Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Key Concepts of Finance: Understanding Risk
Hochgeladen von
Akshay HemanthOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Key Concepts of Finance: Understanding Risk
Hochgeladen von
Akshay HemanthCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
A QUALITY E-LEARNING PROGRAM BY WWW.LEARNWITHFLIP.COM
Understanding Risk
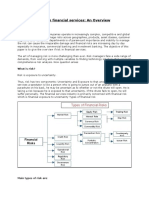
Risk is the probability that financial loss will occurred. Risk management is a three stage process:
1. Identify the Risk
A financial institution such as a bank, faces the following typical types of risks: Credit risk - This is the risk of default by a borrower. Regulatory risk - This refers to the risk of loss if a Financial Institution (FI) does not comply with the regulations needed by a countrys regulator. Liquidity risk - This is the risk of not having cash when it is needed. This risk is critical for a bank, as it needs to always have sufficient money on hand to repay withdrawals by depositors. Operational risk - This is the risk of loss occurring from inefficiency in a banks people, process and systems. This includes risk of theft, fraud, process inefficiency and so on. Legal risk - This is the risk of loss resulting from not being adequately protected by legal contract. Market risk - Any entity when trading in a market is exposed to the risk of loss, and a bank is no different, if it trades in financial markets. Depending on the specific market, the market risk can be further categorized into: Equity risk (risk of loss in the stock markets), Interest rate risk (risk of loss in bond markets), etc.
Credit risk, operational risk and market risk are regulated by a global standard called the Basel Norms. By global, we mean that, the norms are broadly similar across the world for all banks.
2. Measuring Risk
There are different methods of measuring the types of risk. All methods consider the following factors to arrive at a measure of riskProbability of an adverse event: The measurement of this probability uses various statistical techniques. Monetary impact of the adverse event: If the adverse or loss-causing event occurs, how much money would be lost?
3. Managing Risk
Once the risk is identified and measured, steps can be taken to lessen its impact.
Diversification- Diversification refers to spreading risk across different actions or options.
Hedging- This refers to protecting oneself against risk, using specific financial instruments. Insurance- Another way to manage risk is to transfer it to an insuring party, paying a fee (called the premium). Setting risk limits- A business can set risk limits to the amount of risk it is willing to face, and thus manage risk.
Finitiatives Learning India Pvt. Ltd. (FLIP), 2010. Proprietary content. Please do not misuse!
KEY CONCEPTS OF FINANCE
A QUALITY E-LEARNING PROGRAM BY WWW.LEARNWITHFLIP.COM
Avoid the risk- If a business feels that a particular event will prove too risky, it need not expose itself to that risk at all.
The Risk-return Principle The higher the expected return, the higher is the attached risk and the lower the risk; the lower is the potential reward. That means, if you expect higher returns from any investment, there will be a higher risk associated with it, and vice versa. Risk Management Systems Technology plays an important role in risk management. Banks need risk management systems to manage the different types of risk they face. For example, a market risk management system tracks the investments of a bank at any point, their prices, and the notional profit/loss of the portfolio. It will also have alerts when a trader has exceeded limits such as maximum amount s/he can trade, maximum loss s/he can be exposed to, etc.
Finitiatives Learning India Pvt. Ltd. (FLIP), 2010. Proprietary content. Please do not misuse!
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- FRM Mid 1Dokument13 SeitenFRM Mid 1VINAY BETHANoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Chapter 9 - Risk Management in Banks NBFCsDokument4 Seiten12 Chapter 9 - Risk Management in Banks NBFCsgarima_kukreja_dceNoch keine Bewertungen
- TYBFM 109 Urvil Desai SemV Technical AnalysisDokument5 SeitenTYBFM 109 Urvil Desai SemV Technical AnalysisURVIL DESAINoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Management in Islamic Financial Institutions: Week 11Dokument33 SeitenRisk Management in Islamic Financial Institutions: Week 11Asfand YarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundation of Financial Risk ManagementDokument23 SeitenFoundation of Financial Risk Managementrichard kapimpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A5 - Risk ManagementDokument30 SeitenA5 - Risk ManagementNoel GatbontonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Project AssignmentDokument27 SeitenResearch Project AssignmentSam CleonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Risk: Minimum Correct Answers For This Module: 4/8Dokument12 SeitenPrinciples of Risk: Minimum Correct Answers For This Module: 4/8Jovan SsenkandwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Finance Q4 Week 2 1Dokument12 SeitenBusiness Finance Q4 Week 2 1ajinxtersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Uncertainty On Objectives) Followed by Coordinated and Economical Application of Resources ToDokument6 SeitenEffect of Uncertainty On Objectives) Followed by Coordinated and Economical Application of Resources ToKatrina Vianca DecapiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report About RM 1Dokument20 SeitenReport About RM 1Zaid ZatariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Risk Management: BY S.LingeswariDokument26 SeitenFinancial Risk Management: BY S.Lingeswarilvinoth5Noch keine Bewertungen
- ACT1110 Fundamental Concepts of Risk ManagementDokument61 SeitenACT1110 Fundamental Concepts of Risk ManagementRica RegorisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk in Financial ServicesDokument3 SeitenRisk in Financial Servicesk gowtham kumar0% (1)
- Financial Risk Management & Derivatives: Unit 1Dokument30 SeitenFinancial Risk Management & Derivatives: Unit 1DEEPIKA S R BUSINESS AND MANAGEMENT (BGR)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of Risk ManageinentDokument20 SeitenFoundations of Risk Manageinentrachit uppalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free BFM PreviewDokument13 SeitenFree BFM PreviewAnonymous l0MTRDGu3MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro to Risk ManagementDokument21 SeitenIntro to Risk ManagementRaghavendra.K.ANoch keine Bewertungen
- 4-Step Financial Risk ManagementDokument4 Seiten4-Step Financial Risk ManagementHemant AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Analysis And Management ToolsDokument8 SeitenRisk Analysis And Management ToolsBHARATH TEJA REDDY MUNAKALANoch keine Bewertungen
- Alternative Risk TRF e 02Dokument5 SeitenAlternative Risk TRF e 02Vladi B PMNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 April 2023Dokument2 Seiten3 April 2023kfatrisyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Risk Management NotesDokument95 SeitenFinancial Risk Management Notesafeefa siddiquaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hard Copy.. UBDokument27 SeitenHard Copy.. UBGristy GranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Screenshot 2022-12-05 at 6.19.06 PMDokument10 SeitenScreenshot 2022-12-05 at 6.19.06 PMMehar MujahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper On Risk ManagementDokument8 SeitenPaper On Risk ManagementSANTOSHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treasury Management and Risk MitigationDokument4 SeitenTreasury Management and Risk MitigationNIKHILPATNINoch keine Bewertungen
- Mba Iii Financial Risk ManagementDokument75 SeitenMba Iii Financial Risk ManagementSimran GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Risk ManagementDokument38 SeitenFinancial Risk Managementsaif khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 101-Introduction To Derivatives Trading and SettlementDokument25 Seiten101-Introduction To Derivatives Trading and SettlementAmruta PeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk ManagementDokument27 SeitenRisk ManagementAnujPradeepKhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haf 422 Assigment No TwoDokument7 SeitenHaf 422 Assigment No Twopalaiphilip23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management 113Dokument11 SeitenFinancial Management 113ali purityNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding The Essence of Financial Risk Management: Unit TwoDokument37 SeitenUnderstanding The Essence of Financial Risk Management: Unit Tworichard kapimpaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 6 Risk ManagementDokument45 SeitenTopic 6 Risk Managementcaroon keowNoch keine Bewertungen
- LFSL LWL - CH 1 CH 7 Risks of Financial InstitutionsDokument22 SeitenLFSL LWL - CH 1 CH 7 Risks of Financial InstitutionsHelen JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin Risk MGTDokument11 SeitenFin Risk MGTmahipal2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Management:: A Helicopter ViewDokument2 SeitenRisk Management:: A Helicopter ViewTony NasrNoch keine Bewertungen
- MFS- Risk Management in Banks muskanDokument54 SeitenMFS- Risk Management in Banks muskansangambhardwaj64Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To FRMDokument29 SeitenIntroduction To FRMRahul AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BFM Module B SnapshotDokument17 SeitenBFM Module B SnapshotVenkata Raman RedrowtuNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Concept of RiskDokument3 SeitenThe Concept of RiskMickaela GulisNoch keine Bewertungen
- TYPES OF RISKS EXPLAINEDDokument7 SeitenTYPES OF RISKS EXPLAINEDsanu gawaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Risk and Management ModuleDokument11 SeitenFinancial Risk and Management ModulehunegnawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk and Types of RisksDokument2 SeitenRisk and Types of RisksSmritiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk management project overviewDokument26 SeitenRisk management project overviewKinjal Rupani100% (1)
- A222 BWBB3193 Topic 04 Management of Risk in BankingDokument38 SeitenA222 BWBB3193 Topic 04 Management of Risk in BankingNurFazalina AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimize Risk Management for Improved ReturnsDokument62 SeitenOptimize Risk Management for Improved ReturnsArun Kumar100% (2)
- Lecture 2-Chapt 2-Financial Risk MGTDokument47 SeitenLecture 2-Chapt 2-Financial Risk MGTBrenden KapoNoch keine Bewertungen
- BkriskmgtDokument39 SeitenBkriskmgtAtul VikashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary - Key Concepts in FinanceDokument9 SeitenSummary - Key Concepts in FinanceABHISHEK DALAL 23Noch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Management Framework Finance Department of APS: 1. DefinitionDokument6 SeitenRisk Management Framework Finance Department of APS: 1. DefinitionAsef KhademiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operational Risk ManagementDokument29 SeitenOperational Risk Managementsaurabh thakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Subject Code & Name Mf0016 Treasury Management: AssignmentDokument7 SeitenSubject Code & Name Mf0016 Treasury Management: AssignmentNIKHILPATNINoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Management Techniques and ProcessesDokument19 SeitenRisk Management Techniques and ProcessesSweta PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Management DefinedDokument3 SeitenRisk Management DefinedCabdixamiid CaduurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Navigating Financial Risk: Strategies for a Dynamic WorldVon EverandNavigating Financial Risk: Strategies for a Dynamic WorldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Risk Management Fundamentals: An introduction to risk management in the financial services industry in the 21st centuryVon EverandRisk Management Fundamentals: An introduction to risk management in the financial services industry in the 21st centuryBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Roduction Usiness OrganizationDokument24 SeitenRoduction Usiness OrganizationAkshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Economics For Managers Dr. Chandrima Sikdar BM I Yr Trim I 2012 13.doc1Dokument4 SeitenEconomics For Managers Dr. Chandrima Sikdar BM I Yr Trim I 2012 13.doc1Akshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Economics - ppt1Dokument13 SeitenIntroduction To Economics - ppt1Akshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncert Fm-Ac-xi Chapter 7Dokument52 SeitenNcert Fm-Ac-xi Chapter 7shaannivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keac 108Dokument52 SeitenKeac 108Ias Aspirant AbhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demand & Supply - ppt2Dokument59 SeitenDemand & Supply - ppt2Akshay Hemanth100% (1)
- Analysis of Cost - ppt4Dokument25 SeitenAnalysis of Cost - ppt4Akshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keac 105Dokument31 SeitenKeac 105Akshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDDDDDDokument106 SeitenSDDDDDAkshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keac 103Dokument50 SeitenKeac 103Akshay Hemanth0% (1)
- Trial BalanceDokument46 SeitenTrial BalanceChetan MetkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Green Banking Research PaperDokument12 SeitenGreen Banking Research PaperPoonam Ilag88% (8)
- Keac 102Dokument19 SeitenKeac 102Akshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncert Fm-Ac-xi Chapter 4Dokument59 SeitenNcert Fm-Ac-xi Chapter 4shaannivasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cbse 11th Class PDFDokument21 SeitenCbse 11th Class PDFPallavi JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solar Atm LaunchDokument5 SeitenSolar Atm LaunchVishnu MohanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keac 1 PsDokument10 SeitenKeac 1 PsAbhishek Walter PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDDDDDDokument40 SeitenSDDDDDAkshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0406004Dokument6 Seiten0406004Akshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.K.School of Business ManagementDokument21 SeitenS.K.School of Business ManagementManan Gondaliya0% (1)
- Indusind Bank LTDDokument77 SeitenIndusind Bank LTDbhupsaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banking Laws & Their Applications-Prof. S.K.bagchi-BM-I Yr Trim I-2011-12Dokument1 SeiteBanking Laws & Their Applications-Prof. S.K.bagchi-BM-I Yr Trim I-2011-12Akshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- GreenlawnDokument41 SeitenGreenlawnAkshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Concepts of Finance: Understanding MoneyDokument4 SeitenKey Concepts of Finance: Understanding MoneyAkshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- FinanceDokument4 SeitenFinanceAkshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fera To Jhdjjfema 1Dokument15 SeitenFera To Jhdjjfema 1Mohammad AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge Management Initiatives at ICICI BankDokument30 SeitenKnowledge Management Initiatives at ICICI BankAkshay HemanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Exercisefor Prmaelimtobesubmittedon Dec 05Dokument42 SeitenAssignment Exercisefor Prmaelimtobesubmittedon Dec 05Shane LAnuzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Porter-1991-Strategic Management Journal PDFDokument23 SeitenPorter-1991-Strategic Management Journal PDFJuan Martín Romero100% (1)
- Department of The Air Force: Headquarters 36Th Wing (Pacaf) Andersen Air Force Base GuamDokument6 SeitenDepartment of The Air Force: Headquarters 36Th Wing (Pacaf) Andersen Air Force Base GuamLawlesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disaggregated Consumer Prices and Oil Price Pass-Through: Evidence From MalaysiaDokument16 SeitenDisaggregated Consumer Prices and Oil Price Pass-Through: Evidence From MalaysiaPrasanjit BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Studies Notes Chapter 1Dokument11 SeitenBusiness Studies Notes Chapter 1Pawansharma kusum68Noch keine Bewertungen
- (Intermediate Accounting 1A) : Lecture AidDokument10 Seiten(Intermediate Accounting 1A) : Lecture AidShe RCNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Volume ProfitDokument14 SeitenCost Volume ProfitMohamed SururrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Premium CH 2 Thinking Like An EconomistDokument36 SeitenPremium CH 2 Thinking Like An EconomistdavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipe Fitting Accessories: Import Price ListDokument13 SeitenPipe Fitting Accessories: Import Price Listgabriel240371Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gitman pmf13 ppt09Dokument56 SeitenGitman pmf13 ppt09Sarah Julia Gushef100% (3)
- Vietnamese Capital Market and ParticipantsDokument22 SeitenVietnamese Capital Market and Participantsngoclm90Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Export BusinessDokument22 SeitenIntroduction To Export BusinessasifanisNoch keine Bewertungen
- 43 CPT Icai Dec 2009 Question Paper With Answer KeyDokument16 Seiten43 CPT Icai Dec 2009 Question Paper With Answer Keymmohanc100% (1)
- Jra Phils Vs CirDokument5 SeitenJra Phils Vs Cirdianne rebutarNoch keine Bewertungen
- S-Op FolioDokument24 SeitenS-Op FolioThanh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting Equation Powerpoint NotesDokument28 SeitenAccounting Equation Powerpoint NotespsrikanthmbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- When The Tail Wags The DogDokument5 SeitenWhen The Tail Wags The DogrhlthkkrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Padhle 11th - 2 - Consumer's Equilibrium - Microeconomics - EconomicsDokument12 SeitenPadhle 11th - 2 - Consumer's Equilibrium - Microeconomics - Economicssrishti AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Review Inventory Model WithDokument18 SeitenPeriodic Review Inventory Model WithDr-Mohammed FaridNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group EnggDokument2 SeitenGroup EnggabhishekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everything You Need to Know About Value-Added Tax (VATDokument67 SeitenEverything You Need to Know About Value-Added Tax (VATkmabcdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reasons Behind The Fall of Keya GroupDokument4 SeitenReasons Behind The Fall of Keya Grouptanjinrahmankhan038Noch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of a sound tax systemDokument34 SeitenPrinciples of a sound tax systemDenise DianeNoch keine Bewertungen
- On-Campus Housing Feasibility StudyDokument75 SeitenOn-Campus Housing Feasibility StudyGrace De la CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mcqs-Work-Flow22 23 14Dokument15 SeitenMcqs-Work-Flow22 23 14Sakthi RoyalhunterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multidisciplinary Action Project ReportDokument52 SeitenMultidisciplinary Action Project ReportShaikh Mohammadimran AbdulsaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cement Industry ResearchDokument9 SeitenCement Industry ResearchSounakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Profitability Analysis ReportDokument13 SeitenProfitability Analysis ReportJocelyn CorpuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS ASSIGNMENTDokument7 SeitenINTERNATIONAL ECONOMICS ASSIGNMENTJash ShahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discounted Cash FlowDokument5 SeitenDiscounted Cash FlowEKANGNoch keine Bewertungen