Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Pharmacology-Last Years' Questions
Hochgeladen von
GaYda'a Kana'anOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Pharmacology-Last Years' Questions
Hochgeladen von
GaYda'a Kana'anCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
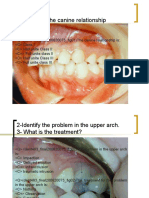
11) 2) 3) 4) 5) 21) 2) 3) 4) 5) 31) 2) 3) 4) 5) 41) 2) 3) 4)
Hypokalemia isnt a side effect of : Spiranalactone Amiloride Triamterene Enalapril All of the above All are nitrate effects except : Bradycardia Headache Cyanosis Flushing Tolerance All are morphine effects except : Miosis Vomiting Constipation Cough Hyposis One is selective B2 agonist : Isoprinaline Noradrenaline Salbutamole Timolol
5) 51) 2) 3) 4) 5) 61) 2) 3) 4) 5)
Amphetamine Carbacol (cholinergic agonist) : Used in enuresis among children Antagonized by neostigmine Relax skeletal and smooth muscle Increase BP Decrease IOP (intraocular pressure ) One matched correctly with its source : Sulfonamide / synthetic Insulin / plants Erythropoietin / microbes Digoxin / synthetic None of them
7- All increase drug concentration in blood except : 1) Given parentally 2) Liver and kidney disease 3) c-p 450 inhibitors 4) Combined with drug displace it from its receptor and having low VD 5) All of the above 81) 2) Potency : The ability of drug to bind a receptor The maximum effect of a drug
3) 4) 5)
The effect of drug per unit of weight The dose needed to reach the maximum effect of the drug None of them
91) 2) 3) 4) 5)
All are side effect of frusemide except : Hyperlipidemia Hyperglycemia Hyperuricemia Hyperkalemia Hyponatremia
10-Hair growth is noticed in which drug used in hypertension : 1) Methyldopa 2) Na nitroprusside 3) Minoxidil 4) Hydralazine 5) Nifedipine 11- Pethidine compared to morphine : 1) Produces sedation more than restlessness 2) Less antimuscarinic effect 3) More potent 4) Has negative inotropic effect 5) More antitussive action
12-Adrenalin used in all except : 1) Asthma 2) Heart block 3) Glaucoma 4) Local bleeding 5) Angina
13-The drug reactivate inhibited Ach esterase : 1) Atropine 2) Neostigmine 3) Thiosulphate 4) Adrenaline 5) PAM 14-Succinylcholine used in : 1) Malignant hyperthermia 2) Intestinal and biliary colic 3) Rapid endotracheal intubation 4) Motion sickness 5) Glaucoma 15-1st pass effect definition : 1) Drug metabolism when given by IV route 2) Drug metabolism when not bounded to plasma albumin 3) Drug metabolism in the liver before distribution when given internally
4) 5)
Drug metabolism outside the liver Drug elimination upon manipulating urine PH
16-The half life of a drug : 1) The time needed for a drug to change concentration by 50% 2) The time needed for a drug to bind to its receptor 3) The time needed for a drug to excreted completely from the body 4) The time needed to reach the maximum concentration
17-Zero order kinetic : 1) Few drug follow it 2) Kinetic at high drug concentration 3) Fixed amount of drug metabolized per unit time 4) Rate of metabolism is time independent 5) All of the above 18-All are uses of digoxin except : 1) Heart failure 2) Atrial flutter 3) Atrial fibrillation 4) Ventricular ectopic 5) Used for all of them 19- All true regarding digoxin except :
1) 2) 3) 4) 5)
Negative inotropic agent Negative chronotropic agent Na /K pump inhibitor Given enterally and parentally Characterized by all of them
20-One anti-arrhythmic drug acts by inhibiting ventricular excitation : 1) Digoxin 2) Adenosine 3) Metoprolol 4) Verapamil 5) Lignocaine
21-About morphine : 1) Safe to be given in pregnant and lactating women 2) Respiratory center stimulants , useful in asthmatics 3) Mydriatic agent 4) Indicated in post partum urinary retention 5) Contraindicated in acute undiagnosed abdominal pain 22-NE primary terminated by : 1) Reuptake to neurons 2) Metabolized by MAO 3) Metabolized by Ach-esterase
4) 5)
Passively diffused out of synapses Metabolized by COMT
23-Prazosin : 1) The 1st choice in glaucoma management 2) Used in migraine treatment and prophylaxis 3) Contraindicated in hypertension management 4) Used in benign prostate hyperplasia BPH 5) Partial opioid agonist 24-Digoxin toxicity in increase in which of the following conditions : 1) Hypothyroidism {myxedema} 2) Thiazide diuretics 3) Renal failure 4) Hypokalemia 5) All of them
25-Angina is best managed by : 1) Oral propranolol 2) Oral isosorbid dinitrate 3) GTN patches 4) Chewed isosorbid mononitrate 5) GTN sublingually
26-Acute morphine toxicity is best managed by : 1) naltrexone 2) methadone 3) mepridine 4) Na thiosulpate 5) naloxone 27-all are side effects of B blockers except : 1) hyperglycemia 2) arrhythmias 3) bradykardia 4) sexual dysfunction 5) cold extremities 28-anticholinergic best used for mydriasis : 1) homatropine 2) benzatropine 3) pirenzpine 4) ipratropium 5) probanthine
29-the name of drug given by the manufacturers is the : 1) chemical name 2) generic name 3) official name
4) 5)
trade name approved name
30-drug absorption depends in all except : 1) blood flow at absorption site 2) contact time at absorption site 3) lipid solubility 4) volume of distribution 5) all of the above 31-therapeutic effects of a drug increase when : 1) displaced from albumin 2) bound strongly to plasma protein 3) dissociate from its receptor 4) ionized in liver set of metabolism 5) become water soluble 32-drug enters CNS readily are : 1) lipid soluble 2) highly bound to albumin 3) hydrophilic 4) polar 5) large in weight
33-one is calcium channel blocker : 1) varapamil 2) clonidine 3) timolol 4) pentazocin 5) minoxidil 34-B blockers used in all except : 1) Angina 2) Hyperthyroidism 3) Glaucoma 4) Migraine 5) Asthma 35-Neostigmine indicated in all except : 1) Organophosphate poisoning 2) Post operative urinary retention 3) Tubocurarine poisoning 4) Mysthena gravis 5) All of the above 36- Atropine indicated in all of the following except : 1) Vomiting 2) Pyloric stenosis 3) Insecticide poisoning 4) Urine retention 5) Preanesthesia
37-Drug of wide therapeutic index : 1) Toxic at low doses 2) Variation in patient response occur at the same dose 3) Minimally bound to plasma protein 4) Safe drug 5) 2 and 4 38-Bioavilability describes : 1) Percentage of drug dose not bind plasma proteins 2) Percentage of drug bind to the intracellular receptor 3) Percentage of drug reaches the plasma unchanged 4) Volume of blood containing drug excreted per unit of time 5) Percentage of drug not metabolized in the cp-450 system 39-Rectal form of drugs include : 1) Ointment 2) Suspension 3) Bolus 4) Patches 5) Suppository 40-All used in hypertension management except : 1) Alpha adrenergic antagonists 2) Vasodilator
3) 4) 5)
ACE inhibitor Cholinesterase inhibitor Calcium channel blockers
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Frequencies - ListDokument171 SeitenFrequencies - Listparamatman111199100% (3)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- 640RH00059 CancerDokument36 Seiten640RH00059 CancerViolin_teacher100% (2)
- General Pathology MCQsDokument32 SeitenGeneral Pathology MCQsedcrfvtgb12345684% (37)
- Pedo MCQs Questions ImpDokument15 SeitenPedo MCQs Questions ImpGaYda'a Kana'an100% (3)
- NYU CSAAH Testimony Re: Jails PlanDokument4 SeitenNYU CSAAH Testimony Re: Jails PlanS SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation 3Dokument36 SeitenPresentation 3GaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morphology of Deciduous DentitionDokument28 SeitenMorphology of Deciduous DentitionAli Al-Qudsi100% (1)
- Presentation 2Dokument21 SeitenPresentation 2GaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ortho SpotDokument27 SeitenOrtho SpotGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- AbstractDokument2 SeitenAbstractGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- C & BDokument2 SeitenC & BGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perio Pictures For Spot ExamDokument24 SeitenPerio Pictures For Spot ExamGaYda'a Kana'an100% (1)
- 3333333333Dokument10 Seiten3333333333GaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Previous QuestionsDokument5 SeitenPrevious QuestionsGaYda'a Kana'an100% (1)
- Surgery - Mid Exam QsDokument3 SeitenSurgery - Mid Exam QsGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prostho Pictures For Spot ExamDokument129 SeitenProstho Pictures For Spot ExamGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Term Question Prostho 3: D) Patients Satisfaction Is More Than RPD Constructed For Bounded Edentulous AreaDokument3 SeitenMid Term Question Prostho 3: D) Patients Satisfaction Is More Than RPD Constructed For Bounded Edentulous AreaOsama SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1111111111Dokument9 Seiten1111111111GaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggested Questions For Internal MedicineDokument9 SeitenSuggested Questions For Internal MedicineGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
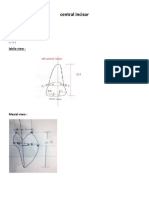
- Central Incisor: DimensionsDokument3 SeitenCentral Incisor: DimensionsGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Average CalculatorDokument1 SeiteAverage CalculatorGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pedo QsDokument13 SeitenPedo QsGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surgery-Past Years QsDokument10 SeitenSurgery-Past Years QsGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Suggested Questions For Internal MedicineDokument9 SeitenSuggested Questions For Internal MedicineGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Years & Suggested Question - Oral HistoDokument7 SeitenPast Years & Suggested Question - Oral HistoGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1 Answer SheetDokument9 SeitenLab 1 Answer SheetGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec4 130302030014 Phpapp02Dokument19 SeitenLec4 130302030014 Phpapp02GaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Endo Lec#4Dokument11 SeitenEndo Lec#4GaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid-Term QsDokument2 SeitenMid-Term QsOmar YahyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scr.4 Working Length Determination, Endodontic RadiologyDokument12 SeitenScr.4 Working Length Determination, Endodontic Radiologyبراءة أحمد السلاماتNoch keine Bewertungen
- Previous Year Qustions (1st Exam)Dokument10 SeitenPrevious Year Qustions (1st Exam)GaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Year Questions For The Epidemiology CourseDokument3 SeitenPast Year Questions For The Epidemiology CourseGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diseases of Salivary Glands LabDokument41 SeitenDiseases of Salivary Glands LabGaYda'a Kana'anNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Quiz 1Dokument4 SeitenAnatomy Quiz 1Jacob BorongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastric Outlet Obstruction: AgonaDokument4 SeitenGastric Outlet Obstruction: AgonalxnalexanderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opportunities AMSA-IndiaDokument4 SeitenOpportunities AMSA-Indiadeepanshu narangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coca ColaDokument28 SeitenCoca ColaPriyam SaraogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mefenamic AcidDokument6 SeitenMefenamic AcidArisa VijungcoNoch keine Bewertungen
- STD Pre TestDokument2 SeitenSTD Pre TestCrystal Ann Monsale TadiamonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breast Cancer in Pakistan - Awareness and Early DetectionDokument3 SeitenBreast Cancer in Pakistan - Awareness and Early DetectionMurk NiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cancer Trend Analysis Using Joinpoint Regression Part 1 The BasicsDokument5 SeitenCancer Trend Analysis Using Joinpoint Regression Part 1 The BasicsAndré Luiz LimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soal Regarding Menoupause ConditionDokument6 SeitenSoal Regarding Menoupause ConditionfeliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rebozet Tykerb PDFDokument33 SeitenRebozet Tykerb PDFWinda AgustinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Klasifikasi Tindakan Bedah Digestif Update 20 Juni 2022 (BPJS)Dokument7 SeitenKlasifikasi Tindakan Bedah Digestif Update 20 Juni 2022 (BPJS)Eko RistiyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cancer 2Dokument3 SeitenCancer 2Charissa Magistrado De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- DRNB Medical Gastroenterology Paper1Dokument4 SeitenDRNB Medical Gastroenterology Paper1Srinivas PingaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2013 Claw Disease in Dogs Part 1 - Anatomy and Diagnostic ApproachDokument5 Seiten2013 Claw Disease in Dogs Part 1 - Anatomy and Diagnostic Approachdr Alex stanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slots 2019 Periodontal Herpesvirus Morbidity and TreatmentDokument11 SeitenSlots 2019 Periodontal Herpesvirus Morbidity and Treatmentmaria ocampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of XenoDokument2 SeitenHistory of XenoShania LoveresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Whipple ComplicationDokument34 SeitenWhipple ComplicationMike Hugh100% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment & ManagementDokument12 SeitenEctopic Pregnancy Treatment & ManagementDebi SumarliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sex HormonesDokument11 SeitenSex Hormonesharishmore596Noch keine Bewertungen
- Procedural AnesthesiaDokument40 SeitenProcedural AnesthesiaJovian LutfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- LP Askep Hernia Inguinal DextraDokument81 SeitenLP Askep Hernia Inguinal Dextraicn8Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anemias VCMDokument64 SeitenAnemias VCMPaz VidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AminofostineDokument5 SeitenAminofostinePedro JuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- About Stomach Cancer: Overview and TypesDokument14 SeitenAbout Stomach Cancer: Overview and TypesMuhadis AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perception of New Medicine Among GynaecologistsDokument49 SeitenPerception of New Medicine Among GynaecologistsYashruti1Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECB3e Chapter 20Dokument80 SeitenECB3e Chapter 20Sarifa Ghina RaquelleNoch keine Bewertungen