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate Particulars Quantity Rupees Rate Particulars Quantity RupeesDokument7 SeitenRate Particulars Quantity Rupees Rate Particulars Quantity RupeesmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phone Scheme PlanDokument1 SeitePhone Scheme PlanmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sre Plumbing & Electrical QuotationsDokument2 SeitenSre Plumbing & Electrical QuotationsmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Syllabus Vao Services UpdatedDokument12 SeitenNew Syllabus Vao Services Updatedவெங்கடேஷ் ராமசாமிNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dimethyl Amine SL Salts of 2,4-DDokument1 SeiteDimethyl Amine SL Salts of 2,4-DmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Depo StockDokument33 SeitenDepo StockmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TNPSC Group-I AnsDokument13 SeitenTNPSC Group-I AnsmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soil and Water Conservation EnggDokument142 SeitenSoil and Water Conservation EnggShakeel Ayjaz67% (6)
- Tet Original Que Paper I Latest 2012Dokument29 SeitenTet Original Que Paper I Latest 2012AMU SHAHUL HAMEEDNoch keine Bewertungen
- EpfoDokument9 SeitenEpfoVinay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test E&mckupDokument9 SeitenTest E&mckupmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Personal Alarm: Circuit DiagramDokument30 SeitenPersonal Alarm: Circuit DiagrammanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Std10 Tamil 1Dokument93 SeitenStd10 Tamil 1ஹரிஷ் கமுகக்குடி மாரிமுத்துNoch keine Bewertungen
- Agri and General Knowledge QuestionsDokument35 SeitenAgri and General Knowledge QuestionsmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redgram Transplanting TechnologyDokument95 SeitenRedgram Transplanting TechnologymanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Phone A Ban or A BoonDokument14 SeitenMobile Phone A Ban or A BoonmanirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TNPSC Group 2 2009Dokument7 SeitenTNPSC Group 2 2009manirathinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Numerical Simulation of Screw Displacement Pile Interaction With Non-Cohesive SoilDokument12 SeitenNumerical Simulation of Screw Displacement Pile Interaction With Non-Cohesive Soilmohamed magdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19174the Rise of Industrial Big Data WP Gft834Dokument6 Seiten19174the Rise of Industrial Big Data WP Gft834em01803257Noch keine Bewertungen
- Caterpillar 360 KWDokument6 SeitenCaterpillar 360 KWAde WawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GHT 2001 Chino 12 Point Temperature Recorder EH3127 001Dokument1 SeiteGHT 2001 Chino 12 Point Temperature Recorder EH3127 001gawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Semester All Courses-100Dokument194 Seiten2nd Semester All Courses-100Ejiade PeterNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Ph Induction MotorDokument246 Seiten3-Ph Induction MotorAn00pgadzillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sco 2Dokument15 SeitenSco 2rkhandelwal9604Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 31. Current and Resistance Chapter 31. Current and Resistance Current and ResistanceDokument11 SeitenChapter 31. Current and Resistance Chapter 31. Current and Resistance Current and ResistanceArwaa AlmaghrabiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iot Finals Clap Switch Group 5Dokument15 SeitenIot Finals Clap Switch Group 5RICHYBOY SALACNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2021 Vallourec Universal Registration DocumentDokument368 Seiten2021 Vallourec Universal Registration DocumentRolando Jara YoungNoch keine Bewertungen
- GBDokument10 SeitenGBQuoctytranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Plan of Easy Meal ServiceDokument41 SeitenBusiness Plan of Easy Meal ServiceCeddie UnggayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anorexia NervosaDokument2 SeitenAnorexia NervosaDhea Mae MadisNoch keine Bewertungen
- BASIC IMMUNOLOGY TERMSDokument2 SeitenBASIC IMMUNOLOGY TERMSAnnicoldjohn LariozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 - Flight Recorder - OcrDokument19 Seiten5 - Flight Recorder - OcrtmhoangvnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRP104 Course Outline: Introduction to Key Topics in Human GeographyDokument26 SeitenGRP104 Course Outline: Introduction to Key Topics in Human GeographyKelvin WatkinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical Methods To Measure The Constants of Fats and OilsDokument5 SeitenAnalytical Methods To Measure The Constants of Fats and OilsPenicillium Notatum67% (3)
- Dialyser Reprocessing Machine Specification (Nephrology)Dokument2 SeitenDialyser Reprocessing Machine Specification (Nephrology)Iftekhar AhamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS-MS Analysis Programs - 2012 SlidesDokument14 SeitenMS-MS Analysis Programs - 2012 SlidesJovanderson JacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Debashish & HemantDokument31 SeitenNew Debashish & HemantEshwar KothapalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weekly Report 52Dokument196 SeitenWeekly Report 52Erceanu DanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shiva Home - DCFDokument2 SeitenShiva Home - DCFshyamsundar_ceNoch keine Bewertungen
- ABB Price Book 714Dokument1 SeiteABB Price Book 714EliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cryptography 01092014Dokument19 SeitenCryptography 01092014Anshu MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete Variable Probability Distribution FunctionsDokument47 SeitenDiscrete Variable Probability Distribution FunctionsJanine CayabyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- AkzoNobel-Trigonox 239Dokument6 SeitenAkzoNobel-Trigonox 239Wafa AjiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Development of Manually Operated ReaperDokument8 SeitenDesign and Development of Manually Operated ReaperIOSRjournalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hufenus 2006 Geotextiles GeomembranesDokument18 SeitenHufenus 2006 Geotextiles Geomembranesbkollarou9632Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instrukcja Pellets Fuzzy Logic - ENGDokument53 SeitenInstrukcja Pellets Fuzzy Logic - ENGxilef84Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lea 2 PDFDokument21 SeitenLea 2 PDFKY Renz100% (1)
- The Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraVon EverandThe Big, Bad Book of Botany: The World's Most Fascinating FloraBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (10)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (31)
- Last Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderVon EverandLast Child in the Woods: Saving Our Children From Nature-Deficit DisorderBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (283)
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorVon EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (137)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeVon EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (699)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildVon EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (44)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldVon EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (18)
- The Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceVon EverandThe Mind of Plants: Narratives of Vegetal IntelligenceBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (11)
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanVon EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanNoch keine Bewertungen
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsVon EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (221)
- Soil: The Story of a Black Mother's GardenVon EverandSoil: The Story of a Black Mother's GardenBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (16)
- Spoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeVon EverandSpoiled Rotten America: Outrages of Everyday LifeBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (19)
- The Hummingbirds' Gift: Wonder, Beauty, and Renewal on WingsVon EverandThe Hummingbirds' Gift: Wonder, Beauty, and Renewal on WingsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (60)
- The Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateVon EverandThe Hidden Life of Trees: What They Feel, How They CommunicateBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1002)
- Gathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesVon EverandGathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (347)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsVon EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (63)
- Come Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogVon EverandCome Back, Como: Winning the Heart of a Reluctant DogBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (10)
- A Garden of Marvels: How We Discovered that Flowers Have Sex, Leaves Eat Air, and Other Secrets of PlantsVon EverandA Garden of Marvels: How We Discovered that Flowers Have Sex, Leaves Eat Air, and Other Secrets of PlantsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nature Fix: Why Nature Makes us Happier, Healthier, and More CreativeVon EverandThe Nature Fix: Why Nature Makes us Happier, Healthier, and More CreativeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (157)
- Remnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsVon EverandRemnants of Ancient Life: The New Science of Old FossilsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (2)