Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
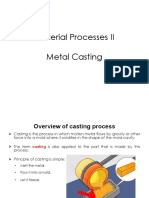
Casting
Hochgeladen von
Tasnim ArifCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Casting
Hochgeladen von
Tasnim ArifCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
METAL CASTING
CHAPTER CONTENTS
1.1 Overview of Casting Technology Definitions Casting nomenclature Heating and pouring Solidification and cooling Casting Processes Expandable mold casting Permanent mold casting Casting quality
1.2 1.3
1.1
OVERVIEW OF CASTING TECHNOLOGY
Definitions
Casting is a process in which molten metal flows into a mold where it solidifies in the shape of the mold cavity. The part produced is also called casting. Complex shapes Net-shape ability Very large parts Variety of metals Mass production
Advantages
Poor accuracy Poor surface Disadvantages Internal defects Mechanical properties Environmental impact Casting technology involves the next steps:
Mold preparation Metal heating Pouring Cooling Processing
Selection of castings of various materials, shapes, and sizes
Casting nomenclature
The figure in the right shows the nomenclature of mold and castings in sand casting.
Casting nomenclature
Metal Casting
Valery Marinov, Manufacturing Technology
Pouring cup
The pouring cup, downsprue, runners, etc., are known as the mold gating system, which serves to deliver the molten metal to all sections of the mold cavity.
Downsprue Gates to casting Runner Runner extension Runner well
Heating and pouring
Heating The total heat required is estimated as the sum of Pouring Major factors affecting the pouring action Pouring temperature Pouring rate Turbulence
Downsprue well
Gating system in sand casting
Heat to raise the temperature to the melting point Heat of fusion Heat to raise the molten metal temperature to the temperature of pouring
Some important equations in pouring: Velocity of the liquid metal at the base of the sprue: Volumetric flow rate: Mold filling time:
v
Gravitational acceleration constant
2 gh
Sprue height
Q = vA
Castings cross-sectional area
MFT = V/Q
Mold cavity volume
Fluidity Fluidity is a measure of the capability of a metal to flow into and to fill the mold before freezing. It defines to the great extend the quality of casting. Factors affecting fluidity: Pouring temperature Metal composition Heat transfer to the surroundings Viscosity of the liquid metal Standard testing method
Pouring cup
Downsprue
Limit of flow before freezing
Spiral mold
In the foundry practice, test for fluidity is carried out for each ladle just before pouring the molten metal into the mold
Valery Marinov, Manufacturing Technology
Metal Casting
Solidification and cooling
Solidification of metals Pure metals solidify at a constant temperature equal to their freezing point
Most alloys freeze over a temperature range
Solidification time Chvorinovs rule
TST Cm
V A
TSTtotal solidification time Cmmold constant Vvolume of the casting Asurface area of the casting nconstant, usually n=2
Example: Calculate the total solidification time for a 10/100/200-mm steel plate if Cm = 0.2 min/mm2 Solution:
Metal Casting
Valery Marinov, Manufacturing Technology
Shrinkage
Directional solidification By a proper design of the casting By external and internal chills
Riser design Several riser designs are used in practice as shown in the figure. The riser must remain molten until after the casting solidifies. The Chvorinovs Rule is used to calculate the risers dimensions.
Riser design Open Blind
Riser
Mold
Riser
Mold
Top
Casting
Casting
Riser
Mold
Riser
Mold
Side
Casting
Casting
Possible types and positions for risers in sand casting
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- FUNDAMENTALS OF METAL CASTING (Autosaved)Dokument45 SeitenFUNDAMENTALS OF METAL CASTING (Autosaved)İREM TaşlıNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Metal CastingDokument39 SeitenFundamentals of Metal CastingYASHFEEN AYUBBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Metal CastingDokument45 SeitenFundamentals of Metal CastingsuntharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valery Marinov, Manufacturing TechnologyDokument168 SeitenValery Marinov, Manufacturing TechnologyAbir Roy100% (3)
- Ch10 Casting Fund WileyDokument38 SeitenCh10 Casting Fund WileyAbdur Rahman SultanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and CoolingDokument37 SeitenFundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and CoolingSachin RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valery Marinov Manufacturing Technology PDFDokument168 SeitenValery Marinov Manufacturing Technology PDFMostafa Adil50% (2)
- Chapter Ten - Fundamental of Metal CastingDokument35 SeitenChapter Ten - Fundamental of Metal CastingWael W. AlsousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casting in Manufacturing ProcessesDokument106 SeitenCasting in Manufacturing ProcessesAhsan MukhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundry and Casting OperationDokument176 SeitenFoundry and Casting OperationABHINAV KUMAR ROY100% (26)
- L5-Fundamentals of Metal CastingDokument22 SeitenL5-Fundamentals of Metal CastingKhayrulIslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and CoolingDokument40 SeitenFundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and Coolingalemu170Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To CastingDokument16 SeitenIntroduction To CastingOkari100% (1)
- Lecture 2 - Manufacturing Processes - Fundamentals of Metal Casting and Casting Design - DR Bilal AhmadDokument99 SeitenLecture 2 - Manufacturing Processes - Fundamentals of Metal Casting and Casting Design - DR Bilal Ahmadjawad khalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 1and3 2Dokument110 Seiten3 1and3 2MPRajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2nd Class Notes 17.01Dokument48 Seiten2nd Class Notes 17.01EDISON OCHIENGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Casting: Weeks 1 - 2Dokument125 SeitenMetal Casting: Weeks 1 - 2obvertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing Processes Ch.4 (10 and 11) CastingDokument143 SeitenManufacturing Processes Ch.4 (10 and 11) Castingashoku24007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Casting Lectures NotesDokument125 SeitenMetal Casting Lectures NotesSabir AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Casting: Compiled By: Norliana Mohd AbbasDokument34 SeitenMetal Casting: Compiled By: Norliana Mohd AbbasAziful AimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1st Class 13.01.2020Dokument18 Seiten1st Class 13.01.2020EDISON OCHIENGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: - Overview of Casting Technology - Heating and Pouring - Solidification and CoolingDokument35 SeitenFundamentals of Metal Casting: - Overview of Casting Technology - Heating and Pouring - Solidification and Coolingb0zzch4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Foundry CourseDokument62 SeitenFoundry CoursePradip Gupta0% (1)
- Casting Lecture NoteDokument12 SeitenCasting Lecture NoteHARIMETLYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 Casting IDokument38 SeitenChapter 10 Casting IMinhaj UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Casting TechnologyDokument5 SeitenOverview of Casting TechnologySK Kushwah RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casting Processes: March 2020Dokument26 SeitenCasting Processes: March 2020Bhavin DesaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Casting I: Manufacturing ProcessesDokument36 SeitenMetal Casting I: Manufacturing Processesavinash 879Noch keine Bewertungen
- Peleburan & Pengecoran Logam: (Ir. Abrianto Akuan, MT.)Dokument48 SeitenPeleburan & Pengecoran Logam: (Ir. Abrianto Akuan, MT.)b0zzch4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: 1. Overview of Casting Technology 2. Heating and Pouring 3. Solidification and CoolingDokument32 SeitenFundamentals of Metal Casting: 1. Overview of Casting Technology 2. Heating and Pouring 3. Solidification and CoolingAkash GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Metal CastingDokument18 SeitenFundamentals of Metal CastingtmcoachingcentreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manu Fact Ech Lecture 2 and 3Dokument125 SeitenManu Fact Ech Lecture 2 and 3Sasi aeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casting Processes CompleteDokument49 SeitenCasting Processes CompleteRavi KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- IE 337 W10 Lecture 7.casting 1Dokument48 SeitenIE 337 W10 Lecture 7.casting 1linkinunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 2castingpdfDokument26 SeitenLec 2castingpdfHải TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal Casting Dies: Thoguluva Raghavan VijayaramDokument4 SeitenMetal Casting Dies: Thoguluva Raghavan VijayaramcombinationcoffeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 1 Metal Casting Processes-NVRDokument287 SeitenUnit - 1 Metal Casting Processes-NVRPrashon GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5Dokument14 SeitenChapter 5Phuc Truong DucNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting CastingDokument6 SeitenFactors Affecting CastingMuhammad BilalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Surface & Sub Surface Control of Cast Iron ComponentsDokument22 SeitenSurface & Sub Surface Control of Cast Iron ComponentsAditya PratapNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casting - Lec 2.2Dokument17 SeitenCasting - Lec 2.2Ahmed MahmoudNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solidification Analysis in Continuous Casting Process - Barman TambunanDokument11 SeitenSolidification Analysis in Continuous Casting Process - Barman TambunanBarman TambunanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATEMfg LatestDokument210 SeitenGATEMfg LatestniteshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casting: 2.810 Prof. Timothy GutowskiDokument65 SeitenCasting: 2.810 Prof. Timothy GutowskiRoberto LaurindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and CoolingDokument30 SeitenFundamentals of Metal Casting: Overview of Casting Technology Heating and Pouring Solidification and Coolingchincha chuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casting Manufacturing Processes Fundamentals of Metal Casting Metals For CastingDokument47 SeitenCasting Manufacturing Processes Fundamentals of Metal Casting Metals For CastingarobaidiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casting ProcessesDokument48 SeitenCasting ProcessessumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal CastingDokument22 SeitenMetal CastingANKIT RAJNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE MFG LatestDokument210 SeitenGATE MFG LatestRanjan Kumar PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter10 PDFDokument42 SeitenChapter10 PDFJayson SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic of Metal CastingDokument80 SeitenBasic of Metal CastingJayant ChaudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacturing Processes-I (TA 201A) : 6 Credit CourseDokument44 SeitenManufacturing Processes-I (TA 201A) : 6 Credit Coursejamessupermann1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Casting PDFDokument48 SeitenCasting PDFsanjay_lingotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enme 331-Fundamentals of CastingDokument48 SeitenEnme 331-Fundamentals of CastingAhmed AbdulrhmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal-Casting Processes and EquipmentDokument48 SeitenMetal-Casting Processes and EquipmenttemesgenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.1 Casting ProcessDokument4 Seiten3.1 Casting Processزينب عبد الخالق كاملNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thixoforming: Semi-solid Metal ProcessingVon EverandThixoforming: Semi-solid Metal ProcessingGerhard HirtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Welding Engineering: Processes, Codes, and StandardsVon EverandApplied Welding Engineering: Processes, Codes, and StandardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to the Physical Metallurgy of WeldingVon EverandIntroduction to the Physical Metallurgy of WeldingBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Ngineering Rogramme Ohort Emester Odule Ssignment OF Fluid DrivesDokument2 SeitenNgineering Rogramme Ohort Emester Odule Ssignment OF Fluid DrivesTasnim ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inventor and Its Applications Chapter 1: Introduction To Autodesk InventorDokument4 SeitenInventor and Its Applications Chapter 1: Introduction To Autodesk InventorTasnim ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Darshan R. Kanjiya: KSKV Kachchh UniversityDokument31 SeitenDarshan R. Kanjiya: KSKV Kachchh UniversityTasnim ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved Numericals On Heat Conduction and Extended Heat SurfaceDokument20 SeitenSolved Numericals On Heat Conduction and Extended Heat SurfaceTasnim ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat ExchangerDokument26 SeitenHeat ExchangerTasnim Arif100% (2)
- Applications and Processing of CeramicsDokument17 SeitenApplications and Processing of CeramicsTasnim Arif100% (1)
- Me e 211 Handouts 09Dokument8 SeitenMe e 211 Handouts 09Tasnim ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yaesu VR 120Dokument44 SeitenYaesu VR 120Chema MelidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eaturing: To Smaller Recording Performance Speakers: - The GuideDokument76 SeitenEaturing: To Smaller Recording Performance Speakers: - The GuideMatthew WalkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Life-Saving Rules: Tool Box Talk SeriesDokument86 SeitenLife-Saving Rules: Tool Box Talk SeriesSalahBouzianeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSMT Solution ManualDokument12 SeitenSSMT Solution ManualPraahas Amin0% (1)
- 7.sieve Analysis AhmedDokument9 Seiten7.sieve Analysis AhmedJin AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Programming in C++ For BCA BIT BE PDFDokument129 SeitenProgramming in C++ For BCA BIT BE PDFRajan BagaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Assignment - Aritificial LiftDokument10 SeitenOnline Assignment - Aritificial LiftfatenamiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment No. 1: Aim: Study of Tanner Tools THEORY: Tanner ToolsDokument24 SeitenExperiment No. 1: Aim: Study of Tanner Tools THEORY: Tanner ToolsVarun GargNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecen 607 CMFB-2011Dokument44 SeitenEcen 607 CMFB-2011Girish K NathNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALL SYSTEMS GO by Zenovia AndrewsDokument225 SeitenALL SYSTEMS GO by Zenovia AndrewsTanya Gillie100% (3)
- Value Creation Through Project Risk ManagementDokument19 SeitenValue Creation Through Project Risk ManagementMatt SlowikowskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bomba Submersa FE - Petro STPDokument6 SeitenBomba Submersa FE - Petro STProbsonlagambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revista Stiinte Politice Issue 42Dokument264 SeitenRevista Stiinte Politice Issue 42Costel111Noch keine Bewertungen
- Guideline On Smacna Through Penetration Fire StoppingDokument48 SeitenGuideline On Smacna Through Penetration Fire Stoppingwguindy70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Xpulse200t Manual de PartesDokument92 SeitenXpulse200t Manual de PartesAthiq Nehman100% (2)
- Project Goals/ ObjectivesDokument51 SeitenProject Goals/ ObjectivesJoyce Abegail De PedroNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenSAP Byd4 Week 5 Unit 5 Additional ExerciseDokument2 SeitenOpenSAP Byd4 Week 5 Unit 5 Additional ExerciseHong YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selected Books For Electronic Hobby Center (EHC) : A. Books (Available in The Resource Centre)Dokument9 SeitenSelected Books For Electronic Hobby Center (EHC) : A. Books (Available in The Resource Centre)Rajalakshmi BashyamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mass Flow SensorDokument0 SeitenMass Flow Sensorwong_arifNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6seater Workstation B2BDokument1 Seite6seater Workstation B2BDid ProjectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Journal Approval WorkflowDokument46 SeitenJournal Approval Workflowvarachartered283Noch keine Bewertungen
- ASME B16.47 Series A FlangeDokument5 SeitenASME B16.47 Series A FlangePhạm Trung HiếuNoch keine Bewertungen
- KEDA Quotation of 2 3 4 Inch Mini Gold DredgerDokument3 SeitenKEDA Quotation of 2 3 4 Inch Mini Gold DredgerShane CapstickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kendriya Vidyalaya, Tagore Garden Recruitment of Contractual Teachers For The Session 2013-14Dokument8 SeitenKendriya Vidyalaya, Tagore Garden Recruitment of Contractual Teachers For The Session 2013-14ombidasarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - 1935 Rife Ray #4 Rife MachineDokument2 SeitenChapter 8 - 1935 Rife Ray #4 Rife MachineKhalid IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atoll 3.3.2 Technical Reference Guide RadioDokument912 SeitenAtoll 3.3.2 Technical Reference Guide Radioratelekoms100% (4)
- Domus Ventilation Guide 2019Dokument96 SeitenDomus Ventilation Guide 2019Regie CayasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bangkok-Singapore CDM JournalDokument20 SeitenBangkok-Singapore CDM JournalvasidhartaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turnitin Originality ReportDokument47 SeitenTurnitin Originality ReportStillward Laud Mark-MillsNoch keine Bewertungen