Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Emteaz Ophthalmology
Hochgeladen von
Raouf Ra'fat SolimanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Emteaz Ophthalmology
Hochgeladen von
Raouf Ra'fat SolimanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
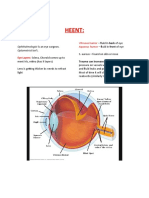
The eye is the most delicate organ in the body , any trivial proplem in the eye must be managed
under supervision of ophthalmologist , this is only simplified hand out for house officers about the common eye complains , and the author is not responsible of any harm or mistakes done by non specialist depending on data in this hand out .
Non traumatic red eye 1- viral conjunctivitis :
H: sudden onset , history
2- MPC :
H : O/E : redness mainly palbebral + MP discharged + adherent lashes . TTT : 1- 2- Antibiotic ED : levoxin ED x5 3- Ab EO : Terramycin EO Prognosis : = infectious :
of recent ARI , watery discharge , severe FB sensation , start in one eye then affect the other . O/E : diffuse injection bulbar and palpepral lid edema conjunctival chemosis or even subconj hemorrhage follicles in the conj ( slit lamp ) .A palpable preauricular lymph node strongly supports the diagnosis but is not present in the majority of cases. TTT : 1- : decrease 2- Combined ED : maxitrol , optidex , x 5 3- Tears guard , orchatears ED x 5 ( for FB sensation ) . Prognosis : = infectious : = self limited in 2 weeks viral proliferation .
3- Allergic conjunctivitis : H: O/E : TTT : itching + recurrence + allergies watery discharge diffuse redness + lid edema 1- 2 - Combined ED : ( skin , chest , nose ) +
maxitrol , optidex , x 5 3- Tears guard , orchatears ED x 5 ( for FB sensation ) . 4 Mast cell stabilizers or anti H .
NB : ###In pediatric better to avoid quinlones and miphenicol : use Tobrex ED x5
Also better avoid terramycin ( may cause allergy ) : use Fusithalmic Viscous ED ### Hyperacute bacterial conjunctivitis characterized by an abrupt onset, a copious purulent discharge, and rapid progression, is usually associated with a gonococcal infection in a sexually active adolescent or adult. The conjunctiva becomes bright red and chemotic, and an inflammatory membrane (consisting predominantly of leukocytes and fibrin) may develop on the tarsal conjunctival surface. Preauricular adenopathy is often present, and there is marked swelling of the lids, with aching and tenderness on palpation. if left untreated, the infection may involve the cornea, rapidly causing peripheral ulceration and ultimately leading to perforation. Treatment with topical antibiotics (ciprofloxacin) + a single 1-g dose of intramuscular ceftriaxone
4- Spring cattarah : ( severe allergy ) H : child 5-15 years , recurrence in the summer of O/E : diffuse redness + lid edema + dirty sclera papillae on the palbepral conj ( cobble stone ) jelly like mass on upper limbus or pannus of previous attacks milky discharge on the palbepral conj . TTT : 1- + 2- Combined ED : maxitrol , optidex , x 5 3- Tears guard , orchatears ED x 5 ( for FB sensation ) . 4 Mast cell stabilizers or anti H . * Mastocytx ED durations > 1.5 month ) . * Orchazide Ed x4 ( 2 weeks only ) : x2 ( rapid effect but contraindicated for long
* Tears guard . * Mirolast ed x3 ( mast cell stabilizer can be used for 3 months safely but not for children < 3 years old ) . Prognosis : = usually resistant to TTT with keratoconus . 5- Dry eye ( diagnosed by exclusion and some specific tests ) H : discomfort itching O/E : exposed areas more affected ( 3^ , 9 ^ ) whitish frothy discharge at the canthi white palbebral conj . TTT : 1- tears guard ED .x5 ( ) 2- Thilotears gel , or corner gel .. x 3 = some times its associated
6- phylectenular conjunctivitis : O/E : 123TTT : 1- combined : Tobradex Ed x5 Terracortil EO . 2- anti inflammatory : Epifenac Ed . X3 3- __________________________________________________________ 7- Episcleritis : self-limited, recurrent, presumably autoimmune inflammation of the episcleral vessels *Usually adult or old bilateral associated with auto immune diseases , TB or sepsis . phylectn : painless 1-3 mm , grayish nodule may be multible . localized superficial conjunctival injection blanch by ocumethyl , ,
ED (decongestant ).
* purpule nodule 2-4 mm with radially distributed blood vessels , recurrent , Tender but not painful . * conj can be moved over it and it doesnot blanch with prisoline ED ( decongestant ) TTT : like phylectn + oral NSAID e.g. Rivo , Rhonal ..x3 +
8-Subconjunctival Hemorrhage the redness, which is unilateral, is localized and sharply circumscribed, the underlying sclera is not visible, the adjacent conjunctiva is free of inflammation, and there is no discharge. There is also no pain, and vision is unaffected.
Causes * trauma
* fragile conjunctival vessels, bleeding disorders, anticoagulation therapy *hypertension. weeks. *prolonged coughing, Prognosis : reassure that the hemorrhage will clear gradually in two to three
9- Scleritis (rare) or connective-tissue disease (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis).. The redness may be focal or diffuse, and the underlying sclera is pink. Typically, there is moderateto-severe, deep ocular pain and tenderness on palpation. an oral nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug may help relieve symptoms in the interim. Treatment often requires systemic corticosteroids, antimetabolites,
10- Acute angle closure glaucoma : H : sudden headache , nusea , vomiting brusting eye pain, diminution of vision ( DD acute headache , acute abdomen ) .
O/E : * tension is stony hard unreactive to light. * iris is stormy . TTT : 1234Admission . Timolol , pilocarbine ED , cidamex , slow k Mannitol 20% 50 21 06 / 3 Tobradex ED , EO . * cornea is hazy + ciliary injection . * pupil is greenish vertically dilated
5- Laser peripheral iridectomy
11- Acute Anterior Uveitis
Apparoach to red eye
Red eye may be active hyperaemia = inflammation or passive congestion due to venous obstruction e.g. Glucoma , CST. History : ask for the main eye symptoms : 1- Red eye : - O C D - PPT : traumatic or non traumatic ? use contact or not ? recent respiratory infection ? - Past history of similar condition or systemic disease .
2- Vision :
Any discharge may cause colored halos , however vision may be markedly affected in acute glaucoma , corneal ulcer , uvitis . 3- Pain , itching , burning . 4- Discharge : - MP ( yellowish or greenish = ) MPC - watery : allergy , viral , lacrimation ( corneal ulcer or FB) Examination : 1- lid : - rubbing lash may be the cause of red eye . - blepharospasm usually indicates corneal ulcer or uvitis. - lid edema is common in allergy or venous obstruction . - scales of blepharitis . - lower lid (ectropion) may cause dryness . 2- cornea : important to confirm its clear .
3- conj : - site of redness - follicles ( viral or trachoma ) - papillae ( chronic irritation e.g. CL , spring catarrh , drugs , trachoma ) - chemosis : usually allergy or viral . 3- AC : - to exclude glaucoma ( shallow AC ) - KPS , flare , hypopyon . 4- Pupil : e.g . - vertical dilated in glaucoma . - constricted in iridocyclitis . 5- Lens 6- Tension : palpatory and compare eyes . 7- periauricular LN : viral infection . Summary of red eye : 1- Red eye + discomfort (only) = conjunctiva A) diffuse : -young : Allergy (tobradex) or infection (levoxin , tobrex + fusithalmic VED ) - old : dryness (tearsgaurd x5 , cornergel x3). B) localized : phylectn (tobradex,epifenac,terracortil Eo) , episcleritis (+rivo tab ) , angular blepharits (tetra EO + prisoline zink) , subconj hge (reassurance ). 2- Red eye + discomfort + pain , photophobia , blepharospasm: * corneal ulcer,FB,photophthalmia cover + isoptatropine + tobrex + fusithalmic benox,epifenac(in photophthalmia) Diflucan (in organic trauma ) * Uvitis * acute glaucoma 3- Red eye + discomfort + proptosis &\or ocular motility : * tumor of the orbit . * thyrotoxicosis . 4- Red eye + proptosis &\or ocular motility + pain : * orbital cellulitis * CS thrombosis ( + headace, coma + edema over mastoid ) 5- Red + proptosis &\or ocular motility + pain + ring abcess + No PL : Panophthalmitis 6- red eye + pain only : Scleritis ( rare)
Ocular trauma
1- FB
. Sites : cornea , conj , sulcus subtarsalis slit lamp : DD : TTT . Benox . ) (Rust . : : 1- pure AB levoxin , tobrex Ed .X5 , Terramycin Eo 2- if its plant orgin there is risk of : fungal keratitis * Diflucan ED * Isoptatropine ED * Zymer Ed ( or ) tobrex * miphenicol EO ) ( or fusithalmic VED 06 bevel . peripheral 1- 2- 3- 4- . conjunctivitis , allergy , corneal erosion
NB # . # Rupture ) slit lamp 54 ( .
2- Rupture globe : O/E : cornea and\or sclera is torn , tension is soft , AC is lost , iris may prolapse . Seidels test ( for diagnosis of perforated corneal ulcer ): Concentrated fluorescein is dark orange but turns bright green under blue light after dilution. This indicates aqueous leakage which is diluting the green dye : )( to exclude IO FB
* R/ vigamox ED 01 3- Hyphema : Emergence due to risk of : 1- 2ndry glaucoma 2- corneal staining 3- rebleeding . * NPO .
: )( to exclude IO FB . : 1- . 2- 54 3- 42 2 4- . 5- 4- Black eye : R/ alphentern tab x2 5- Corneal abrasion : or maxilase syrup x2 R/ tobradex ed .. x3
Usually after FB , trauma , bad use of contact lens . . slit lamp TTT (steroids is contraindicated ) R/ tobrex ed.. x5 6- chemical burn : . ) ( saline 1- . Benox 2- . 3- saline ( Alkali burn usually needs continous irrigation by 1000- 4- . ( 2000 cc saline . 5- 6- R/ tobrex ED x5 corner gel ..x 3 isoptatropine EDx3 7- . , R/ Fusithalmic VED x1 .
Ocular emergincies
Closed-angle glaucoma Retinal detachment Foreign body
Orbital fractures Chemical burns Retrobulbar hematoma
Corneal abrasions, lacerations, ulcers Ruptured globe CRAO
Retinal detachment
Signs and symptoms black curtain coming down over visual field bright flashes of light (photopsia) increasing floaters decreased visual acuity distortion of objects (metamorphopsia) +RAPD on exam.
- ophthalmoscopy. Direct ophthalmoscopy is not very effective at visualizing periphery where most RDs occur.
Treatment Surgery. Signs & Sxs: Enophthalmos Diplopia Impairment of eye movement 20 to EOM entrapment, orbital hemorrhage Orbital emphysema Infraorbital n. anesthesia CT should include axial and coronal cuts Orbital blowout fracture Disposition - If no diplopia, minimal displacement, and no muscle Surgery - For enophthalmos, muscle entrapment, or visual loss. Management: Ice packs beginning in clinic/ED and for 48 hrs will help decrease swelling Elevate head of bed (decrease swelling). If sinuses have been injured, give prophylactic antibiotics and instruct
Orbital Blowout Fracture
or nerve damage
entrapment, discharge with ophthalmology follow up within a week.
associated with injury.
patient not to blow nose. Central Retinal Artery Occlusion
Sudden onset severe monocular vision loss over seconds with totally 90% will have visual acuity of counting fingers or less Marcus gun pupil RAPD (relative afferent papillary defect ) : when
irreactive pupil . Usually preceded by amaurosis fugax
swinging light rapidly between 2 eyes the diseased eye will constrict normally when light on the other eye ( consensual reflex) but when light is moved rapidly to the diseased eye it will dilate ( no direct reflex ) i.e. pupil dilates to light .
fundoscopic exam attenuated arterioles ,cattle trunk .
Optic disc and retinal pallor Cherry red spot at fovea (due to maintained perfusion of cilio-retinal Emboli seen 20%
artery)
Treatment of CRAO
. Retina can become irreversibly damaged in 100 min. Breath in a bag , massage , paracentesis . Mannitol 0.25-2.0 g/kg IV or acetazolamide 500 mg PO once to reduce Oral nitrates Lay the patient flat on his/her back Massage orbit. This is thought to help dislodge the clot from a larger to 9. Retrobulbar hematoma
IOP.
smaller retinal artery branch, minimizing area of visual loss. Acute orbital compartment syndrome 2 to blunt or penetrating trauma Hemorrhage into closed space of orbit IOP leading to vision loss from optic nerve damage / retinal ischemia Clinical diagnosis:
Ocular pain, APD, proptosis, ophthalmoplegia, diminished vision, IOP Others .
Problems in CL : 1- Cornea : - abrasion - acanthaemba . - Band degeneration . 2- Conj : giant papillary conjunctivits . 3- blurring of vision . Blepharitis Squamous : R/ orchadoxilline ED x 3 or terracortil EO R/ jonson baby shampo : 2Ulcerative : R/ tobrex ED or terramycin EO. X5
1-
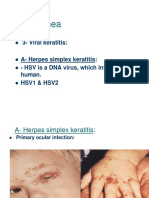
R/ fusithalmic VED . Remove the crusts , control DM . 3Angular : localized red eye + skin maceration at the canthi R/ tetra EO .. R/ prisoline zink ED .. x3 Dendritic ulcer : Pain , lacrimation , photophopia , blepharospasm , flourscen stain . R/ Zovirax EO Rest to the eye : * Cover * R/ isoptatropine ED R/ tobrex ED R/ orchatears ED
Allergy (itch) , blepharitis , conjunctivits(burn) , dryness(burn) , error of refraction
13567-
stitching : corneal ulcer 2- bursting : glaucoma . severe neuralgic : uvitis 4- scleritis . pain on eye movement : optic neuritis . pain around the eye : DD of headache . lid pain : stye , chalazion .
5limbal spring catarrh
3phylectn 4nodular episcleritis
1a 2-
pinguacul pteriguim
1-
Sudden ( vascular or hysterical ) : CRAO , vitrous Hge .
2Rapid : a) painless : RD , CRVO . b) painful : Acute glaucoma , optic neuritis ( loss of vision in few days with pain in eye movement history of viral infection or MS , O/E : RAPD , swollen optic disk ) . 3Gradual : 1- Cataract 2- 1ry optic atrophy 3- senile MD 4- OAG 5- progressive myopia .
Usually in-significant but fundus ex is to exclude : - Vitrous hge . retinal tear .
Anti allergic 1- Orchazide EDx4: Anti H , mast cell stabilizer , use only for 2 weeks . 2- Mastocytx EDx2: Anti H , mast cell stabilizer , use only for 4 weeks Has rapid effect . 3- Mirolast ED x2 or x4 (according to sevirty) : mast cell stabilizer , can be used for 4 months without complications , not used in toddlers < 3 years . 4- Tavegyl syrup x 3 : in lid edema e.g insect
5- steroids : orchapred , FML , Anti bacterial
Aminoglycosides 1Tobramycin Tobrex (16) Tobrin 2Gentamycin Apigent 3Neomycin Neo-pol
Quinlones Oflicin Oflox Ocuflox Optiflox Eye Drops Ofloxacin Oflox Ciprocin Ciprofar Okacin Orchacine Vigamox Tymer Zymer Levoxin
Chlormphinecol Isomephenicol Isoptophenicol Ocuphenicol (Miphenicol ( EO chloramrphinicol isomephinicol Terramycin.... ointment Tetra................ ointment
( Fusidic acid ( anti staph
fucithalmic Viscous ED optifucin Viscous ED
: NB Avoid chlormphinecol in children , pregnancy , long duration . Avoid using contact lens when administrating fusithalmic or optifuscin Antibiotic + Cortisone *avoid steroids in : 1- corneal ulcer 2- FB removal 3- children ( if necessary Tobradex , trrracortil EO, FML neo the least penetrating corticosteroids ) .
* predinsolone acetate is the most potent most penetration used after operations ( predforte , Apicorte forte ) . * when prescribe steroids write : " " )( 02 Tobradex :sulfa + predinsolone -5 Blephamide :chlormphincol + dexa-6 Orchadexoline : Neomycin + fml -3 FML neo
: Neomycin + dexa -1 Isoptomaxitrol ED Maxitrol EOint Dexaron plus ED, oint Dexatrol ED, oint : Neomycin + predinslon -2 Predmycin-P Neopred-p
: Hydrocortisone -3 Terra cortil Eoint Topradex (20) ED , Oint -4 Optidex-T Dexatobrin ED, Oint
Antiviral Eye Preparations Zoviax oint. 31.75 LE Acyclovir oint. 1.75 LE Decongestant Prisoline , visine , ocumethyl Dont prescribe , prolonged use conjunctivitis medicamentosa only in angular blepharitis R/ prisoline zink ED Tears substitutes ED ..x5 : orchatears , tears natural , normotears , tearsgaurd (no preservatives can be used for life ) , refresh plus (20) . EO ..x3 : thilotears , cornergel . Analgesic 1- local anaesthesia : Benox , Boxinate ED 2- NSAID : epifenac , voltaren Ed . Mydriatic preparations Cyclopentolate Isopto Atropine Mydrapid 0.5
Tropicamide 0.5%
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- # Diseases of ConjunctivaDokument4 Seiten# Diseases of Conjunctivaameerabest100% (1)
- OphthalmologyDokument12 SeitenOphthalmologyAmy StampNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ettinger CH 11 - Ophthalmic Manifestations of Systemic DiseaseDokument6 SeitenEttinger CH 11 - Ophthalmic Manifestations of Systemic Diseasehalf_frozen_cho6435Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Eye DiseasesDokument5 SeitenPediatric Eye DiseasesfrnksusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye & ENTDokument12 SeitenEye & ENTShandar SadafNoch keine Bewertungen
- HEENT Cheat SheetDokument22 SeitenHEENT Cheat SheetKatrina FeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The EyelidsDokument64 SeitenThe EyelidsSarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trauma and Chemical BurnsDokument62 SeitenTrauma and Chemical BurnsSarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anterior UveitisDokument12 SeitenAnterior UveitisHalawahtul EemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- #The EyelidDokument7 Seiten#The Eyelidameerabest100% (1)
- Ophtho - Neuro Exam 1Dokument21 SeitenOphtho - Neuro Exam 1AbbyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Senses 2014 - 1Dokument91 SeitenSpecial Senses 2014 - 1Winz DolleteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integumentary SystemDokument6 SeitenIntegumentary SystemClark LlameraNoch keine Bewertungen
- High Fever, Maculopapular Rash, Perianal Desquamation, and Conjunctivitis in A 3-Year-Old BoyDokument8 SeitenHigh Fever, Maculopapular Rash, Perianal Desquamation, and Conjunctivitis in A 3-Year-Old BoyTri ApriastiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Past Years Ophthalmology Q&asDokument24 SeitenPast Years Ophthalmology Q&asmhasbullah_725% (4)
- Trauma & Benda Asing Pada MataDokument14 SeitenTrauma & Benda Asing Pada MataTeguh Imana NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology For JordanianDokument24 SeitenHistology For JordanianKhaldoun AlmomaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmology NotesDokument79 SeitenOphthalmology NotesWise AmroNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Ocular TraumaDokument31 Seiten1 - Ocular TraumadeoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sni 3950-2014Dokument88 SeitenSni 3950-2014Dya Yda'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infeksi Kelainan Kongenital Dan TumorDokument54 SeitenInfeksi Kelainan Kongenital Dan Tumorniska darliantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmology For 5th Year Exams: Visual AcuityDokument7 SeitenOphthalmology For 5th Year Exams: Visual AcuitySaloni PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grodno State Medical University: Assistant Lecturer of The Department of OphthalmologyDokument24 SeitenGrodno State Medical University: Assistant Lecturer of The Department of OphthalmologyTeguh Imana NugrahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The UIC Eye ManualDokument37 SeitenThe UIC Eye ManualkabeerismailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periorbital CellulitisDokument2 SeitenPeriorbital CellulitisNurliyana GhazaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- File BookDokument13 SeitenFile BookusamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conjunctivitis and Other Ocular Lesions Opthalmology ClassDokument43 SeitenConjunctivitis and Other Ocular Lesions Opthalmology ClassJaikrit SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- ENT Ear I Scenarios (Compiled)Dokument35 SeitenENT Ear I Scenarios (Compiled)rumman tariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trauma OcularDokument47 SeitenTrauma OcularCucu Ne Eyang KakungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eyelids, Lacrimal Apparatus and Orbit: Yonas Abraham, M.DDokument43 SeitenEyelids, Lacrimal Apparatus and Orbit: Yonas Abraham, M.DTemie EshetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Eye ProblemsDokument33 SeitenCommon Eye ProblemsrobyalfNoch keine Bewertungen
- شيت اوف ٠٠Dokument25 Seitenشيت اوف ٠٠Omar KojerNoch keine Bewertungen
- 079 Muhammad Khairul Nizam Bin Khir 7.1Dokument30 Seiten079 Muhammad Khairul Nizam Bin Khir 7.1Ilham RafisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opt Halm OlogyDokument1 SeiteOpt Halm OlogyAnonymous q16bp7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Preseptal CellulitisDokument4 SeitenPreseptal CellulitisKm PlegariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cornea PDFDokument24 SeitenCornea PDFMariam QaisNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Acute Painful Red Eye: History of Presenting Complaint - The Time and Speed of OnsetDokument4 SeitenThe Acute Painful Red Eye: History of Presenting Complaint - The Time and Speed of Onsetleigh_zaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Derma 2Dokument40 SeitenDerma 2tyleree3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eye LidDokument36 SeitenEye Lidعبدالسلام ميلاد درباشNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case ReportDokument43 SeitenCase ReporttsazuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase 4 Ophthalmology 2021-22Dokument62 SeitenPhase 4 Ophthalmology 2021-22Olivia Genevieve El JassarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Points To Diagnose Scenarios of OphthalmologyDokument57 SeitenImportant Points To Diagnose Scenarios of Ophthalmologyaleena naz.164Noch keine Bewertungen
- Important Points To Diagnose Scenarios of OphthalmologyDokument57 SeitenImportant Points To Diagnose Scenarios of OphthalmologyHadra NuviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blefaritis EarlyDokument28 SeitenBlefaritis EarlyPaomo Zhixia EarlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kelainan Kelopak Mata DKKDokument28 SeitenKelainan Kelopak Mata DKKbinto akturusianoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bahan Pemicu 5 Penginderaan: Ivan Buntara 405120049Dokument62 SeitenBahan Pemicu 5 Penginderaan: Ivan Buntara 405120049AdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConjunctivaDokument40 SeitenConjunctivaSarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocular EmergDokument41 SeitenOcular EmergMohd SyazrinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 792 Viral Protozoal Corneal UlcerDokument33 Seiten792 Viral Protozoal Corneal UlcerMounika PapireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opthal Summary Handout (Word)Dokument4 SeitenOpthal Summary Handout (Word)myat25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eyelid & Lacrimal DisordersDokument35 SeitenEyelid & Lacrimal Disordersputri wid100% (1)
- Pimp Questions-SmithDokument66 SeitenPimp Questions-SmithJulie100% (2)
- 13.10.10-Eyelid and Adnexal Disease 2, PPT Presentasi 23 Okt 2009Dokument51 Seiten13.10.10-Eyelid and Adnexal Disease 2, PPT Presentasi 23 Okt 2009Ronald Ariyanto Wiradirnata0% (1)
- Dermato - Emergemencies (Acute Blistering and Exfoliative Skin) Nyoman Suryawati ObjectiveDokument9 SeitenDermato - Emergemencies (Acute Blistering and Exfoliative Skin) Nyoman Suryawati ObjectiveLong LieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocular EmergenciesDokument4 SeitenOcular EmergenciesJim Jose AntonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The CorneaDokument60 SeitenThe CorneaSarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye Notes From LectureDokument2 SeitenEye Notes From LectureTeehee JonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocular EmergenciesDokument26 SeitenOcular EmergenciesYukianesa100% (1)
- IV PDFDokument63 SeitenIV PDFelbagouryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutti FruttiDokument10 SeitenTutti FruttishadapaaakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac TestsDokument6 SeitenCardiac TestsRobert DowneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Behav SC Board RevDokument55 SeitenBehav SC Board RevyaykataiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology SummaryDokument16 SeitenPharmacology Summarysechzhen96% (46)
- Reference ID: 3418715: Sections or Subsections Omitted From The Full Prescribing Information Are Not ListedDokument34 SeitenReference ID: 3418715: Sections or Subsections Omitted From The Full Prescribing Information Are Not ListedRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro TestDokument9 SeitenNeuro TestHanung MerahbaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves Anatomy Review NoteDokument5 SeitenCranial Nerves Anatomy Review NoteOlu FasanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIT 3 Part 2 (Cirrhosis - Chronic Hepatitis - G.I.T.) Upload PDFDokument76 SeitenGIT 3 Part 2 (Cirrhosis - Chronic Hepatitis - G.I.T.) Upload PDFRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIT 3 Part 1 (HepatitisDokument51 SeitenGIT 3 Part 1 (HepatitisRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Syndromes Internal Medicine NoteDokument4 SeitenMedical Syndromes Internal Medicine NoteFranspolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Antibiotic Guidelines 2012Dokument100 SeitenAntibiotic Guidelines 2012HelenNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIT4 - PART2 (Malabsorption Syndrome - Jaundice) Upload PDFDokument60 SeitenGIT4 - PART2 (Malabsorption Syndrome - Jaundice) Upload PDFRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Git 2 Part 1 (Manifestations of Liver Cell Failure) UploadDokument66 SeitenGit 2 Part 1 (Manifestations of Liver Cell Failure) UploadRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- JaundiceDokument5 SeitenJaundiceRaouf Ra'fat Soliman100% (1)
- Cardiology Scheme and Heart FailureDokument76 SeitenCardiology Scheme and Heart FailureRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Git 1 (Liver Function) Upload PDFDokument37 SeitenGit 1 (Liver Function) Upload PDFRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Git 2 Part 2 (Hepatitis) Upload PDFDokument30 SeitenGit 2 Part 2 (Hepatitis) Upload PDFRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIT 4 - PART1 (IBD - Ascites - Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders) Upload PDFDokument45 SeitenGIT 4 - PART1 (IBD - Ascites - Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders) Upload PDFRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GIT4 - PART3 (Cases) Upload PDFDokument9 SeitenGIT4 - PART3 (Cases) Upload PDFRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chest - DR Abo-ElAsrar - by El Azhar Medical Students 2012Dokument56 SeitenChest - DR Abo-ElAsrar - by El Azhar Medical Students 2012Fatma HelalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acid Base Balance DR Ahmad Mowafy Revision UpdatedDokument18 SeitenAcid Base Balance DR Ahmad Mowafy Revision UpdatedRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- InfectionDokument294 SeitenInfectionRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genetics - DR Abo-ElAsrar - by El Azhar Medical Students 2012Dokument39 SeitenGenetics - DR Abo-ElAsrar - by El Azhar Medical Students 2012Raouf Ra'fat Soliman100% (1)
- Asrar - Ped - Clinical - DMP3Dokument73 SeitenAsrar - Ped - Clinical - DMP3Raouf Ra'fat Soliman100% (1)
- Crdiology - DR Abo-ElAsrar - by El Azhar Medical Students 2012Dokument74 SeitenCrdiology - DR Abo-ElAsrar - by El Azhar Medical Students 2012Raouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- NutritionDokument354 SeitenNutritionRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- EndocrineDokument181 SeitenEndocrineRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infection Control in ArabicDokument105 SeitenInfection Control in ArabicRaouf Ra'fat SolimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rheumatology MRCP1Dokument186 SeitenRheumatology MRCP1Raouf Ra'fat Soliman100% (3)
- Incision and Drainage of AbscessesDokument25 SeitenIncision and Drainage of Abscessesjaphetnwapi100% (1)
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index SELENA ModificationDokument4 SeitenSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index SELENA ModificationaminahrahimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procleix Ultrio Plus AssayDokument61 SeitenProcleix Ultrio Plus AssaydatitoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tonsillitis: Cross Repertorization & Homoeopathic TherapeuticsDokument5 SeitenTonsillitis: Cross Repertorization & Homoeopathic TherapeuticsDr. Indra Gaurav SaxenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vaccination Schedule For Babies and Young ChildrenDokument1 SeiteVaccination Schedule For Babies and Young ChildrenKirana SbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemo Vascular AccessDokument51 SeitenChemo Vascular AccessSankalp Singh Bisht100% (1)
- Immunization RecordDokument1 SeiteImmunization RecordJordan Simmons ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Facts On Hiv AidsDokument20 SeitenBasic Facts On Hiv AidsKenneth Miles100% (2)
- Bloodborne Pathogens: NWSSB, Det. Corona Annual Sustainment Training Instructor: Richard Owens October 3, 2008Dokument50 SeitenBloodborne Pathogens: NWSSB, Det. Corona Annual Sustainment Training Instructor: Richard Owens October 3, 2008jayand_net100% (1)
- 51 Worst Diseases and Conditions To Treat With Black Seed OilDokument9 Seiten51 Worst Diseases and Conditions To Treat With Black Seed Oilsyndicate_mauliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poor Environmental Sanitation NotesDokument3 SeitenPoor Environmental Sanitation Notesraff estradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treatmnt HerpesDokument8 SeitenTreatmnt HerpesZakky FebrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Kesmas Jumal HusniDokument9 SeitenJurnal Kesmas Jumal HusniHumam_Aziz_2281Noch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology 1.1 Immunology - Dr. FontanillaDokument115 SeitenMicrobiology 1.1 Immunology - Dr. FontanillaRyn ShadowNoch keine Bewertungen
- MycobacteriumDokument6 SeitenMycobacteriumRami AlhilliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anti Viral Drugs: Maria Ulfah, M.Si., AptDokument55 SeitenAnti Viral Drugs: Maria Ulfah, M.Si., AptFauzan NurohmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- IMCIDokument3 SeitenIMCIwordlife360Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Studies DetailsDokument36 SeitenCase Studies Detailssiachen26100% (1)
- Cristy Santos BOMDokument111 SeitenCristy Santos BOMLito ObstaculoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Written Revalida 1st 50 QuestionsDokument7 SeitenMicro Written Revalida 1st 50 QuestionsSaravanan Devaraj100% (1)
- VN Shegal - Textbook of Clinical Dermatology, 5th EditionDokument365 SeitenVN Shegal - Textbook of Clinical Dermatology, 5th EditionAlbert Gheorghe93% (14)
- Cepa ATCC 6538Dokument2 SeitenCepa ATCC 6538joshikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gall Bladder USGDokument66 SeitenGall Bladder USGarina31Noch keine Bewertungen
- Garlic CapsuleDokument4 SeitenGarlic CapsulechongtroiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Org - Telegram.messenger - Provider Media Telegram Telegram Documents 4 5920093559716840840 PDFDokument32 SeitenOrg - Telegram.messenger - Provider Media Telegram Telegram Documents 4 5920093559716840840 PDFsameeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vpar Reporting QuestionsDokument4 SeitenVpar Reporting QuestionsSteven Mark MananguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bob Beck Protocol - Natural Cancer Treatments at CancerTutorDokument4 SeitenBob Beck Protocol - Natural Cancer Treatments at CancerTutorThiago NunesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar PustakaDokument7 SeitenDaftar PustakaJonesius Eden ManoppoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 112 Prefinal LectureDokument11 SeitenNCM 112 Prefinal LectureRheeanne AmilasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood BankDokument32 SeitenBlood Bankpikachu100% (1)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (6)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (28)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDVon EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (81)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningVon EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (3)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Von EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Noch keine Bewertungen
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerVon EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (392)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryVon EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (44)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlVon EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (58)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessVon EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (328)
- Dark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingVon EverandDark Psychology: Learn To Influence Anyone Using Mind Control, Manipulation And Deception With Secret Techniques Of Dark Persuasion, Undetected Mind Control, Mind Games, Hypnotism And BrainwashingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1138)
- Troubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassVon EverandTroubled: A Memoir of Foster Care, Family, and Social ClassBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (27)