Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
What Is The Difference Between An ECG and Echo Tests Done For Heart Ailments? An Is Used To Measure
Hochgeladen von
Sathish KumarOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What Is The Difference Between An ECG and Echo Tests Done For Heart Ailments? An Is Used To Measure
Hochgeladen von
Sathish KumarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What is an Echocardiogram: An echocardiogram is a test in which ultrasound is used to examine the heart.
In addition to providing single-dimension images, known as M-mode echo that allows accurate measurement of the heart chambers, the echocardiogram also offers far more sophisticated and advanced imaging. This is known as two- dimensional (2-D) Echo and is capable of displaying a cross-sectional "slice" of the beating heart, including the chambers, valves and the major blood vessels that exit from the left and right ventricle Sticky patches or electrodes are attached to the chest and shoulders and connected to electrodes or wires. These help to record the electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) during the echocardiography test. The EKG helps in the timing of various cardiac events (filling and emptying of chambers). A colorless gel is then applied to the chest and the echo transducer is placed on top of it. The echo technologist then makes recordings from different parts of the chest to obtain several views of the heart.
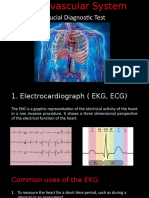
What is the difference between an ECG and Echo tests done for heart ailments? An ECG is used to measure:
* Any damage to the heart * How fast your heart is beating and whether it is beating normally * The effects of drugs or devices used to control the heart (such as a pacemaker) * The size and position of your heart chambers An ECG is a very useful tool for determining whether a person has heart disease. The 12-lead ECG is crucial for establishing many cardiac diagnoses, especially arrhythmias and myocardial ischemia. It can also identify atrial enlargement, ventricular hypertrophy, and conditions that predispose to syncope or sudden death (eg, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, long QT syndrome, Brugada syndrome). A Holter monitor is a machine that continuously records the heart's rhythms. The monitor is usually worn for 24 48 hours during normal activity. An exercise stress test is a screening tool to test the effect of exercise on your heart. It provides an overall look at the health of your heart. You will walk or pedal on an exercise machine while the electrical activity of your heart is measured with an electrocardiogram (ECG), and blood pressure readings are taken. This will measure your heart's reaction to your body's increased need for oxygen.
Echocardiography test
is performed to evaluate the valves and chambers of the heart in a noninvasive manner. The echocardiogram allows doctors to evaluate heart murmurs, check the pumping function of the heart, and evaluate patients who have had heart attacks. It is a very good screening test for heart disease in certain groups of patients.
Abnormal results may indicate heart valve disease, cardiomyopathy, pericardial effusion, or other cardiac abnormalities. A stress echocardiogram includes the following steps: * A resting echocardiogram will be done first. * You will exercise or be given medicine until you reach the target heart rate. This helps reveal how your heart works when you are active. * Your blood pressure and heart rhythm (ECG) will be monitored throughout the procedure. * Ultrasound images will be recorded during the procedure. * Another echocardiogram is taken immediately after your target heart rate has been reached. The ultrasound images will reveal any parts of the heart that may not be receiving enough blood or oxygen because of blocked arteries.
ECG and EEG Electroencephalogram or EEG is related to the brain and electrocardiogram or ECG is related to the heart. EEG is the equipment used for measuring electrical activities of the brain. On the other hand, ECG is used for measuring activities of heart. Doppler echocardiography: is a procedure which uses ultrasound technology to examine the heart and blood vessels.[1] An echocardiogram uses high frequency sound waves to create an image of the heart while the use of Doppler technology allows determination the speed and direction of blood flow by utilizing the Doppler effect. An echocardiogram can, within certain limits, produce accurate assessment of the direction of blood flow and the velocity of blood and cardiac tissue at any arbitrary point using the Doppler effect. One of the limitations is that the ultrasound beam should be as parallel to the blood flow as possible. Velocity measurements allow assessment of cardiac valve areas and function, any abnormal communications between the left and right side of the heart, any leaking of blood through the valves (valvular regurgitation), calculation of the cardiac output and calculation of E/A ratio[2] (a measure of diastolic dysfunction). Contrast-enhanced ultrasound using gas-filled microbubble contrast media can be used to improve velocity or other flow-related medical measurements. Although "Doppler" has become synonymous with "velocity measurement" in medical imaging, in many cases it is not the frequency shift (Doppler shift) of the received signal that is measured, but the phase shift (when the received signal arrives).
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- ECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!Von EverandECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instrumental Diagnostic Methods of Heart DiseasesDokument15 SeitenInstrumental Diagnostic Methods of Heart DiseasesA A D H INoch keine Bewertungen
- EKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!Von EverandEKG and ECG Interpretation: Learn EKG Interpretation, Rhythms, and Arrhythmia Fast!Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Procedures GlossaryDokument2 SeitenHeart Procedures Glossary姜華Noch keine Bewertungen
- EKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!Von EverandEKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosing Heart DiseaseDokument3 SeitenDiagnosing Heart DiseaseJaz SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnostic Test For Heart DiseasesDokument16 SeitenDiagnostic Test For Heart DiseasesJaimee Jonah ChristieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echocardiography: Not To Be Confused WithDokument3 SeitenEchocardiography: Not To Be Confused Withgreathari1998Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tress Test: The Gale Encyclopedia of MedicineDokument7 SeitenTress Test: The Gale Encyclopedia of MedicineSalsabilla KimikoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Monitor: Other Names For An ElectrocardiogramDokument7 SeitenCardiac Monitor: Other Names For An ElectrocardiogramRizzia BalabisNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is an ECG? How to read an electrocardiogramDokument4 SeitenWhat is an ECG? How to read an electrocardiogramAjay Pal NattNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echocardiogram (Heart Ultrasound) : Name:Fatema Ilyas Organization:Tabba Heart Institute ROLL NO:16-02 Batch:ViiDokument28 SeitenEchocardiogram (Heart Ultrasound) : Name:Fatema Ilyas Organization:Tabba Heart Institute ROLL NO:16-02 Batch:ViiFatema IlyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Cardiologist in Pune - Cardiologist in Pune - DR Ajit MehtaDokument10 SeitenBest Cardiologist in Pune - Cardiologist in Pune - DR Ajit MehtaAjit MehtaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Guide: Everything You Need to Know About ElectrocardiographyDokument11 SeitenECG Guide: Everything You Need to Know About ElectrocardiographyHassan AnwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tests to Diagnose Cardiovascular DisordersDokument16 SeitenTests to Diagnose Cardiovascular DisordersMonette Abalos MendovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICu EquipmentDokument3 SeitenICu Equipmentkremlin23455Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrocardiograph Y (ECG / Ekg) : Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHDokument52 SeitenElectrocardiograph Y (ECG / Ekg) : Rose Dyane F - Nunag, RMT, MPHClaire GonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiology Laboratory TestsDokument2 SeitenCardiology Laboratory TestsBeatrice SalgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different DiagnosticDokument26 SeitenDifferent DiagnosticDanica Alyssa EnriquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Chapter TwoDokument10 SeitenECG Chapter Twoد. سعد قاسم الاجهزة الطبيةNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Cardiogram: NCM 112:skills LaboratoryDokument7 SeitenElectro Cardiogram: NCM 112:skills LaboratoryFaye Domini FederisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echocardiogram MayoDokument4 SeitenEchocardiogram MayoMarta KitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Guide: Understanding Heart Rhythms & EKG TestDokument10 SeitenECG Guide: Understanding Heart Rhythms & EKG TestSilver Villota Magday Jr.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Diagnosing Heart Disease-Echo TestDokument4 SeitenDiagnosing Heart Disease-Echo TestjanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectrocardiogramDokument4 SeitenElectrocardiogramazeeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Detects Heart Damage from High Blood PressureDokument2 SeitenECG Detects Heart Damage from High Blood PressureKCrsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction Definition: Types of PacemakersDokument8 SeitenIntroduction Definition: Types of PacemakersPrasann RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrode Placement: Midclavicular LineDokument4 SeitenElectrode Placement: Midclavicular LineJeneleth DayaodaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG MonitoringDokument28 SeitenECG MonitoringGlaiza Mae Olivar-ArguillesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haemodynamic mo-WPS OfficeDokument3 SeitenHaemodynamic mo-WPS Officermconvidhya sri2015Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electro CardiogramDokument2 SeitenElectro CardiogrambinukirubaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Tests Explained: X-Rays, EKGs, Stress Tests, and MoreDokument6 SeitenCardiac Tests Explained: X-Rays, EKGs, Stress Tests, and MoreRajesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecg en LabviewDokument61 SeitenEcg en LabviewHarold David Gil MuñozNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Manifestations: Diagnostic FindingsDokument8 SeitenClinical Manifestations: Diagnostic FindingsMelodia Turqueza GandezaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Report: An Overview of ElectrocardiographyDokument5 SeitenECG Report: An Overview of Electrocardiographyالحارث فخري فياض احمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDokument22 SeitenClick To Edit Master Subtitle StyleSushrut RakshitNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Journey Through Time The History of Heart RateDokument11 SeitenA Journey Through Time The History of Heart RateuatilakarathnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Biomedical Instruments and Their UsesDokument12 SeitenTypes of Biomedical Instruments and Their Usesgzb0120% (2)
- What Is An Echocardiogram? - InformedHealth - Org - NCBI BookshelfDokument1 SeiteWhat Is An Echocardiogram? - InformedHealth - Org - NCBI BookshelfemmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- EKG (How To... When To) : By: Joshua Z. & Patricia PDokument12 SeitenEKG (How To... When To) : By: Joshua Z. & Patricia Papi-462650642Noch keine Bewertungen
- CVS Overview: Clinical Exam and Diagnostic Tests of the Cardiovascular SystemDokument9 SeitenCVS Overview: Clinical Exam and Diagnostic Tests of the Cardiovascular SystemCha AlegriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enc=Encoded=HSWaGzzNzts4jE4gVI6PntMxpFlg0sdiU38ZzpHvV2T1pW5 0JF1G4c=Dokument217 SeitenEnc=Encoded=HSWaGzzNzts4jE4gVI6PntMxpFlg0sdiU38ZzpHvV2T1pW5 0JF1G4c=aarti sahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definition of Cardiology 1Dokument6 SeitenDefinition of Cardiology 1Vindy Rizki AmaliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Records the Heart's Electrical ActivityDokument1 SeiteECG Records the Heart's Electrical Activitydian5christiani5malaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic ECG InterpretationDokument7 SeitenBasic ECG InterpretationAprilJaedeeSanAgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dar Shahid Yousuf, Moradiya Jemish Kumar, 361, Internal DiseasesDokument28 SeitenDar Shahid Yousuf, Moradiya Jemish Kumar, 361, Internal DiseasesShahid Yousuf DarNoch keine Bewertungen
- All ProcedureDokument247 SeitenAll ProcedureRakesh ChoudhryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electro Cardiograph yDokument215 SeitenElectro Cardiograph yToufique KaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrocardiogram IntroductionDokument20 SeitenElectrocardiogram IntroductionGajendra TodakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Attack Diagnosis TestsDokument2 SeitenHeart Attack Diagnosis TestsChristopher John Balagot100% (1)
- Echocardiography Heart ExamDokument17 SeitenEchocardiography Heart ExamClaire GonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Detecting Atrial Fibrillation with Ambulatory ECGDokument6 SeitenDetecting Atrial Fibrillation with Ambulatory ECGFaiza ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2D Echo with Doppler Heart ImagingDokument7 Seiten2D Echo with Doppler Heart ImagingAb Staholic BoiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System TestDokument28 SeitenCardiovascular System TestEla Angela RumapeaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CardiovascularDokument16 SeitenCardiovascularMilena VargasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosisDokument38 SeitenElectrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosislorhenzsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of Iraq: Medical DevicesDokument6 SeitenRepublic of Iraq: Medical Devicesالحارث فخري فياض احمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echocardiography Guide to Cardiac Anatomy & FunctionDokument57 SeitenEchocardiography Guide to Cardiac Anatomy & FunctionKEN KIZITONoch keine Bewertungen
- Non Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarDokument32 SeitenNon Invasive Diagnostic Instruments: By. Kailash - Pandey Aditya - MayekarkrupalithakkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understand Your ECG TestDokument14 SeitenUnderstand Your ECG TestYamlak NegashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fci 2012 Nicmks1 PDFDokument57 SeitenFci 2012 Nicmks1 PDFSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Agriculture - LECTURE NOTESDokument8 SeitenBasics of Agriculture - LECTURE NOTESSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Faculty Handbook IitdDokument99 SeitenNew Faculty Handbook IitdSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brochure NOTESDokument4 SeitenBrochure NOTESSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrainingDokument10 SeitenTrainingSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fci 2012 Nicmks1 PDFDokument57 SeitenFci 2012 Nicmks1 PDFSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roll L1 PDFDokument78 SeitenRoll L1 PDFSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rules and manuals maintained by organizationDokument2 SeitenRules and manuals maintained by organizationsridharpalleda53% (19)
- Preview To Swamy's HandbookDokument3 SeitenPreview To Swamy's Handbooklrajat1991Noch keine Bewertungen
- ApplDokument1 SeiteApplSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSC Combined Recruitment for Assistant Grade-III 2012 exam resultsDokument2 SeitenSSC Combined Recruitment for Assistant Grade-III 2012 exam resultsAshima MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ugc NotificationDokument44 SeitenUgc NotificationMuqthiar AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Csir Net 2013 PDFDokument8 SeitenCsir Net 2013 PDFSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSIR Ib CHALLAN PDFDokument1 SeiteCSIR Ib CHALLAN PDFSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cgls Cut Off PDFDokument115 SeitenCgls Cut Off PDFSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cgls PDFDokument115 SeitenCgls PDFSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ApplDokument1 SeiteApplSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSDDokument7 SeitenDSDSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Brains TNPSC Question Bank - 1Dokument13 SeitenBest Brains TNPSC Question Bank - 1Sathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10a (1) Rules - DocxsDokument2 Seiten10a (1) Rules - DocxsSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Brains TNPSCD GK Question Tamil Version 1Dokument12 SeitenBest Brains TNPSCD GK Question Tamil Version 1Sathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Best Brains TNPSCD GK Question Tamil Version 1Dokument12 SeitenBest Brains TNPSCD GK Question Tamil Version 1Sathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ApplDokument1 SeiteApplSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alphabet ChartDokument1 SeiteAlphabet ChartfindarunhereNoch keine Bewertungen
- ApplDokument1 SeiteApplSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ApplDokument1 SeiteApplSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Immunological Relationships Bacillus Subsp.: Proteins Making Up The Thuringiensis Israelensis Crystalline ToxinDokument6 SeitenImmunological Relationships Bacillus Subsp.: Proteins Making Up The Thuringiensis Israelensis Crystalline ToxinSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ApplDokument1 SeiteApplSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ApplDokument1 SeiteApplSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- DSDDokument7 SeitenDSDSathish KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pacemaker Basics ExplainedDokument5 SeitenPacemaker Basics ExplainedPoonam ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Low Blood PreasureDokument9 SeitenLow Blood PreasureNhs VacancyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of The Effects of Music Therapy Using Todi Raga of Hindustani Classical Music On Blood Pressure, Pulse Rate and Respiratory Rate of Healthy Elderly MenDokument8 SeitenEvaluation of The Effects of Music Therapy Using Todi Raga of Hindustani Classical Music On Blood Pressure, Pulse Rate and Respiratory Rate of Healthy Elderly MenAprilinda SafitriNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7th Grade Natural Science Reinforcement WorksheetDokument3 Seiten7th Grade Natural Science Reinforcement WorksheetnataliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prac Exam Style Paper 3 PDFDokument11 SeitenPrac Exam Style Paper 3 PDFanubhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Print This Guide and Record Your Progress On Paper. Or, Import This Document Into Your School E-Learning System and Record Progress ElectronicallyDokument21 SeitenPrint This Guide and Record Your Progress On Paper. Or, Import This Document Into Your School E-Learning System and Record Progress ElectronicallySalanap OnielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiac Monitoring: An OverviewDokument5 SeitenCardiac Monitoring: An OverviewJ-rold AnthonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syncope: Submitted By, Nikketta Nunez Iv Part Ii BdsDokument45 SeitenSyncope: Submitted By, Nikketta Nunez Iv Part Ii BdsAngello Nikketta NunezNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Ultimate Krok2 Companion Comprehensive Explanations and InsiDokument263 SeitenThe Ultimate Krok2 Companion Comprehensive Explanations and InsiRamy Aso ZainalNoch keine Bewertungen
- KUHS B.SC Nursing 1st Year Physiology Important Question BankDokument10 SeitenKUHS B.SC Nursing 1st Year Physiology Important Question BankShabir Khan100% (1)
- अश्वगंधा का दवा के रूप में सैकड़ों वर्षों से उपयोग किया जाता रहा हैDokument66 Seitenअश्वगंधा का दवा के रूप में सैकड़ों वर्षों से उपयोग किया जाता रहा हैflexwalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preparing For Post Offer Evaluation & Health History Form 4.26.22Dokument13 SeitenPreparing For Post Offer Evaluation & Health History Form 4.26.22Antonella VitaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Vessels NotesDokument5 SeitenBlood Vessels NotesJan Vincent GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 038 Health In1 PDFDokument281 Seiten038 Health In1 PDFbhatchinmay7100% (1)
- Dopamine Drug StudyDokument6 SeitenDopamine Drug StudyGeorge RussellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Housestaff Manual 2023-2024 - MeadeDokument267 SeitenHousestaff Manual 2023-2024 - MeadeMelchor Alcántara Barrera100% (2)
- Embryology of the Heart Tube FormationDokument65 SeitenEmbryology of the Heart Tube Formationnisha24Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inhouse Cardiac Surgery Team LaunchDokument2 SeitenInhouse Cardiac Surgery Team LaunchUmeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- April 20, 2015 - RATIODokument23 SeitenApril 20, 2015 - RATIOLouie BelloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emedica MRCGP AKT Curriculum ChecklistDokument42 SeitenEmedica MRCGP AKT Curriculum ChecklistSana Mustafa100% (1)
- Suspected Heart Failure: Section 5 Section 7 Section 8Dokument10 SeitenSuspected Heart Failure: Section 5 Section 7 Section 8Javier TapiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine All DIagnosis by AVI SeriesDokument8 SeitenMedicine All DIagnosis by AVI SeriesMuhammad Awais Hassan AwaanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDokument7 SeitenCoronary Artery Diseasejmar767Noch keine Bewertungen
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDokument30 SeitenCoronary Artery Diseasesarguss14100% (1)
- Quit Smoking BrochureDokument21 SeitenQuit Smoking BrochureDumitrita NegoitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12A BT Điền Từ - Đục Lỗ (10 Bài)Dokument7 Seiten12A BT Điền Từ - Đục Lỗ (10 Bài)Class LaceyNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Pharmacy I Yr Syllabus 2009-2010Dokument15 SeitenB. Pharmacy I Yr Syllabus 2009-2010harikrishna2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Lecture NotesDokument10 SeitenChapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Lecture Notesapi-3728508100% (2)
- Jugular Venous Pressure: It's Easier Than It LooksDokument25 SeitenJugular Venous Pressure: It's Easier Than It LooksOktaviano Satria PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Changes with Aging: A Guide to Normal SenescenceDokument53 SeitenPhysical Changes with Aging: A Guide to Normal SenescenceRohit SejwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (402)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (13)
- The Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearVon EverandThe Comfort of Crows: A Backyard YearBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (23)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsVon EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityVon EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedVon EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (78)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeVon EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsVon EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementVon EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (40)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossVon EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (4)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (8)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsVon EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (169)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (33)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingVon EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (5)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Von EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (110)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesVon EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (34)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaVon EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeVon EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (253)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingVon EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsVon EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recovering from Emotionally Immature Parents: Practical Tools to Establish Boundaries and Reclaim Your Emotional AutonomyVon EverandRecovering from Emotionally Immature Parents: Practical Tools to Establish Boundaries and Reclaim Your Emotional AutonomyBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (201)
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossVon EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (4)