Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
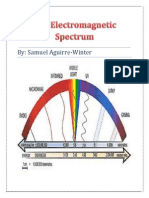
Year 10-Electromagnetic Spectrum Research Ayesha Khan, 10M1 Radio Waves
Hochgeladen von
Sanah KhanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Year 10-Electromagnetic Spectrum Research Ayesha Khan, 10M1 Radio Waves
Hochgeladen von
Sanah KhanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Year 10-Electromagnetic Spectrum Research Ayesha Khan, 10M1 Radio Waves: The highest wavelength is 1-2 km.
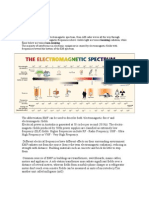
Radio wave frequencies range from roughly 300 000 Hz to 3000 million Hz. Radio waves are longer in frequency than microwaves. We use them to carry radio, mobile phone & TV signals. We can use radio waves instead of cables to connect computers to printers, etc. For example, devices with Bluetooth are able to share media, etc, provided that they are within a 10m range of each other. This is done through the use of radio waves. We use radio waves because they are longer in wavelength and lower in frequency than microwaves. Its speed in a vacuum is 300,000km/s or 300 million m/s. However, large doses are said to cause cancer (ie through mobile phone use). They were first predicted by a man called James Clerk Maxwell in 1867. He noticed wavelike properties of light and similarities in electric and magnetic observations by generating radio waves in his lab. Lots of inventions followed his amazing discovery, ie transferring radio waves through space.
Microwaves: Microwaves lie between radio waves and infrared radiation in the EM Spectrum. They have a shorter wavelength than radio waves. We can use them to carry mobile phone signals, because microwaves dont diffract as much as radio waves. They are also used in satellite TV because they are able to penetrate the Earths atmosphere and travel through a vacuum. Also, they can be used to beam signals from one place to another. Its speed in a vacuum is 300,000 km/s or 300 million m/s. However, microwaves can cause internal heating of the cells. Usually have a wavelength of a couple of cm. Can also be used for radar, fixed traffic cameras, etc. However, too much exposure to them can lead to cataracts in the eye. Furthermore, research suggests that it may affect the brain in some ways, especially those of young children, as their skulls are thinner, and it is easier for microwaves to penetrate their skulls. It was discovered accidentally in 1945, after high powered microwave radar transmitters were developed by WWII, using British technology shared with US company. Percy Spencer, an engineer from Maine, worked at the time. He was working on an active radar set when his colleagues chocolate bar in his pocket began to melt due to the microwaves. The first food to be deliberately cooked with Spencers microwave was popcorn, the second an egg. The first time the public could use a microwave was in 1947 when the first vending machine was placed in the Grand Central Terminal to dispense sizzling hot dogs.
Infra red radiation: There are many, many things infrared radiation can be used for. Firstly, it can be used for medicinal purposes; it locates the warmer areas of the body where tissues beneath could potentially be unhealthy or feverous. Another use of infrared is through police work or perhaps criminal investigations through a use of infrared cameras, sometimes known as thermal imagery. It enables us to see animals and people far more clearly in the dark than we normally would. Thirdly, it is used in communications systems in the form of optical fibres- They use infrared rather than light because infrared radiation would be absorbed less than light, and we want the signal/message to be as clear as possible, with as little absorption as possible. Also, it can be used in our remote control handsets for our TVs when signals are transmitted; whenever you click a button, a series of infrared pulses are sent out. However, infrared radiations can cause burns! It was discovered in 1800 by a Sir Frederick William Herschel. He decided to investigate the temperature of each colour of the spectrum produced when sunlight is passed through a prism. To do this, he used three thermometers whose bulbs were black. One bulb was placed directly in the colour and the other two past the spectrum. He noticed two things: the temperature of the thermometer placed in colour was bigger than controls, and that there was a temp increase from violet to red. When he noticed the temp of the region beyond the red part of the spectrum was higher than the red itself. He called this calorific rays. He carried out further experiments to find out infrared radiation could be absorbed, transmitted, reflected and refracted.
Visible light: White light, as we know, contains all the colours of the spectrum; Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo and Violet. The wavelength increases as we get closer to the red side of the spectrum. We can see this if we split the light using a glass prism. In some professions, a clear understanding of visible light is crucial. For example, photographers; they need to know how shades and colours of light affect the exposure of the photographs. In a film camera, light is focused by the camera lens onto a light sensitive film, which then needs to be developed in order for you to see your photograph, whereas in a digital camera, light is focused by the lens onto a sensor, which consists of thousands of pixels. Each pixel represents one part of the image, so when we put them together, the image is formed- we can see this image on a small screen. When a photo is taken, the image is saved electronically onto a memory card. A problem/danger is that too much or bright light can damage your retina. The discovery stages are very interesting In 1666, Newton passed sunlight through a prism and watched it break into a kaleidoscope of colours. Just like the wavelength differences, the array of colours are made of waves
of different lengths.This is how he found red waves are the longest and violet waves are the shortest Ultraviolet: Ultraviolet rays can be used to kill Also, severe burns occur. It can be used to get a suntan, although too much could obviously be incredibly harmful to your skin cells, later perhaps causing skin cancer. It can be used also to detect forged bank notes in shops and can also harden some types of dental filling. They can also be used to sterilize surgical equipment and air in operating theatres. Suitable doses make the body produce vitamin D, used by doctors to treat vitamin d deficiency and a few skin disorders. However, large doses can damage your retina internally. In 1801, Johann Ritter discovered ultraviolet light. He decided to conduct experiments to determind if invisible light existed past the violet part of the spectrum aswell. He was experimenting with silver chloride. He had heard that exposure to blue light caused a bigger reaction in silver chloride than exposure to red light. Ritter measured the rate at which silver chloride reacted when exposed to diff colours of light. He placed silver chloride in each colour of the spectrum. He noticed there was little change in the red part of the spectrum, but increasingly darkened in the violet end of the spectrum. He then decided to place silver chloride in the area just beyond the violet end of the spectrum. To his surprise, the silver chloride displayed an intense reaction well beyond the violet, where no visible light could be seen. This proved there was an invisible form of light: Ultra violet. X-Rays: X-Rays have a very high frequency and carry lots of energy. They are useful to us in medicine and different sorts of industry because they help us see inside things as they will pass through most substances. They are given off by stars. How an X-Ray machine works is basically, a beam of electrons is fired at a specific target. If we fire the electrons with enough energy, we will produce X-Rays. They are used in airport security checks, in X-Rays and by astronomers. However, some dangers of using XRays include cancers and cell damage, which is why radiographers stand behind a shield while carrying out an X-Ray. In 1895, W.C. Roentgen was in his lab, working with a cathode ray tube, similar to fluorescent light bulbs. He removed all air, filled it with a gas and passed a high voltage through it. When he did this, there was a fluorescent light. He shielded the tube and found a green coloured light could be seen from a screen. He realized he had produced an unknown invisible ray being emitted from the tube, and it was somehow capable of passing through heavy paper. He found it passed through most solid objects. He called it X-Ray because of the mathematical symbol x meaning, unknown quantity. He also found it passed through human tissue leaving bones and metal visible. (He experimented with his wifes ring)!
Gamma Rays: They are radioactive and have an extremely high frequency. They pass through many substances and there are very few things that stop them travelling through these substances- you need lead or concrete to block them out! They are used to kill cancer cells, however they also attack our body cells, sometimes leading to bigger problems. Secondly, they can be used in tracers: doctors insert slightly radioactive substances into a patients body, then scan the patient to locate the gamma rays and get an image of what is happening inside the body. This is useful, because they can see the body processes as they are being carried out; it is not just a still picture. However, there are problems with Gamma rays. For example, they can cause cell damage, mutations in some unborn babies and cancers. In 1896, Henri Becquerel discovered natural radioactivity. He discovered it while looking at properties of fluorescent minerals. One was a uranium compound. Uranium ores produce naturally occurring gamma radiation. Becquerels discovery was unnoticed by scientists. Only a few of the scientists were interested in his findings. It wasnt till the radium discovery by Marie Curie and her husband two years later that everyone became interested in radioactivity. What is the relationship between the wavelength, frequency and energy levels of the different waves? The greater the energy, the larger the frequency and the shorter the wavelength. The higher the frequency, the shorter the wavelength; it follows that short wavelengths are more energetic than long wavelengths. What is a photon? A photon is a particle representing light or other EM radiation. A photon carries energy proportional to the radiation frequency, but has zero rest mass.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Physics ReportDokument3 SeitenElectromagnetic Spectrum Physics ReportElizabeth Cooper100% (3)
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument8 SeitenElectromagnetic SpectrumAndres GalarragaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCIENCE 10: Types-and-Applications-of-EM-wavesDokument32 SeitenSCIENCE 10: Types-and-Applications-of-EM-wavesInsigne HarietteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Untitled DocumentDokument6 SeitenUntitled DocumentMichaela CuarteroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveDokument10 SeitenSpectrum) of Electromagnetic Radiation and Their RespectiveJabez Edwin SivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument13 SeitenThe Electromagnetic Spectrumapi-246728123Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Waves and Their UsesDokument2 SeitenElectromagnetic Waves and Their UsesIbn FulaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EM WavesDokument2 SeitenEM WavesMyyo TabunoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radio WavesDokument4 SeitenRadio WavesSophia Nicole ZaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Radiation Works: Light Radio)Dokument2 SeitenHow Radiation Works: Light Radio)NabilaPutriClpdhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics I (SMP) (Hbsc4103)Dokument21 SeitenPhysics I (SMP) (Hbsc4103)johariNoch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsbookyayDokument12 SeitenPhysicsbookyayapi-249153555Noch keine Bewertungen
- History 2 Radiation Physics 5: What Is Medical Physics?Dokument21 SeitenHistory 2 Radiation Physics 5: What Is Medical Physics?djoumblatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Concerns: History of Radiation 13Dokument4 SeitenHealth Concerns: History of Radiation 13CristinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soft X RayDokument10 SeitenSoft X RayMadeleine PaggaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RDG213Dokument27 SeitenRDG213adamufatimamaajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- History of RadiographyDokument139 SeitenHistory of RadiographySamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uses of Electromagnetic WavesDokument4 SeitenUses of Electromagnetic WavesMarlou PrincesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared Radiation ReportingDokument6 SeitenInfrared Radiation ReportingJoy Mary100% (1)
- 2nd Q ReviewerDokument7 Seiten2nd Q ReviewerFeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proton Beam Radiotherapy: Physics and BiologyVon EverandProton Beam Radiotherapy: Physics and BiologyKoji TsuboiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument3 SeitenThe Electromagnetic SpectrumKyle WilliamsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiation Medicine: Topic 1. IntroductionDokument16 SeitenRadiation Medicine: Topic 1. IntroductionMadhusmita NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiographic TestingDokument98 SeitenRadiographic TestingWoodrow FoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiology: Historical PerspectiveDokument4 SeitenRadiology: Historical PerspectiveJeya Plays YTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2Dokument5 SeitenWeek 2jia aganaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic WavesDokument27 SeitenElectromagnetic WavesKatrinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Physics of LightDokument6 SeitenThe Physics of LightprashantsheetalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared and Ultraviolet LightDokument3 SeitenInfrared and Ultraviolet LightSheraz Abdul HayeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- By NaanaDokument29 SeitenBy Naanajuicypine14Noch keine Bewertungen
- X-Rays: Medical: Since Röntgen Discovered That X-Rays Allow Bone Structures To BeDokument2 SeitenX-Rays: Medical: Since Röntgen Discovered That X-Rays Allow Bone Structures To BeKaaren Dayanaa AguiirreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alison ProjectDokument8 SeitenAlison Projectjalefaye abapoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final OneDokument63 SeitenFinal OneAmanda TeacaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Report AboutDokument8 SeitenScience Report AboutLexaNoch keine Bewertungen
- X RayDokument68 SeitenX Rayأياام زمانNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of Light WavesDokument9 SeitenDefinition of Light WavesJF BatucalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waves Reading PassageDokument2 SeitenWaves Reading PassagedavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics ProjectDokument13 SeitenPhysics ProjectGanesh harkalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biomedical Engineering - X-Ray ImagingDokument3 SeitenBiomedical Engineering - X-Ray ImagingjoshuahealyNoch keine Bewertungen
- X Ray LectureDokument13 SeitenX Ray LectureSudeepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dronsfield tcm18-200827 PDFDokument4 SeitenDronsfield tcm18-200827 PDFasdjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Photography For RevieweesDokument19 SeitenPhotography For RevieweesMaricar TapiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Za Ss 74 Se The Development of X Rays Comprehension Ver 2Dokument6 SeitenZa Ss 74 Se The Development of X Rays Comprehension Ver 2Halid LepanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electromagnetic Waves & SpectrumDokument6 SeitenElectromagnetic Waves & SpectrumAman LilaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT-103 AssignmentDokument10 SeitenRT-103 AssignmentMichaela SuarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- X Rays Preventing Sickness: By: Gagandeep GujarDokument16 SeitenX Rays Preventing Sickness: By: Gagandeep GujarGagandeep SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionVon EverandCancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Electromagnetic Spectrum ReadingDokument2 SeitenElectromagnetic Spectrum Readingapi-369452118Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sia83 3notesDokument5 SeitenSia83 3notesAmaechi ZalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Chapter 4: Many PropertiesDokument45 SeitenGrade 8 Science Unit 2: Optics: Chapter 4: Many PropertiesMary-Rose CasuyonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication 6 4604 1651Dokument8 SeitenPublication 6 4604 1651علي عبدالرضا محمد العطافيNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Ojal Grover, Adorcille Abat, Patrick Trollope & Vijay MahatmaDokument62 SeitenBy Ojal Grover, Adorcille Abat, Patrick Trollope & Vijay MahatmaDuy NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8 Unit 2 CH 4 Slideshow 09Dokument45 Seiten8 Unit 2 CH 4 Slideshow 09api-238589602Noch keine Bewertungen
- Infrared WavesDokument52 SeitenInfrared WavesJuliever EncarnacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uses of EM WavesDokument3 SeitenUses of EM WavesPallika DhingraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The TygerDokument16 SeitenThe TygerSanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amatus of MontecassinoDokument18 SeitenAmatus of MontecassinoSanah Khan100% (1)
- Course ReaderDokument141 SeitenCourse ReaderSanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- William Blake Critical Essays - EnotesDokument6 SeitenWilliam Blake Critical Essays - EnotesSanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Significance of Colours in Tess of The D'urberviollesDokument1 SeiteSignificance of Colours in Tess of The D'urberviollesSanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coas b1 AcksDokument1 SeiteCoas b1 AcksSanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecotourism:: A Force For orDokument5 SeitenEcotourism:: A Force For orSanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Crimean War - NOTESDokument13 SeitenThe Crimean War - NOTESSanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Old Favourites New Alternatives: FreshDokument2 SeitenOld Favourites New Alternatives: FreshSanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCSE Geography - Topic 4 - Tourism: What Are The Key Ideas For This Topic?Dokument3 SeitenGCSE Geography - Topic 4 - Tourism: What Are The Key Ideas For This Topic?Sanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry IsotopesDokument8 SeitenChemistry IsotopesSanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 008 - The Cell Surface MembraneDokument2 Seiten008 - The Cell Surface MembraneSanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GCE Biology 2008: Unit 3-Research SkillsDokument28 SeitenGCE Biology 2008: Unit 3-Research SkillsSanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Guide For Statistics GCSEDokument89 SeitenRevision Guide For Statistics GCSESanah KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology AS Revision NotesDokument58 SeitenBiology AS Revision NotesSanah Khan100% (1)
- Ge Hid LampsDokument32 SeitenGe Hid LampsamamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum ChemistryDokument71 SeitenQuantum Chemistrybinseung skzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optical FiberDokument177 SeitenOptical FiberManish ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algodoo LessonsDokument30 SeitenAlgodoo LessonsMickey HD100% (2)
- Unit 2 Principles of Radio CommunicationDokument34 SeitenUnit 2 Principles of Radio CommunicationAnonymous j3WOut100% (1)
- Sylvania Photolamps Catalog 1974Dokument64 SeitenSylvania Photolamps Catalog 1974Alan MastersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super-Quiet Xenon Lamp Super-Quiet Mercury-Xenon LampDokument16 SeitenSuper-Quiet Xenon Lamp Super-Quiet Mercury-Xenon LampGunwant SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- US FDA Microwave Radiation HazardsDokument13 SeitenUS FDA Microwave Radiation HazardsPerry LanghamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiwavelength Universe Poster All 8x11 PDFDokument10 SeitenMultiwavelength Universe Poster All 8x11 PDFnabilanabnabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Analysis of Single Patch Antenna For Radar ApplicationsDokument4 SeitenDesign and Analysis of Single Patch Antenna For Radar ApplicationsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Att#2-1 SES-5 (Structure in P220)Dokument118 SeitenAtt#2-1 SES-5 (Structure in P220)Elle ShagzzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erco Guide 3 Indoor Lighting enDokument75 SeitenErco Guide 3 Indoor Lighting enGilberto A. YlaganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Structure of AtomDokument115 SeitenStructure of AtomHarshtej Singh MakkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2D Design (Art 107) Color Wheels - Color SystemsDokument7 Seiten2D Design (Art 107) Color Wheels - Color SystemsajawaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disusun Oleh: Inggri Ocvianti Ningsih Pembimbing: Mayor CKM (K) Dr. Lollytha C. Simanjuntak, SP - KJDokument29 SeitenDisusun Oleh: Inggri Ocvianti Ningsih Pembimbing: Mayor CKM (K) Dr. Lollytha C. Simanjuntak, SP - KJInggriOcviantiNingsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIMO Radar: Snake Oil or Good Idea?: RaytheonDokument5 SeitenMIMO Radar: Snake Oil or Good Idea?: RaytheontianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biophoton Research Proves That The Human Body Is Actually Made of LightDokument7 SeitenBiophoton Research Proves That The Human Body Is Actually Made of LightsavingtaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vp-Green Vale Academy, Inc.: Curriculum Map GRADE: 10 SUBJECT: ScienceDokument5 SeitenVp-Green Vale Academy, Inc.: Curriculum Map GRADE: 10 SUBJECT: ScienceRegina Minguez Sabanal100% (1)
- Forensic PhotographyDokument56 SeitenForensic PhotographySEUNGWANderingNoch keine Bewertungen
- G.C.E. (Advanced Level) CHEMISTRYDokument297 SeitenG.C.E. (Advanced Level) CHEMISTRYMaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emf Shielding GuidesDokument2 SeitenEmf Shielding GuidesSivasankar LoganathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Intensity Discharge Lamps Spectrum Catalogue en Tcm181-25048Dokument11 SeitenHigh Intensity Discharge Lamps Spectrum Catalogue en Tcm181-25048gonzaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introductory Agrometeorology and Climate ChangeDokument62 SeitenIntroductory Agrometeorology and Climate ChangeAwasthi Parth100% (1)
- PHILIPS LIGHT Price List May 2012 - NewDokument51 SeitenPHILIPS LIGHT Price List May 2012 - Newachuus0% (1)
- Types of LightingDokument48 SeitenTypes of LightingJhon Carlo Arimado100% (1)
- Vallejo Grey TriadsDokument1 SeiteVallejo Grey TriadsEdouard DecaenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fiber Optic Color ChartDokument1 SeiteFiber Optic Color Charttohamy2009100% (2)
- Sharp LC-60LE640U CNET Review Calibration ResultsDokument7 SeitenSharp LC-60LE640U CNET Review Calibration ResultsDavid KatzmaierNoch keine Bewertungen
- COLIPA MétodoDokument51 SeitenCOLIPA MétodoRafaella Resende100% (1)
- Unit 3 - Practice Exam QuestionsDokument35 SeitenUnit 3 - Practice Exam QuestionscripzrafNoch keine Bewertungen