Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
ATNR
Hochgeladen von
mohitnet1327Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ATNR
Hochgeladen von
mohitnet1327Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ATNR
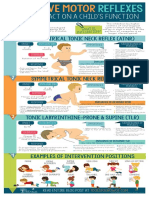
What Is It? Tests for ATNR Exercises To Do Studies When a baby reflex is not integrated, in can cause learning problems later on. Here are some symptoms of a Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (ATNR) in an older child. A retained ATNR can cause difficulties with:
horizontal tracking eyes struggle to cross the midline binocular coordination eyes cannot work together for convergence saccades the rapid eye movements required for reading cerebral specialization the brain remains symmetrical and doesnt develop a dominant side un-established hand dominance child switches between hands, is ambidextrous, doesnt develop a dominant hand until 7 or 8, or uses one hand for fine motor and another for gross motor mixed eye dominance child ends up reading with both sides of the brain letter reversals confusion with place value like the difference between 21 and 12 no intuitive sense of right and left he has to figure it out each time
What is the ATNR?
Definition When the head turns to the side, the arm and leg on that side extend, and the hand on that side opens. Simultaneously, the arm and leg on the opposite side bend (flexion), and the hand on the opposite side forms a fist. When should it be integrated? Emerges at around 18 weeks in utero and is inhibited or suppressed between 6-8 months after birth, while awake. It persists till three and a half years while asleep. (Aung Kyaw Sein. Persistent Primitive Reflexes: A Prognostic Study on School-aged Children with Intellectual Disability, 217) ATNR with Line Diagram ATNR on a Wriggling Baby Coen the Fencer
Checking for ATNR Schilder Test
You may find it helpful to do this test on a neuro-typical child first, to get an idea of what the response should look like. The Schilder Test is as follows: 1. Explain and demonstrate what you are going to do. Tester stands behind the child and gives the instruction: In a moment, you will close your eyes and I will turn your head slowly first to one side and then the other, all you have to do is to keep your arms in exactly the same position as they are now; only your head moves. 2. Child assumes test posture.
Stand upright with feet together Arms held straight out in front at shoulder level Wrists are relaxed and hands floppy Eyes are closed
3. Test the child
Slowly turn childs head to one side until chin is over shoulder Pause for 10 seconds Move head back to midline, and pause. Slowly turn childs head to other side until chin is over shoulder Pause for 10 seconds Repeat on both sides
Indicators of the reflex include
movement of the arms in the same direction as the head turn dropping of the arms elbow bends swaying and loss of balance
Adapted from: Philips and Sheehy, Prevalence of Persistent Primary Reflexes and Motor Problems in Children with Reading Difficulties, 2004.
Test Ease in Crossing Midline
Check the childs ability to make a lazy-8, and check how she normally writes a regular 8. SeeCorpus Callosum for a description of test.
Test Ear and Eye Dominance
See the Ear Dominance and Eye Dominance pages respectively. A child with a retained ATNR will often not have established dominance, so you could expect the child to choose L on some of the tests, and R on others.
Test for Unestablished Hand Dominance
Present all objects at midline (belly button). Do not let child know you are checking which hand he uses. Hand preference (uses the same hand 60% of the time) should be established by age 3-4, and hand dominance should be established by 5-6. Lack of established hand dominance is a symptom of a retained ATNR. Print out the below list, and circle which hand child uses. Gross Motor L L L L R R R R Touch your nose Hold up three fingers. Sword fight with a stick Tap two pencils together 3x. Which hand is moving? If a child over the age of 5 moves both hands,
that is a strong indicator of unestablished dominance. Fine Motor L L L L L R R R R R Six chocolate chips in a row straight out from belly button pick each one up and eat it Open container Twirl top Sort beads divide them in piles based on shape and color Blow bubbles which hand hold the wand
Skilled Activities L L L L L L L L L L L R R R R R R R R R R R Throw ball Eat with fork or spoon Drink with cup Cut with a knife (no fork involved) Cut with scissors Hammer Sew Comb hair Sweep with broom (upper hand) Toothbrush Write
The writing hand is the worst way to check, because it is so often culturally influenced. So check which hand is used for multiple activities. Mixed hand dominance could be caused by being genetically left in a right-handed society, or by the prenatal environment, or by an unknown cause, or by a retained ATNR.
What To Do About Retained ATNR Exercises
If you see symptoms of a retained ATNR in an older child, you can attack the problem from multiple angles. Itd be best to work from all three angles concurrently. 1. Work on Integrating Reflex Directly Integration of Infant Dynamic and Postural Reflex Patterns, by Svetlana Masgutova, Ph.D. If your child has more than one retained reflex, it is worth getting this manual. The Robot, as shown by AdahCampany, also known as the Lizard Bow and Arrow, as shown by KeiserNeuro ATNR Marionette, as shown by PlanForLearning Hippy Sitting, as shown by PlanForLearning Say Hi, as described by Grinden. This is similar to Eat the Ball, as shown by eentaliges30. Lie on back with arms and legs parallel to sides. Turn head all the way so the ear touches the floor, and greet the imaginary neighbor on the left. Then turn head back to midline, pause, then turn head all the way to the right. Repeat.
2. Work on Increasing Communication Between Hemispheres See Corpus Callosum. 3. Work on Vision See Convergence See Horizontal Tracking Pursuits and Saccades
Studies on Retained ATNR in Dyslexia and ADHD
These three sites show the following: 1. Those with poor reading are more likely to have a retained ATNR. 2. Work with specific exercises, and the ATNR integrates. The study used the INPP movement sequence. 3. As the ATNR integrates, reading improves. Prevalence of persistent primary reflexes and motor problems in children with reading difficulties Three groups of 41 children were drawn from a representative, cross-sectional sample of 409 children (aged 9 10 years) The three groups represented the bottom, middle and top 10% respectively of readers from the total sample population. The relative persistence (on a scale of 0 to 4) of the Asymmetrical Tonic Neck Reflex (ATNR) and the prevalence of motor difficulties were assessed for these 3 groups. It was found that the lowest reading group had a significantly higher mean level of ATNR . 17% of children in the lowest reading group had extremely high levels of the ATNR while 24% showed no presence of ATNR. Effects of replicating primary-reflex movements on specific reading difficulties in children: a randomised, double-blind, controlled trial Children (aged 811 years) with persistent primary reflexes and a poor standard of reading were enrolled into one of three treatment groups: experimental (children were given a specific movement sequence); placebocontrol (children were given non-specific movements); and control (no movements). The experimental group showed a significant decrease in the level of persistent reflex over the course of the study whereas the changes in the placebo-control and control groups were not significant. Primary Movement Program and Dyslexia Researchers from the Dept of Psychology, Queens University, Belfast began research into the effect of such movements on the performance of dyslexic children and completed in 1999. It involved dyslexic children between the ages of 8 and 11. There were three groups; one experimental, one control and one placebo. After one year on the program, the reading ages were retested using the Neale Analysis of Reading Ability. The control and placebo groups had average increases to their reading ages of 7 months
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Attention, Balance and Coordination: The A.B.C. of Learning SuccessVon EverandAttention, Balance and Coordination: The A.B.C. of Learning SuccessNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primitive Reflexes and How They Affect PerformanceDokument3 SeitenPrimitive Reflexes and How They Affect Performancemohitnet1327100% (1)
- Essential Mechanisms in Neurological Pediatric RehabilitationVon EverandEssential Mechanisms in Neurological Pediatric RehabilitationNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4sb Reflex InfographicDokument1 Seite4sb Reflex Infographicvombyandi100% (1)
- A Field Guide to Sensory Motor Integration: The Foundation for LearningVon EverandA Field Guide to Sensory Motor Integration: The Foundation for LearningNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primitive Reflex Free GuideDokument22 SeitenPrimitive Reflex Free Guideristeacristi100% (2)
- Assessing Neuromotor Readiness for Learning: The INPP Developmental Screening Test and School Intervention ProgrammeVon EverandAssessing Neuromotor Readiness for Learning: The INPP Developmental Screening Test and School Intervention ProgrammeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Infant ReflexesDokument2 SeitenInfant ReflexesJose Raphael Delos SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Rhythmic Movement Method: A Revolutionary Approach to Improved Health and Well-BeingVon EverandThe Rhythmic Movement Method: A Revolutionary Approach to Improved Health and Well-BeingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primitive ReflexesDokument10 SeitenPrimitive Reflexesbun_yulianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrating ReflexesDokument2 SeitenIntegrating ReflexesAna G. VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masgutova MethodDokument7 SeitenMasgutova MethodDisha SolankiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integrating ReflexesDokument2 SeitenIntegrating ReflexesAbigail Tan100% (2)
- Integrating Primitive ReflexesDokument5 SeitenIntegrating Primitive Reflexesmohitnet132780% (5)
- Rhythmic Movement Training International - Primitive ReflexesDokument4 SeitenRhythmic Movement Training International - Primitive ReflexesIris De La Calzada0% (2)
- Neuro Senso Motor Reflek IntegrationDokument19 SeitenNeuro Senso Motor Reflek Integrationajeng fisio100% (1)
- Masgutova Neurosensorimotor Integration MethodDokument14 SeitenMasgutova Neurosensorimotor Integration MethodristeacristiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primitive Reflexes and Righting Reactions - Dave BergerDokument13 SeitenPrimitive Reflexes and Righting Reactions - Dave BergerAdmir0% (1)
- Primitive ReflexesDokument85 SeitenPrimitive ReflexesBernadette hauw90% (10)
- Integrating NDT and SI-Theory and PracticeDokument7 SeitenIntegrating NDT and SI-Theory and PracticePaulinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early Development Sensory Integration Processes and Communication DevelopmentDokument75 SeitenEarly Development Sensory Integration Processes and Communication DevelopmentCarmen Llerenas100% (3)
- Chapter 1Dokument12 SeitenChapter 1mohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Neurodevelopmental Therapy Inhibition of Primitive ReflexesDokument11 SeitenNeurodevelopmental Therapy Inhibition of Primitive ReflexesZoran Constantinescu80% (5)
- Primitive RefelexDokument24 SeitenPrimitive RefelexGokul SriniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Affects of Reflexes and Sensory Systems On Gross Motor SkillsDokument43 SeitenThe Affects of Reflexes and Sensory Systems On Gross Motor SkillsΒασίλης ΒασιλείουNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory Integration and Learning Disabilities Ayres' Factor Analyses ReappraisedDokument9 SeitenSensory Integration and Learning Disabilities Ayres' Factor Analyses ReappraisedFernanda PratesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infant ReflexesDokument41 SeitenInfant ReflexesamwriteaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro Motor Readiness Pl2011Dokument94 SeitenNeuro Motor Readiness Pl2011mohitnet1327100% (3)
- Babkin Palmomental ReflexTextDokument3 SeitenBabkin Palmomental ReflexTextdankopsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflex Testing Method For Evaluating CNS DevelopmentDokument55 SeitenReflex Testing Method For Evaluating CNS DevelopmentPJHG100% (6)
- Sensory IntegrationDokument5 SeitenSensory IntegrationcrownesyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cap 1 Sensory Integration Theory and PracticeDokument33 SeitenCap 1 Sensory Integration Theory and PracticeLuz Dianeth ZapataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bu Windsor - Rhythmic Movement Training - Sabbatical Report 2020Dokument21 SeitenBu Windsor - Rhythmic Movement Training - Sabbatical Report 2020John Lock100% (1)
- Hypotonia in ChildrenDokument12 SeitenHypotonia in Childrenrosiuariana100% (2)
- OT Relevance RMTDokument12 SeitenOT Relevance RMTFredy RamoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory Integration ModuleDokument48 SeitenSensory Integration ModuleMadhu sudarshan ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Working With Children With Atypical Tone 07Dokument37 SeitenWorking With Children With Atypical Tone 07Martha FrankNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Gross Motor (PT)Dokument63 SeitenManagement of Gross Motor (PT)Xulkanain ZENoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review of Pediatric Assessment Tools For Sensory Integration AOTADokument3 SeitenA Review of Pediatric Assessment Tools For Sensory Integration AOTAhelenzhang888Noch keine Bewertungen
- INPP ProgramDokument14 SeitenINPP ProgramVardhman Jain100% (1)
- Primitive ReflexesDokument3 SeitenPrimitive Reflexesicrs_aamirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16: Application of Motor Control and Motor LearningDokument8 SeitenChapter 16: Application of Motor Control and Motor LearningJireh Chambers100% (1)
- Low Muscle Tone, Muscle Weakness or Poor Learning Strategies?Dokument5 SeitenLow Muscle Tone, Muscle Weakness or Poor Learning Strategies?Ruztiqa Kasih Pramudya VardaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflex Testing Methods For Evaluating CNS DevelopmentDokument80 SeitenReflex Testing Methods For Evaluating CNS DevelopmentTaufik100% (4)
- Persistence of Primitive Reflexes in Developmental DisordersDokument8 SeitenPersistence of Primitive Reflexes in Developmental DisordersGeotamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory Motor IntegrationDokument8 SeitenSensory Motor IntegrationAdelinaPanaetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using Sensory Integration andDokument9 SeitenUsing Sensory Integration andVero MoldovanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Estrategias Conductuales ASDDokument66 SeitenEstrategias Conductuales ASDSuperfixenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cerebral PalsyDokument23 SeitenCerebral Palsyane2sa100% (1)
- Fear Paralysis ReflexDokument2 SeitenFear Paralysis ReflexIris De La CalzadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatment Approaches For A CP ChildDokument17 SeitenTreatment Approaches For A CP Childpraveen0% (1)
- An Integrated Approach - in Every SenseDokument4 SeitenAn Integrated Approach - in Every SenseSpeech & Language Therapy in PracticeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PrimitiveReflexes Low VisionDokument8 SeitenPrimitiveReflexes Low Visionmohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ota Watertown Si Clinical Assessment WorksheetDokument4 SeitenOta Watertown Si Clinical Assessment WorksheetPaulinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primitive Reflexes RoadmapDokument6 SeitenPrimitive Reflexes RoadmapLőrincz TündeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory Integration PDFDokument1 SeiteSensory Integration PDFmofasorgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ot and VisionDokument25 SeitenOt and Visionapi-433536062100% (1)
- Avoiding Double SubjectsDokument2 SeitenAvoiding Double SubjectsManuel Garcia GrandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Development of Infants and Toddlers: Prepared By: Cedrick A. Caintic & WalocDokument15 SeitenPhysical Development of Infants and Toddlers: Prepared By: Cedrick A. Caintic & WalocMildred Gonzales SumalinogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primitive ReflexesDokument6 SeitenPrimitive ReflexesMarikit2012100% (1)
- Shadi Resume 2Dokument2 SeitenShadi Resume 2mohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shadi ResumeDokument1 SeiteShadi Resumemohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Color Tracking 1-1Dokument1 SeiteColor Tracking 1-1mohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shadi ResumeDokument1 SeiteShadi Resumemohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Meta-Analysis of Cognitive Remediation in SchizophreniaDokument12 SeitenA Meta-Analysis of Cognitive Remediation in Schizophreniamohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mobilization Techniques in Subjects With Frozen Shoulder Syndrome 2Dokument1 SeiteMobilization Techniques in Subjects With Frozen Shoulder Syndrome 2mohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carolyn T Wadsworth: Frozen Shoulder 1Dokument1 SeiteCarolyn T Wadsworth: Frozen Shoulder 1mohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- En Abre Cov ChapterDokument15 SeitenEn Abre Cov Chaptermohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- 97 319 1 PBDokument10 Seiten97 319 1 PBmohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aaseesment Scale For Cog RehabDokument9 SeitenAaseesment Scale For Cog Rehabmohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spinal Cord Brain Sensory Receptors Central Nervous SystemDokument2 SeitenSpinal Cord Brain Sensory Receptors Central Nervous Systemmohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Musculoskeletal Disorder Risk Assessment in Small Scale Forging Industry by Using RULA MethodDokument6 SeitenMusculoskeletal Disorder Risk Assessment in Small Scale Forging Industry by Using RULA Methodmohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Names:: Group Building Activities Stage 1: OrientationDokument4 SeitenLearning Names:: Group Building Activities Stage 1: Orientationmohitnet1327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Problem Solving and Decision MakingDokument46 SeitenEffective Problem Solving and Decision Makingmohitnet1327100% (3)
- Smart System For Potholes Detection Using Computer Vision With Transfer LearningDokument9 SeitenSmart System For Potholes Detection Using Computer Vision With Transfer LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Employee Empowerment and Interpersonal Interventions: An Experiential Approach To Organization Development 8 EditionDokument69 SeitenEmployee Empowerment and Interpersonal Interventions: An Experiential Approach To Organization Development 8 EditionjocaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group-8 Filipino-ScientistsDokument11 SeitenGroup-8 Filipino-ScientistsAljondear RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neha Ajay UpshyamDokument2 SeitenNeha Ajay UpshyamSantoshKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- QF Plumber Cts Nsqf-4Dokument31 SeitenQF Plumber Cts Nsqf-4Pta NahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDT 323 Ass # 1-LeeDokument7 SeitenEDT 323 Ass # 1-LeeLeedon HepoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal KingdomDokument5 SeitenAnimal KingdomArthav KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Units 4, 5, 6Dokument9 SeitenTest Units 4, 5, 6Roxana StoianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scholarly Writing and Publishing PrincipleDokument13 SeitenScholarly Writing and Publishing PrincipleEdessa MasinasNoch keine Bewertungen
- JD For Digital Marketing Specialist TQH and YLAC Apr23Dokument2 SeitenJD For Digital Marketing Specialist TQH and YLAC Apr23Naveed HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Julian Sowa General ResumeDokument1 SeiteJulian Sowa General Resumeapi-336812856Noch keine Bewertungen
- Prim Maths 5 2ed TR End of Year Test AnswersDokument3 SeitenPrim Maths 5 2ed TR End of Year Test Answersheyansh.kohliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journey As A LibrarianDokument2 SeitenJourney As A LibrarianKritika SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- WLP - English 7 - Week 1Dokument4 SeitenWLP - English 7 - Week 1Judith GuillermoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Task - SPSS InterpretationsDokument14 SeitenPsychology Task - SPSS InterpretationsAmna HayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qdoc - Tips Physical Metallurgy Principles and Practice ThirdDokument2 SeitenQdoc - Tips Physical Metallurgy Principles and Practice ThirdAkhil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 57: Health AssessmentDokument2 SeitenNCM 57: Health AssessmentEmvie Loyd Pagunsan-ItableNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aviral Mishra: Education SkillsDokument1 SeiteAviral Mishra: Education SkillsAVIRAL MISHRANoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Process: Presented By:-Aditi GargDokument12 SeitenResearch Process: Presented By:-Aditi Gargpllau33Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Habits in Short 1Dokument30 Seiten7 Habits in Short 1api-3725164Noch keine Bewertungen
- SO E U1 TestBDokument1 SeiteSO E U1 TestBTess DurbervilleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questionnaire Échelle Subjective Lysholm GilquistDokument5 SeitenQuestionnaire Échelle Subjective Lysholm GilquistHoudhaifa KlaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeroom Guidance Learner'S Development Assessment School Year 2021 - 2022 GRADE 4-6 (Intermediate Level) Cherry Belle F. Del Rosario, Ed.DDokument2 SeitenHomeroom Guidance Learner'S Development Assessment School Year 2021 - 2022 GRADE 4-6 (Intermediate Level) Cherry Belle F. Del Rosario, Ed.Dpatrick henry paltepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diss 14Dokument4 SeitenDiss 14Marc EstañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 002LLI Castillo LTDokument6 Seiten002LLI Castillo LTJohnny AbadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coaching Philosophy PortfolioDokument2 SeitenCoaching Philosophy PortfolioBella BastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 13 (Managing TheDokument14 SeitenChapter 13 (Managing TheGizelle AlviarNoch keine Bewertungen
- National Strength and Conditioning Association.1Dokument19 SeitenNational Strength and Conditioning Association.1Joewin EdbergNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume of Mohammad Arif MohiuddinDokument3 SeitenResume of Mohammad Arif MohiuddinMohammad Arif Mohiuddin100% (1)
- Characteristics of PlanningDokument11 SeitenCharacteristics of PlanningNajeeb khan100% (1)
- Relentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableVon EverandRelentless: From Good to Great to UnstoppableBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (788)
- Power of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionVon EverandPower of 10: The Once-A-Week Slow Motion Fitness RevolutionBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (11)
- Functional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindVon EverandFunctional Training and Beyond: Building the Ultimate Superfunctional Body and MindBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (1)
- Chair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouVon EverandChair Yoga: Sit, Stretch, and Strengthen Your Way to a Happier, Healthier YouBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (5)
- Aging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayVon EverandAging Backwards: Reverse the Aging Process and Look 10 Years Younger in 30 Minutes a DayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingVon EverandBoundless: Upgrade Your Brain, Optimize Your Body & Defy AgingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (67)
- Strong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerVon EverandStrong Is the New Beautiful: Embrace Your Natural Beauty, Eat Clean, and Harness Your PowerBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Which Comes First, Cardio or Weights?: Fitness Myths, Training Truths, and Other Surprising Discoveries from the Science of ExerciseVon EverandWhich Comes First, Cardio or Weights?: Fitness Myths, Training Truths, and Other Surprising Discoveries from the Science of ExerciseBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (47)
- Strength Training Over 40: The Only Weight Training Workout Book You Will Need to Maintain or Build Your Strength, Muscle Mass, Energy, Overall Fitness and Stay Healthy Without Living in the GymVon EverandStrength Training Over 40: The Only Weight Training Workout Book You Will Need to Maintain or Build Your Strength, Muscle Mass, Energy, Overall Fitness and Stay Healthy Without Living in the GymBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- Pranayama: The Yoga Science of BreathingVon EverandPranayama: The Yoga Science of BreathingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (8)
- Own the Day, Own Your Life: Optimized Practices for Waking, Working, Learning, Eating, Training, Playing, Sleeping, and SexVon EverandOwn the Day, Own Your Life: Optimized Practices for Waking, Working, Learning, Eating, Training, Playing, Sleeping, and SexBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (646)
- Peak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsVon EverandPeak: The New Science of Athletic Performance That is Revolutionizing SportsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (97)
- The Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessVon EverandThe Yogi Code: Seven Universal Laws of Infinite SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (104)
- Calisthenics: Guide for Bodyweight Exercise, Build your Dream Body in 30 MinutesVon EverandCalisthenics: Guide for Bodyweight Exercise, Build your Dream Body in 30 MinutesBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (5)
- True Yoga: Practicing With the Yoga Sutras for Happiness & Spiritual FulfillmentVon EverandTrue Yoga: Practicing With the Yoga Sutras for Happiness & Spiritual FulfillmentBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (22)
- Light on Yoga: The Definitive Guide to Yoga PracticeVon EverandLight on Yoga: The Definitive Guide to Yoga PracticeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Somatic Exercises for Beginners: Transform Your Life in 30 Days with Personalized Exercises for Body and MindVon EverandSomatic Exercises for Beginners: Transform Your Life in 30 Days with Personalized Exercises for Body and MindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!Von EverandMuscle for Life: Get Lean, Strong, and Healthy at Any Age!Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (22)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: Built for This: The Quiet Strength of PowerliftingBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (133)
- Not a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Von EverandNot a Diet Book: Take Control. Gain Confidence. Change Your Life.Bewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (7)
- Yoga Nidra: The Art of Transformational SleepVon EverandYoga Nidra: The Art of Transformational SleepBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (24)
- Yin Yoga: How to Enhance Your Modern Yoga Practice With Yin Yoga to Achieve an Optimal Mind-Body Connection: Yoga Mastery SeriesVon EverandYin Yoga: How to Enhance Your Modern Yoga Practice With Yin Yoga to Achieve an Optimal Mind-Body Connection: Yoga Mastery SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wheels of Life: A User's Guide to the Chakra SystemVon EverandWheels of Life: A User's Guide to the Chakra SystemBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (34)
- The Big Book of Endurance Training and RacingVon EverandThe Big Book of Endurance Training and RacingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (6)
- Mind Your Body: 4 Weeks to a Leaner, Healthier LifeVon EverandMind Your Body: 4 Weeks to a Leaner, Healthier LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- Enter The Kettlebell!: Strength Secret of the Soviet SupermenVon EverandEnter The Kettlebell!: Strength Secret of the Soviet SupermenBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (29)
- Yamas & Niyamas: Exploring Yoga's Ethical PracticeVon EverandYamas & Niyamas: Exploring Yoga's Ethical PracticeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (111)