Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Critical Care Nursing
Hochgeladen von
veinslasherOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Critical Care Nursing
Hochgeladen von
veinslasherCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Critical Care Nursing Prepared by: Ms. Elizabeth D. Cruz, R.N., M.A.N.
CRITICAL CARE UNIT
Is a hospital area in which an increased concentration of specialty trained staff and monitoring equipment allow more detailed and frequent monitoring and more frequent intervention in seriously ill patients
CRITICAL CARE
Is defined as the care of seriously ill patients from point of injury or illness until discharge from Intensive Care This encompasses ambulatory services, disaster medicine, emergency medicine and preventive medicine
PERSONNEL IN ICU
Involves medical, nursing and allied health CRITICAL CARE NURSE - is a licensed professional nurse who is responsible for ensuring that acutely and critically ill patients and their families receive optimal care
ROLES OF A CRITICAL CARE NURSE
Bedside clinicians Nurse educators Nurse researchers Nurse managers Clinical nurse specialist Nurse practitioners
CRITICALLY ILL PATIENTS
Are defined as those patients who are at high risk for actual or potential lifethreatening health problems More critically ill patient, the more likely he or she is to be highly vulnerable, unstable and complex, thus require intense and vigilant nursing care.
ROLES OF CCN FOR CRITICALLY ILL PATIENT
Respect & support the right of the patient or patients designated surrogate to autonomous informed decision-making Intervene when the best interest of the patients in question Help patient obtain necessary care Respect the values,beliefs & rights of the patient Support the decision of the patient or designated surrogate, or transfer care to an equally qualified critical care nurse Intercede for patient who cannot speak for themselves in situation that require immediate action Monitor & safeguard the quality of care the patient recieves Acts as a liaison between the patient, the patients family & other healthcare professionals
3 PHYSICALLY DISTINCT ICU AREAS
NICU (NEONATAL CARE UNIT)
= will care for premature babies, low-weight babies,full term infants born with critical care condition or babies with severe congenital malformation, = will acquire care skills to care for all babies needing surgical interventions posy-op care, thus limiting necessary transfer between ICUs NICU (NEONATAL CARE UNIT) defined as needing continuous ventilatory support, ongoing invasive monitoring, close clinical supervision, and corrective therapies to reverse potentially lifethreatening conditions.
PICU (PEDIATRIC INTENSIVE CARE UNIT) Will be a multidisciplinary intensive care unit offering all critical care services to infants, children, and adolescents Will develop & implement tertiary services & remain on the leading edge of advanced therapies and procedures Will also provide consultation resources to the emergency department, the in patient wards and other referring centers
ADULT INTENSIVE CARE UNIT Will be defined as those needing continuous ventilatory and hemodynamic support, ongoing invasive monitoring, close supervision and corrective therapies to prevent or reverse potentially & immediately life-threatening conditions Will care for all critical care patients within the same physical environment and will include a mix of medical, surgical, trauma and neuro/neurosurgery patients
ICU EQUIPMENT Hemodynamic & cardiac monitoring systems Mechanical ventilator therapy Intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) Ventricular assist devices Continuous renal replacement equipment Extracorporeal mechanical oxygenation circuits
INTRA-AORTIC BALLOON PUMP
VENTRICULAR ASSIST DEVICES
CONTINUOUS RENAL REPLACEMENT EQUIPMENT
EXTRA CORPOREAL MECHANICAL OXYGENATION CIRCUITS
MONITORING EQUIPMENT IN ICU: - CARDIAC or HEART MONITORS = are used to monitor the electrical activity of the heart = looks like a computer screen with lines, or tracings, moving across the screen = the monitor has electrodes that are attached to the chest of the patient with sticky pads
- PULSE OXIMETER = allows the critical care team to monitor the saturation of oxygen in the blood = looks like a clothespin and is attached to a patients finger, or it may be smaller & clipped onto the earlobe
- SWAN-GANZ CATHETER =or PULMONARY ARTERY CATHETER = used to measure the amount of fluid filling the heart as well as to determine how the heat is functioning. = is inserted through the large vessels of the neck or upper chest & threaded into the heart
- ARTERIAL LINES (a-lines) = are used for continuous monitoring of blood pressure = catheter are inserted into an artery, usually in the wrist or, less often in the bend of the elbow or groin. = arterial lines produce a tracing on a monitor that is similar to that of a heart monitor but with a different wave form
TUBES & CATHETERS IN ICU - CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETER(CVC) = is a soft, pliable tube that is inserted into a large vessel(vein) in the neck, the upper chest, or in the groin area = can carry some risk of bloodstream infection & thrombosis CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETER
USE OF CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETER To administer frequent or continuous medication To administer large amounts of fluid, including blood & nutrition, that would damage smaller vessels such as those in arms - To measures central venous pressure(amount of fluid in the vessels) - INTRAVENOUS(IV) = Is a plastic catheter (tube) that is inserted into the veins (peripheral IV) or a larger size catheter inserted into large veins of the neck = Fluids, medications, nutrition preparations, & blood products are administered through IV catheters. = patients in ICU often have multiple IVs
INTRAVENOUS LINE
- CHEST TUBES = Are inserted through the chest wall into the space around the lung to drain fluid or air that has accumulated & prevent the lung from being able to expand
- URINARY CATHETER =Referred to as Foley catheters, are inserted through the urethra into the bladder = continuous drain the bladder and allow for accurate measurement of urinary output, which is extremely important in fluid management and is assessing kidney function
- ENDOTRACHEAL TUBES = are used when mechanical ventilation is necessary = a plastic tube is inserted either through the nose or mouth between the vocal cords & into the trachea = a small soft balloon at the end of the tube in trachea is inflated to prevent air from escaping, thus allowing adequate ventilation by a respirator.
LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES - VENTILATOR or RESPIRATOR = is a breathing machine that helps patients breathe when they are too ill to breathe on their own. = patient is connected to the ventilator by an endotracheal tube as patient;s lungs recover, the amount of ventilator support is gradually de creased until it is felt a patient can breathe on his or her own
MECHANICAL VENTILATOR
- NUTRITION = is very important for critically ill for healing process = nutritional solutions can be administered through feeding tubes inserted through either the nose or the mouth into the stomach or through central venous catheters = special nutritional preparations are available to provide the nutritional needs of the critically & are calculated & monitored PARENTERAL NUTRITION
INFORMED CONSENT Prior to initiating any procedure in the ICU, physicians must secure informed consent from the patient Except in emergency situations, physicians obtain consent directly from patient ADVANCE DIRECTIVE = contains instructions regarding care decisions DO NOT RESUSCITATE (DNR) = is a patients instructions not to re start a failed heart beat or respiration
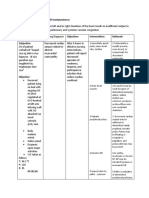
CARE OF PATIENT Physically Psychologically considering:
1. Attitude of patient towards disease 2. Attitude of patient towards treatments 3. Attitude of patient towards patient 4. Attitude of relatives towards patient 5. Attitude of patient towards death OBJECTIVES OF CARE Maintenance of life support system Prevention of complications
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Mastering ICU Nursing: A Quick Reference Guide, Interview Q&A, and TerminologyVon EverandMastering ICU Nursing: A Quick Reference Guide, Interview Q&A, and TerminologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care Nursing Notes 2 - Med SurgDokument42 SeitenCritical Care Nursing Notes 2 - Med Surgpauchanmnl100% (3)
- Intravenous Therapy Administration: a practical guideVon EverandIntravenous Therapy Administration: a practical guideBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Critical Care NursingDokument61 SeitenCritical Care NursingAnju Radhika75% (4)
- Schaum's Outline of Critical Care Nursing: 250 Review QuestionsVon EverandSchaum's Outline of Critical Care Nursing: 250 Review QuestionsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Critical Care NursingDokument26 SeitenCritical Care NursingBarbie Sarabia100% (2)
- Critical Care Unit / Intensive Care UnitDokument83 SeitenCritical Care Unit / Intensive Care Unitpreet kaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Criticalcare Nursing-1Dokument70 SeitenConcept of Criticalcare Nursing-1victor100% (1)
- Critical Care NursingDokument17 SeitenCritical Care Nursingsanish4u100% (1)
- Critical Care NursingDokument159 SeitenCritical Care Nursinggretchen marie80% (5)
- Scope of Critical Care Nursing-FirstDokument5 SeitenScope of Critical Care Nursing-FirstJo Traven AzueloNoch keine Bewertungen
- 118A - Chapter 1 - CRITICAL CARE NURSING LEC (EDITED) Handout #1Dokument14 Seiten118A - Chapter 1 - CRITICAL CARE NURSING LEC (EDITED) Handout #1Joanna Taylan100% (5)
- Critical Care NursingDokument85 SeitenCritical Care NursinganreilegardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care NursingDokument1 SeiteCritical Care NursingMelissa David0% (1)
- Critical Care NursingDokument90 SeitenCritical Care NursingThirdy Aquino100% (5)
- Critical Care Nursing Notes 1Dokument10 SeitenCritical Care Nursing Notes 1pauchanmnlNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care NursingDokument22 SeitenCritical Care NursingIan Mizzel A. DulfinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hemodynamic Monitoring PDFDokument20 SeitenHemodynamic Monitoring PDFretsmd67% (6)
- Critical Care Nursing (NCM 410) Notes 1Dokument66 SeitenCritical Care Nursing (NCM 410) Notes 1Danielle OnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care NursingDokument20 SeitenCritical Care NursingEdwin Delos Reyes AbuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 118A - Chapter 1 - CRITICAL CARE NURSING LECDokument12 Seiten118A - Chapter 1 - CRITICAL CARE NURSING LECJoanna TaylanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care NursingDokument10 SeitenCritical Care Nursingianecunar100% (10)
- Acute Liver FailureDokument24 SeitenAcute Liver FailureMohd Johari Mohd ShafuwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Notes 1Dokument23 SeitenStudy Notes 1mildred alidon100% (1)
- Critical Nursing Care ExamDokument42 SeitenCritical Nursing Care ExamRandy80% (5)
- Critical Care NursingDokument159 SeitenCritical Care NursingJoy Jarin50% (2)
- 1 - Scope of Critical Care NursingDokument20 Seiten1 - Scope of Critical Care Nursinghanimozaghi100% (1)
- Care For Mechanical VentilationDokument14 SeitenCare For Mechanical Ventilationmaeya186135100% (3)
- CriticalCare - ICU Skills ChecklistDokument8 SeitenCriticalCare - ICU Skills Checklistyash Inficare100% (2)
- Assessment of The Critically Ill Patients and Their FamiliesDokument48 SeitenAssessment of The Critically Ill Patients and Their Familiesjhing_apdan100% (1)
- Introduction To Critical Care HandoutDokument30 SeitenIntroduction To Critical Care HandoutAvy PHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Critical CareDokument21 SeitenIntroduction To Critical CareBritanny NelsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care NursingDokument6 SeitenCritical Care NursingZam PamateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care Nursing ConceptsDokument5 SeitenCritical Care Nursing ConceptsGodwin Babista GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care NoteDokument10 SeitenCritical Care NoteHanis Rozib99% (69)
- Acute Critical Care Nursing HandoutDokument17 SeitenAcute Critical Care Nursing HandoutJulie May100% (6)
- ICU Procedures ManualDokument64 SeitenICU Procedures Manualenumula kumar100% (1)
- Intra Aortic Balloon PumpDokument51 SeitenIntra Aortic Balloon PumpDeeksha Rajput100% (2)
- Functions of Nurse in ICUDokument2 SeitenFunctions of Nurse in ICUSharmila Laxman Dake67% (3)
- Cardiogenic Shock HandoutsDokument2 SeitenCardiogenic Shock HandoutsAileenNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLASH CardsDokument3 SeitenFLASH Cardsclarheena100% (2)
- Critical Care Nursing Manuall IDokument90 SeitenCritical Care Nursing Manuall ILesley Gonzalez75% (4)
- Intensive Care Unit (Student Version)Dokument41 SeitenIntensive Care Unit (Student Version)Skywalker_92100% (2)
- Gastrointestinal NursingDokument8 SeitenGastrointestinal Nursingohsnapitslei90% (10)
- ECG Rhythm InterpretationDokument16 SeitenECG Rhythm InterpretationJanettNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8-Hemodynamic Monitoring: Central Venous Pressure (CVP)Dokument6 Seiten8-Hemodynamic Monitoring: Central Venous Pressure (CVP)AsmaaYL100% (1)
- Concept of Critical CareDokument4 SeitenConcept of Critical CareLohrhen Lheighh Cahreeniyow100% (6)
- Sub - Medical Surgical Nursing: Assignment On CVP MonitoringDokument11 SeitenSub - Medical Surgical Nursing: Assignment On CVP Monitoringkamini ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morton Critical Care Nursing 9eDokument4 SeitenMorton Critical Care Nursing 9eblue_blood_boyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iv AnsapDokument7 SeitenIv AnsapromeojrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology Checklist - Rationale 02Dokument30 SeitenPharmacology Checklist - Rationale 02Tisha DeiparineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Nursing PDFDokument39 SeitenEmergency Nursing PDFJustin John NavarroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept Map AsthmaDokument3 SeitenConcept Map AsthmaKaren HutchinsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Care NursingDokument3 SeitenCritical Care NursingMa Christina Herrera AntesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency and Disaster NursingDokument8 SeitenEmergency and Disaster NursingJOvie RectinNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Cardiomyopathy PPT NEWDokument62 SeitenA Cardiomyopathy PPT NEWShetal Sharma100% (1)
- Emergency Nursing: A. General Information: Emergency Nurses Association (ENA)Dokument21 SeitenEmergency Nursing: A. General Information: Emergency Nurses Association (ENA)Sarah Loraine100% (3)
- Scope of Critical Care Practice: Study GuideDokument6 SeitenScope of Critical Care Practice: Study GuideDan Dan ManaoisNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICU Orientation ManualDokument107 SeitenICU Orientation Manualhery100% (2)
- Manual IcuDokument229 SeitenManual IcuMauricio PinneaparNoch keine Bewertungen
- NEET-SS UrologyDokument59 SeitenNEET-SS Urologyadi100% (1)
- Adverse Drug ReactionDokument15 SeitenAdverse Drug ReactionPuji Arifianti RamadhanyNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Journal of Surgery Open: Amir Forouzanfar, Jonathan Smith, Keith S. ChappleDokument3 SeitenInternational Journal of Surgery Open: Amir Forouzanfar, Jonathan Smith, Keith S. ChappleSiti Fildzah NadhilahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lacunar Infarct - Radiology Reference Article - RadiopaediaDokument8 SeitenLacunar Infarct - Radiology Reference Article - RadiopaediaRismanto TorsioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000: Key Indexing TermsDokument4 SeitenSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000: Key Indexing TermsRandom PersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- LINKSERVE Training MaterialsDokument15 SeitenLINKSERVE Training MaterialslisingynnamaeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sudeep SrivastavaDokument202 SeitenSudeep Srivastavasandeepsrivastava41Noch keine Bewertungen
- Steroids Other Appearance Performance Enhancing Drugs Apeds Research ReportDokument34 SeitenSteroids Other Appearance Performance Enhancing Drugs Apeds Research ReportFit and LiftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linhart Continuing Dental Education ProgramDokument2 SeitenLinhart Continuing Dental Education ProgramnallatmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infection and Tumorigenesis of Biomaterials by Smit Prajapati-200280103028 and Yukta Dodia - 200280103052Dokument18 SeitenInfection and Tumorigenesis of Biomaterials by Smit Prajapati-200280103028 and Yukta Dodia - 200280103052Yukta DodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MHC PDFDokument2 SeitenMHC PDFYuvarani AruchamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Terrorist Inside My Husband's Brain PDFDokument5 SeitenThe Terrorist Inside My Husband's Brain PDFraymondnomyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment MarketDokument3 SeitenGlobal Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment MarketiHealthcareAnalyst, Inc.Noch keine Bewertungen
- CHF NCPDokument8 SeitenCHF NCPZy Hallasgo100% (1)
- BrochureDokument14 SeitenBrochurePrakash KumbharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ascites Hrs B WPDokument101 SeitenAscites Hrs B WPGhias Un Nabi TayyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vasopressors For ShockDokument21 SeitenVasopressors For ShocknugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Consent To Surgery/Anaesthesia: Ilocos Sur Provincial Hospital-Gabriela SilangDokument1 SeiteConsent To Surgery/Anaesthesia: Ilocos Sur Provincial Hospital-Gabriela SilangRyrey Abraham PacamanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTDokument1 SeiteCKD + HPN Concept Map DRAFTInah Floresta BesasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708Dokument3 SeitenTumors of The Orbit by Dr. Jonathan Del Prado 082708CitrusNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXERCISE Stress Testing FOR HEARTDokument52 SeitenEXERCISE Stress Testing FOR HEARTBenjamin GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animals Should Not Be Used As A Laboratory ToolsDokument6 SeitenAnimals Should Not Be Used As A Laboratory ToolsLuisa Castillo100% (1)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDokument3 SeitenNew Microsoft Word DocumentHazim YusoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Childbirth Cheat Sheet For Dads-To-be - Baby CenterDokument3 SeitenA Childbirth Cheat Sheet For Dads-To-be - Baby CenterDrhtrth AsdfghsfgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reffered PainDokument26 SeitenReffered PainHappy Septianto SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary Reading Comprehension Test 02 PDFDokument4 SeitenElementary Reading Comprehension Test 02 PDFroxanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Patient Evaluation, Diagnosis and Treatment PlanningDokument5 Seiten1 - Patient Evaluation, Diagnosis and Treatment PlanningMohammed100% (1)
- Secondary Amenorrhea Therapy With Accupu 2c484cf6Dokument5 SeitenSecondary Amenorrhea Therapy With Accupu 2c484cf6NurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Musculoskeletal Summary For Osce ExamDokument53 SeitenPediatric Musculoskeletal Summary For Osce Examopscurly100% (2)
- Patient Delivery Receipt: Product Delivery Location: FacilityDokument1 SeitePatient Delivery Receipt: Product Delivery Location: FacilityPat Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (24)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (80)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Summary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: The Myth of Normal: Trauma, Illness, and Healing in a Toxic Culture By Gabor Maté MD & Daniel Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (9)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningVon EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (328)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeVon EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (253)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerVon EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (392)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsVon EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (169)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceVon EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (51)
- An Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyVon EverandAn Autobiography of Trauma: A Healing JourneyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosVon Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (207)