Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Untitled
Hochgeladen von
mehakOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Untitled
Hochgeladen von
mehakCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
If a cirtain thing or event can happen favourably in n favourable cases and fail to happen in n unfavourable cases then the
probability of the successful happening of the even m/n+n If a dice is rolled, calculate the probability: i. (i) Probablity of getting an odd no. ii. (ii) Probablity of getting an even no. iii. (iii) Probablity of getting a no > 4 Terms: dependent events- Two events A and B are said to be dependent if the occurance of B depends on the occurance of A. B can occur if and only if when A occurs. InDependent events- To events A and B are said to be independent if when A occurs, it is not possible to definitely indicate the occurance or non occurance of B. eg. If two coins are tossed and if head appears on one, it is not possible to influence the occurance or non- occurance of head on the other. Mutually exclusive events- Two events A and B are said to be mutually exclusive if, when A happens, B does not happen at the same time. Mutually exclusive and exhaustive- Two events are said to be mutually exclusive and exhaustve if the sub of their probability = 1. If a coin is tossed, the two possible events are head and tail. If head occurs p=1/2, and q= . Therefore p+q = 1. Theorems of Probablity (i) Addition Theorem of probability- If two events, A and B are mutually exclusive, then the probability of A happening or B happening = Probablity of A + Probablity of B. (ii) Multiplication theorem If A and B are two events, then probability of A and B happening together is probability of A * P of B. P(A+B)= P (A) + P (B) (iii)Modified addition theorem- If A and B are not necessarily exclusive events, then the probability of event A happening oe B happening or both happening= P of A+P of B- P of A In a box there are 150 tickets of the same size and colour and numbers 1 50 are written on these. A ticket is selected at rndom from those tickets. What is the probability that the ticket so selected will have a no which is divisible by 3 or 5 or by both. A= Event divisible by 3 B= Event divisible by 5 AB= Event divisible by 15. POA= 50/150 POB= 30/150= POAB= 10/150 Probablity= 50/150+30/150 10/150= 70/150
i. (iv) Modified multiplication theorem- If A and B are 2 events such that A can happen if and only if B has happened, then the probability of the happening of A = PAB/ Two dice are rolled, find the probability that in the sum of the scores 8, the digit 3 only occurs. Binomial Probablity distribution Calculate 11P9= 11C8= 7P7 Binomial If 5 coins are tossed, find the probability of getting 3 successes. If 9 coins are tossed find the i. (i) P 3 <=x<7 ii. (ii) Px>=6
In a factory the probability of accidental death in a year is 0.2. What is the probability that two deaths may take place out of 9 workers in a year in the same factory. N=9 X=2 P= 0.2 On an average 5 railway accidents take place in a zone in India, every year. What is a probability that no accidents take place in a year and a probability that more than 5 take place in a year.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- PPTCH 23Dokument8 SeitenPPTCH 23Jovie DangananNoch keine Bewertungen
- BRANDSDokument39 SeitenBRANDSmehakNoch keine Bewertungen
- O. Dev. ch08Dokument7 SeitenO. Dev. ch08sani0Noch keine Bewertungen
- O. Dev. ch02Dokument9 SeitenO. Dev. ch02sani0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Organization Development and Change: Chapter Seven: Collecting and Analyzing Diagnostic InformationDokument11 SeitenOrganization Development and Change: Chapter Seven: Collecting and Analyzing Diagnostic Informationsani0Noch keine Bewertungen
- PPTCH 05Dokument14 SeitenPPTCH 05iufreiendNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organization Development and Change ExplainedDokument10 SeitenOrganization Development and Change ExplainedfiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice 5: Manage Priority Cultural Realignment Levers: BehaviourDokument13 SeitenPractice 5: Manage Priority Cultural Realignment Levers: BehaviourmehakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Erp Case StudyDokument2 SeitenErp Case StudymehakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Price ElasticityDokument1 SeitePrice ElasticitymehakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Price ElasticityDokument1 SeitePrice ElasticitymehakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Returns to Scale in IT IndustryDokument2 SeitenReturns to Scale in IT IndustrymehakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Returns to Scale in IT IndustryDokument2 SeitenReturns to Scale in IT IndustrymehakNoch keine Bewertungen
- History Trade UnionDokument18 SeitenHistory Trade UnionabhpaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Returns to Scale in IT IndustryDokument2 SeitenReturns to Scale in IT IndustrymehakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quants Question Bank 1Dokument8 SeitenQuants Question Bank 1mehakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quants Question Bank 1Dokument8 SeitenQuants Question Bank 1mehakNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Njhs Application EssayDokument4 SeitenNjhs Application Essaycjawrknbf100% (2)
- 1 Starter WBDokument88 Seiten1 Starter WBHYONoch keine Bewertungen
- OJT Form 03 Performance EvaluationDokument2 SeitenOJT Form 03 Performance EvaluationResshille Ann T. SalleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of MatterDokument2 SeitenClassification of Matterapi-280247238Noch keine Bewertungen
- Operation Manual 11-3000psi Shear Ram BopDokument30 SeitenOperation Manual 11-3000psi Shear Ram BopBoedi SyafiqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calibration GuideDokument8 SeitenCalibration Guideallwin.c4512iNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Ego?Dokument2 SeitenTypes of Ego?S.UdhayakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absolute Value - WikipediaDokument10 SeitenAbsolute Value - WikipediaVenu GopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Reporting Statement Analysis Project Report: Name of The Company: Tata SteelDokument35 SeitenFinancial Reporting Statement Analysis Project Report: Name of The Company: Tata SteelRagava KarthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hong Kong A-Level Chemistry Book 3ADokument69 SeitenHong Kong A-Level Chemistry Book 3AMARENG BERNABENoch keine Bewertungen
- Tender Evaluation Template GuideDokument15 SeitenTender Evaluation Template GuideKhalid NaeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Microwave Lab ManualDokument35 SeitenNew Microwave Lab ManualRadhikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adapting Cognitive Behavioral Techniques To Address Anxiety and Depression in Cognitively Able Emerging Adults On The Autism SpectrumDokument3 SeitenAdapting Cognitive Behavioral Techniques To Address Anxiety and Depression in Cognitively Able Emerging Adults On The Autism SpectrumVini PezzinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nelson Sanchez GE Module October 2020Dokument92 SeitenNelson Sanchez GE Module October 2020Nneg Gray0% (1)
- (The Heritage Library of African Peoples) Tiyambe Zeleza - Akamba-The Rosen Publishing Group (1995)Dokument72 Seiten(The Heritage Library of African Peoples) Tiyambe Zeleza - Akamba-The Rosen Publishing Group (1995)BlackFlix Legendas em PortuguêsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Open MPDokument30 SeitenOpen MPmacngocthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DOW™ HDPE 05962B: High Density Polyethylene ResinDokument3 SeitenDOW™ HDPE 05962B: High Density Polyethylene ResinFredo NLNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAU Paleoart Workbook - 2023Dokument16 SeitenLAU Paleoart Workbook - 2023samuelaguilar990Noch keine Bewertungen
- Safety Data Sheet for Instant AdhesiveDokument6 SeitenSafety Data Sheet for Instant AdhesiveDiego S. FreitasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optimal Inspection and Preventive Maintenance Scheduling of Mining EquipmentDokument9 SeitenOptimal Inspection and Preventive Maintenance Scheduling of Mining EquipmentLucia QuispeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PanimulaDokument4 SeitenPanimulaCharmayne DatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appraisal Sample PDFDokument22 SeitenAppraisal Sample PDFkiruthikaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Big Band EraDokument248 SeitenBig Band Erashiloh32575% (4)
- Book 2 - Test 1Dokument2 SeitenBook 2 - Test 1Đức LongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Double Burden of Malnutrition 2017Dokument31 SeitenDouble Burden of Malnutrition 2017Gîrneţ AlinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Critical Thin...Dokument7 SeitenChapter 1 Critical Thin...sameh06Noch keine Bewertungen
- JKR Specs L-S1 Addendum No 1 LED Luminaires - May 2011Dokument3 SeitenJKR Specs L-S1 Addendum No 1 LED Luminaires - May 2011Leong KmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penilaian Risiko Kerja Menggunakan Metode Hirarc Di Pt. Sinar Laut Indah Natar Lampung SelatanDokument7 SeitenPenilaian Risiko Kerja Menggunakan Metode Hirarc Di Pt. Sinar Laut Indah Natar Lampung SelatanIndun InsiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Resume Android Developer Format1Dokument3 SeitenResume Android Developer Format1Shah MizanNoch keine Bewertungen
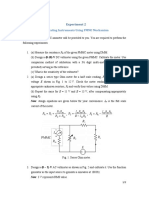
- PMMC ExperimentDokument2 SeitenPMMC ExperimentShyam ShankarNoch keine Bewertungen