Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
H3K4me3 - Active Transcription Start Sites
Hochgeladen von
spirocateOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
H3K4me3 - Active Transcription Start Sites
Hochgeladen von
spirocateCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Bromodomain -> acetyllysine in H4 Lys16
Lysine Methylation H3K4me3 -> active transcription start sites H3K9me3 -> constitutive heterochromatin H3K27me3 -> silent genes in euchromatic regions or facultative heterochromatin Bivalent domains -> stem-cell development H3K4me3 + H3K27me3 Histone lysine methylation in the recruitment of DNA damage repair proteins H3K4me3 -> near the promoters and 5 ends of highly transcribed genes, H3K4me2 -> coding region of genes that are either active or poised for transcription H3K36me3-> highly enriched throughout the entire transcribed region Chromodomains -> di- and trimethyllysine in H3K9 and H3K27 contexts Heterochromatin protein-1 (HP1) --> H3K9me3 + H3K9me2 Polycomb --> H3K27me3 Double chromodomains Chromo helicase DNA-binding (CHD) proteins includes SWI/SNF nucleosome remodeling complex target methyllysine in H3K4 Double tudor domains Jumonji domaincontaining protein-2A (JMJD2A) H3K4me3 Plant homeodomain (PHD) fingers bind H3K4me3 -> recruiting or stabilizing downstream complexes BPTF -> largest subunit of the nucleosomal remodeling factor (NURF) ATP-dependent chromatinremodeling complex Yng1p -> part of Nucleosomal acetyltransferase of histone H3 (NuA3) complex NuA3 -> H3-specific H3K14 HAT -> acetylation for TFIID basal transcription machinery
Cysteine-rich ADD domain ->Unmodified H3K4 DNMT3L -> lacks intrinsic methyltransferase Germline-specific DNA methylation defective in mice deficient in the DNMT3L
WD40 protein WDR5 -> Unmodified H3R2 WD40-repeat protein WDR5 - common component of SET1-family histone methyltransferase complexes Binding to H3R2 promotes H3K4 3Xme
Phosphoserine marks On all core histone tails & linker histone H1 Important in cell-cycle control, DNA damage repair and transcriptional regulation 14-3-3 Proteins -> phosphoserine in H3S10 There are many examples of two or more putative histone-binding modules linked within the same protein or within the same multisubunit complex, allowing for combinatorial PTM readout at the histone or nucleosomal level. 2 Domains, 1 binding site double chromodomains of CHD1 double tudor domains of JMJD2A tandem tudor domains of 53BP1 tandem BRCT domains of MDC1 TAF1 double bromodomain -> 2 x acetylated histones on H4 tail MBT repeats of L3MBTL1: two of the three repeats may be used simultaneously to engage two sites/marks in a histone tail
modules that bind H3K4me3 are found in both complexes that activate transcription and complexes that repress it. The biophysics of multivalency may resolve this conundrumfor example, an activating complex might bind H3K4me3 and additional activating PTMs, whereas a silencing complex might also bind H3K4me3 but simultaneously engage silencing PTMs.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Harper's Illustrated Biochemistry CH 35Dokument11 SeitenHarper's Illustrated Biochemistry CH 35Richelle Dianne Ramos-Giang100% (1)
- Daniel Grimanelli & Mathieu Ingouff : DNA Methylation Readers in PlantsDokument37 SeitenDaniel Grimanelli & Mathieu Ingouff : DNA Methylation Readers in PlantsWenye WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chasin DHFRDokument31 SeitenChasin DHFRashutoshrvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and Rnai in Heterochromatic Gene Silencing: Marc Bu Hler & Danesh MoazedDokument8 SeitenTranscription and Rnai in Heterochromatic Gene Silencing: Marc Bu Hler & Danesh MoazedRocio Valverde PastorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research ProposalDokument7 SeitenResearch ProposalBitan BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
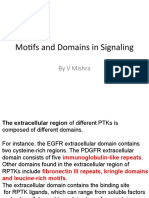
- Motifs and Domains in Signaling VMDokument23 SeitenMotifs and Domains in Signaling VMShishir SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA-RNA Structure and FunctionDokument332 SeitenDNA-RNA Structure and FunctionazeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organization Replication Repair: DR S K BansalDokument71 SeitenOrganization Replication Repair: DR S K BansalSanjiv BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recombinant Human CTCF Protein Ab153114: DatasheetDokument3 SeitenRecombinant Human CTCF Protein Ab153114: DatasheetnutjabberNoch keine Bewertungen
- SUV39 SET Domains Mediate Crosstalk of Heterochromatic Histone MarksDokument26 SeitenSUV39 SET Domains Mediate Crosstalk of Heterochromatic Histone MarksPaul OneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Role of Chromatin in Regulating Gene Expression and Gene SilencingDokument19 SeitenRole of Chromatin in Regulating Gene Expression and Gene SilencingVinod NNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0genex DECKER 6thB NEU2020Dokument3 Seiten0genex DECKER 6thB NEU2020Katarina Kaca GacevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced ColiDokument16 SeitenAdvanced ColiAyu WikhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Genetics Chapter 8Dokument49 SeitenMolecular Genetics Chapter 8byunus88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Epigenetic Regulation in Plants: Ryza Aditya Priatama (리자 아디티아)Dokument30 SeitenEpigenetic Regulation in Plants: Ryza Aditya Priatama (리자 아디티아)lordniklausNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Organization of PericentroDokument33 SeitenThe Organization of PericentroTunggul AmetungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanisms Underlying Epigenetic and Transcriptional Heterogeneity in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) Cell LinesDokument16 SeitenMechanisms Underlying Epigenetic and Transcriptional Heterogeneity in Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) Cell LinesAnita RosdianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 1.1 Protocol - Easy Lithium Acetate Transformation of Yeast - UPDATEDDokument10 SeitenLab 1.1 Protocol - Easy Lithium Acetate Transformation of Yeast - UPDATEDcolby mcintoshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fransz 2003 ChromR Heterochromatin in Interphase Nuclei of atDokument14 SeitenFransz 2003 ChromR Heterochromatin in Interphase Nuclei of atAJMRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles and Applications of Inorganic, Organic, and Biological ChemistryDokument40 SeitenPrinciples and Applications of Inorganic, Organic, and Biological ChemistryJansen Arquilita RiveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eukaryotic Transcriptional Control: Major ConsiderationsDokument40 SeitenEukaryotic Transcriptional Control: Major ConsiderationsShantanu ChakrabortyNoch keine Bewertungen
- G - Lecture 6 - 15.10.2019 - NotesDokument11 SeitenG - Lecture 6 - 15.10.2019 - Notesmystudykit.vbNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2023 12 19 572350v1 FullDokument41 Seiten2023 12 19 572350v1 Fullgundeepdsc8423Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eukaryotic Chromosome PresentationDokument14 SeitenEukaryotic Chromosome PresentationmadatoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure and Functions of Chromosomes and ChromatinDokument78 SeitenStructure and Functions of Chromosomes and ChromatinosefresistanceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromosomes: Strcture and FoldingDokument25 SeitenChromosomes: Strcture and FoldingANUPAM ANAND KUMAR PANDEY MBA-INoch keine Bewertungen
- Her2/Neu (Also Known As Erbb-2) Stands For "Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2"Dokument4 SeitenHer2/Neu (Also Known As Erbb-2) Stands For "Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2"Bima AnantaNoch keine Bewertungen
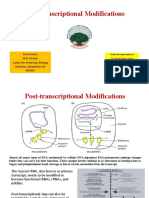
- Post-Transcriptional Modifications: Arun Kumar PHD Scholar Centre For Molecular Biology Central University of JammuDokument67 SeitenPost-Transcriptional Modifications: Arun Kumar PHD Scholar Centre For Molecular Biology Central University of JammuARUN KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Molecular Genetics: Fourth EditionDokument67 SeitenHuman Molecular Genetics: Fourth EditionMousumi BalNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMYD5 Catalyses Histone H3 Lysine 36 Trimethylation at PromotersDokument19 SeitenSMYD5 Catalyses Histone H3 Lysine 36 Trimethylation at PromotersdffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biochem 442 Ruohola-Baker Midterm 2Dokument18 SeitenBiochem 442 Ruohola-Baker Midterm 2bpwalshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poxvirus DNA Replication: Paula TraktmanDokument24 SeitenPoxvirus DNA Replication: Paula Traktmanpersian2845Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gene RegulationDokument16 SeitenGene RegulationMarkrobert MagsinoNoch keine Bewertungen
- GKZ 618Dokument16 SeitenGKZ 618Andrea EscartinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mammalian Artificial ChromosomesDokument5 SeitenMammalian Artificial ChromosomesKanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 MBV4230 05 ChromatinDokument112 Seiten05 MBV4230 05 Chromatinsinte beyuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pmic 200400943Dokument18 SeitenPmic 200400943leilany casillasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Cloning - Pt1Dokument5 SeitenLab Report Cloning - Pt1Ezad juferiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 14 Chromatin Regulation of TranscriptionDokument20 SeitenLecture 14 Chromatin Regulation of TranscriptionNezrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Truncated Intracellular HER2neu Receptor Produced by Alternative RNA Processing Affects Growth of Human Carcinoma CellsDokument11 SeitenA Truncated Intracellular HER2neu Receptor Produced by Alternative RNA Processing Affects Growth of Human Carcinoma CellsSean KwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOI 6 (I) DNA Organisation, Replication & RepairDokument81 SeitenFOI 6 (I) DNA Organisation, Replication & RepairSohail RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Biology - Notes On Organisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomesDokument15 SeitenH2 Biology - Notes On Organisation and Control of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic GenomesSefLRho100% (5)
- BMC BiotechnologyDokument18 SeitenBMC Biotechnologyfather45Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hartmann 2014Dokument10 SeitenHartmann 2014bkadlakhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromatin Higher Order Structure: Opening Up Chromatin For TranscriptionDokument11 SeitenChromatin Higher Order Structure: Opening Up Chromatin For TranscriptionSarahi ElizondoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucl. Acids Res. 2011 Drechsel 1427 38Dokument12 SeitenNucl. Acids Res. 2011 Drechsel 1427 38Norma VillalvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiochemistryDokument40 SeitenBiochemistrykhaledNoch keine Bewertungen
- ThrombopoietinDokument18 SeitenThrombopoietinactivnetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription-Coupled Methylation of Histone H3 at Lysine 36 Regulates Dosage Compensation by Enhancing Recruitment of The MSL Complex in Drosophila MelanogasterDokument9 SeitenTranscription-Coupled Methylation of Histone H3 at Lysine 36 Regulates Dosage Compensation by Enhancing Recruitment of The MSL Complex in Drosophila MelanogasterWasim ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Activation of Homologous Recombination in G1 Preserves Centromeric IntegrityDokument25 SeitenActivation of Homologous Recombination in G1 Preserves Centromeric Integritymbernasconi.fclNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulasi Ekspresi GenDokument41 SeitenRegulasi Ekspresi GenJohn'sSujonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics - The Eukaryotic ChromosomeDokument85 SeitenGenetics - The Eukaryotic Chromosomes.medura.mamarielleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competent Cells Novagen DetailedDokument23 SeitenCompetent Cells Novagen DetailedPhosphatidylserinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vento Et Al 2023Dokument34 SeitenVento Et Al 2023pampetraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chloroplast TransformationDokument14 SeitenChloroplast TransformationShuddhodana MukthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Zhou Chromosome and Chromatin 1 NewDokument88 SeitenZhou Chromosome and Chromatin 1 Newapi-3700537Noch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Plant Reviews, Regulation of Transcription in PlantsVon EverandAnnual Plant Reviews, Regulation of Transcription in PlantsKlaus D. GrasserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antigen Presenting Cells: From Mechanisms to Drug DevelopmentVon EverandAntigen Presenting Cells: From Mechanisms to Drug DevelopmentHarald KropshoferNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nine Circles of Scientific HellDokument3 SeitenThe Nine Circles of Scientific HellspirocateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histone ModificationDokument5 SeitenHistone ModificationspirocateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free RadicalsDokument7 SeitenFree RadicalsspirocateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioinfo - BLAST - Scores PDFDokument8 SeitenBioinfo - BLAST - Scores PDFspirocateNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Comprehensive View of The Epigenetic Landscape Part IIDokument26 SeitenA Comprehensive View of The Epigenetic Landscape Part IIBetzabethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chromatin RemodellingDokument234 SeitenChromatin RemodellingBetsabé Vega AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aiims - Biochemistry Q&ADokument198 SeitenAiims - Biochemistry Q&APrahladRao KulkarniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions Manual To Accompany Molecular Biology of The Gene 6th Edition 9780805395921Dokument7 SeitenSolutions Manual To Accompany Molecular Biology of The Gene 6th Edition 9780805395921BriannaJimenezojmrs100% (82)
- Chromatin RemodelingDokument5 SeitenChromatin RemodelingRohit GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseDokument29 Seiten1 Cell As A Unit of Health and DiseaseRholter Dave LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- molecules: Computational Design of Macrocyclic Binders of S100B (ββ) : Novel Peptide TheranosticsDokument23 Seitenmolecules: Computational Design of Macrocyclic Binders of S100B (ββ) : Novel Peptide TheranosticsГульнара ХакимоваNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epigenetics in Teleost Fish - From Molecular Mechanisms To Physiological Phenotypes PDFDokument35 SeitenEpigenetics in Teleost Fish - From Molecular Mechanisms To Physiological Phenotypes PDFTiago TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gene Regulation in Eukaryotes: @usbfirdausDokument25 SeitenGene Regulation in Eukaryotes: @usbfirdausnur maliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA PackagingDokument4 SeitenDNA PackagingPriyanshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Molecular Biology Principles and Practice 1st Edition Michael M CoxDokument9 SeitenTest Bank For Molecular Biology Principles and Practice 1st Edition Michael M CoxAnthonyRogersydtfp100% (64)
- Genomic Focus on EpigeneticsDokument45 SeitenGenomic Focus on Epigeneticslordniklaus100% (1)
- Chromatin RemodellingDokument234 SeitenChromatin Remodellingplastioid4079Noch keine Bewertungen
- Deneme Sinavi Soru Da: K IN K Bilim R T L Bili LERDokument62 SeitenDeneme Sinavi Soru Da: K IN K Bilim R T L Bili LERgülsüm önalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assay Development and High-ThroughputDokument12 SeitenAssay Development and High-ThroughputJuan AspilcuetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Biology Lecture NotesDokument108 SeitenCell Biology Lecture NotesMert PolatNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 Smarcal1 Human Molecular GeneticsDokument867 Seiten2012 Smarcal1 Human Molecular Geneticsrameshramyb100% (1)
- Understanding of HDAC Inhibitors in CancerDokument19 SeitenUnderstanding of HDAC Inhibitors in CancerRahul JanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Structure and OrganizationDokument47 SeitenDNA Structure and Organizationhjklknnm jhoiolkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prokaryotic Genome OrganizationDokument53 SeitenProkaryotic Genome OrganizationAqsa YaminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eukaryotic ChromosomeDokument94 SeitenEukaryotic ChromosomeRtNoch keine Bewertungen
- 50 TOP DNA STRUCTURE Questions and Answers PDF 2019Dokument7 Seiten50 TOP DNA STRUCTURE Questions and Answers PDF 2019kassaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbial Communication Leading To The Activation of Silent Fungal Secondary Metabolite Gene ClustersDokument13 SeitenMicrobial Communication Leading To The Activation of Silent Fungal Secondary Metabolite Gene ClustersLini MaliqisnayantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pcna, The Maestro of The Replication Fork2007Dokument15 SeitenPcna, The Maestro of The Replication Fork2007gisin touNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cell Bio Exam 1 Lecture QuizzesDokument50 SeitenCell Bio Exam 1 Lecture QuizzesHafiza Dia Islam100% (1)
- Structure and Organization of ChromatinDokument11 SeitenStructure and Organization of Chromatincassidy conchaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Translating The Histone Code PDFDokument8 SeitenTranslating The Histone Code PDFLorena RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNA Structure and ChemistryDokument37 SeitenDNA Structure and ChemistryDozdi100% (4)
- Biochem 442 Ruohola-Baker Midterm 2Dokument18 SeitenBiochem 442 Ruohola-Baker Midterm 2bpwalshNoch keine Bewertungen